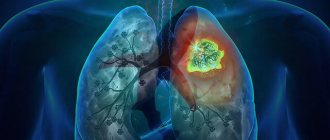
Pneumonia is an acute infectious lesion of the lower respiratory tract, which is confirmed by x-ray methods, dominates the picture of the disease and is not associated with other known causes.
The necessary conditions have been created for the treatment of patients with pneumonia at the Yusupov Hospital. The chambers are equipped with ventilation and air conditioning, which allows you to create a comfortable temperature regime. Patients are provided with the necessary hygiene products. The staff of the therapy clinic is attentive to all the wishes of patients. The examination is carried out on modern devices that are regularly updated. Pulmonologists use all diagnostic methods to identify the causative agent of the disease, determine its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs, and assess the severity of the patient’s condition. The therapy clinic employs candidates and doctors of medical sciences, doctors of the highest category, with knowledge and experience in treating various forms of pneumonia. All complex cases are discussed at a meeting of the Expert Council, where a collegial decision is made on patient management tactics.
In case of severe pneumonia, patients are hospitalized in the intensive care unit. Oxygen is supplied centrally to each room. Resuscitation doctors monitor the condition of patients using cardiac monitors. If indicated, artificial ventilation of the lungs is performed using modern stationary or portable ventilators.
Types of pneumonia
What types of pneumonia are there? There are community-acquired, hospital-acquired and aspiration pneumonias. Community-acquired pneumonia occurs at home or during the first 48 hours of hospital stay. Hospital-acquired pneumonia develops after 48 hours of the patient being in the hospital. Aspiration pneumonia occurs in patients with impaired swallowing and a weakened cough reflex, when large amounts of oropharyngeal contents are swallowed by unconscious patients. When gastric contents flow into the upper respiratory tract, chemical pneumonitis develops.
Depending on the pathogen that caused pneumonia, the following types of pneumonia are distinguished:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- mixed (bacterial-viral);
- fungal;
- pneumonia caused by protozoa.
Pulmonologists distinguish the following forms of pneumonia according to severity: mild, moderate, severe, extremely severe. Depending on the location of the pathological process, the following types of pneumonia are distinguished:
- focal (within the acinus and lobules);
- segmental, polysegmental (within one or several segments);
- shared (within one share);
- total, subtotal (can cover the entire lung).
The inflammatory process in the lungs can be one-sided or two-sided.
Who is a pulmonologist and what does he treat: what does he do?
Pulmonologist
A pulmonologist is a doctor whose competence is the treatment and study of diseases of the entire respiratory system. But there are pathologies that a pulmonologist diagnoses and treats together with other specialists.
These include:
- Phthisiatrician – pulmonary tuberculosis
- Resuscitator – relief of an acute process that is associated with impaired respiratory function
- Thoracic surgeon – surgical operations on organs located in the chest
What does a pulmonologist do? This specialist treats the following pathologies:
- Sarcoidosis, fibrosis, cystic fibrosis
- Acute and chronic types of bronchitis
- Occupational and chronic diseases
- Pneumonia of various etiologies
- Bronchial asthma
- Alveolitis
- COPD
- Pleurisy
Can diagnose, but other specialists will treat:
- Emphysema
- Tuberculosis
- Cancer
- Upper respiratory tract diseases
A referral to a pulmonologist is given by a general practitioner or pediatrician due to the similarity of symptoms, which makes it difficult to make a diagnosis.
Causes and risk factors of pneumonia
The most common causative agents of pneumonia are pneumococci. The following microorganisms can cause pneumonia:
- β-hemolytic group streptococcus;
- staphylococcus;
- hemophilus influenzae;
- Klebsiella;
- enterobacteria.
In recent years, there has been an increase in pneumonia caused by mycoplasma, legionella and chlamydia. A relatively new disease in which interstitial pneumonia develops is Q fever. The source of microorganisms is domestic small and large livestock. Against the background of an immunodeficiency state, pneumonia occurs due to Pneumocystis.
Fungi and actinomycetes are ubiquitous. They develop in the soil, enter the air, and through it onto the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract and cause pneumonia. The role of viruses in the nature of pneumonia is ambiguous. Primary viral pneumonia usually occurs in the first 3 days of the disease, and viral-bacterial pneumonia - no earlier than 3-5 days. Most viral pneumonia is caused by the influenza virus. Pneumonia also develops under the influence of adenovirus, coronavirus, and respiratory syncytial virus.
The leading role in the origin of hospital-acquired pneumonia belongs to opportunistic microorganisms and opportunistic microbes. Pneumonia develops against the background of a decrease in the immunological resistance of the body, which occurs after irradiation or invasive procedures, when taking immunosuppressants.
Microorganisms detected in the environment of hospitals are conventionally divided into representatives of the microflora of the patients themselves (streptococci, staphylococci) and pathogens that appeared in the external environment not from humans (legionella).
Aspiration pneumonia occurs when inhalation of anaerobes, fusobacteria, bacteroides, staphylococci, peptostreptococcus and gram-negative bacilli that colonize the mucous membrane. Hospital-acquired pneumonia is widespread during immunosuppressive therapy and is caused by cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex viruses, as well as Coxsackie and ECHO enteroviruses.
Half of pneumonia develops under the influence of mixed microflora. In this case, it is difficult to identify the causative agent of pneumonia. In 40% of patients suffering from pneumonia, associations of pneumococcus or other gram-positive cocci with viral agents are detected. Legionnaires' disease is often detected in combination with adenoviral and influenza infections caused by influenza B virus, pneumococcus, Haemophilus influenzae, mycoplasma and chlamydia.
The main risk factors for community-acquired pneumonia include:
- alcoholism;
- smoking;
- chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases;
- intravenous drug administration;
- exposure to air conditioners and humidifiers.
The risk of developing hospital-acquired pneumonia increases after surgery, head injury, or stroke. Pneumonia often develops in patients receiving high doses of glucocorticoids, antibiotics, and cytostatics.
Phthisiologist or pulmonologist: what is the difference?
The competence of a pulmonologist has already been mentioned above. Let's talk a little about the phthisiatrician. What is the difference? What does this specialist do:
- His field of study is narrower than that of a pulmonologist. He practically deals only with the diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis. In medicine there is even such a section - phthisiology - treatment of tuberculosis.
- The workplace of a phthisiatrician is located in a clinic, in sanatorium-resort institutions according to the profile, as well as in tuberculosis dispensaries and research centers.
A phthisiatrician can diagnose and treat leprosy and sarcoidosis. He can conduct specific examinations, carry out rehabilitation of patients, evaluate BCG, assess a person’s ability to work, carry out medical examinations and hospitalization.
Stages of pneumonia
A typical example of a bacterial lung infection is lobar pneumonia caused by pneumococci. The inflammatory process in the lungs during lobar pneumonia goes through a number of phases. In the initial phase of pneumonia (flushing stage), serous or serous-hemorrhagic exudate with a low fibrin content is formed. It occurs due to the expansion of capillaries and increased permeability of their walls with the release of plasma into the interstitial tissue and into the cavity of the alveoli. Alveolar edema develops, the tissue of the affected part of the lung is edematous, elastic, and serous-hemorrhagic fluid drains from the surface.
After this, the stage of hepatization of the lung tissue begins. It is associated with the migration of cells from the blood into the lung tissue and into the cavity of the alveoli, followed by the capture and digestion of the pathogen and the loss of fibrin. Fibrin stretches the alveoli, the lung looks enlarged. Depending on the predominance of erythrocytes or leukocytes in the alveolar fluid, red and gray liver are distinguished.
The function of the smooth muscles of the respiratory region is impaired, and the bronchi do not clear. The pleura is involved in the inflammatory process. Serous exudate with fibrin inclusions accumulates in the pleural cavity.
Pneumonia in the resolution stage is characterized by resorption of exudate, and inflammatory edema disappears over time. The exudate shows signs of reverse development of the inflammatory reaction. Changes in the interstitial tissue persist for a certain time after the patient’s clinical condition has normalized. If fibrin lysis is impaired, dense foci appear within the pulmonary lobules.
Pneumonia, caused by staphylococci and streptococci, is of a different nature. These microorganisms produce toxins that cause necrosis of lung tissue. Suppurative processes develop. In the acute stage, pronounced edema of the lung tissue is observed, extensive exfoliation of the bronchial epithelium occurs with infiltration and the formation of areas of necrosis in the walls of the bronchi. The capillaries become thrombosed, and areas of abscess formation appear.
The first stage of pneumonia lasts from several hours to three days. The patient's body temperature rises sharply, a dry cough appears, shortness of breath is observed, and he complains of pain when inhaling and coughing. The duration of the second phase is from one to three days. The pain becomes stronger, the body temperature is steadily elevated, and “rusty” sputum appears. Breathing with pneumonia is rapid.
The third stage of pneumonia lasts from 4 to 8 days. The cough becomes productive, the patient coughs up purulent or mucous sputum. The pain dulls, shortness of breath decreases. Body temperature decreases. During the fourth stage of the disease, the exudate is reabsorbed, the airiness of the lungs is restored, and recovery occurs.
With pneumonia, half of the chest lags behind when breathing. Already on the first day of the disease, doctors detect dullness of percussion sound with a tympanic tint. By the end of the first day or on the second day, initial crepitus is heard. In subsequent days, the dullness becomes more distinct, bronchial breathing is heard during auscultation, bronchophony and vocal tremor intensify, and crepitus disappears. In the stage of resolution of pneumonia, bronchial breathing is replaced by vesicular breathing, and crepitus reappears.
What is pneumonitis?
Pneumonitis or pulmonitis is understood as an inflammatory process that occurs in the vascular wall of the alveoli, which is characterized by scarring. Sometimes this term refers to the occurrence of atypical pneumonia. Main symptoms:
- Cough with sputum production
- Fever is often present
- Symptom of an asthmatic - lack of air
What is the general prognosis for recovery and relapse of the disease? It all depends on the person’s age, the presence of other chronic diseases, the immune system, and also on the treatment performed. With timely treatment and an uncomplicated option, as a rule, everything ends well. But there are other options:
- Lung tissue can recover by 70%
- Local pneumosclerosis may form - 20%
- Local carnification occurs – 7%
- The share in size decreases – 2%
- Segment shrinkage – 1%
Which doctor should I contact for these pathologies? Read on.
X-ray diagnostics in different stages of pneumonia
The X-ray picture depends on the phase of pneumonia. The inflammatory process does not take over an entire lobe of the lung immediately, but gradually. Initially, one or several inflammatory foci appear, from which inflammation spreads to the entire lobe. Lobar pneumonia is called lobar pneumonia on the grounds that the inflammatory process spreads to the entire lobe.
By the end of the first day of the disease, the radiograph clearly shows an enhanced pulmonary pattern in the affected lobe, which soon turns into large foci of shading, merging and enlarging. X-ray examination in the stage of hyperemia reveals a homogeneous darkening of the pulmonary parenchyma of medium intensity. Against its background, the shadows of the ribs and the pattern of the bronchi are clearly visible. The X-ray picture in the gray hepatization stage is the same as in the red hepatization phase. At the resolution stage, the radiograph shows inhomogeneous darkening. This is explained by the fact that the process develops non-simultaneously and unevenly. Pneumonia is characterized by rapid changes in the X-ray picture, which occurs over 1-2 days, especially at the onset of the disease and in the resolution stage. Often, after a crisis, the darkening of the lung quickly disappears, however, the normal pulmonary pattern is restored after 2-3 weeks.
Get a consultation with a pulmonologist by making an appointment over the phone. At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors examine patients using modern methods. When making a diagnosis and prescribing treatment, the causes, risk factors and phases of development of pneumonia are taken into account.
Full recovery
— At the beginning of June this year, the Sverdlovsk region developed a procedure for medical rehabilitation of patients who suffered from coronavirus. Does it still apply?
— This rehabilitation program is in effect, but it is advisory in nature. Now in our region there are several centers for the rehabilitation of patients after coronavirus. Those who have had moderate or severe COVID-19 and who have had changes in the lung tissue often require rehabilitation of the respiratory system, which includes a special set of exercises and breathing exercises. If a person who has recovered from coronavirus experiences an exacerbation of his chronic diseases, then he is referred for rehabilitation to an appropriate specialist.
— Is it possible to completely restore the lungs after they are damaged by coronavirus?
— Of course, but in general, recovery depends on the extent of lung damage and the age of the patient. If a young man does not have chronic diseases and his lungs were affected by less than 25 percent, then he will recover in a month, and the disease will pass without a trace for him. We see a clear positive trend in the condition of the lungs already four weeks after the end of treatment for coronavirus in a patient with pronounced changes in lung tissue who suffered a serious illness from COVID-19. In general, lung recovery takes from four weeks to six months.
IMPORTANT
Due to an increase in the number of people calling on coronavirus issues to the hotline of the Office of the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare in the Sverdlovsk Region, the agency has organized the operation of additional telephone numbers.
You can contact specialists regarding the following questions: – algorithm of actions in case of receiving a positive result for COVID-19;
– contact insulation;
– disinfection of COVID-19 outbreaks;
– prevention of coronavirus;
– in case a Rospotrebnadzor employee has not contacted a COVID-19 patient or a contact.
List of new hotline numbers for COVID-19 in the Sverdlovsk region:
Ekaterinburg
| (343) 350-21-64 (343) 374-16-59 on the weekend 8-952-142-91-51 |
Ekaterinburg
Berezovsky Upper Pyshma | (343) 307-40-77 (343) 307-42-99 (343) 307-40-40 |
Ekaterinburg
Polevskoy Sysertsky district | (343) 266-55-21 (343) 266-55-15 |
| Alapaevsk and Alapaevsky district Rezhevskaya district Artyomovsky district | (34346) 3-18-66 (34346) 3-20-69 |
| Asbestos Beloyarsky district | 8-902-260-30-13 (34365) 2-48-18 |
| Irbit and Irbitsky district Slobodo-Turinsky district Tavdinsky district Taborinsky district Turin district | (34355) 6-36-45 (34360) 5-34-87 |
| Kamensk-Uralsky and Kamensky district Sukholozhsky district Bogdanovichsky district | (3439) 36-43-84 (3439) 37-87-08 (3439) 36-48-22 |
| Kachkanar and Kushva Krasnouralsk Nizhnyaya Tura | (34344) 2-60-03 (34341) 6-35-21 |
| Krasnoufimsk and Krasnoufimsky district Artinsky district Achitsky district | (34394) 7-59-43 (34394) 7-59-40 |
| Nizhny Tagil and Suburban district Verkhnesaldinsky district Nizhnyaya Salda Kirovgrad Nevyansky district | 8-912-689-91-27 |
| Pervouralsk Revda Shalinsky district Nizhneserginsky district | 8-800-222-45-60 (3439) 24-51-17 |
| Severouralsk Ivdel Krasnoturinsk Karpinsk | (34380) 2-34-56 (34384) 6-30-61 (34384) 6-48-41 |
| Serov and Serovsky district Garinsky district Verkhotursky district Novolyalinsky district | 8-908-900-39-77 8-952-734-02-10 8-908-913-00-89 |
| Talitsky district Baikalovsky district Tugulymsky district Kamyshlov and Kamyshlovsky district Pyshminsky district | (34371) 2-18-98 (34375) 2-05-80 |
Prepared in accordance with the criteria approved by the order of the Department of Information Policy of the Sverdlovsk Region dated 01/09/2018 No. 1 “On approval of the criteria for classifying information materials published by government agencies of the Sverdlovsk Region, in respect of which the functions and powers of the founder are exercised by the Department of Information Policy of the Sverdlovsk Region, as socially significant information."
- Published in No. 202 dated 10.28.2020