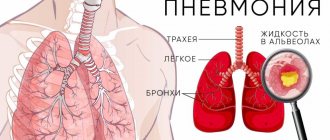
Pneumonia (Pneumonia)
To ensure proper treatment of pneumonia and select the appropriate treatment method, a preliminary consultation and examination conducted by a therapist or pulmonologist is necessary. Only after a diagnosis has been made and the form of the disease has been determined can treatment begin.
Methods and methods for treating pneumonia are determined by the degree, age category of the patient and the presence of indications and complications. Hospitalization with pneumonia is carried out only on the recommendation of a doctor, if good reasons and reasons for this are identified.
To cure pneumonia in adults, it is necessary to use a combination of etiological and symptomatic therapy methods. The effectiveness of the first group of treatment methods is due to the complete destruction of all foci of the disease, and the second group of treatment methods are aimed at getting rid of the manifestations of pathologies associated with pneumonia.
During the treatment of pneumonia, antibacterial medications, antibiotics, and other medications are used to cure cough, stabilize breathing and body temperature, and rid the lungs of accumulated phlegm. Medicines are prescribed based on the stages of pneumonia and severity. Also, in order to successfully treat pneumonia, do not forget about physical and magnetic therapy, and breathing exercises.
Let us consider in detail what methods can be used to effectively treat pneumonia, regardless of its stages.
Symptomatic treatment of pneumonia
Aimed at improving the general condition of the patient, reducing temperature, normalizing breathing due to the fight against dry cough. The key drugs of therapy are mucolytic agents and medications with an antipyretic effect to actively lower body temperature in adults.
The principles of treatment imply that mucolytics promote the effective removal of mucus from the respiratory system, and many drugs also support the action of antibacterial agents, which helps to more effectively cope with pneumonia. The following drugs are used to treat pneumonia:
- Carbocysteine;
- ACC;
- Ambroxol and derivatives of these drugs.
The required dosage is prescribed only by doctors after conducting an appropriate examination, and the duration of administration also varies depending on what stage of pneumonia the patient has.
Moreover, we note that bringing down the temperature in adults should be carried out only when the temperature has reached 39 degrees, and the patient’s well-being sharply and dramatically worsens.
Antibiotic therapy for pneumonia
To get rid of pronounced symptoms of the disease and effectively combat high fever, treatment of the disease with antibiotics is used. However, before prescribing active antibiotics, which can cause irreparable harm to the body, the doctor prescribes tests and a comprehensive examination. In practice, there are separate categories of patients for whom the method of combating pneumonia and the use of drugs will differ significantly:
- The first category is patients in the age group under 60 years of age, whose symptoms are similar and treatment is carried out according to a similar scheme. This group of patients has no pathologies or chronic diseases, pneumonia occurs easily and without significant complications, the temperature does not rise above 38 degrees. Penicillins and macrolides are used in the treatment of the disease; in most cases, therapy is carried out at home under the strict supervision of a doctor as the disease progresses. If it is necessary to bring down the temperature, antipyretics are used orally; in case of difficulty breathing, mucolytics are prescribed;
- the second category is patients aged 60 years or more who have concomitant pathologies of the cardiovascular system, kidneys, and respiratory organs. This group also includes patients who have problems with alcoholism; they are more susceptible to developing pneumonia; this category is recommended to be checked in a timely manner in case of a prolonged cough, as well as if the body temperature has been elevated for a long time against a background of general malaise. The most effective treatment for pneumonia involves third-generation cephalosporins and aminopenicillins. Patients in this group always undergo therapy in the clinic’s hospital under the supervision of doctors;
- the third category includes people of any age whose pneumonia is extremely severe, while patients complain of breathing problems, and the temperature remains at 39-40 degrees for a long time. Depending on the stage and severity, pneumonia in patients of this category is treated by doctors in the intensive care unit using the most effective and fast-acting medications.
The prognosis for pneumonia implies that with timely medical care the patient will fully recover. However, signs and symptoms disappear completely no earlier than after 20-30 days. If in the future the patient begins to suffer from a cold, regardless of the causes that caused it, it is necessary to take careful measures so that, if the corresponding symptoms occur, to prevent a recurrence of the disease, which may occur in a more severe form.