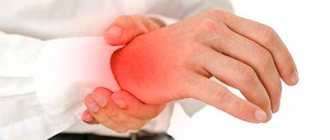
The structure of human hands distinguishes him from representatives of other biological species. Thanks to them, we can not only serve ourselves, but also perform a wide variety of work. The fingers of the human hand are parts of the upper limbs, which in the process of development received a very important functional load. That's why, when your fingers hurt, it becomes difficult to hold a fork or spoon, type text on a PC, cook food, or even just lace up your shoes.
The reasons why your fingers hurt can be different. In addition to being susceptible to injury, there are a number of medical conditions that can affect their mobility. In addition, pain in the joints of the fingers can be caused by inflammatory processes (arthritis).
At CELT you can get advice from a specialist algologist.
- Initial consultation – 4,000
- Initial consultation with the head of the Pain Clinic - 4,500
Make an appointment
What causes pain in the finger joint when bending?
Pain in the fingers can occur for various reasons.
The most obvious of these are injuries. In addition, a number of pathologies can lead to discomfort: inflammatory processes, autoimmune diseases, hormonal imbalance and many other disorders. The most common causes of pain: 1. Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune pathology in which small and subsequently large articular joints suffer. In case of this violation:
- the joints of the index and middle fingers on the hand hurt;
- the skin of the fingers turns red and swells;
- at night and in the morning there is a feeling of stiffness in the hands;
- joints are often affected symmetrically.
2. Psoriatic arthritis – joint inflammation associated with psoriasis. Characteristic:
- pain in the area of the distal (nail) digital phalanx;
- severe swelling;
- redness of the skin with slight cyanosis;
- difficulty when trying to straighten bent thumbs or hands.
3. Infectious arthritis - inflammation of the joints due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into them. Signs:
- acute pain (short-term or long-term - up to several days);
- fever (usually local, sometimes general), chills.
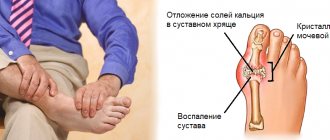
4. Gouty arthritis (gout) is a joint pathology that develops as a result of too much uric acid compounds in the body. Peculiarities:
- burning pain in fingers;
- redness up to cyanosis, swelling;
- motor dysfunction;
- sudden onset of an attack (often at night).
5. Ostearthrosis is a non-inflammatory disease accompanied by the destruction of intra-articular cartilage. Appears as:
- pain in the joints of the hand;
- finger deformations: thickening, formation of subcutaneous nodules, swelling.
6. Rhysarthrosis is a pathology in which the thumb joint hurts as a result of overload, as well as a previous infection or injury. Signs:
- increased pain at the slightest load (later and at rest);
- deformation of the articular joint;
- lack of mobility.
7. Stenosing ligamentitis - damage to the tendons and ligaments of the fingers. Signs:
- a characteristic click when bending a finger;
- “jamming” of the clenched palm;
- pain when moving the hand.
8. Carpal tunnel syndrome is a consequence of injury or pinching of the median nerve passing through the wrist. Usually develops with prolonged and constant work at the computer. The most common joint that hurts is the index finger; there may also be pain in the other fingers except the little finger. Other signs:
- decreased sensitivity, numbness of fingers;
- deterioration of hand mobility;
- pale skin on the hands.
9. Rheumatism is a systemic disease that affects connective tissue. Usually develops as a result of infectious diseases. If the joints of the fingers are swollen and painful after a sore throat, this may be a symptom of rheumatic disease. You may also experience:
- redness of the skin, rash;
- elevated temperature;
- decreased hand mobility.
Factors predisposing to damage to the finger joints:
- problems with the immune system;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- metabolic disorders;
- hereditary tendency to joint pathologies;
- chronic infections;
- injuries, frequent microtraumas;
- prolonged exposure to harmful environments: very cold or hot water, chemicals, etc.
Treatment for inflammation of the joints of the fingers should only be prescribed by a doctor: a therapist, an orthopedic traumatologist, a neurologist or a rheumatologist. Attempts at self-medication can lead to further deterioration of the condition: deformation of the fingers and decreased mobility.
Diagnostics
Orthopedic traumatologists are involved in identifying the causes of pain in the fingers. The diagnosis is made based on a conversation with the patient, external examination data, and additional studies. The diagnostic program includes:
- Survey
. The doctor finds out when and under what circumstances the pain syndrome and other symptoms first appeared, determines the dynamics of the development of the disease, the factors that provoke improvement or deterioration of the patient’s condition. Study life history, family history. - Physical examination
. The specialist evaluates the appearance of the fingers, identifies deformations, inflammation, cracks, dry skin, temperature and color disturbances, swelling, and other manifestations of pathology. Examines sensitivity, range of motion, pulsation in peripheral arteries. - Radiography.
It is performed in two projections, covering the affected fingers or the entire hand. Confirms the presence of fractures, dislocations, tumors, inflammatory and degenerative processes, areas of destruction of solid structures in deep forms of panaritium. - Electrophysiological studies.
Performed for pain of neurological origin to clarify the level of nerve damage, assess the condition of the muscles, and nerve conduction. - Lab tests
. They are produced to determine inflammation, assess the general condition of the body, and detect specific markers for collagenosis.
According to indications, patients are referred for consultation to an endocrinologist, neurologist, vascular surgeon, and other specialists. They prescribe MRI and other instrumental techniques. A biopsy of hard and soft structures is performed for cytological or histological examination.
Clarification of complaints and examination of fingers is the first stage of diagnosis
How to treat when the joints on your fingers hurt?
Therapy for this ailment helps eliminate both the unpleasant sensations themselves and the causes of their occurrence. Thus, for inflammatory processes, non-steroidal or hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, as well as antibiotics in case of infection. In case of dystrophic damage, the task of treatment is to restore cartilage tissue with the help of chondroprotectors, physiotherapy and massage. Performing special exercises also helps restore finger mobility.
The most effective way to restore the functionality of small joints is physical therapy: magnetic resonance therapy, electrophoresis with novocaine, electrosleep and some other procedures. During the period of remission, sanatorium-resort treatment using hydrogen sulfide and radon sources is recommended. Therapeutic nutrition for joint pathologies:
- seafood and fish - contain calcium, iron and phosphorus;
- apple cider vinegar – helps rid the body of toxins;
- flaxseed oil, fish oil - contain fatty acids, help restore fat metabolism.
In addition, it is advisable to include lettuce, radishes, nuts, currants, pomegranate, figs, and ginger in your diet. Limit your consumption of fatty dairy products, mayonnaise, sweets, baked goods, spicy foods and smoked foods.
Treatment of arthritis of the fingers
After a final diagnosis has been established, treatment for arthritis of the fingers is prescribed, which is carried out by a rheumatologist (sometimes together with other specialists - a surgeon, a dermatovenerologist). It should be comprehensive, aimed at suppressing the progression of the pathological process and preventing disorders of joint function. The complex treatment includes:
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- therapeutic exercises and massage;
- reflexology courses;
- folk remedies.
Drug therapy
The primary goal of drug therapy is to alleviate the condition of a sick person. For this purpose, NSAID medications are prescribed to relieve pain, inflammation and tissue swelling. Depending on the degree of activity of the inflammatory process, these drugs are prescribed in the form of injections (shots) or tablets for oral administration. In addition, drugs in this group are prescribed externally in the form of gels, ointments and creams.
The most effective NSAID is Diclofenac, but it has an irritating effect on the walls of the gastrointestinal tract, so it cannot be taken for a long time. Instead of Diclofenac, more modern drugs of the NSAID group are prescribed - Nise, Celebrex, etc. Such products as Pentalgin gel and Diclofencac ointment are used externally. The best ointment for arthritis of the fingers is Voltaren emulgel. The use of NSAIDs can bring significant relief to the patient.
Drugs for the treatment of hand arthritis
Sometimes the inflammatory process is so severe that it cannot be relieved with NSAID medications. In this case, glucocorticoid hormones are used - Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, etc. in the form of injections, orally in tablets or externally in the form of ointments. Intra-articular injection of hormones into small joints is rarely practiced.
To suppress autoimmune processes, basic group drugs are prescribed - Methotrexate, Sulfasalazine, Leflunomide and biological agents (MabThera, Redditux). These drugs are selected by a rheumatologist and prescribed according to a special regimen in long courses.
To restore joint function, chondroprotectors are prescribed - medications that restore the cartilage tissue of joints (Dona, Structum, etc.). They are also prescribed in long courses.
Agents that improve blood circulation and metabolism in tissues - Pentoxifylline, Actovegin, etc. help restore tissue trophism.
Vitamins and minerals are prescribed as general tonics, improving metabolism and helping to restore overall balance in the body.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
The complex treatment of arthritis of the fingers necessarily includes physiotherapeutic procedures. They, just like medications, are selected individually depending on the clinical form and activity of the pathological process. This can be electrophoresis with Hydrocortisone, UHF, laser or magnetic therapy, etc.
Crunching in joints - when to worry
Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid
Massage and exercise therapy
Courses of massage and therapeutic exercises are prescribed during the period of subsidence of the inflammatory process. They help improve blood circulation and metabolism in tissues, restore the function of small joints. At home, you can do the following physical exercises to improve mobility:
- roll a small elastic ball on the table surface with your finger surfaces for a minute, actively involving the affected finger joints in the process;
- with the fingertips of one hand, touch the pad of the 1st finger of the opposite hand; start with the little finger and end with the index finger; repeat the exercise 10 times;
- position your hands so that your fingertips are slightly bent and touch the surface of the table; bend each finger in turn and hit the table with it (like the keys of a piano);
- repeat three times.
Such exercises should be done daily, gradually increasing the number of approaches.
Folk remedies
A doctor should tell you how to treat arthritis of the fingers with folk remedies. He also selects the most suitable method. You can use both herbal decoctions and infusions for oral administration and external agents:
- a compress of kefir mixed with crushed chalk at the rate of 50 g of chalk per 75 - 100 ml of kefir; You should get a thick mixture that needs to be applied once a day at night; to do this, you need to apply it on a cotton napkin, apply it to the sore spot, and put polyethylene and insulation on top; leave it like that all night; perfectly relieves swelling and pain;
- infusion of celery roots; Place 20 g of crushed raw materials (dry or fresh) in a thermos overnight, pour 200 ml of boiling water; the next day, drink 3 to 4 times before meals; course of treatment – 2 weeks; relieves pain and swelling well.
Surgery
This type of treatment for arthritis of small joints is rarely used. In cases of severe arthritis that cannot be treated conservatively, a synovectomy is sometimes performed - removal of part of the synovial membrane that produces a large volume of exudate.
In some cases, the joint is replaced with an artificial one, but this is a fairly rare operation.
Modern treatment strategy for rheumatoid arthritis in this article.
Prevention of joint diseases
The following recommendations will help protect yourself from joint diseases:
- try not to overcool your hands;
- stop smoking and consuming large amounts of alcohol;
- eat more fresh fruits and vegetables and as little canned and spicy foods as possible;
- If you have an acute respiratory viral infection, be sure to get treatment, do not try to endure the disease “on your feet”;
- watch your weight;
- Don't snap your fingers.
So that you don’t have to ask the question: “How to treat if your thumbs hurt?”, periodically perform a simple exercise to prevent carpal tunnel syndrome, especially if your activity involves a lot of work on a PC: raise your thumbs and clench the rest into a fist (gesture of approval). Rotate your thumbs clockwise and counterclockwise. Specialists from the “Hello!” network of clinics will help you determine the exact cause of the discomfort. Are you trying to figure out what to do if the joint on your finger hurts or is swollen? Make an appointment with us - experienced doctors will perform an examination using the latest diagnostic equipment and prescribe the most effective course of treatment using modern non-drug methods.
General clinical recommendations
For patients suffering from arthritis of the fingers, it is recommended:
- lead a healthy lifestyle, toughen up;
- be treated in a timely manner, eliminate all foci of infection that may become a trigger in the development of exacerbations of arthritis;
- get rid of bad habits;
- eat right, regulate sleep and wakefulness;
- if arthritis worsens, do not put stress on your fingers, do not do housework, including washing dishes;
- during remission, do physical exercises for your arms at home; classes should be held daily;
- completely abandon self-medication and adhere to the doctor’s recommendations in everything.
Prevention of arthritis of the fingers
Preventing arthritis is especially important for people who have a genetic predisposition to this disease (close relatives with this pathology). In order to maintain health, they need to adhere to the following recommendations:
- you should not overload your hands with heavy physical or long-term painstaking work, including at home;
- you should not overcool, you should avoid overcooling your hands;
- lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right, toughen up;
- engage in feasible sports, conduct daily training;
- avoid prolonged stress.
Diet
Special nutrition is required only for gouty arthritis of the fingers. The diet of such patients should not contain strong broths, offal, meat of young animals, alcohol, sorrel, lettuce, strong tea, coffee, or chocolate.
If you have gouty arthritis, you should follow a diet
In other cases, it is enough to adhere to the principles of a healthy diet: eat lean meat and dairy products, fish (fatty sea fish is healthy), grains, cereals, vegetables, and fruits. High-calorie foods, sweets, baked goods, spicy seasonings, fried and smoked foods should be avoided. Meals should be regular.
What actually happens with osteoarthritis?
With this disease, intensive aging of the articular cartilage occurs. The result is a loss of elasticity of the articular cartilage. In addition to the fact that the articular surfaces become rough, cracks also appear on them. In many cases, the cartilage wears away so much that the bone is exposed. All this leads to a decrease in the elasticity of the articular cartilage and causes dysfunction of the joints. Further, all of the above changes can be accompanied by inflammation, which causes bone tissue to grow, and this leads to disease and deformation of the joints.
Causes
Arthrosis can be primary and secondary.
Primary arthrosis appears due to problems with the cartilage tissue of the joint, namely:
- genetic disorders in the composition of joint cartilage tissue;
- joint hypermobility;
- dysplasia, flat feet, wide feet.
Secondary arthrosis is the result of joint damage and other diseases. Among its reasons:
- injuries, microtraumatization of joints;
- acute and chronic arthritis, synovitis;
- metabolic disorders, lack of calcium, phosphorus and other minerals;
- gout, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis;
- diabetes mellitus and other diseases of the endocrine system.