For normal functioning of the human body, a regular supply of vitamins, nutrients and minerals is necessary. A deficiency of any element causes a malfunction of the entire body and leads to various health problems.
Calcium is an essential element of metabolism and its deficiency is acutely felt by all organs and systems of the body. The most common diseases caused by calcium deficiency are hypocalcemia, hypocalcinosis, and osteoporosis.
Why is calcium needed in the body?
As almost everyone knows, calcium is the main element of bones and teeth, but its role in the body is not limited to this. Calcium regulates the contractile function of the heart, nourishes nervous tissue, ensures the conduction of nerve impulses, reduces the level of bad cholesterol, regulates blood pressure, maintains normal blood pH levels, is involved in the transport of nutrients and the removal of metabolic products, etc. The need for this element increases significantly during pregnancy, and a lack of calcium makes normal development of the fetus impossible and worsens the condition of the expectant mother.
Nutrition for calcium deficiency
In order to correct microelement deficiency, individuals at risk are prescribed a diet enriched with calcium. A diet rich in calcium is also indicated for diseases of the cardiovascular system. It is known that arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis, and circulatory failure are calcium-dependent diseases.
The basic principles of nutrition are simple - ensure a sufficient daily supply of microelements and vitamins that facilitate their absorption in the intestines and minimize factors that impede this process. Calcium diet includes:
- milk, fermented milk products.
- vegetables, fruits and nuts (listed with the highest content): parsley, garlic, dill, persimmon, dried apricots, celery greens, dandelion leaves, lettuce, green onions, leeks, watercress, cilantro.
- protein of animal and plant origin (lean meat, legumes).
Vitamin D ensures complete absorption of calcium from the small intestine. Its daily dose should be 800 IU. Vitamin D3 is synthesized in the skin under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, and vitamin D2 is absorbed through food in the gastrointestinal tract.
Sources of this vitamin: sea bass, herring, tuna, mackerel, seafood, fish liver (halibut and cod), fish oil, cheese, sour cream, cocoa, eggs. Magnesium reduces calcium loss in urine. A sufficient amount of it is found in peas, oatmeal, walnuts, beans, mustard and buckwheat.
What can cause calcium deficiency in the body?
A lack of calcium in the body occurs in two cases. When there is insufficient intake of a mineral from food or when the body’s ability to absorb this trace element decreases. Calcium deficiency can be caused by:
- dysfunction of the thyroid and parathyroid glands;
- impaired absorption of calcium in the intestine caused by intestinal diseases (dysbacteriosis, allergies, colitis, etc.)
- metabolic disorder, which is characterized by low levels of vitamin D and high levels of lead, zinc, phosphorus, magnesium, iron, cobalt, potassium and sodium, which contribute to the excretion of calcium;
- uncontrolled use of diuretics and diuretics;
- hormonal disorders (lack of estrogen);
- elderly age.
Abuse of coffee-containing drinks, alcohol and smoking are pathogenic factors in the occurrence of calcium deficiency in the body.
Calcium preparations
Pharmacological enterprises offer vitamin complexes containing calcium in tablets, in the form of soft chewable lozenges or lozenges. The flavored chewable tablet is especially convenient for maintaining calcium balance in children.
Calcium supplements must contain vitamin D.
Optimal proportions - for 500 mg of calcium there should be at least 200 IU of vitamin D3 or cholecalciferol.
- Kalcemin
contains calcium carbonate, calcium citrate and vitamin D. Small children need to take one tablet. Older children and adults - 2 each. - Calcium D3 Nycomed
Available in the form of chewable lozenges. The maximum dose for adults is 3 tablets per day. - Vitrum Calcium+Vitamin D3
contains calcium carbonate obtained from oyster shells. Cholecalciferol ensures complete absorption of the mineral. The dose for the treatment of calcium deficiency is prescribed by the doctor. - Complivit Calcium D3
with the active component calcium carbonate and cholecalciferol, it has a pleasant fruity taste and smell. The drug may cause side effects in the form of gastrointestinal disorders. - Calcepan
in the form of a coated dragee is enriched with herbal extracts. The drug is taken in courses of 28-36 days.
The disadvantage of all vitamin complexes is that the microelement content is too low, which does not provide the daily intake.
Symptoms of calcium deficiency in the body
Calcium deficiency does not have specific, pronounced symptoms. As a rule, a general deterioration in health is diagnosed, expressed in the following disorders:
- increased nervous excitability, sleep disturbances, irritability, fatigue, decreased performance;
- muscle cramps, tingling, numbness of fingers and toes, with periodic pain;
- dry and flaky skin, brittle nails, increased sweating, especially in the head area;
- tooth decay, increased bleeding gums;
- frequent fractures and cracks of bones, development of osteoporosis;
- disruption of heart function up to the development of heart failure, cardiac arrhythmia;
- blood clotting disorder;
- decreased immunity, which is expressed in a long course of the disease and frequent morbidity;
- increased sensitivity to cold, chilliness, body aches, severe chills.
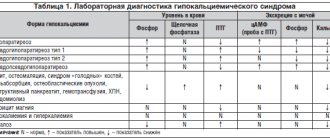
Causes of hypocalcemia
Endocrine organs are sensitive to effects on them, so calcium metabolism can be disrupted for various reasons.
A decrease in plasma Ca may occur for the following reasons:
- neck trauma with bleeding;
- complication after surgery on the thyroid gland;
- inflammatory processes;
- ionizing radiation;
- metastasis in endocrine organs;
- adrenal insufficiency;
- autoimmune diseases;
- systemic diseases.
Identifying the causes is considered the basis of treatment, since if the influence of negative factors continues, therapy will not be effective.
Treatment of Ca deficiency
The disease can occur in acute and chronic form. An acute condition requires treatment in a hospital setting, as it threatens the patient’s life. In case of chronic calcium deficiency in the body, synthetic calcium-containing preparations, vitamin and mineral complexes are prescribed, the diet is adjusted to increase the intake of microelements in food, and concomitant pathologies are treated. To speed up metabolic processes, sufficient physical activity is recommended.
Calcium deficiency cannot be treated on your own. Self-medication is especially dangerous during pregnancy or childhood. An overdose of calcium in the body, which occurs from uncontrolled intake of calcium supplements, can pose a serious health hazard. You should take any medications only after examination and consultation with a specialist.
At a medical clinic, you can undergo a comprehensive examination to determine the level of calcium in the body and, based on its results, receive qualified consultation from a doctor. It is important to remember that uncontrolled use of calcium supplements is dangerous to health. Without determining the degree of calcium deficiency, the causes of pathology, identifying and treating diseases that could provoke a lack of the mineral, you cannot take calcium supplements. Treatment of complications of the disease may also be necessary, and this should also be done by a specialist. You can make an appointment by phone: +, +.
When there is not enough calcium in a person's bones...
As you know, there are many bones in the structure of the skeleton, each of which performs its own function. Moreover, bone is a living element of the system that requires nutrition and renewal. Moreover, the bones themselves cannot function normally if they do not receive the appropriate load.
Why is there not enough calcium in the skeletal system: what are the reasons?
Every part of the bone skeleton contains calcium, which makes bones strong and hard. If the body does not receive this chemical element in full, pathological changes may begin in the bones, and serious changes do not require much time. If a person breaks his leg and walks in a cast for even thirty days, we can already talk about the beginning of disorders in the bone tissue.
But not only bone injury leads to calcium deficiency. Scientists have already proven that human aging is accompanied by a sharp leaching of calcium from the body. This is why bones in older people become less strong and brittle. A disease such as osteoporosis appears. He can accompany any elderly person. This disease begins much earlier. This calcium deficiency is considered normal and cannot be avoided. If you have osteoporosis, treatment should only be carried out under the supervision of specialists.
Decalcification of the skeletal system can be caused by various diseases:
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, when the body is not able to obtain enough calcium from the foods it eats.
- In case of kidney disease, when a huge amount of calcium is washed out along with the urine.
- In women expecting the birth of a baby, the fetus requires calcium in large quantities for the proper formation of the skeleton. But, in fact, it is produced in such a large amount that it leads to damage to bone tissue and makes the bones completely fragile.
- If a person takes a large number of medications that are hormonal drugs. In this case, the balance of calcium in the skeletal system is also disturbed, since these medications capture free calcium and remove it from the body.
How can you determine that there is a calcium deficiency in the body?
If bone tissue lacks an element such as calcium, the bones begin to lose hardness, become less strong and brittle. It is for this reason that older people get broken bones when they fall.
Sometimes there is not even a fall, but the bones break: this is due to bone deformations, most often the vertebral bodies are deformed. If the cartilage and bone endplate breaks, part of the nucleus pulposus is displaced. It is embedded in the spongy substance. Due to such an injury, an intervertebral hernia appears.
Elderly people often experience fractures:
- In the area of the femoral neck.
- The vertebral bodies themselves.
- Spongy bones can have microfractures, after which microcalluses subsequently form.
What you need to know about the treatment of diseases associated with calcium deficiency?
Decalcification is a serious process, sometimes leading to irreparable consequences. The fight against such a disease is never easy.
If a person does not have problems with the intestines or kidneys, and the metabolism is not impaired, then maintaining the functioning and structure of the skeletal system is not so difficult. It is enough to adhere to a healthy lifestyle. Dealing with decalcification is often very difficult. This is an effective method that has a beneficial effect on the cells responsible for the structure of bone tissue.
But in our fast-moving times, it is not always possible to find the opportunity to visit the gym. You can purchase a Swing Machine, with which you can not only load your spine physically, but also receive the necessary dose of massage.
In order for the metabolism in the body not to be disturbed, it is necessary to treat nutrition correctly; products should be healthy and properly balanced. Food should contain enough calcium-rich foods. We should not forget that in addition to this element, other minerals and vitamins must be supplied to the body in the required quantities.
A lot of calcium is found in a number of foods that you need to have in your diet:
- Milk and dairy products, including cheese. You need to eat it every day.
- Fish.
- Don't shun cow butter and eggs.
- Spinach, legumes, cabbage.
Complete absorption of calcium is possible only with the presence of vitamin D, so milk, margarine, and liver should be present in your diet.
Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Causes of hypercalcemia
Excess Ca in plasma can be caused by several factors. It is not uncommon for calcium metabolism disorders to occur due to the development of malignant tumors or benign tumors.
In 80% of patients, hypercalcemia develops due to disorders resulting from the formation of a solitary adenoma on the pituitary gland. Adenoma, in turn, is formed due to stress, low blood pressure, hormone intake, etc.
In 12% of cases, the cause is the primary form of hyperplasia. 2% of patients are diagnosed with parathyroid cancer. About 6% of patients have multiple adenoma.
Reasons can also include:
- deficiency in the diet of foods containing calcium;
- violation of malabsorption functions of the intestine;
- chronic renal failure.
Treatment in this case involves eliminating the cause. If after this the indicators do not change, targeted therapy or even surgery is performed.
Products containing calcium
If you need to make up for the deficiency of a mineral such as calcium, it is important to pay attention to products with a high content of calcium, and not go to the pharmacy for powders and tablets.
Proper (healthy) nutrition contributes to comprehensive prevention and health improvement, and stimulates the body's absorption of calcium. Here is a list of the main foods that are rich in calcium:
- dairy products (milk, cream, cheeses, cottage cheese, yogurt, sour cream);
- nuts (hazelnuts, almonds, pistachios);
- vegetables and herbs (broccoli, white cabbage, garlic, onions, mustard, parsley, mint, cumin, basil);
- legumes (peas, beans);
- fish and meat (pork, veal, salmon, sardines);
- cereals (oatmeal
It is important to take a responsible approach to organizing your diet. For an adult, the recommended daily dose of calcium is 1000 mg. Athletes engaged in active training should receive at least 1200 mg of calcium. Approximately the same amount is established for older people.
The category of pregnant women and nursing mothers deserves special attention. Their need for microelements is significantly higher, so the daily norm is 1200 mg.
Hypercalcemic crisis
A rare but dangerous complication is hypercalcemic crisis. In an acute condition, the patient’s entire nervous system is disrupted and blood clotting accelerates. Increased blood density implies increased risks for the patient’s life, as this can lead to the formation of blood clots or complete cardiac arrest.
Hypercalcemic crisis has symptoms:
- maintaining temperature above 40°C;
- internal bleeding;
- signs of fever;
- severe itching of the skin.
Disturbances of the central nervous system lead to the occurrence of psychosis, and subsequently shock. The patient's condition leads to the fact that he does not understand what is happening. If medical assistance is not provided in a timely manner, respiratory paralysis begins, followed by cardiac arrest and death.