Myocardial function is restored as soon as the required amount of potassium
. Usually sodium cannot withstand the onslaught of its opponent and gives up its occupied place without unnecessary resistance.
What about "friends"? Potassium _
There is an excellent relationship with
magnesium
. Potassium is poorly absorbed from food if there is a magnesium deficiency. Conversely, it fully exhibits its beneficial properties if magnesium is contained in sufficient quantities. Therefore, these two microelements need to be consumed together. Fortunately, they are often found in the same foods (vegetables, herbs, fruits), and a combination of potassium and magnesium is easy to find in mineral preparations.
60% magnesium
is found in human bones, the rest is in the cells of the heart and brain, as well as in soft muscle tissue.
When there is a lack of magnesium
, its physiological antagonist, calcium, comes to the fore. Like sodium, it occupies empty territory. Working in excess, calcium causes strong or abnormal muscle contractions. Muscle cramps and pain can be felt throughout the body: most often in the calves and feet. Such seizures, due to a deficiency of microelements, typically occur at night. With an excess of potassium/lack of magnesium, the myocardium also suffers: heart rhythm disturbances occur, increased vascular tone develops, which negatively affects blood pressure (a tendency to increase it), and metabolic processes in the myocardium are disrupted.
So, with a deficiency of potassium and/or magnesium, the heart muscle (myocardium) feeds and contracts incorrectly and, one might say, does not “rest” normally.
The main causes of potassium and magnesium deficiency:
increased sweating (sports, hot climate, work in hot shops, frequent visits to baths or saunas)
diarrhea or use of laxatives
use of diuretics (except potassium-sparing ones)
hormonal treatment, including contraception
diabetes
diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, ulcers, diseases of the gallbladder and pancreas)
chronic stress and depression
regular consumption of coffee and/or alcohol
cardiovascular diseases
Magnesium and potassium deficiency in the body: symptoms and signs
Home first aid kit MIRRA
In recent years, the Company has actively conducted research on the possibility of using health and cosmetic products to solve general and cosmetic problems. Almost all the leading employees of the Company worked in this direction - I. Rudakov (Dr. Sc.), S. Chubatova (Dr. Sc.), E. Aitova (Ph.D.), L. Conde ( Ph.D.), A. Golubkov (Ph.D.), Production Director V. Tulsky, Chief Technologist B. Gorodnichev. Also, consultants and distributors of some DCs began to take part in scientific developments. Since 2010, numerous scientific articles, how-to guides and product references have been published, addressing a range of modern cosmetology (cosmeceutical) concepts and the need for new product development, as well as the idea that beauty and health products need to be used in combination. The result of the scientific and practical work was the development of an information testing method for assessing the micronutrient supply (MS) of the body. This information was published in the issues of our monthly under the heading “Home First Aid Kit MIRRA”.
This publication is about potassium and magnesium deficiency.
POTASSIUM
(K)
Potassium is found in many foods and is 90-95% absorbable. On average, it enters the body with food in an amount of 1−3 g per day. A total of 160−180 g of potassium is present in the human body. Below is a questionnaire containing a list of negative states (NS). Their cause may be potassium deficiency, or rather, insufficient micronutrient supply. To understand whether there is a deficiency of potassium in the body, you need to identify the NS characteristic of your health condition and, depending on their quantity, estimate the potassium MO.
- Apathy, indifference to what is happening around.
- Tendency to depression.
- Decreased performance.
- Fatigue, frequent weakness.
- Decreased resistance to stress.
- Allergic reactions and diseases.
- Muscle weakness.
- Skin itching.
- The skin slowly recovers from cuts and wounds.
- Excessive dry skin.
- Excessive peeling and roughness of the skin.
- Severe hair loss.
- Loss of hair flexibility.
- Hair has become thinner.
- Hair dulling.
- The mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue are inflamed.
- Tendency to diarrhea.
- Heart rhythm disturbances, heart pain.
- Change in blood pressure.
- Tendency to inflammatory processes with the formation of erosion (gastritis, cervical erosion).
The results obtained allow us to judge the degree of potassium supply in the body. If NS is 6 or less, this indicates a normal level of MO. When choosing 7−12 NS, we can talk about a slight or moderate decrease in MO. Potassium deficiency in the body may be indicated by NS levels of 13 or more.
The reason for the decrease in the body's supply of potassium may be its insufficient intake from food. However, this is not the only explanation. Thus, the body intensively consumes potassium during nervous, mental overload, excessive or chronic stress.
Another important reason for the decrease in potassium MO is its displacement by excess sodium entering the body, taking hormonal drugs, diuretics, and laxatives. Potassium is consumed faster when the excretory systems (skin, intestines, lungs, kidneys) are disrupted.
Thus, if a potassium deficiency is detected, i.e., a decrease in MO, it is necessary to reconsider the diet. By adding potassium-rich foods to it, MO can be restored. The rapid restoration of potassium levels can be facilitated by over-the-counter drugs containing this micronutrient in the form of aspartate, which is well absorbed by the body (Panangin, Asparkam). They also contain magnesium aspartate. If the body is exposed to various stress factors for a long time, MO may be disrupted not only by potassium, but also by other substances, which requires the selection of a group of means to restore it.
If there is a pathology of the excretory systems, drug treatment is often prescribed. If potassium metabolism processes are disrupted at the organismal level, regulatory therapy with homeopathic remedies may be recommended. If potassium MO is normal, no interventions should be performed. If MO is reduced, its normalization becomes extremely important, and sometimes even vital for the body.
MAGNESIUM
(Mg)
On average, 200−400 mg of magnesium enters the body with food and water per day, and about half of this dose is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. This microelement is an important component of every cell, where, together with calcium and sodium, it participates in ensuring the most important intracellular processes.
Below is a list of negative conditions (discomfort, symptoms, diseases) that often indicate magnesium deficiency, or its insufficient MO. This condition may require correction by normalizing the diet and taking dietary supplements. Count the number of NS characteristic of your health condition.
- Increased nervous excitability.
- Dizziness.
- Anxiety, restlessness.
- Sleep disorders, insomnia.
- Tendency to depression.
- Increased fatigue, weakness.
- Decreased performance.
- Deterioration in concentration.
- Decreased resistance to stress.
- Hearing loss.
- Immunodeficiency states.
- Hair loss.
- Thin and brittle nails.
- Tingling and numbness in fingers and toes.
- Twitching of eyelids.
- Cramps and muscle pain.
- Fluctuations in blood pressure.
- Heart rhythm disturbances.
- Heartache.
- Tendency to diarrhea or constipation.
If the number of selected NS does not exceed 6, we can talk about a conditionally normal level of MO. The likelihood of a slight or moderate decrease in MO is indicated by the choice of 7−12 NS. A sign of magnesium deficiency may be the release of 13 NS or more.
In addition to those indicated in the list of NS, symptoms of magnesium deficiency (i.e., insufficient MO) may include unexplained headaches, increased irritability and tearfulness, and the appearance of absurd character. Of the entire complex of NS, restlessness, anxiety, and decreased perseverance are very often observed. The state of magnesium deficiency in the body and the disruption of its metabolism are greatly influenced by chronic stress.
These factors are not the only ones that can influence magnesium deficiency. To their number you can also add inflammatory processes or dysbiosis of the gastrointestinal tract, due to which the absorption of nutrients is impaired. Impaired magnesium metabolism can result from taking certain medications. An increased need for magnesium is observed during pregnancy or recovery after a long illness. At the same time, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of magnesium deficiency due to a monotonous diet, in which foods poor in this microelement predominate.
To eliminate the nervous system associated with magnesium deficiency, it is often enough to normalize the diet. MO can also restore the intake of magnesium-containing over-the-counter medications and dietary supplements. They may contain magnesium and potassium in the form of aspartates (Asparkam, Panangin), or magnesium and vitamin B6, as well as other mineral and vitamin complexes. Normal supply of the body with magnesium does not require taking any measures, but if it is insufficient, normalization of this condition is not only desirable, but often necessary.
I. Rudakov, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Director of Science
*When using article materials, a hyperlink to the source is required.
How to compensate for potassium deficiency?
As a rule, potassium chloride is prescribed. Less commonly, potassium bicarbonate or potassium citrate. Most drugs are prescribed in tablet or capsule form, but for very severe forms of the disease, injections and droppers are used. In case of improper redistribution of potassium in the body, the drug cannot be administered intravenously.
To replenish the supply of potassium in the blood, potassium-containing drugs are used. As a rule, potassium chloride is prescribed. Less commonly, potassium bicarbonate or potassium citrate. Most drugs are prescribed in tablet or capsule form, but for very severe forms of the disease, injections and droppers are used. In case of improper redistribution of potassium in the body, the drug cannot be administered intravenously.
Important. A very important factor both for the treatment of potassium deficiency and for its prevention is the correct diet.
Let's figure out how to compensate for the lack of potassium in the human body. Try to eat as much plant food as possible, give up high-calorie foods, fast food, processed foods, and accustom yourself to tasty and healthy vegetable soups and decoctions. Instead of frying, bake vegetables and meats. The daily requirement for potassium is 3 to 5 grams. For people with heavy physical activity, children and adolescents, as well as for patients constantly taking diuretics, the norm is slightly higher.
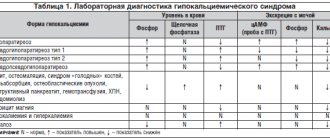
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis of hypokalemia is diverse and determined by its form. The kidneys play a major role in maintaining potassium homeostasis. The level of potassium is determined by a combination of several processes, namely: potassium filtration, secretion and reabsorption. Since potassium in the blood plasma is in a free state, it is completely filtered in the renal glomeruli; potassium ions passing through the filter are almost completely reabsorbed in the distal/proximal tubules.
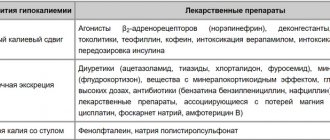
The process of potassium excretion by the kidneys is under humoral control, the main role in which belongs to mineralocorticoids ( aldosterone ), which both increases the penetration of potassium ions into the cells of the distal tubule and increases the permeability of the cell membrane to potassium, promoting potassium secretion. insulin also takes part in the processes of regulation of potassium excretion by the kidneys , which reduces the excretion of potassium by the kidneys. The state of acid-base balance has a significant influence on kaliuria. Thus, with alkalosis, hypokalemia develops as a result of the transition of potassium found in the blood plasma into cells. Potassium deficiency is observed with increased/accelerated breakdown of proteins in the body, which helps to force the release of potassium.
The role of minerals
Magnesium is a mineral responsible for the delivery of calcium and sodium ions to cells. It controls the condition of the cell membrane. Participates in strengthening and expanding the walls of blood vessels, normalizes the functioning of the heart. Thanks to magnesium, the functioning of the nervous system is normalized, tension goes away, and resistance to stress increases. The mineral takes an active part in hydrolysis, improves intestinal motility, and promotes the removal of waste and toxins from the body.
A lack of magnesium increases the risk of developing kidney and bladder stones. Deficiency of the element leads to rapid destruction of joints and bones. They become soft and porous. Often, magnesium deficiency causes a heart attack.
The main role of potassium is participation in water-salt balance. It delivers water to cells and removes excess water. Affects muscle function and increases resistance to physical stress. Potassium normalizes heart rhythm and has a beneficial effect on the condition of the myocardium. It provides oxygen to the brain and increases mental activity.
Lack of potassium leads to pathologies of the kidneys, liver, and disrupts the activity of the endocrine glands. Lack of the mineral causes the development of sclerosis and the accumulation of sodium in the vessels. This in turn provokes allergic reactions.
The daily intake of magnesium for an adult is 280–320 mg, potassium – from 200 to 500 mg. For pregnant women and athletes, the mineral content should be increased by 50–100 mg.
Treatment
To identify a lack of potassium and magnesium, you should not take into account only external signs. Doctors recommend blood and urine tests, an electrocardiogram, and a study of the mineral composition of hair and nails. After the deficiency of elements is confirmed, the doctor prescribes therapy to replenish them: vitamin preparations, IVs, injections or a special diet.
If there is a slight lack of minerals, drinking freshly squeezed juices will help replenish their amount. Substances in drinks are considered good catalysts and allow better absorption of food. Also, the diet should contain a lot of greens, vegetables, and fruits.
To replenish magnesium, eat nuts (hazelnuts, almonds, cashews and peanuts), wheat bran, buckwheat porridge, millet and wheat. Dried fruits are especially rich in minerals. For good health and replenishment of elements, regularly include dates, dried apricots, raisins, prunes, and dried coconuts in your menu.
All varieties of cabbage, fruits (apples, avocados, peaches, cherries and gooseberries), mint, sunflower seeds and various types of nuts are good for eliminating potassium deficiency. Do not neglect dairy and fermented milk products. There is especially a lot of potassium in fatty cheeses, sour cream, and fermented baked milk.
During heat treatment, products lose most of their nutrients. Therefore, try to include as much fresh food in your diet as possible. It is not recommended to soak potatoes and other vegetables in water before cooking. They need to be cut immediately before use: storing them in chopped form significantly reduces the number of useful elements.
To replenish minerals using pharmacological agents, you should not purchase them without consulting your doctor. An experienced medical specialist will recommend a suitable remedy, prescribe a dose and course duration. If there is a lack of magnesium, Magnesium Diasporal, Magne B6 Forte, Magnelis B6 and others are usually prescribed. Popular drugs containing potassium are Asparkam, Panangin, Potassium orotate and others.
What you need to know about potassium levels and kidney disease
Potassium is a mineral and electrolyte needed by the body to support key processes.
It is one of the seven essential macronutrients that plays a role in kidney function. Too much or too little potassium can lead to complications affecting the kidneys. Potassium plays a key role in many processes in the body, including nerve signal transmission, cardiac contractility, cellular transport and normal kidney function. It is important to get enough potassium from your diet, as an imbalance can cause problems in the body.
In this article, we look at the connection between potassium and kidney health. We also explain how people with chronic kidney disease (CKD) can manage their dietary needs to improve their health.