Pain in the joints of the arms and legs can be of a very diverse nature, just as the causes of its occurrence differ. The appearance of pain in the joints of the hands can be caused by inflammatory processes or degenerative changes in the joints themselves or the tissues surrounding them. Pain can be felt in the elbow or wrist joints of the hands, it can be muscular and neurogenic; it is better to entrust the determination of the cause of its occurrence and the choice of a means to reduce pain to a doctor without self-medication.
Why does pain occur in the elbow joint of the right arm (left arm)?
The vast majority of cases of pain in the elbow joint are associated with the development of the following diseases:
- epicondylitis of the elbow joint;
- arthrosis of the elbow joint;
- arthritis.
In addition, pain in the elbow joint of the left arm (as well as the right) can come from the damaged segment of the cervical and thoracic spine and be considered referred.
Pain in the elbow joint of the right hand, treatment for epicondylitis
Most often, pain in the joints of the hands is caused by epicondylitis of the elbow joint, which accounts for 60-80% of cases.
This disease occurs at any age and is associated with overload or injury to the tendons of the hands. Epicondylitis is characterized by pain in the joint of the right hand (or left hand), the occurrence of which is caused by stress on the hand, carrying heavy objects and attempts to lift a heavy object.
With this pathology, there is no change in the mobility of the elbow joint; its full flexion and extension is not impaired. Visually, the joints look completely healthy and unchanged, pain occurs only in the area of the condyles of the joint (in its bones, protruding on the sides).
Pain in the elbow joint of the right hand, treatment for arthrosis
Much less frequently (about 10% of cases), pain in the elbow joint of the right and left arm is caused by arthrosis. The pain syndrome in this disease is less pronounced. Painful sensations appear when trying to maximally flex the elbow and extend it to the limit.
When moving, a crunching sound may be heard in the joint. As arthrosis develops, there is a gradual decrease in the mobility of the elbow joint. Patients have difficulty fully flexing and extending the arm at the elbow joint. The arm of patients with advanced arthrosis is constantly bent at the elbow, the bones of the joint are deformed, but upon palpation the joint is not painful and does not feel hot.
Pain in the elbow joint of the right hand, treatment for arthritis
Even less often (from 5 to 7% of cases) pain in the elbow joint is caused by arthritis. With arthritis, in addition to damage to the elbow joint, inflammation of other joints is also observed (depending on the type of arthritis).
Joint pain due to arthritis is quite pronounced and can be felt both during movement and at rest. In addition, any arthritis is accompanied by severe swelling of the inflamed elbow, its swelling, and often redness.
In some cases, against the background of arthritis of the elbow joint, bursitis develops, a disease in which the periarticular serous bursa becomes inflamed. In patients with bursitis, an elastic formation in the form of a hemisphere filled with liquid appears on the back surface of the elbow.
Pain in the elbow joint of the left arm, treatment for damage to the cervical and thoracic spine
Every fifth case of pain in the elbow joint is associated with damage to a segment of the cervical or thoracic spinal column. There are no changes in the appearance or impairment of mobility of the elbow joint. Joint pain in these cases can bother patients not only when moving, but also at rest.
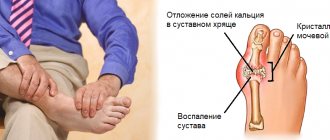
Gout
Gouty joints usually involve paroxysmal episodes of pain, stiffness, inflammation and redness in the joints. The reason for this lies in the excess production of uric acid, which is not completely utilized by the kidneys and is deposited in the form of crystals in the joints, which leads to inflammation. As a rule, this disease develops after 50 years. Therefore, it must be remembered that with age, the excretory function of the kidneys may decrease, which can lead to gout. Gout usually affects the feet, but if left untreated, other joints can also be affected.
Pain in the joints of the fingers: treatment, causes
Pain in the joints of the fingers is most often caused by the following diseases:
- polyosteoarthrosis of the fingers;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- psoriatic arthritis;
- gout, gouty arthritis;
- de Quervain's tenosynovitis;
- rhizarthrosis.
In addition, pain in the joints of the fingers, accompanied by numbness, may be associated with carpal tunnel syndrome and Raynaud's syndrome.
Pain in the joints of the fingers with polyosteoarthrosis
In 40% of cases, pain in the joints of the fingers is associated with polyosteoarthrosis, which is diagnosed mainly in people over 40 years of age, most often in women.
Characteristic signs of polyosteoarthrosis are special nodules (the so-called Heberden's nodes) on the dorsal or lateral surfaces of the joints, localized near the nails. The development of Heberden's nodes occurs symmetrically, simultaneously on the left and right hands, with the same localization. Similar formations can occur on any finger.
In some people, Heberden's nodes form, accompanied by burning and pain, swelling and redness. In others, this pathology develops asymptomatically, pain and burning are absent.
In addition, polyosteoarthrosis is characterized by the appearance of mildly painful Bouchard nodes on the proximal interphalangeal joints located in the middle of the fingers. The shape of these nodules is spindle-shaped, development is slow, and there is no pain.
Pain in the joints of the fingers with rheumatoid arthritis
About 5-8% of cases of pain in the joints of the fingers are caused by rheumatoid arthritis. Most often, this disease occurs in people over 30 years of age, mainly in women. As a rule, rheumatoid arthritis is caused by severe stress, flu, severe colds, infectious diseases or hypothermia.
Early in the development of rheumatoid arthritis, the metacarpophalangeal joints of the middle and index fingers become inflamed and swollen. Most often, against the background of their inflammation, the wrist joints of the hand also become inflamed and swollen.
The fingers and wrist joints in patients with rheumatoid arthritis become inflamed symmetrically: when the joints on the left hand are affected, the same joints on the right hand are affected.
In most cases, there is involvement in the pathological process of other joints of the upper and lower extremities, as well as large joints - knees, elbows, ankles, etc.
As a rule, the above symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis are accompanied by general weakness, fever, weight loss and chills. Thus, the disease is the cause of a general deterioration in the patient’s well-being.
Pain in the joints of the fingers with psoriatic arthritis
About 5% of cases of pain in the joints of the fingers are also associated with psoriatic arthritis, which can be diagnosed in people aged 20 to 50 years, most often when they have skin psoriatic manifestations - dry, scaly reddish spots (psoriatic plaques) on the body or hairy area. parts of the head.
Psoriatic arthritis is characterized by so-called “axial” inflammation with swelling of all joints on a particular finger, which turns red and looks like a sausage.
Pain in the joints of the fingers due to gout or gouty arthritis
In less than 5% of cases, pain in the joints of the hands occurs due to gout or gouty arthritis. In persons suffering from these ailments, the big toe is deformed. Women most often experience arthrosis of the thumb, and men, as a rule, develop “classic” gout – gouty arthritis.
The disease can manifest in people from 20 to 50 years of age. It begins with inflammation of the joints of the toes, knees or ankles. Most often, inflammation and pain appear in the joint of the thumb, but sometimes the inflammatory process affects other fingers, both the right and left hands.
Gout attacks happen completely unexpectedly, most often at night. The pain in the joints of the hands during gout attacks is quite intense. Redness of the affected joint is observed.
Women usually have a milder course of attacks, there is no acute pain, and the joint, as a rule, does not redden.
A gout attack is characterized by a sudden onset, duration from three to ten days and relapses after some time.
Pain in the joints of the fingers with de Quervain's tenosynovitis
Pain in the joints of the fingers may occur in patients with de Quervain's tenosynovitis. With this disease, the ligaments and “small” muscles of the thumb become inflamed. Inflammation of other fingers with de Quervain's tenosynovitis is excluded.
De Quervain's syndrome affects both men and women equally and can occur at any age. The pathology is characterized by pain in the joint of the thumb - at its base and at the point of contact of the thumb with the wrist joint.
Pain in the thumb joint with rhizarthrosis
Another cause of pain in the fingers is rhizarthrosis, which is characterized by damage to the joint located at the base of the thumb and connecting the thumb to the wrist joint.
Rhizarthrosis can be a manifestation of polyosteoarthrosis of the fingers, but sometimes it is an independent disease, the development of which is associated with heavy loads on the thumb.
Rhysarthrosis and de Quervain's tenosynovitis have similar symptoms. The only difference between rhizarthrosis is that with this disease, the bones of the diseased joint are deformed in patients, which can be detected during examination and on x-rays. With de Quervain's tenosynovitis, only the soft tissues surrounding the joint change, and even then in rare cases.
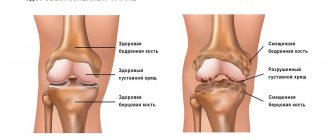
Morning stiffness of the knee joints
The knee joint has a complex structure - it consists of three bones, synovial lining (cartilage 5-6 mm thick), ligaments, and two menisci. Therefore, diagnosis of his diseases that cause stiffness is available only to a doctor.
Most often, the knees are affected by arthrosis (especially in overweight people, professional athletes, injured patients or people over 40 years old). These joints are also vulnerable to arthritis, a similar-looking disease that often affects patients under 40 years of age. At night, arthritic knee pain can interfere with healthy sleep, and in the morning, swelling makes it difficult to begin daily activities.
Stiffness in the knees can cause damage to the meniscus (even a small partial tear), which is accompanied by pain. In the absence of severe pain, it is worth considering the option of obesity.
A lesser known disease is also characteristic of the knee joint - Baker's cyst, which is associated with the accumulation of excess synovial fluid. It is common among athletes, elderly and sedentary people, and can occur with severe physical stress. May be accompanied by fever, tingling in the knee area, cramps, stiffness, and may manifest as a swelling noticeable upon palpation behind the knee.
Pain in the wrist joint of the left hand, right hand: causes
Pain in the wrist joint of the right hand can be caused by a variety of reasons; the pain syndrome itself can be pronounced or barely noticeable.
The pain may be constant or felt when moving your fingers.
The most common causes of pain in the wrist joints are the following:
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- gout;
- osteoarthritis;
- arthritis;
- tunnel syndrome.
Wrist pain due to rheumatoid arthritis
As a result of prolonged inflammation, joints and bones are gradually destroyed, and rheumatoid arthritis occurs. The characteristic signs of this pathology are:
- the appearance of pain in symmetrically located joints;
- limited mobility of the hands.
Pain in the wrist joint due to gout
Gout is often characterized by damage to the joints of the lower extremities, but in some cases this disease can cause unbearable pain (throbbing, burning, bursting) in the hands. The intensity of such pain increases at night and decreases in the morning.
Pain in the wrist joint due to osteoarthritis
Due to a degenerative disease such as osteoarthritis, pain occurs in the hands, elbow, shoulder joints, and in the joints of the thumbs. The pain is dull in nature and intensifies during the daytime with physical activity. Characteristic clinical manifestations of this pathology are: clicking and crunching of the joints. Attacks can last for several days or several months.
Arthritis wrist pain
With arthritis, patients suffer from incessant pain in the wrist joint. The disease is manifested by local redness of the skin, a local increase in temperature, pronounced pain and swelling in the joint area. In the morning, there may be a decrease in joint mobility.
Pain in the wrist joint due to carpal tunnel syndrome
As a result of prolonged work at the computer, painful sensations may occur in the hands. The appearance of this pain is associated with compression of the nerve in the metacarpal tunnel.
When to go to a rheumatologist
In fact, the profile of a rheumatologist is very wide and includes several dozen diseases and pathologies. For example, a predisposition to sore throats and viral diseases may have a rheumatological cause. Of course, there are certain age indicators, but if you are young and rule out the possibility of injury, then the reason to contact a rheumatologist is pain, discomfort, or some changes in the structure or shape of the joints. Especially if all this is accompanied by fever, unexplained weight loss, and changes in blood tests. In this case, the process cannot be delayed. Contact your rheumatologist directly to get into the “therapeutic window.”
Pain in the joints of the hands: diagnosis at the Yusupov Hospital
Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital Therapy Clinic recommend seeking medical help if you have the following symptoms:
- pain in the joints of the hands that persists for more than two days;
- swelling in the joint area;
- hand deformities, impaired joint mobility;
- increased pain during physical activity;
- decreased nerve sensitivity.
Experienced, highly qualified doctors at the Yusupov Hospital - rheumatologists, traumatologists and neurologists - will determine the nature of the pain, establish the exact root cause of the pain and develop an effective individual treatment regimen for each patient of the clinic. Diagnosis is carried out using manual muscle testing, radiography, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging.
Thanks to complex therapy using modern medical techniques, our specialists are able to achieve the fastest possible elimination of pain in the patient, stop the development of the pathological process, improve the patient’s general well-being and completely get rid of the disease without the use of surgical intervention.
Mechanism of disease development
Arthrosis begins with impaired blood circulation in the subcartilaginous layer of the periosteum.
Because of this, the nutrition of the cartilage deteriorates, it loses its elasticity, becomes thinner, and cracks appear on it. The amount of synovial fluid decreases, due to strong friction, the joints become inflamed. Progressive arthrosis is very dangerous. If treatment for arthrosis of the hand or foot is not started in time, the joints begin to take on unnatural, ugly shapes and may lose mobility.
The disease often occurs in women during menopause. Hormonal levels change in the female body and less estrogen is produced. Because of this, the body loses a lot of moisture, which makes cartilage and joints more brittle.
Risk factors
Risk factors for the disease include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- heavy physical labor, heavy load on the finger joints;
- overweight, excessive alcohol consumption;
- long-term wearing of uncomfortable tight high-heeled shoes;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- hypothermia of the feet.
If your work often puts stress on the joints of your fingers and toes, or you have relatives who suffer from arthrosis of small joints, you should think about prevention. We will talk about it at the end of the article.