How to treat genital herpes in men and women on the genitals
Genital herpes is one of the main diseases that are sexually transmitted. According to statistics, it is given second place; doctors call trichomoniasis the first STD. Genital herpes is caused by the herpes simplex viruses HSV-II, and sometimes HSV-I. The concept of simple virus was applied to such viruses for obvious symptoms - the appearance of blisters and ulcers on the skin.
However, over the past decades, scientists and immunologists have come to disappointing conclusions. Because of its “simplicity,” the disease has become widespread, and yet it causes not only specific rashes, but can also cause serious disruptions in the functioning of internal organs. The virus will not necessarily “manifest” in the form of skin lesions.
And the name “genital” is nominal: every fifth PCR test detects the HSV-II virus in a vesicular rash outside the genital area. This means that 20% of patients do not attach importance to the rash, are treated incorrectly, do not consult a doctor and spread the disease.
How is genital herpes transmitted?
The cause of the disease is two types of herpes simplex viruses, mainly HSV-2. The first type of virus was previously associated with diseases of the skin and oral cavity. HSV-2 causes genital herpes and meningoencephalitis. Now there are cases of illness caused by the first type of virus or a combination of them. Often the carrier does not have any symptoms of the disease and does not suspect that he is the source of the infection.
How can you become infected with this disease? The most common routes of transmission of genital herpes are sexual and contact. Most often, infection occurs through sexual contact with a carrier of the virus or with a sick person. You can become infected by kissing, as well as by sharing common household items (spoons, toys). The virus can also be transmitted through airborne droplets.
There are several risk groups of people susceptible to infection:
- persons with frequent changes of sexual partners;
- sexually active age from 20 to 40 years;
- people practicing non-standard sexual practices;
- persons suffering from other sexually transmitted diseases;
- Women are more likely to get sick;
- people with immunodeficiency conditions;
- patients who have undergone surgery, organ transplantation, or immunosuppressive therapy;
- women using intrauterine devices for contraception.
For many people with the herpes virus, herpes outbreaks may be triggered by the following:
- general diseases;
- fatigue;
- physical or emotional stress;
- loss of immunity, such as due to a cold, AIDS, or medications such as chemotherapy or steroids;
- trauma, including during sexual activity;
- menstruation.
The pathogen enters the child's body from the mother during childbirth. The risk of such transmission depends on the type of lesion in the patient. It is up to 75%. In addition, infection of the fetus is possible through the blood during the period of viremia (the release of viral particles into the blood) during an acute illness in the mother.
Children in most cases become infected with HSV-1 in the first years of life. By the age of 5, HSV-2 infection also increases. During the first six months of life, babies do not get sick, this is due to the presence of maternal antibodies. If the mother was not previously infected and did not pass on her protective antibodies to the child, then children at such an early age become very seriously ill.
Prevention of genital herpes virus infection
To prevent infection, you must remember to use a condom during casual sexual intercourse, as well as the use of antiseptics to treat areas of the skin where the virus can get. Relapses of the disease are observed with a decrease in immune defense, various diseases, stress, and even with frequent overheating and hypothermia. Therefore, in order for the clinical signs of herpes to make themselves felt as rarely as possible or not to appear at all, you must try to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat well and get enough rest, as well as regularly take vitamin supplements recommended by your doctor.
To prevent self-infection, in order to prevent the virus from being transferred from the face in the presence of rashes on the lips to the genital area, it is necessary to adhere to the rules of personal hygiene and wash your hands more often. Each family member should have separate towels for different parts of the body.
After unprotected sexual intercourse, during sexual relations with a carrier of the herpes simplex virus, and when planning pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations with a doctor.
Reference and information material
Author of the article
Belyaev Dmitry Alexandrovich
General doctor
Loading...
Take other surveys
What happens after infection?
One of the characteristics that distinguishes viruses from the herpes virus family from other types of viruses is latency. HSV and other herpes viruses have the ability to create small but permanent colonies of viral particles inside the body. These colonies are often completely inactive (or dormant), but they remain in the body for life.
As soon as HSV gains a foothold in the body, it begins to create copies of itself and spread. This can lead to a clinical picture of the infection ranging from mild and unnoticed symptoms to severe illness. In response to this, the immune system mobilizes its forces and limits the spread of HSV. Regardless of the severity of symptoms, the virus remains in the body. To avoid the immune system, HSV “retreats” along the nerve fibers and hides in the nerve ganglia. In the case of genital herpes, the virus is located in the sacral plexus of ganglia, located at the base of the spine. In the ganglia, the virus remains inactive (latent) for an indefinite period of time.
The phenomenon of latency is similar to the sleep cycle. Basically, the virus remains dormant in a safe place, sometimes for a very long time. Unfortunately, various biological events can activate HSV, after which the virus spreads along nerve fibers back to the skin. This may cause the symptoms and signs of genital herpes to reappear.
It is difficult to answer the question of how often the virus can be activated. Previously, it was believed that all cases of HSV activation lead to the development of a clinical picture of the disease. Research then revealed that the virus can become active without causing noticeable symptoms or signs—no itching, no pain, no rash. This phenomenon is called "asymptomatic reactivation."
Asymptomatic reactivation refers to the following situations:
- Some herpetic eruptions may appear in places that are difficult or impossible to see.
- Some herpetic lesions can be mistaken for something else, such as an ingrown hair.
- Some manifestations of herpes cannot be seen with the naked eye.
The fact is that when the herpes virus is activated and moves to the surface of the skin or mucous membranes, it is difficult for even a doctor to notice. In addition, even for a person with symptoms and signs of genital herpes, several days pass before the full clinical picture develops, during which he will not be aware of the reactivation of the virus.
How to recover
Treatment of herpetic infection of the genital organs in women is quite long and complex. Many gynecologists believe that it is generally impossible to completely cure HSV types 1 and 2, and the most that can be counted on is a stable remission for several years.
Until recently, it was traditionally believed that virus damage to the upper part of the body was caused by herpes of the first type, and the lower part by the second. However, the sexual revolution and the fashion for oral sex in both directions changed this idea. Today, type 1 virus can cause genital herpes, and type 2 can cause fever on the lips, and types 1 and 2 can cause blisters on the anus. That is, each type feels quite free in the human body and manifests itself where direct infection occurred.
By the way, in 80-90% of people, a blood test for herpes infections reveals antibodies that protect against infection or exacerbation. The initial encounter of a person with these viruses apparently occurs in childhood and in the vast majority of cases is asymptomatic. But the body produces IgG antibodies, which makes it quite resistant to infection. This balance can only be disrupted by provoking external factors.
It should also be remembered that various medical tests for herpes virus types 1 and 2 can detect it in saliva, tears, blood, urine, vaginal secretions, anal folds, semen and cerebrospinal fluid. Therefore, you can “catch” it not only through sexual contact, but also through a towel, cream, shared utensils, cosmetics, etc. The disease cannot be treated independently, at home.
Our clinic in Moscow treats herpes in women with good therapeutic results thanks to the presence of competent specialists and preliminary diagnosis. Good gynecologists, any tests and effective treatment regimens for genital herpes! We invite you to make an appointment with a gynecologist right now!
Forms of the disease
There are two forms of genital herpes: primary and recurrent. Primary genital herpes is said to occur when clinical signs appear for the first time after infection, which can happen after a couple of weeks or in some cases months. Recurrent herpes is a periodic exacerbation of the disease with the slightest weakening of the immune system. Depending on the number of exacerbations of relapses of genital herpes throughout the year, 3 degrees of severity are distinguished:
- mild degree – the number of relapses is 3 or less per year;
- moderate – exacerbations occur 4–6 times a year;
- severe - relapses occur monthly.
During the course of the disease:
| Primary infection | usually occurs sexually from a sick person to a healthy person. Manifested by the following symptom complex: rash (vesicles) on the genitals – purulent pustules – purulent ulcers – scabs. The duration of the disease is 30 days. Discharge, problems with urination, and enlarged or inflamed lymph nodes in the groin are also observed. |
| Secondary infection | occurs when there is HSV-II in the body, which remains in a latent state. It is activated after weakening of the immune system or re-infection. Symptoms are the same as during primary infection. |
| Recurrent herpes | This is a virus carrier, in which there are stages of exacerbation and remission, depending on the state of the body’s immune forces. |
| Atypical course | characterized by manifestations of other pathologies. It is usually detected during laboratory testing. |
| Asymptomatic form | occurs quite often (in 6 out of 10 people with herpes) and is considered the most dangerous in terms of the epidemic spread of this disease. |
All factors that suppress immunity in genital herpes are also causes of exacerbation.
Development of disease relapses
Some people sometimes experience recurrences of genital herpes. Scientists are unable to explain why, after the latent stage, the virus is activated from time to time, that is, the reasons for the relapse have not been established. Factors that contribute to the development of the virus and relapse of the disease are known:
- influenza, ARVI, other diseases with high body temperature;
- local damage to the external genitalia, as well as the mouth and lips;
- decreased defense mechanisms, immunodeficiency;
- ultraviolet radiation, a side effect of radiation therapy;
- changes in a woman’s immune system during menstruation;
- hypothermia;
- stress;
- excessive alcohol consumption.
ARVI
Stress
Relapses are often milder and last shorter than the first wave of the disease. In case of relapses, symptoms usually occur within 7 to 10 days. Most people do not complain of either elevated body temperature or poor health. A relapse of the disease may be indicated by a slight tingling sensation or itching of the genitals for 12-24 hours.
Over time, relapses of genital herpes appear less frequently. The frequency of their occurrence may vary. For some people they occur six or more times during the year, for others much less often. As a rule, during the first 2 years from the first wave of symptoms, relapses occur 4 to 5 times. Some people do not relapse at all.
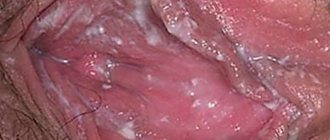
Symptoms of genital herpes
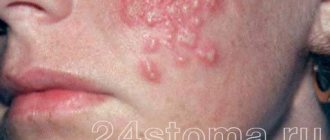
For primary infection with herpes, the incubation period is up to 8 days. Then the following symptoms appear (see photo):
- itching, redness and burning in the genital area;
- small blisters filled with cloudy liquid form on the skin or mucous membrane;
- burst blisters transform into small erosions or ulcers covered with a crust;
- itching and tingling sensation during urination;
- when the cervix is affected, the mucous membrane becomes hyperemic, erosive, with purulent discharge;
- the lymph nodes in the groin are enlarged.
Sometimes there is general weakness and malaise. It may take up to 30 days for the symptoms of the disease to completely disappear. Effective treatment of genital herpes shortens this period.
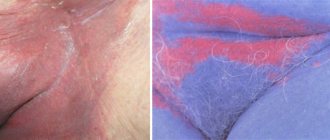
With genital herpes in the fairer sex, the rash is localized:
- near the external opening of the urethra;
- in the vestibule of the vagina and on the labia;
- on the cervix;
- near the anus or in the buttocks area.
In men, during exacerbation of herpes, the rash is located on the skin or mucous membranes:
- scrotum;
- around the anus or on the thighs;
- on the head or foreskin of the penis.
With secondary infection, the disease manifests itself with similar symptoms. Once the virus enters the human body, it turns him into a carrier of the disease. In this case, periods of remission are replaced by exacerbations.
The reddened areas where the rash appears are itchy, and the inguinal lymph nodes are enlarged. The remaining symptoms of genital herpes are the same in men and women. Herpetic manifestations gradually fade away after 1-2 weeks, and the manifestations of primary herpes completely disappear after 3-5 weeks.
You can see what genital herpes looks like in the photo.
Relapse
If the disease reappears, general malaise may not bother you. Blistering lesions appear in the same places. The frequency of relapses depends on the general condition of the body and the immune system; in some cases, 4-5 exacerbations may occur. However, recently, genital herpes occurs in an atypical or asymptomatic form, when the rash is almost invisible. A frequent manifestation in this case may be constant itching in the perineum for no obvious reason, rashes that go away on their own after 1-2 days, cracks in the skin and mucous membranes. Even if the manifestations of herpes are mild, a person can be dangerous to others, since the possibility of transmission is still high.
Recurrent herpes
Recurrences of genital herpes are observed in 50-70% of women and men after the disappearance of the primary signs of the disease.
The frequency of relapses and the duration of remissions are very variable - from once every 2-3 years to monthly exacerbations. The frequency of relapses and the severity of the clinical picture can be criteria for the severity of the process. With a mild form of chronic herpetic infection, exacerbations occur no more than 1-3 times a year, with a moderate form - 4-6 times a year. Severe course is characterized by monthly exacerbation of the disease.
General information about the virus
Herpes is one of the most common viral infections in humans. Over 85% of the world's population is infected with herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 1 or 2 and up to 25% of them have some clinical manifestations of infection and positive tests for herpes in the blood or PCR smears.
Infection with the herpes virus usually occurs through airborne droplets or contact, often through household or sexual contact (genital herpes), and sometimes due to blood transfusion. It infects a human cell by integrating into the gene apparatus. With each subsequent division, it is automatically transferred to the newly formed cells along with hereditary information. That is why herpes becomes our eternal companion, lurking in the body until the first opportunity. Primary infection with the herpes virus in adults usually results in very extensive rashes. Relapses occur more calmly, but the frequency of their occurrence is purely individual and depends primarily on the state of the person’s immune system, that is, on the body’s ability to produce antibodies and resist infection. Typically the relapse lasts about two to three weeks. And during this period - even if you just have a “cold” on your lips or a rash on your genitals - it is best to have personal dishes, soap, a towel in the house and at work, and under no circumstances kiss, especially with children, and also absolutely exclude any (!) sexual contacts.
Types of herpes
One of the herpes viruses, zoster , causes common chickenpox, which many of us suffered from in childhood. And this is good, because in such a case we are insured with lifelong immunity from a very serious and unpleasant disease - herpes zoster, which only affects adults. It is accompanied by a long-term pain syndrome, which is not so easy to get rid of. The infection penetrates the nerve fibers, and they react with pain, most often in the intercostal space. In this case, a strip of bubbles filled with liquid usually appears on the surface of the chest. This type of virus does not affect the genitals of women and men.
Another herpes virus, cytomegalovirus , is especially dangerous for an unborn baby. It is able to penetrate the placenta and infect the fetus in the womb. Infection is also possible when a child passes through the birth canal. In this case, pregnant women either do not carry the fetus to term or give birth to a dead child. However, adults can also become infected with this type of virus. Then the virus mainly affects the liver - it enlarges, jaundice appears, acute liver failure develops, and even death is possible.
Another type of herpes, the Epstein-Barr virus , most often causes a disease such as mononucleosis, in which the spleen and liver enlarge, and a sore throat develops. Possible complications in this case are stomatitis, otitis, pneumonia, serous meningitis, jaundice.
viruses of the sixth and seventh types were discovered quite recently, and so far little is known about them, and even then only speculatively. For example, some experts believe that a positive test for herpes type 6 is associated with a disease such as “chronic fatigue syndrome.” It is characterized by enlarged lymph nodes, headache, cough, runny nose, sore throat, and loss of strength. This type of pathogen does not infect the intimate area.
Herpes type 1
The first type of virus usually manifests itself as a “fever” on the lips during a cold or ARVI. However, this does not mean that it is introduced only there - the disease affects the entire body and, starting on the lips, can gradually infect other mucous membranes. This virus mainly affects the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract and skin, often the eyes, and with a sharp decrease in immunity, the liver, intestines and even the brain.
If the disease is localized in the mouth, the familiar pattern of “fever” is observed, which often accompanies an acute respiratory disease. However, if the patient has reduced body resistance, such ulcers can often appear on the palate, inner surface of the cheeks, tongue, and tonsils. The herpes virus type 1 can also spread to the mucous membranes of the eyes. In this case, conjunctivitis and even keratitis develop - inflammation, swelling appears, and pus is released. In severe cases of herpes, branching ulcers form on the cornea of the eye, which heal with the formation of a scar, which can even lead to blindness.
Herpes type 2
Serious problems are caused by the second type of herpes virus (genital herpes). It causes superficial ulcers on the genital mucosa. Outwardly, it looks like a “fever”, only the affected area can be much wider. In men, rashes appear on the head of the penis, foreskin, in women - in the vulva, on the labia majora and minora, buttocks, and on the skin of the pubis. Often, genital herpes affects the testicles and prostate. At the same time, local lymph nodes swell, urination is impaired, and pain in the lower abdomen is often noted. Typically, the rash is preceded by fever, chills and lower back pain. The presence of herpetic blisters in virgins on the anus is more likely to allow the gynecologist to draw a conclusion about the girl’s experience of anal sex.
In 75-80% of cases, fever or a slight burning sensation when urinating may be the only symptoms of genital herpes. Completely asymptomatic forms are also common. In addition, genital herpes in women can “masquerade” as sexually transmitted diseases or chlamydia. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion of something like this, you should immediately see a doctor and get tested for sexually transmitted infections.
Genital herpes
Based on the location of the lesions, there are 3 stages of genital herpes:
Stage I - genital herpes affects the external genitalia; Stage II - foci of herpes affect the vagina, cervix, urethra; Stage III - the virus invades the uterus, appendages, bladder, prostate.
With atypical forms of genital herpes, a sick person sometimes spends months visiting doctors of various specialties (urologists, gynecologists, dermatovenerologists) with complaints of discomfort in the genital area, but without special laboratory methods it is almost impossible to make a diagnosis.
The development of relapses of genital herpes occurs in 50-70% of patients who have suffered a primary infection. Depending on the frequency of repeated episodes, several forms of recurrent genital herpes are distinguished:
- mild form (exacerbations no more than 3 times a year),
- moderate form (exacerbations 4 to 6 times a year),
- severe form (monthly exacerbations).
Often the disease leads to the formation of clusters of condylomas in intimate places, similar to round warts. As they grow, they take on the appearance of cauliflower and are localized in the genital area, perineum and anus. A similar picture is often observed with sexually transmitted diseases, such as syphilis, so it is very important to immediately make an accurate diagnosis.
Photo of herpes
Photo 1. Herpes type 1
Photo 2. Herpes type 2
Photo 3. Herpes type 6
Atypical form
The atypical form of the pathological process is characterized by an erased abortive course, which affects not only the external genitalia, but also the internal genital organs. As a rule, this form of infection is characteristic of chronic recurrent herpes, but at the same time, it can also occur with primary lesions.
It's no secret that many chronic pathologies of the genital organs are diagnosed as diseases of unknown etiology. This is due to the inability to identify the cause of the disease, and therefore the prescribed treatment is very often ineffective. It is in such cases that good specialists suspect the development of an atypical form of herpesvirus infection.
The causative agent of the disease
Herpes (from the Greek ἕρπης - creeping, spreading skin disease). Genital herpes is a viral infection that affects the penis in men (penile herpes) and the external genitalia and vagina in women (herpes vaginalis, labia), as well as the area around the genitals, usually the perineum. Infection is manifested by the appearance of blisters on the skin. Sometimes they can occur on the buttocks and anus.
The causative agent of the disease is the human herpes virus. There are two types of AI virus: herpes virus type 1 and herpes simplex virus type 2.
- AI virus type 1 most often leads to the appearance of herpes on the lips. Causes half of the cases of genital herpes.
- AI virus type 2 is responsible almost exclusively for the development of genital herpes. Very rarely it can also cause herpes on the lips.
Herpes on the lips
Complications
Genital herpes itself does not cause serious illness. However, its complications, which are often observed in people with weak immune systems (especially those with HIV infection), can pose a serious threat to health and even life.
- Herpetic eczema is a skin lesion that leads to the appearance of a rash similar to that of eczema;
- Herpetic keratoconjunctivitis is a lesion of the cornea and mucous membrane of the conjunctiva of the eye. Manifested by photophobia, burning, lacrimation, redness of the eye. Small white spots appear on the surface of the cornea, causing itching and pain. Without treatment, vision loss is possible;
- Herpetic encephalitis is an inflammation of the brain caused by the HSV type 2 virus. Without treatment, the complication leads to death. The virus infects nerve cells in the cerebral cortex, leading to focal and general brain symptoms. Complete cure is possible with adequate and timely therapy;
- Intrauterine herpes is the transmission of infection from mother to child. Primary infection is dangerous, which leads to damage to the fetal nervous system;
- Herpetic meningitis is an inflammation of the meninges caused by the HSV type 2 virus. A severe complication leading to a number of neurological symptoms, including convulsions, severe headaches, and disturbances in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
In people with normal immune status, complications are rare. On average, the acute phase of infection during primary infection lasts several weeks. During this period, the infected person releases a large number of viral particles with biological fluids. Carriage lasts up to 1 year. In most cases, the immune system controls the infection and suppresses its activity. This occurs due to the production of antibodies directed against the virus. During the period of remission, the virus remains only in the nerve cells of the sensitive nerve plexuses.
In patients with immunodeficiency, the herpes simplex virus often causes complications. Infection is especially dangerous in patients with AIDS. Herpetic lesions in such patients are extensive and often occur in the form of severe meningoencephalitis with a fatal outcome.
Herpes in the intimate area: features of viral infection
The reasons for the development of herpes in the genital area are well known.
The main factor is the entry into the body of a small virus, which is called in medical practice the herpes virus of the second type.
It is characterized by damage to the genital area with the appearance of characteristic rashes on the skin.
The disease affects both men and women equally often.
Moreover, as doctors note, today it is quite difficult to meet a person who has not been in contact with this infection throughout his life.
Herpes has one significant feature.
It begins to actively manifest itself if a person’s immunity decreases.
This can happen, for example, against the background of other infectious diseases, due to congenital or acquired pathologies of the immune system, or with HIV.
Once the virus has entered the body, it will no longer be possible to destroy it.
The person’s task in this case is to suppress the activity of the pathogen with the help of special medications.
Then maintain immunity at a high level to avoid relapses in the development of pathology.
The average incubation period for infection is several weeks.
However, if the immune system of a sick person is strong, the virus may not appear for years.
Genital herpes and pregnancy
Pregnant women with genital herpes should be careful to avoid passing the virus to their baby, but not be overly concerned about it.
- A mother can infect her baby during childbirth, often fatally. But if a woman becomes infected with genital herpes before becoming pregnant, or if she is infected early in pregnancy, the chance that her baby will be infected is very low—less than 1%. Women with genital herpes are carefully monitored for herpes symptoms before giving birth. If there are signs that a herpes outbreak is occurring during labor, a caesarean section is necessary.
- The risk of infection of the child is high (30% to 50%) when a woman becomes infected late in pregnancy. This is because the mother's immune system has not produced protective antibodies against the virus. Women with a recurrent herpes infection have antibodies against the virus, which help protect the baby. If you are pregnant and you think you may have been recently infected, tell your doctor.
Women who are not infected with genital herpes should be careful about sex during the third trimester of pregnancy. Unless you know your partner does not have the herpes virus, you should avoid sex altogether during the third trimester. If your partner has herpes labialis, avoid sex during this time.
Some doctors believe that all pregnant women should be tested for herpes, especially if their sexual partner is infected. Check with your doctor if you or your partner need to be tested. Only a doctor can judge the advisability of taking antiviral and other drugs for herpes during pregnancy. The decision is made in each case individually.
During pregnancy, HSV-2 may be one of the causes of recurrent miscarriage and the development of fetal deformity. Perinatal losses due to neonatal herpes are 50-70%, with 70% of infected children born to mothers with asymptomatic genital herpes. Ignoring the fact of the possible presence of HSV-2, especially in premature birth, and fetal weight retention syndrome contributes to the fact that newborns do not receive timely antiviral therapy, and therefore they develop meningoencephalitis, damage to parenchymal organs, lungs (pneumonitis), etc.
Congenital genital herpes is observed in 1 child per 30 thousand alive, but the mortality rate in this group is 70%; the surviving children suffer severe neurological consequences. The virus is 4 times more common in premature babies than in those born at term. As a consequence of late intrauterine infection, the following anomalies occur in children: microcephaly, chorioretinitis, retinal dysplasia, microphthalmia, lens opacification, heart defects, hepatosplenomegaly, viral pneumonia. In the United States, between 400 and 1,000 babies are born each year with neonatal herpes.
In most cases, infection of the fetus occurs immediately before birth, through the ascending route after rupture of the membranes (critical period 4-6 hours) or during childbirth when passing through an infected birth canal. Infection of the fetus before 20 weeks of gestation leads to spontaneous abortion or fetal anomalies in 34%, in periods from 20 to 32 weeks - to premature birth or antenatal death of the fetus in 30-40% of cases, after 32 weeks - to the birth of a sick child. Typically, the entry points for infection are the skin, eyes, oral mucosa, and respiratory tract. Once infection has occurred, the virus can spread through contact or hematogenous routes.
Risk factor during pregnancy
Genital herpes is dangerous for pregnant women. If a woman first encounters the virus during pregnancy and develops a primary episode, this can cause complications - missed abortion, spontaneous miscarriage, developmental abnormalities and fetal death.
If a woman was a carrier of HSV before she became pregnant, then her immune system can protect the baby, but in case of exacerbations, the risk of complications remains. Infection of a child is possible during childbirth, provided that it occurs during the active phase of the disease. Therefore, it is important to closely monitor your health while carrying a baby to prevent relapses.
When the genitals are affected by a blistering rash caused by HSV, some patients experience embarrassment, discomfort, shame, and depression. Many people try to hide information about the presence of genital herpes from new sexual partners, for fear of being rejected. However, if characteristic symptoms appear, you should not hesitate - you must seek medical help in a timely manner. In case of bubbles in the intimate area, you can contact a gynecologist, dermatovenerologist, men can also visit a urologist. The diagnosis is established by a specialist and confirmed by laboratory tests. To do this, a PCR test is performed on scrapings from the area of vesicles and ulcers, which makes it possible to identify the pathogen.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by a doctor based on the patient’s complaints and examination, during which a characteristic rash and enlarged lymph nodes can be detected. If an external examination does not reveal a rash, the doctor takes material for laboratory tests.
In addition, you need to know how to detect genital herpes using laboratory methods. Can:
- Determine the disease using the PCR method during the period of relapse (the most effective), which determines not only the presence of the virus in the body, but also its type. Subject to sterility and temperature conditions, material taken from the site of the rash allows you to obtain results within 5 hours;
- Identify antibodies to the virus by conducting blood tests;
- Identify the virus by examining material taken from the location of the rash;
- Conduct an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, which determines the presence of antibodies and evaluates the patient's immunity.
Since there are diseases similar to genital herpes in their manifestations (ulcers and erosions on the genitals), self-medication should not be done.
Herpes or so-called stomatitis on the genitals resembles:
- Chancroid, sexually transmitted but rare in Europe and Asia;
- Erosion resulting from trauma;
- Syphilis.
Since the presence of antibodies alone cannot serve as a basis for the diagnosis of “genital herpes” (in women, the presence of antibodies to type 2 herpes is more likely, and antibodies are formed by 6-12 weeks after infection), it is additionally necessary to isolate the virus or use the PCR method.
Herpes test
When diagnosing, the doctor takes into account complaints, anamnesis and objective examination.
Identifying typical cases of genital herpes is usually not difficult and is based on clinical manifestations. No special preparation is required to take blood tests for the herpes virus. You can get tested for herpes in Moscow at our clinic. Collection of biological material (separated from the genital tract, saliva, etc.) for a PCR smear for women, children and virgin girls is carried out on any day of the cycle, except for menstruation itself. It is possible to take material for diagnosis from the following places: “U” - urethra “C” - cervix (except virgins) “V” - vagina “R” - rectum “O” - oropharynx
Recommendations for patients on how best to get tested for the herpes virus
It is not recommended to take biomaterial earlier than 24-48 hours after sexual intercourse.
Scraping for PCR analysis of herpes types 1 and 2 from the urogenital tract (in men): it is recommended to take it no earlier than 2 hours after the last urination.
Scraping from the urogenital tract (in women): smears for genital herpes should not be taken: • during menstruation (1, 2, 3, 4 days); • earlier than 5 days after using vaginal suppositories, tampons or spermicides; • after a vaginal examination (pelvic ultrasound, colposcopy), douching.
Diagnostics
What tests for herpes are performed and their cost, ₽
| List of tests | Prices |
| Analysis for herpes types 1 and 2 | 550 |
| Test for herpes type 6 (mouth/nose/throat swab) | 550 |
| Blood test for herpes | |
| PCR blood for herpes type 1 and 2 | 750 |
| Antibodies to herpes type 1 IgG | 850 |
| Antibodies to herpes type 2 IgG | 850 |
| Antibodies 1 and 2 IgG | 950 |
| Antibodies 1 and 2 types IgM | 850 |
| Antibodies type 1 and 2 IgG (avidity) | 950 |
| Test for herpes type 6 IgG | 850 |
| Herpes virus type 6 (colic) | 750 |
Treatment regimen for genital herpes
For diagnosed genital herpes, five therapeutic treatment methods are used:
- Pathogenetic therapy. Immunomodulators, including agents that increase and decrease the immune status and its individual components in the form of native substances (natural, crude biological products), individual fractions and synthetic stimulants of immunogenesis.
- Etiotropic therapy. Antiviral drugs that suppress the replication of the herpes virus.
- Symptomatic therapy. Medicines that relieve pain, itching and fever.
- Specific prevention is vaccination.
- Physiotherapy is sometimes used.
The medical arsenal of drugs that can directly affect the virus has a limited range of drugs. Direct-acting antiviral therapy is based on medications from the group of synthetic analogues of acyclic purine nucleosides. The base drug of this group of drugs is acyclovir.
Several treatment regimens for patients with typical genital herpes:
- Treatment regimen for recurrent genital herpes. Used during the period when warning signs of recurrent disease appear. The choice of therapy, their combination and preparative forms (ointments, solutions, tablets) depend on how often relapses of herpes occur, as well as on the recommendations of the attending physician. The universal regimen includes a combination of treatment of herpes with acyclovir (and analogues) with the use of immunostimulants, vitamins and other restoratives. At the very beginning of the appearance of precursors of the disease (itching in the area of the future lesion), interferon preparations are indicated. They are most effective in the early stages of pathogenesis. At the height of the disease, the use of interferon or its stimulants does not make sense.
- Preventive treatment regimen for genital herpes. Treatment is prescribed in the remission stage if there is a suspicion of rapid activation of the virus. This treatment option is used for frequent (more than 6 times a year) relapses in order to prevent their development. Drugs that stimulate the general immune status of the body are indicated. Optional: Cycloferon, Ribotan, Gradex, Vegetan, Immunofan and other medications, the dosage and frequency of use is determined by the doctor. Vitamins of group B (B1, B6) are also shown, improving the overall resistance of the body. Interferon stimulators are used limitedly during this period due to their almost complete uselessness at this stage. It makes no sense to use antiviral drugs (acyclovir and others) - the virus is in an inactive phase, inaccessible to drugs. It is advisable to begin treatment with acyclovir, Zovirax and other drugs of this group only after detecting an active herpes virus in the blood.
- Treatment regimen for genital herpes at initial contact. Optional: Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, Farmciclovir and other medications in a clinical dosage, which is determined based on individual sensitivity (drug tolerance, patient weight, doctor’s recommendations) orally up to five times a day for ten days or until symptoms disappear. The effect increases if treatment is started in the early stages of the disease.
The above regimens include means of etiotropic, pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy (to eliminate the symptoms of herpes - pain, itching, fever). The herpes vaccine is prescribed by the attending physician, based on therapeutic feasibility. Treatment of atypical forms of genital herpes is carried out taking into account the symptoms of pathogenesis and the results of laboratory tests.
Which doctor should I go to if symptoms of herpes appear in the intimate area?
Sick people often want to know which doctor will help cope with the infection.
Especially if its severity is quite strong, and there is neither the strength nor the desire to wait for the rash to disappear on its own.
In most cases, you should contact a dermatovenerologist.
This doctor treats diseases that are transmitted from one person to another during sexual intercourse.
And genital herpes just belongs to this group of infections.
In addition to a dermatovenerologist, a urologist or gynecologist, if we are talking about a woman, can provide assistance to the patient.
These doctors who work with the genital organs know the symptoms of herpes, and also understand the principles of diagnosis and subsequent treatment of the pathology.
In rare cases, consultation with an immunologist or infectious disease specialist is required.
Patients want to know where to go if specific rashes appear.
First of all, you should visit a skin and venereal disease clinic or clinic.
This is where you can find the specialists needed to prescribe and monitor treatment.
A private medical center can always serve as an alternative to government institutions.
There you can undergo any necessary examinations and then be treated for infection.
Diet
When doing treatment at home, you must follow a diet. This will help prevent the herpes from getting worse. The principle of the diet is a high content of lysine, a small amount of arginine.
- Allowed foods include low-fat dairy products, beef, chicken, various fish and seafood.
- For dessert you can eat ice cream or drink coffee with cream.
- Blackberries, black currants, peaches, apples, bananas help cleanse the body.
- Additionally, your daily diet should include garlic and brewer's yeast (you can use pharmaceutical preparations in the form of capsules).
- You can eat a little green onion salad dressed with olive oil three times a day. The dish is rich in retinol and ascorbic acid, which helps strengthen the body.
Alcohol should be avoided completely. Minimize consumption of sugar, sweets and nuts.
External preparations for herpes in the intimate area
Ointment for herpes in the intimate area is the most popular option for a drug that helps cope with the infectious process.
With the help of external means, it is possible to defeat the multiplication of the virus in foci, reduce the feeling of itching, and reduce the severity of pain, if present.
It is important to keep in mind that many doctors prefer to initially prescribe ointments or creams in the fight against the virus.
This reduces the burden on the body and helps protect the body from the side effects of drugs that occur when taken systemically.
There are many names for ointments for herpes in the intimate area.
As with tablets, the most popular drug is Acyclovir.
In the form of an ointment, it does not lose its effectiveness, quickly relieving unpleasant symptoms and contributing to the disappearance of rashes on the lips.
Levomekol is also successfully used for herpes in the intimate area, as doctors note.
The drug easily copes with the disease if it is possible to catch it in the early stages of development, and the virus itself does not show very high activity.
In addition to Levomekol and Acyclovir, for example, Panavir, Herpferon can be used.
Ointments can be combined with systemic therapy if such a recommendation is given by the attending physician.
Often, local treatment enhances the effect of the systemic drug, helping to quickly defeat the disease.
Prevention
In order to prevent genital herpes, experts recommend constantly taking measures to strengthen the immune system, as well as directing your efforts to preventing possible infection.
usually occurs sexually) from a sick person to a healthy person. Manifested by the following symptom complex: rash (vesicles) on the genitals – purulent pustules – purulent ulcers – scabs. The duration of the disease is 30 days. Discharge, problems with urination, and enlarged or inflamed lymph nodes in the groin are also observed.
Currently, many developed countries are actively developing preventive herpetic vaccines that protect against infection, and therefore we can hope that in a few years humanity will be able to receive an effective vaccine against herpes.
Treatment of herpes in the intimate area in pregnant women
During pregnancy, the herpes virus poses a particular danger, since the lives of two people are at risk.
Moreover, as doctors say, pregnancy is always an immunosuppressive condition, which can be one of the triggers that triggers the activation of pathogens in the body.
So it is not surprising that pregnant women seek medical help for rashes in the genital area.
It is worth keeping in mind that herpes is a pathogen that can lead to the formation of various abnormalities and deformities in the fetus.
Its activation poses the greatest danger in the first weeks of pregnancy.
When the child’s body is just at the stage of formation, and the main organs and systems have not yet been formed.
Patients whose pregnancy is combined with genital herpes should only be treated by a doctor.
At the same time, when choosing medications, the doctor will be able to take into account not only the effectiveness, but also the potential harm to the fetus.
Acyclovir preparations in any form are almost never used in pregnant women.
Preference is given to Panavir, Vivorax and other more harmless medications.
Immunostimulating therapy is also prescribed with great caution.
Since there is a possibility of harming the pregnancy process.