According to WHO, among viral infections, the ARVI group of viruses is in first place, and the herpes simplex virus, which can affect the genital area, is in second place. The uniqueness of this virus lies in its ability to invade various organs and systems, causing a wide variety of clinical manifestations and complications. For this reason, the formation of a unified approach to the diagnosis and treatment of patients with herpes is one of the most important tasks of modern healthcare.
- Causes of herpes
- Types
- Manifestations and symptoms in men and women
- Diagnostics
- How to treat during pregnancy
- Is it possible to resort to folk ones?
- Prevention
In total, 8 types of herpes viruses are known: HSV-1, HSV-2, varicella zoster virus, Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, HSV-6, HSV-7, HSV-8. The structure of virus particles of different types is practically no different from each other. The virus shell contains antireceptors, thanks to which it can attach to almost any tissue and affect the skin, mucous membranes, central and peripheral nervous systems, liver, blood vessels and blood cells. In addition, in some cases, HSV can lead to malignant transformation of cells.
Genital herpes is caused by herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2), and less commonly by herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). Previously, it was believed that HSV-1 manifested itself exclusively as rashes on the face, but it has now been established that each of these two types of viruses can also infect the genitals.
What is genital herpes
The disease is caused by herpes simplex virus type 2 (less commonly, type 1). Genital herpes type 1 is transmitted from an infected person to a healthy person by droplets or through skin-to-skin contact.
The second type of genital herpes is transmitted through unprotected sex. The pathogen enters the human body through cracks and abrasions in the mucous membranes of the genital organs. Oral infection is also possible; it occurs when the lips come into contact with sores on the genitals caused by herpes.
The fluid that is inside the herpes blisters serves as a source of infection. If at least one herpes blister breaks during sexual intercourse, the partner will most likely be infected. Even if the abscesses have healed, infection will occur through contact with saliva, semen, vaginal or prostate secretions.
Once in the blood, the virus spreads to organs and tissues. The genitals, thighs and buttocks are primarily affected. Swelling and painful rashes appear on the vulva or vagina, penis, scrotum, testicles, anus or thighs. These are typical signs of genital herpes . This type of herpes does not cause rashes on the face or form sores in the mouth.
You can get genital herpes from:
- sexually;
- in close contact with the body of a sick person using the “skin to skin” type. Infection is possible if both people have lesions on the skin or mucous membranes (microsadines);
- during childbirth, the newborn can get an infection from the mother;
- if you use the things of a sick person. Herpes is unstable in the external environment, so cases of this type of infection are rare.
Features of treatment for pregnant women
The herpes virus poses the greatest danger to pregnant women; it can cause serious disruptions during pregnancy and provoke the appearance of abnormalities and deformities in the unborn child. Therefore, in the acute form, especially if it is a primary infection, you need to start treatment as quickly as possible. During pregnancy there are some nuances during therapy.
Acyclovir and its analogues are used only in exceptional cases due to possible harm to the pregnant woman and the fetus. The following drugs are used with caution:
- Panavir;
- Zovirax;
- Vivorax and others.
The acute phase immediately before childbirth is dangerous, including. As long as the fetus is inside the womb, infection is unlikely. Most newborns become infected during childbirth, passing through the birth canal or touching the mother's genitals. Therefore, if an exacerbation or relapse occurs at the expected time of delivery, a cesarean section is offered.
Mechanism of disease development
The first signs of genital herpes can appear from 2 to 30 days after infection. Or hide inside the host’s body.
Immediately after infection, the immune system tries to eliminate the virus. It produces antibodies that destroy virus particles in the general bloodstream of the body. But some of the virus DNA is masked in the nuclei of nerve cells in the spinal cord.
This is why immunity does not completely destroy the virus - antibodies cannot identify and attack it.
As soon as favorable conditions arise, the virus begins to actively multiply. Painful rashes characteristic of herpes appear on the lower part of the body - small watery blisters.
The herpes rash matures, bursts, and its contents spill onto the skin. The resulting ulcers become crusty. The skin recovers in 2-3 weeks,
The active stage of herpes makes a person defenseless against other sexually transmitted infections.
The virus present in the body may not be active for a long time. An outbreak of the disease can be caused by:
- pregnancy, menstrual cycle changes, hormonal changes;
- stress or heavy physical activity;
- skin diseases or burns;
- ARVI, bacterial infections and generally increased body temperature;
- cancer;
- HIV or AIDS.
If the infection is not treated, it will begin to move up the body, invading new organs and tissues. The further you go, the more severe the consequences will be. If genital herpes affects internal organs, it causes infertility, cervical or prostate cancer and severe immunodeficiency.
Classification of the disease
How of genital herpes appear depends on the person’s immunity. After the initial acute stage, they may recur within 2-3 weeks. And then signs of genital herpes appear after a certain period . Classification by severity:
- Mild if the active stage of herpes occurs no more than 3 times a year.
- Moderate, if exacerbations occur no more often than once every 2 months.
- Severe when relapses return every month.
According to clinical signs, herpes is classified into several types:
- primary;
- secondary;
- recurrent;
- asymptomatic;
- atypical.
Folk remedies
Herpes in an intimate place is treated with folk recipes in combination with medications. It is imperative to coordinate the chosen treatment with a specialist.
- Compresses with arnica. A decoction of arnica inflorescences is prepared from 12 g of herb and 400 ml of water. The product is infused for an additional 2 hours, pieces of natural fabric are soaked in it and applied to the inflamed areas.
- This recipe is for women. Candles made from beeswax with the addition of aloe and kalanchoe are very useful. Making them at home is not difficult. The plants are crushed, vitamins are added in ampoules B1 or B12, poured with molten wax and mixed thoroughly. The resulting product is laid out on a piece of bandage and a small candle is formed. Inserted into the anus or vagina. Depending on which organs the rash has formed on: in the back of the perineum or on the labia, you need to approach use specifically for each place.
- Infusion of birch buds. The drug is prepared from 25 g of phyto-raw materials and 1 glass of 70% alcohol. It is infused in the dark for 2 weeks, then filtered and used to rub herpes blisters.
- There is an effective folk method to strengthen the immune system. You need to extract juice from apples and onions. The proportions are taken 1/1. Dilute the liquid with pumpkin juice and consume a tablespoon 3 times a day. These products contain vitamins that have a positive effect on the immune system.
The simplest and most affordable recipe at home is aloe juice. The plant leaf is washed, cut and applied to the areas of infection. If there is a rash on the labia. You can grind aloe into a paste, apply it to the affected area, secure it with a bandage, and put on underwear on top. Compresses are changed after 1-3 hours.
Symptoms of the disease
Infection with genital herpes can occur in childhood through airborne transmission. This usually happens if the family has a low social status, lives in areas with high population density and cannot afford quality medical care, or if personal hygiene standards are not observed.
Genital herpes is most likely to occur:
- due to early onset of sexual activity;
- frequent change of partners;
- if a person does not use condoms;
- if he already suffers from sexually transmitted diseases;
- with weak immunity;
- if the patient is a woman. The weaker sex is especially predisposed to herpes.
Sometimes the initial symptoms of genital herpes are so mild that they can easily be mistaken for insect bites, shaving irritation, abrasions, pimples or hemorrhoids.
When the immunity of an infected person weakens, the painful process suddenly becomes active and affects the genital area, anus, and perineum. If the disease progresses, it spreads to the buttocks, inner thighs, legs and even the feet.
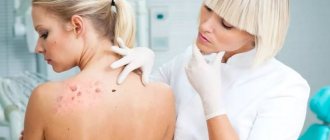
The characteristic symptoms of genital herpes are:
- colonies of small but very painful blisters appear on the skin. They are filled with a clear liquid;
- the skin and tissues around the rash are inflamed and swollen;
- the rash causes painful itching and burning;
- the inguinal lymph nodes are inflamed.
In men, blisters are located on the penis, testicles, buttocks, or around the anus. Women suffer from rashes on the vagina, near the anus and buttocks.
In addition, at the initial stage of the disease it may:
- body temperature rises;
- pain appears when urinating;
- the head of the penis, or the vulva and vagina become inflamed;
- increased headache, general weakness;
- worry about pain in the back and muscles.
Genital herpes can be mild or severe. In the worst case, the rashes are especially massive and swollen, covering large areas of the body, causing acute pain or unbearable itching.
Manifestations and symptoms of herpes in the intimate area in women and men
Herpetic cystitis of women
Herpetic cystitis is a pathology characterized by inflammatory processes in the bladder caused by the herpes virus. This disease manifests itself as discomfort when urinating and hyperemia of the skin and mucous membranes. Women are especially often bothered by the urge to urinate at night. If left untreated, herpetic cystitis can lead to complications, including herpetic salpingoophoritis. In this case, the inflammation affects the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
Herpes of the urethra and bladder
The disease makes itself felt by painful sensations and pain when urinating. There is a frequent urge to go to the toilet, there may be blood in the urine and discomfort in the bladder area. In men, detection of the herpes simplex virus in the urine may indicate inflammation of the prostate gland.
If you suspect herpetic prostatitis, which is characterized by frequent relapses, the patient must undergo a special examination for sexually transmitted infections of a viral nature.
Herpetic lesions of the anal area and rectum
The disease manifests itself with itching, burning and pain in the affected area. Bleeding may occur during bowel movements. As the disease develops, erosions and cracks form on the mucous membrane, which are often attempted to be treated only surgically, without the use of drug antiviral treatment.
How to make a diagnosis
Typically, the patient consults a doctor if he has already clearly developed symptoms of primary herpes. At your appointment, your doctor will ask you to remember the following information:
- when did the first complaints arise?
- whether the patient has had similar symptoms before;
- whether the patient had sex during the active phase of the disease;
- whether he tried to treat himself and with what exactly;
- whether there are chronic diseases and what medications the patient takes;
- does he suffer from allergies?
During the examination, the doctor will pay attention to whether there are itchy blisters on the body and where they are located, how severe the swelling and inflammation of the tissues affected by herpes are. For women, an obligatory step will be an examination in a gynecological chair. For men - palpation of the prostate.
The patient will be prescribed the following laboratory tests:
- general blood analysis. In the moderate and severe stages of the disease, an increase in ESR and a decrease in the number of leukocytes will be detected;
- general urine analysis. When the genitourinary system is damaged, leukocytes are present in the urine, its appearance is changed;
- blood chemistry. Particular attention is paid to the presence of C-reactive protein - it indicates an inflammatory process;
- growing the herpes simplex virus on tissue scraped from the site of the lesion, or a smear from the urethra. The grown virus is examined by electron microscopy;
- linked immunosorbent assay. This is a blood test that detects antibodies to the herpes virus even if the disease is asymptomatic. The level of IgM antibodies is present in the blood serum only in the first weeks of the disease, and IgG - throughout life;
- polymerase chain reaction. The main and most accurate analysis is to determine whether there is DNA of the herpes virus in the blood.
How to treat genital herpes
Any therapy only inhibits the reproduction of the virus, but does not completely destroy it. Correctly selected treatment alleviates the patient's suffering and makes relapses rare.
The most commonly used drugs are from the group of acyclic nucleosiodes. They usually come in the form of tablets and creams.
Drugs from the interferon group are also used - in the form of ointments and rectal suppositories. These are immunomodulators that have antiviral activity.
Combination drugs from the groups of acyclic nucleosides and interferons have proven themselves well. They shorten the treatment time, but are effective at the very beginning of the disease.
The patient may be prescribed painkillers (anesthetic cream).
Ultraviolet irradiation of blood helps heal ulcers and allows you to achieve stable remission.
Antibiotics should not be used to combat genital herpes. They are powerless in the fight against viruses and suppress the immunity of an already weakened person.
Important! For the entire period of treatment, you must avoid all types of sex and physical contact, including kissing.
Moreover, a patient with genital herpes will forever remain a source of infection to his sexual partners and must always use a condom.
Synthetic antiviral topical drugs
This group of drugs can be roughly divided into drugs used for genital herpes infection and antiviral drugs prescribed for the treatment of papillomas and condylomas associated with papillomavirus infection.
Local medications for genital herpes
Several drugs registered in the Russian Federation are used for the treatment and prevention of relapses of genital herpes.
Tromantadine
An antiviral drug for herpes, an adamantane derivative (similar to the well-known antiviral drugs rimantadine and amantadine). Inhibits the attachment of the virus to the surface of the cell membrane, preventing the pathogen from penetrating into the cell. Prevents cell fusion and makes it difficult for the virus to spread by changing the synthesis of glycoproteins [5]. Available in the form of a gel for external use, which can be applied to mucous membranes during exacerbation of HSV infection [5].
Vacation: without prescription.
!
There is evidence of the development of a contact allergic reaction when using the drug [7].
Sodium aminodihydrophthalazindione
An immunomodulator capable of regulating the activity of innate and acquired immune cells, including macrophages, neutrophils and natural killer cells. At the same time, this antiviral drug against herpes increases the body's resistance to bacterial, viral and fungal infections, reducing their frequency, severity and duration (5). In addition, the drug normalizes the formation of antibodies and regulates the production of interferons, and also blocks the excessive synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines and reduces the level of oxidative stress (5).
Vacation: Without prescription
+
High safety profile (5).
Azoximer bromide
A Russian drug supposedly exhibiting an immunostimulating effect. According to the instructions [5], it directly affects phagocytes and natural killer cells, stimulates the formation of antibodies and the synthesis of interferon, and exhibits antioxidant and detoxifying properties. In domestic practice, it is used for a wide range of diseases - from influenza to malignant neoplasms.
Azoximer bromide vaginal suppositories are used to prevent recurrence of genital herpes.
Vacation: without prescription.
+
High safety profile. According to the manufacturer [5], no side effects have been reported.
!
Azoximer bromide suppositories are not indicated for the treatment of active herpes!
Complications and prognosis of the disease
At first glance, genital herpes does not seem to be a serious disease, especially if a person has had it in a mild form. However, this virus can seriously complicate the life of an infected patient. The disease causes the following complications:
- dryness of the vagina and cervix;
- dryness of the mucous membrane of the urethra;
- the formation of adhesions of the labia, cracks or erosions with further gross scarring;
- urinary retention;
- formation of pain syndrome;
- opens up the possibility of secondary bacterial infection.
- general decrease in immunity. A carrier of the genital herpes virus will often suffer from inflammatory diseases and become susceptible to infections;
- affects the liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract and even lungs;
- affects the nervous system, causing neuralgia, encephalitis and meningitis.
Infection and pregnancy
If a pregnant woman is a carrier of the genital herpes virus, and the disease is not in its active phase, there is no danger to the baby’s intrauterine development.
Even if a recurrent attack occurs in the early stages of pregnancy, there will be no serious consequences for infection of the developing fetus.
Intrauterine infection of a child is very rare. And, as a rule, in this case the disease does not manifest itself for a long time. Very rarely, but still, abnormalities in the development of the fetus develop - if the expectant mother gets herpes while carrying a child.
However, the disease in late pregnancy is quite dangerous. It can cause premature birth or miscarriage.
If changes in hormonal levels “awakened” herpes and it entered its active stage, doctors will most likely insist on a cesarean section. The herpes virus is very dangerous for newborns, and infection can occur during childbirth - if it occurs naturally.
Children born with genital herpes may develop blindness and brain damage. 50% of them are not viable.
If a baby is infected with a virus during childbirth (through contact with the vagina), herpetic blisters appear on his face, body and genitals.
Important! Labial herpes (herpes of the lips) does not pose a danger to a newborn baby. Only infection with genital herpes will have serious consequences.
Atypical form
The atypical form of the pathological process is characterized by an erased abortive course, which affects not only the external genitalia, but also the internal genital organs. As a rule, this form of infection is characteristic of chronic recurrent herpes, but at the same time, it can also occur with primary lesions.
It's no secret that many chronic pathologies of the genital organs are diagnosed as diseases of unknown etiology. This is due to the inability to identify the cause of the disease, and therefore the prescribed treatment is very often ineffective. It is in such cases that good specialists suspect the development of an atypical form of herpesvirus infection.
Prevention
You can try to protect yourself from herpes by getting vaccinated. However, a stable and long-lasting effect cannot be achieved. The herpes virus successfully counteracts the effects of the vaccine.
Therefore, it is especially important to observe precautions and personal hygiene:
- Always use a condom during all sexual contacts. But keep in mind - the virus can penetrate through a small abrasion in an area of the skin that cannot be protected with a condom;
- Treat the area of the body where you think the virus might have entered with antiseptic agents. Do this after intercourse and showering;
- Wash your hands every time, if you have visited public places, traveled in public transport, held money in your hands, and before eating. A huge number of viruses are found on money, mobile phones, door handles and handrails.
- Only you should use your hygiene products. Keep combs, washcloths and towels strictly separate from the hygiene items of other people.