Pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys that has a bacterial basis.
Pyelonephritis can be primary or secondary (obstructive). Obstructive occurs due to other disorders of the urinary system, disturbances in the outflow of urine, so it is important to promptly treat urolithiasis so that the stones do not interfere with the physiological outflow of urine and do not damage the kidneys. Symptoms of pyelonephritis may also differ between acute and chronic forms of the disease.
Symptoms of acute pyelonephritis
The acute form of kidney inflammation manifests itself with striking symptoms:
- chills, loss of strength, general malaise, heavy sweating;
- the temperature can rise to 39-40 ° C;
- headaches, especially in the frontal part;
- nausea and vomiting are a consequence of general intoxication;
- muscle and joint pain scattered throughout the body;
- Sometimes changes occur in the gastrointestinal tract - diarrhea.
With obstructive pyelonephritis, it often begins with renal colic. Acute pain is followed by a rapid rise in temperature and deterioration in general condition. The person begins to sweat profusely, the temperature drops sharply, and a period of imaginary well-being begins. But if the cause of the obstruction of urine outflow is not eliminated, then over time more serious symptoms will appear, especially if we are talking about a purulent form:
- increased pain in the lumbar region;
- muscle tension in the lower back and anterior abdominal wall;
- the affected kidney enlarges, it is clearly felt upon palpation;
- dehydration;
- the patient’s facial features become sharper and their appearance changes;
- sometimes euphoria sets in.
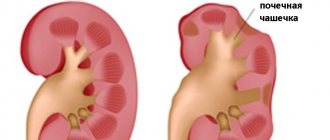
Classification of pathology
Pyelonephritis is classified according to various criteria.
| Name of the sign of the disease | Classification of pyelonephritis according to the specified criteria |
| Number of affected kidneys |
|
| Patency of the urinary tract |
|
| Path of infection |
|
The clinical description of the pathology is most often based on the nature of the course of pyelonephritis (acute, chronic).
Also, the clinical description takes into account the condition of occurrence (primary, secondary).
Indications for diagnosing “complicated pyelonephritis” in women are:
- the appearance of infection in the urinary system after diagnostic or therapeutic procedures using instrumental methods (catheterization, cystoscopy, ureteral stenting, etc.);
- dysfunction of the urinary tract;
- anatomical deviations in the development, structure or position of the organs of the urinary system, congenital or acquired.
In chronic pyelonephritis, there are 4 stages described in the table.
| Stage designation | Damage to the kidney | Brief explanations |
| I | When the glomeruli are preserved, the collecting ducts atrophy. | The collecting ducts play a leading role in the formation of final urine. |
| II | Individual glomeruli become hyalinized (protein is introduced into the structure of the glomeruli). The tubules atrophy to a greater extent. There is a proliferation of connective tissue. | The kidney glomeruli (in a healthy woman their number is about 1.5 million) are the main filter of the body; they filter about 150 liters of liquid per day. The tubules are responsible for ion exchange. The proliferation of connective tissue depresses the internal structure of the kidney |
| III | Most of the glomeruli are destroyed. The tubules are dilated and filled with colloidal mass. | The colloidal mass in the tubules is a suspension of proteins. |
| IV | Characterized by the death of most tubules and glomeruli. The size of the kidney is significantly reduced. | Normal kidney sizes in women are (in mm):
Visualization of the size of the organ is carried out using CT and ultrasound |
Symptoms of pyelonephritis in men and women
The structural features of the urinary system affect the course of pyelonephritis. Since women have a shorter urethra, it is easier for infection to reach the kidneys; pyelonephritis is often a consequence of untreated cystitis. Women more often suffer from kidney inflammation; the symptoms of pyelonephritis are more pronounced in them:
- rise in body temperature above 38 °C;
- characteristic features of general intoxication;
- change in the color of urine - up to a dirty yellow or darker color, and in case of urolithiasis and renal colic, there may be blood impurities in it.
Symptoms of pyelonephritis in men are often more subtle:
- thirst and dry mouth;
- general malaise;
- pain in the lumbar region.
What is the danger of the disease?
Pathology leads to impaired kidney function.
Among the most significant functions of the paired organ, we note:
- Excretory (the kidneys form urine and are released from it. Along with urine, products of protein metabolism, drugs, hormones, etc. are excreted from the body).
- Secretory (through a complex mechanism, the kidneys regulate blood pressure).
- Metabolic (participation in metabolism). In addition, the kidneys maintain a stable environment in the body - homeostasis.
Malfunctions of the kidneys caused by pyelonephritis provoke:
- intoxication (poisoning) of the body;
- impaired blood pressure, which negatively affects the entire cardiovascular system;
- metabolic disorders, which can lead to pathology of many organs and systems of the body.
If the disease is not treated, it will involve the entire body in the pathological process.
Symptoms of chronic pyelonephritis
The chronic course is characterized by alternating acute phases and stages of remission. The active period will be characterized by the symptoms of acute pyelonephritis described above. And in the remission stage, a person may feel the following symptoms of chronic pyelonephritis:
- dull pain in the lower back;
- fatigue and lethargy;
- temperature rise to subfebrile levels;
- loss of appetite, nausea.
Without treatment, chronic renal failure occurs; a secondary wrinkled kidney becomes an ultrasound sign of chronic pyelonephritis. Another symptom of late-stage disease is high blood pressure.
Possible complications
The disease is dangerous for young children, elderly and weakened people. In these cases, a weakened immune system can cause serious pathologies. Among them:
- kidney abscess;
- blood poisoning (sepsis);
- nephronecosis;
- renal failure.
Among the particularly severe forms are xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis and apostematous nephritis - aggressive forms of the disease that can lead to the replacement of functional renal tissue with fibrous substances with partial or complete loss of kidney function.
Symptoms of pyelonephritis in pregnant women
During pregnancy, a woman's kidneys experience maximum stress. The growing uterus puts pressure on the urinary system, the sepal system and ureteral canals expand. All this leads to the fact that pregnant women have an increased risk of pyelonephritis. Symptoms of pyelonephritis in pregnant women are similar to those observed in the acute form of the disease:
- signs of intoxication;
- lower back pain;
- change in urine color;
- fever.
Diagnostics
Acute kidney pyelonephritis requires urgent hospitalization, so the main diagnosis takes place in a hospital setting. In addition to a general examination with temperature measurement, tapping of the lumbar area and palpation of the peritoneum, the doctor prescribes instrumental examination methods and laboratory tests.
Instrumental diagnostics:
- X-ray with contrast - taken in the form of several consecutive images - this allows you to evaluate the shape of the renal calyces and pelvis, identify the pattern of urine movement, the presence of obstructions in the ureters, the presence of stones;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys - opens up a view of the state of the organ in dynamics (on the monitor it is increased in volume, the area of the pelvis is expanded, the parenchyma has an increased density);
- CT and MRI make it possible to study with high accuracy not only the structure of the kidneys themselves, but also their vascular system, including the smallest anomalies and obstructions that ultrasound or X-ray will not show.
List of laboratory tests:
- complete blood count - ESR, leukocyte level;
- biochemical blood test - level of creatinine, urea, potassium;
- serological tests for specific antibodies to the pathogen;
- PCR diagnostics with identification of the gene material of pathogens;
- bacteriological examination of urine;
- general urine analysis with determination of physical and chemical parameters;
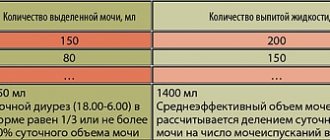
- urine tests according to Nechiporenko (morning), Addis-Kakovsky (24 hours), Amburge (three hours) - give clearer values of indicators;
- the Zimnitsky test allows you to assess the ability of the kidneys to filter blood by the concentration of urine taken every 3 hours
Attention! Any deviation of the potassium level from the natural fixed norm is a reason for prescribing hemodialysis.
Urine indicators for pyelonephritis
| Index | Norm | For pyelonephritis |
| Specific gravity | 1012-1025 units. | > 1025 units |
| Transparency | high transparency | low transparency (cloudy solution) |
| pH | slightly acidic | alkaline |
| White blood cell count | 1-2 pcs. on the field | > 2 pcs. |
| Presence of red blood cells | ≤ 1 piece on the field | ≥ 1 piece on the field |
| Protein | ≤ 0.33 g/l | ≥ 0.33 g/l |
| Cylinders | none | present |
| Bacteria | none | present |
| leukocytes, erythrocytes, cylinders in 1 ml according to Nechiporenko |
|
|
| leukocytes, erythrocytes, cylinders per minute according to Amburge |
|
|
| leukocytes, erythrocytes, cylinders per day according to Addis-Kakovsky |
|
|
Treatment
Since acute pyelonephritis often becomes chronic, which can lead to morphological changes in the kidneys and disruption of the entire urinary system, you should consult a doctor at the first symptoms of pyelonephritis.
At the Clinic of Urology named after R. M. Fronshtein of the First Moscow State Medical University named after I.M. Sechenov (State Urology Center) will definitely help you. Do not self-medicate and do not waste precious time, remember that the kidneys are a vital organ. July 25, 2020
Hakobyan Gagik Nersesovich - urologist, oncologist, MD, doctor of the highest category, professor
All the symptoms of the disease...
Prevention
In order not to lead yourself to pyelonephritis, prevention should be carried out taking into account certain rules:
- The use of medicinal herbs as prophylaxis.
- If the pathological process of infectious etiology is located in any other organs, it must be sanitized, since bacteria can spread to the kidneys with the help of blood.
- Getting rid of bad habits, since alcohol and smoking significantly reduce the body’s immune properties, which inhibits the ability to respond to the penetration of bacteria and viruses into the body.
- The body must receive sufficient rest and sleep, since an exhausted body is not able to fight a bacterial infection.
- Persons who are at risk of developing the disease need to regularly carry out laboratory and instrumental research methods in order to prevent pyelonephritis.
Compliance with these rules does not require significant work; you just need to pay close attention to your own health and carry out treatment in the early stages of the pathological process.