Herpes in the intimate area in women or genital herpes in women is one of the most common clinical types of sexually transmitted herpes infection. Genital herpes in women is characterized by the appearance of characteristic rashes on the skin and mucous membranes in the urogenital and/or anal area, characterized by variability in the clinical picture and a tendency towards a persistent recurrent course.
The causative agent of genital herpes is the herpes simplex virus (HSV, Herpes Simplex virus).
Fact Infection with genital herpes in 76% of cases is caused by HSV-2 and in 24% by HSV-1.
In most patients, the causative agent of genital herpes is herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2). There are cases of genital herpes caused by HSV type 1, which reflects the increased prevalence of oral-genital contact in various population groups. In some patients, the disease can be caused simultaneously by two types of herpes simplex virus (HSV-2 and HSV-1).
What is genital herpes
The content of the article
Genital herpes is one of the most commonly diagnosed sexually transmitted diseases in both men and women. The causative agent is the herpes simplex virus type HSV-1 and HSV-2. In many people, the disease is completely asymptomatic, so the likelihood of infection through sexual contact is very high.
Symptoms of genital herpes are easy to recognize by visual examination. Mild pain and changes appear on the skin of the genitals and perineum, resembling blisters. The first wave of the disease can last from 2 to 3 weeks, sometimes less. When the disease relapses, the symptoms of GG are usually less disturbing than the first time.
Special antiviral drugs alleviate the condition. Patients whose symptoms of genital herpes appear regularly are forced to take medications every day.
How to make a diagnosis
Typically, the patient consults a doctor if he has already clearly developed symptoms of primary herpes. At your appointment, your doctor will ask you to remember the following information:
- when did the first complaints arise?
- whether the patient has had similar symptoms before;
- whether the patient had sex during the active phase of the disease;
- whether he tried to treat himself and with what exactly;
- whether there are chronic diseases and what medications the patient takes;
- does he suffer from allergies?
During the examination, the doctor will pay attention to whether there are itchy blisters on the body and where they are located, how severe the swelling and inflammation of the tissues affected by herpes are. For women, an obligatory step will be an examination in a gynecological chair. For men - palpation of the prostate.
The patient will be prescribed the following laboratory tests:
- general blood analysis. In the moderate and severe stages of the disease, an increase in ESR and a decrease in the number of leukocytes will be detected;
- general urine analysis. When the genitourinary system is damaged, leukocytes are present in the urine, its appearance is changed;
- blood chemistry. Particular attention is paid to the presence of C-reactive protein - it indicates an inflammatory process;
- growing the herpes simplex virus on tissue scraped from the site of the lesion, or a smear from the urethra. The grown virus is examined by electron microscopy;
- linked immunosorbent assay. This is a blood test that detects antibodies to the herpes virus even if the disease is asymptomatic. The level of IgM antibodies is present in the blood serum only in the first weeks of the disease, and IgG - throughout life;
- polymerase chain reaction. The main and most accurate analysis is to determine whether there is DNA of the herpes virus in the blood.
The causative agent of the disease
Herpes (from the Greek ἕρπης - creeping, spreading skin disease). Genital herpes is a viral infection that affects the penis in men (penile herpes) and the external genitalia and vagina in women (herpes vaginalis, labia), as well as the area around the genitals, usually the perineum. Infection is manifested by the appearance of blisters on the skin. Sometimes they can occur on the buttocks and anus.
The causative agent of the disease is the human herpes virus. There are two types of AI virus: herpes virus type 1 and herpes simplex virus type 2.
- AI virus type 1 most often leads to the appearance of herpes on the lips. Causes half of the cases of genital herpes.
- AI virus type 2 is responsible almost exclusively for the development of genital herpes. Very rarely it can also cause herpes on the lips.
Herpes on the lips
Risk factors
Certain conditions and symptoms may contribute to viral invasion.
Risk factors may be associated with primary diseases and a person's lifestyle. Predisposition factors for genital herpes:
- gender (Women are much more likely to be diagnosed with the disease);
- unprotected sex. (using a polyurethane or latex condom helps reduce the chance of infection);
- promiscuity;
- the presence of other infections affecting the genital organs;
- dysfunction of the immune system, including acquired immunodeficiency;
- carrying out various surgical interventions in non-sterile conditions.
Preventive measures help reduce the risk of viral invasion.
Ways of infection with genital herpes
Genital herpes is transmitted primarily through sexual contact with a person who is already a carrier of the virus. The thin, delicate mucous membranes of the mouth, genitals and anus are very vulnerable to viruses and infections. This allows the virus to pass from one person to another during sexual intercourse, including oral and anal sex.
Transmission of the virus from the lips to the genitals occurs during oral sex, when one of the partners has signs of herpes on the lips. The herpes simplex virus can also enter the body of another person through wounds or cracks in the skin on other parts of the body: fingers, palms, knees, etc., provided that the surface comes into contact with the infected area of the skin. Re-infection with your own virus through accidental touch is unlikely.
Prevention
You can try to protect yourself from herpes by getting vaccinated. However, a stable and long-lasting effect cannot be achieved. The herpes virus successfully counteracts the effects of the vaccine.
Therefore, it is especially important to observe precautions and personal hygiene:
- Always use a condom during all sexual contacts. But keep in mind - the virus can penetrate through a small abrasion in an area of the skin that cannot be protected with a condom;
- Treat the area of the body where you think the virus might have entered with antiseptic agents. Do this after intercourse and showering;
- Wash your hands every time, if you have visited public places, traveled in public transport, held money in your hands, and before eating. A huge number of viruses are found on money, mobile phones, door handles and handrails.
- Only you should use your hygiene products. Keep combs, washcloths and towels strictly separate from the hygiene items of other people.
Asymptomatic course of the disease
The first infection with the herpes simplex virus is often called the primary infection. Such an infection can cause symptoms of the disease, but this does not occur in all cases. After the primary infection, the virus is not eliminated from the body; it lives in it in the form of an inactive form (in sleep mode).
In some people, the virus “wakes up” from time to time and enters the surface of the skin. This, in turn, causes a relapse of the viral disease on both the genitals and lips.
For most people, infection with the herpes virus in intimate areas is not a cause for concern. At least 8 out of 10 people with genital herpes don't even know they have it. Sometimes only very mild symptoms may appear that are difficult to associate with genital herpes. Such symptoms may include a slight burning sensation or slight redness that quickly disappears.
In such people, the virus remains dormant and never causes a wave of symptoms to return. However, even those who develop the disease asymptomatically are dangerous to their sexual partners. It is in such cases that infection with the herpes virus occurs.
Complications
Genital herpes itself does not cause serious illness. However, its complications, which are often observed in people with weak immune systems (especially those with HIV infection), can pose a serious threat to health and even life.
- Herpetic eczema is a skin lesion that leads to the appearance of a rash similar to that of eczema;
- Herpetic keratoconjunctivitis is a lesion of the cornea and mucous membrane of the conjunctiva of the eye. Manifested by photophobia, burning, lacrimation, redness of the eye. Small white spots appear on the surface of the cornea, causing itching and pain. Without treatment, vision loss is possible;
- Herpetic encephalitis is an inflammation of the brain caused by the HSV type 2 virus. Without treatment, the complication leads to death. The virus infects nerve cells in the cerebral cortex, leading to focal and general brain symptoms. Complete cure is possible with adequate and timely therapy;
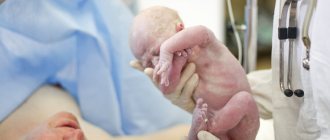
- Intrauterine herpes is the transmission of infection from mother to child. Primary infection is dangerous, which leads to damage to the fetal nervous system;
- Herpetic meningitis is an inflammation of the meninges caused by the HSV type 2 virus. A severe complication leading to a number of neurological symptoms, including convulsions, severe headaches, and disturbances in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
In people with normal immune status, complications are rare. On average, the acute phase of infection during primary infection lasts several weeks. During this period, the infected person releases a large number of viral particles with biological fluids. Carriage lasts up to 1 year. In most cases, the immune system controls the infection and suppresses its activity. This occurs due to the production of antibodies directed against the virus. During the period of remission, the virus remains only in the nerve cells of the sensitive nerve plexuses.
In patients with immunodeficiency, the herpes simplex virus often causes complications. Infection is especially dangerous in patients with AIDS. Herpetic lesions in such patients are extensive and often occur in the form of severe meningoencephalitis with a fatal outcome.
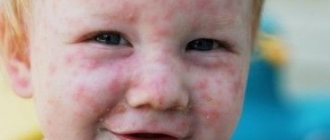
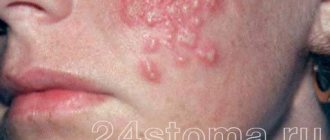
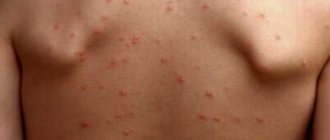
Signs of genital herpes
At the initial stage of the disease, a person is worried about a slight increase in body temperature, general malaise and poor health. Small groups of blisters, often painful, appear around the genitals and/or anus. There may be visible changes on the skin of the labia, as well as the clitoris, in the area of the vaginal opening, on the thighs around the anus.
Herpes blisters
The blisters grow for one to two weeks before bursting and turning into small, painful sores. Lymphatic inguinal nodes are enlarged and identified, palpated as compactions, lumps in the upper thighs. Painful urination is often a concern.
Women may experience unusual vaginal discharge. The herpes virus in women affects the cervix, first blisters appear on it, then ulcers appear. Typically, blisters and ulcerative lesions develop within 10-20 days, after which they gradually disappear without leaving scars.
The first symptoms of genital herpes may appear months or even years after infection. Therefore, the first wave of symptoms may occur while a person is married or in a long-term relationship with a reliable partner.
It is not entirely known why some people experience symptoms of infection and others do not. It is also not fully understood why the first wave of symptoms occurs months or years after the actual infection. This may have to do with how the immune system responds to the virus in individuals.
Infection in newborns
Typically, infection of a child occurs after rupture of the membranes or directly during childbirth. HSV-2 primarily affects the mucous membrane of the mouth and respiratory tract. The virus can subsequently spread through the body through the bloodstream and cause more severe complications. The independent transfer of the pathogen to other anatomical areas should not be ruled out.
Features of the disease in newborns:
- ulceration of the mucous membranes with the formation of foci of hemorrhage;
- eye damage. (pathology causes inflammation of the cornea, conjunctiva and choroid of the organ);
- prolonged fever;
- inflammation of the brain and its membranes;
- neurological disorders;
- breathing problems;
- vascular insufficiency.
The complications listed above most often occur 10-14 days after the manifestation of the disease, when the infectious process becomes generalized.
Development of disease relapses
Some people sometimes experience recurrences of genital herpes. Scientists are unable to explain why, after the latent stage, the virus is activated from time to time, that is, the reasons for the relapse have not been established. Factors that contribute to the development of the virus and relapse of the disease are known:
- influenza, ARVI, other diseases with high body temperature;
- local damage to the external genitalia, as well as the mouth and lips;
- decreased defense mechanisms, immunodeficiency;
- ultraviolet radiation, a side effect of radiation therapy;
- changes in a woman’s immune system during menstruation;
- hypothermia;
- stress;
- excessive alcohol consumption.
ARVI
Stress
Relapses are often milder and last shorter than the first wave of the disease. In case of relapses, symptoms usually occur within 7 to 10 days. Most people do not complain of either elevated body temperature or poor health. A relapse of the disease may be indicated by a slight tingling sensation or itching of the genitals for 12-24 hours.
Over time, relapses of genital herpes appear less frequently. The frequency of their occurrence may vary. For some people they occur six or more times during the year, for others much less often. As a rule, during the first 2 years from the first wave of symptoms, relapses occur 4 to 5 times. Some people do not relapse at all.
How to diagnose genital herpes
To diagnose the disease, a visual examination is generally sufficient. The type of changes, their location and other symptoms are sufficiently characteristic to make a diagnosis of genital herpes.
In case of doubt and for invasive infections, carry out:
- Isolation of the virus from a cell culture, examining the smear or the content of the bubbles, however, the absence of the virus in dilution (negative result) does not exclude infection;
- The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method is a more sensitive method of testing a smear or fluid from the rash, but a negative result also does not rule out infection.
- Serological study. Allows the detection of antibodies to the HSV virus, which appear after a few weeks, as well as differentiation of the type of virus that caused the infection.
If antibodies against HSV-2 are detected, genital herpes is diagnosed, which poses a higher risk of relapse of the disease. Antibodies against HSV-1 indicate herpes simplex virus, so there is less chance of recurrence of lesions in the genital area.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by a doctor based on the patient’s complaints and examination, during which a characteristic rash and enlarged lymph nodes can be detected. If an external examination does not reveal a rash, the doctor takes material for laboratory tests.
In addition, you need to know how to detect genital herpes using laboratory methods. Can:
- Determine the disease using the PCR method during the period of relapse (the most effective), which determines not only the presence of the virus in the body, but also its type. Subject to sterility and temperature conditions, material taken from the site of the rash allows you to obtain results within 5 hours;
- Identify antibodies to the virus by conducting blood tests;
- Identify the virus by examining material taken from the location of the rash;
- Conduct an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, which determines the presence of antibodies and evaluates the patient's immunity.
Since there are diseases similar to genital herpes in their manifestations (ulcers and erosions on the genitals), self-medication should not be done.
Herpes or so-called stomatitis on the genitals resembles:
- Chancroid, sexually transmitted but rare in Europe and Asia;
- Erosion resulting from trauma;
- Syphilis.
Since the presence of antibodies alone cannot serve as a basis for the diagnosis of “genital herpes” (in women, the presence of antibodies to type 2 herpes is more likely, and antibodies are formed by 6-12 weeks after infection), it is additionally necessary to isolate the virus or use the PCR method.
Treatment of genital herpes
The use of antiviral drugs does not remove the virus from the body. Their goal is to suppress the reproduction process of the pathogen. The most effective use of medications is during the first manifestation of signs of the disease. Moreover, it is necessary to start therapy within the first five days from the moment the first symptoms appear. This allows not only to stop the spread of lesions, but also to reduce the duration of the disease.
The course of treatment for genital herpes is most often five days; if the rash persists, it is extended. To shorten the duration and relieve symptoms, you should start taking the drug as quickly as possible. The earlier treatment is started, the greater the chances of a rapid cure, effective reduction of symptoms and prevention of relapse of the disease.
In the treatment of relapses of the disease, antiviral drugs are not always used. Therapy is indicated and brings good results in cases of frequent severe symptoms. In case of frequent relapses, it is possible to take an antiviral drug every day. In people who use this form of treatment, relapses will either be completely absent or their frequency will be significantly reduced.
Treatment of herpes in the intimate area with folk remedies: will traditional medicine help?
Traditional medicine existed in all periods of human history, and the experience of traditional healers multiplied over the millennia and was passed on from generation to generation. True, one cannot help but admit that today many of the recipes that our ancestors used have been lost and forgotten, and the assessment of traditional medicine by specialists is still ambiguous. What happens when treated with traditional medicine methods
Today, traditional medicine offers both rational methods, which, under certain conditions, can really help cope with various diseases, and irrational ones, which deserve critical evaluation by doctors. But this does not stop those who, instead of turning to a specialist, decided to help themselves on their own by testing the effectiveness of traditional medicine recipes. As a rule, such people will be disappointed - no decoctions, infusions, applications of medicinal herbs and other drugs prepared at home can help get rid of the manifestations of herpes in the intimate area. It must be remembered that refusal to see a doctor and lack of adequate treatment can lead to unpredictable consequences and the development of life-threatening complications.
Only antiviral drugs that not only relieve symptoms, but also fight the root cause of the disease can help reduce the severity and shorten the course of the disease.
Drugs for the treatment of genital herpes
Zovirax ®
(Zovirax)
. Original drug. The medicine is manufactured by Glaxo Wellcome, SA. The active ingredient is acyclovir 200 mg. Clinico-pharm. group: antiviral drug. Pharmaceutical therapeutic group: antiviral agent. Pharm. action: a synthetic analogue of purine nucleoside that inhibits the replication of Herpes simplex AI viruses types 1 and 2.
There are known generics of the drug Zovirax - Acyclovir (manufactured by Belupo, Croatia), Acyclovir (manufactured by Akrikhin, JSC Vertex, JSC Sintez, Russian Federation).
Drug for the treatment of genital herpes
Valtrex®. Original drug. The drug is manufactured by Glaxo Smith Kline, SA. Contains the active ingredient valacyclovir hydrochloride 556 mg (= valacyclovir 500 mg). Clinical and pharmacological group: antiviral drug. Pharmacotherapeutic group: antiviral agent. It is an L-valine ester of acyclovir. Valaciclovir is quickly and completely converted into acyclovir and valine in the body.
Genital Herpes – Symptom Relief at Home
A cold compress (ice cubes wrapped in a towel) placed on the lower abdomen for 5-10 minutes may provide relief. Do not apply ice directly to the skin.
It is important to take in plenty of fluids.
Scented soaps, bath products and other similar products that may irritate the skin should be avoided. The best results are obtained by gently washing the genital area with a cotton swab and water. You cannot share towels, washcloths, or sponges. This minimizes the risk of infection to other family members.
Sexual abstinence is recommended until the blisters and ulcers disappear.
Diet
When doing treatment at home, you must follow a diet. This will help prevent the herpes from getting worse. The principle of the diet is a high content of lysine, a small amount of arginine.
- Allowed foods include low-fat dairy products, beef, chicken, various fish and seafood.
- For dessert you can eat ice cream or drink coffee with cream.
- Blackberries, black currants, peaches, apples, bananas help cleanse the body.
- Additionally, your daily diet should include garlic and brewer's yeast (you can use pharmaceutical preparations in the form of capsules).
- You can eat a little green onion salad dressed with olive oil three times a day. The dish is rich in retinol and ascorbic acid, which helps strengthen the body.
Alcohol should be avoided completely. Minimize consumption of sugar, sweets and nuts.
Genital herpes and sexual intercourse
If partners are carriers of the same virus, the possibility of re-infection is excluded. It is recommended to avoid intimate relationships from the moment the first symptoms appear until they disappear completely.
The herpes simplex virus is highly contagious when blistered. Sexual activity in this state is accompanied by a maximum risk of transmitting the virus to a partner. If there are no symptoms of genital herpes, the likelihood of transmitting the virus is reduced. However, this is possible because the virus is present on the surface of the skin of the genitals.
Using a condom during every sexual intercourse helps protect yourself from infection. However, it should be remembered that a condom does not guarantee complete protection against transmission of the virus to a partner, because it only protects the covered area of the body.
People who take antiviral medications for a long time are also less likely to contract the virus.
Genital herpes during pregnancy
To prevent genital herpes from developing in a child, a woman who has ever had symptoms of the disease should see a doctor (sometimes delivery by cesarean section is recommended). Sexual intercourse is prohibited from the third trimester of pregnancy if the woman’s partner not only has signs of genital herpes, but also suffered from the disease in the past. During this period, the risk of fetal infection is very high.
For many years, the development of an effective vaccine against genital herpes has been underway, unfortunately, so far to no avail.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter