From this article you will learn:
- herpes virus - types, symptoms,
- reasons for repeated outbreaks,
- how to treat herpes - the best remedies,
- How effective is the vaccination (Vitagerpavac vaccine).
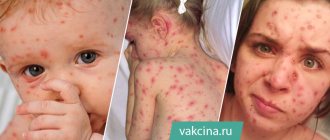
Herpes is a viral disease in which characteristic eruptions of fluid-filled blisters (vesicles) appear on the skin and mucous membranes. But within 2-3 days the blisters burst with the formation of ulcerations, which, if localized on the skin or red border of the lips, become covered with crusts, and if on the mucous membrane, then with a yellowish fibrinous film. There is a whole family of herpeviruses, but people usually have to deal with the “herpes simplex virus” - types HSV-1 or HSV-2.
It is these types of herpes that are responsible for the appearance of rashes - on the skin of the face, lips, oral mucosa, and they are also the cause of genital herpes. It should be noted that if previously the herpes virus HSV-2 was associated only with the development of genital herpes, now it also causes herpes on the face, lips and oral mucosa - in approximately 10% of patients. Herpes type HSV-2 is more pathogenic (than HSV-1), and such patients always experience both more severe clinical manifestations and a higher frequency of relapses.
Herpes: photo
The herpes simplex virus is clinically manifested by the formation of a group of crowded blisters located on an inflamed base (skin or mucous membrane). The bubbles are first filled with transparent contents, which quickly become cloudy. If you have herpes, treatment must be started before the herpetic vesicles open. Otherwise, not only the ointment for herpes, but also the best tablets for herpes will no longer allow any noticeable acceleration of healing.
What does herpes look like?
Important: the appearance of herpetic rashes is almost always preceded by the appearance of itching or burning in this area, or a feeling of tissue swelling. It is very important to teach the patient to “catch” these first symptoms, because if you start treatment for herpes already at this stage (during the prodromal period of the disease), the number and size of the herpetic blisters that subsequently form will be significantly smaller. And besides, the healing of erosions will occur much faster.
In rare cases, early initiation of therapy can even prevent the appearance of herpetic blisters (for example, when using combination drugs containing “5% acyclovir + 1% hydrocortisone”). Faster healing can also be achieved if treatment for herpes is started in the first 12 hours - from the moment the first herpetic blisters appear. You must understand that the later treatment begins, the lower its effectiveness will be. After opening the vesicles, treatment with antiviral ointments and tablets will no longer affect the healing rate, although it will still be indicated for patients with severe herpes.
Types of disease
Today, the herpes virus is divided into six subspecies:
- The first is localized on the lips, mouth area. The skin is affected above the waist.
- The second is located below the waist. This variety causes sexually transmitted infections.
- The third provokes the appearance of herpes zoster, Varicella.
- The fourth is the causative agent of Epstein-Barr (benign lymphoblastosis).
- The fifth is cytomegalovirus.
- The sixth, seventh and eighth are still little studied. There is a suspicion that these pathogens provoke various types of rashes and chronic fatigue.
Herpes virus (how does infection occur) –
Initially, children are born with immunity to the herpes virus - thanks to the antibodies that each child receives from the mother (even during pregnancy). However, gradually the number of antibodies decreases, and usually in the period from 6 months to 3 years maximum, the child develops a primary herpes infection. It usually occurs in the form of primary herpetic gingivostomatitis. And in the future, the herpes virus remains in the body for life, periodically exacerbating.
How is herpes transmitted?
The best remedy for herpes is certainly its prevention, but below we will also talk about special ointments and tablets. You should know that contact is the main route for transmission of herpes infection; Airborne transmission is more rare. Contact transmission means that infection with the herpes virus occurs:
- through kisses and touches,
- when you use personal items that have been in contact with a person with herpes or simply a “carrier”,
- for example, you dried yourself with someone else's towel,
- for example, you tasted your child's food with his spoon,
- for example, you eat with someone from the same plate, etc.
The most contagious are people who have clinical manifestations of herpes - we are talking about whole or newly opened herpetic vesicles. Keep in mind that the risk of infection does not disappear once crusts form, but only decreases slightly. Modern research shows that infection with herpes is possible even from a clinically completely healthy person.
Important: in approximately 10% of people, the herpes virus is constantly detected in the saliva (even against the background of the complete absence of any symptoms of herpes).
What causes relapses of herpes -
After the initial infection, the herpes virus penetrates the nerve cells, then it spreads along the nerve trunks, ultimately ending up in the nerve ganglia. There it remains for life - in the form of a “dormant infection”.
Under the influence of certain triggering factors, the virus is activated and again moves along the nerve trunks to the surfaces of the skin and/or mucous membranes - where it causes the formation of herpetic vesicles (vesicles). Relapses can occur 1 or 2 times a year, but sometimes much more often, which ultimately depends on the state of your immune system and nervous system.
Factors that cause recurrence of herpes –
- contact with a person with clinical manifestations of herpes,
- decreased immunity due to influenza or ARVI,
- immunodeficiency states,
- hypothermia, dehydration,
- physical fatigue and emotional stress,
- cuts and scratches on the skin, for example after shaving,
- after a visit to the dentist (due to the fact that when the mouth is opened wide for a long time, cracks form in the corners of the mouth),
- after invasive cosmetic procedures,
- during menstruation in women,
- prolonged exposure to the sun.
The role of immunity in the occurrence of HSV relapses
Cellular immunity plays an important role in the development of the disease. Exacerbations may be associated with a decrease in local immunity during operations, injuries, sexual contact with damage to the mucous membrane, the use of certain drugs, intensive facial treatment during cosmetic anti-aging procedures, sunburn, and so on. A significant role in the pathogenesis of herpes is played by deficiency of interferons, the level of which can be reduced by ten to twenty times compared to normal.iii. According to the results of studies, a decrease in the production of interferons was noted in the foci of herpetic lesions themselves. Allergy sufferers usually have a more severe infection.
Herpes symptoms –
A striking hallmark of herpes is the appearance of a group of blisters filled with liquid. However, before they erupt, there is always a period (lasting from several hours to 1 day) when there are no clinical manifestations yet, but the virus has already been activated. As a rule, during this period you may feel itching, burning or swelling of the tissue in the area where herpetic blisters should appear in the future (24stoma.ru). Further symptoms depend on the location of the rash...
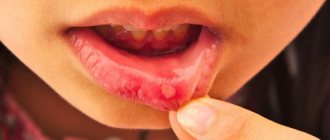
- Herpes on the lips (Fig. 7-9) - the red border of the lips and the skin around the mouth are the most common localization of herpes. Herpes of this localization is called “labial”. The blisters that appear on the skin and red border of the lips burst and dry out after 2-3 days, and the affected surface becomes covered with crusts that persist for a period of 7 to 10 days. Under no circumstances should the crusts be peeled off, because... Removing the crusts can also lead to a new outbreak of herpes.
Labial herpes: photoFor detailed information about the most effective treatment regimens for herpes of this localization, read the article: “How to quickly get rid of herpes on the lip”
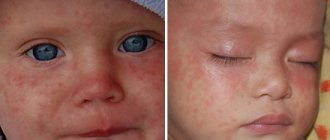
- Herpes on the skin of the face – foci of herpes can appear on any part of the facial skin, which is usually associated with a violation of the integrity of the skin (scratches, cuts, abrasions). Typical localization is herpes on the cheeks and nose, earlobes, chin, and forehead. The skin around the eyes can also be affected, but we have identified this type of lesion in a separate column.
Depending on the extent of skin damage and the severity of clinical manifestations, either a skin cream with an antiviral effect or a cream in combination with tableted antiviral drugs may be prescribed. You can see a detailed review of treatment drugs at the end of the article. - Herpes in the mouth (Fig. 10-11) - herpes of the tongue, gums and other areas of the oral mucosa most often occurs in children, rarely in adults. This disease is called herpetic stomatitis. After the bubbles on the mucous membrane burst, bright red erosions form in their place, which are quickly covered with a whitish-yellow fibrinous coating. Along the perimeter of the lesions there is always a bright red rim of inflamed mucous membrane.
In children, herpetic stomatitis is often accompanied by gingivitis. In this case (in addition to multiple blisters and erosions in some area of the oral mucosa), you can see bright red inflamed gums.
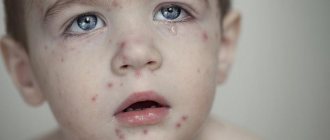
- Ophthalmoherpes
(Fig. 12-13) – the herpes simplex virus can spread to one or both eyes. Most often, this happens when you introduce the virus with unwashed hands that have recently touched areas of the skin affected by herpes. You can spread the virus simply by using a regular face towel. Most often, the virus infects the upper layer of the cornea, causing herpetic keratitis. If rashes may appear on the skin of the eyelids, this option is called “herpetic blepharitis.”Symptoms: pain, blurred vision, sensitivity to light in one eye (if one eye is affected), feeling of “sand in the eyes.” Eye herpes is very dangerous, and untimely or improper treatment can lead not only to dryness of the cornea and the appearance of scars on it, but also to deterioration of vision, constant pain, and even blindness and loss of the eye.
General symptoms of herpes - primary herpes infection can occur with symptoms similar to influenza or ARVI (fever, muscle pain and even enlarged submandibular lymph nodes). But such acute symptoms are observed in only 10% of all patients. With repeated outbreaks, the general condition of the body is usually not disturbed.
Severe consequences of HSV infection
Along with common manifestations of infection on the lips, mouth, nose, face, buttocks and genitals, herpes can affect internal organs, meninges, nerves, causing such severe conditions as meningitis, encephalitis, neuritis, meningoencephaloradiculitis, cause bronchitis, pneumonia , damage to lymphocompetent organs: liver, spleen, pancreas and even sepsis. Some of the criteria for infectious encephalitis - inflammation of the brain - are disturbances in the mental or mental status of the patient, fever, convulsions, neurological symptoms, and changes in the ECG.
How to treat herpes in adults (medicines) –
Very often, patients ask questions about how to cure herpes forever. Unfortunately, at the moment medicine does not have the ability to achieve complete removal of the herpes virus from the body. However, modern antiviral agents (ointments and tablets) can effectively block the replication of the virus, especially when it comes to the herpes simplex virus (types HSV-1 and HSV-2). It can be much more difficult to cure herpes on the body, which is referred to as “shingles” or “herpes zoster”.
Modern antiviral tablets and ointments for herpes can significantly reduce the severity of herpes infection, speed up healing, and also reduce the frequency of relapses. There is also a domestic vaccine against the herpes simplex virus (types HSV-1 and HSV-2) called “Vitagerpavak”, which can reduce the frequency of repeated outbreaks of herpes infection by several times. Below we will tell you about the best remedy for herpes - both among means for external use and among tablet preparations.
But in order for herpes treatment to be as effective as possible, you must strictly follow the following rules:
- Herpes therapy will show good effectiveness if it is started no later than 12 hours from the moment the first herpetic rash appears. Keep in mind that the later treatment is started, the less effective even the best herpes medications will be.
- The maximum effectiveness will be shown by therapy that is started in the prodromal period (i.e., when the actual herpetic blisters have not yet appeared, but the patient already feels itching, burning or swelling of the tissue in this area). If treatment begins during this period, then the number and size of herpetic blisters formed in the future will be significantly smaller, and in this case, complete healing can be achieved in just 4-5 days.
- Remember that if you start treatment later than 48 hours , or after the herpetic blisters have opened, such therapy will not noticeably affect the speed of recovery (healing of lesions). However, in patients with severe and frequent relapses, such therapy can avoid complications.
Systemic disease
Recently, there has been an increase in herpes-associated diseases. It is worth noting that this is not only a skin disease - a herpes infection is a systemic disease of the body. Radiculitis associated with herpetic lesions of the nervous structures of the lumbar and sacral spine can worsen after colds and/or hypothermia. The pain can radiate to the legs, buttocks, and perineum. Viral etiology is confirmed by the fact that in addition to severe, long-term pain in the lumbar region, sacrum, and buttocks, patients develop characteristic herpetic rashes. HSV can be one of the causes of facial paralysis and inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. According to experts, hypothermia activates the virus, which is dormant in the ganglia of the trigeminal nerve.iv
Choosing an ointment for herpes -
If you have herpes, treatment in adults and children is most often carried out with one of the external agents containing 5% Acyclovir (an antiviral agent effective against the herpes virus). Preparations based on acyclovir: Acyclovir cream 5% (Russia), Acyclovir ointment 5% (Russia), Acyclovir-Hexal cream (Germany), Acyclovir-Sandoz cream (Switzerland), as well as original drugs with acyclovir - a line of branded products Zovirax (UK).
Zovirax cream: the original drug of acyclovir
Herpes cream or ointment with acyclovir should be applied to the lesion and the skin around it at least 5 times a day (but better every 2 hours while you are awake). The duration of therapy is usually 5 days, but in case of severe herpetic lesions, the duration of use can be increased to 7-10 days. It should be noted that the cream form is more preferable to the ointment, because from the ointment substance, the active substances penetrate the skin much worse.
It is worth paying attention to the composition, for example, the effective concentration of acyclovir is exactly 5% (although in pharmacies you can also find products with a 3% concentration). In addition, the composition should preferably contain propylene glycol and/or cetomacrogol, which increase the penetration of acyclovir molecules through the surface layers of the skin. This is important because Acyclovir itself penetrates quite poorly through the epidermis of the skin and the resulting crusts.
For women, it may be important to be able to apply cosmetics on top of the absorbed cream. In this case, you should choose a cream that contains dimethicone (silicone). Today, dimethicone in combination with propylene glycol and cetomacrogol is found in the following products - Zovirax cream, Zovirax Active-Duo cream, Acyclovir-Sandoz cream.
The best remedy for herpes with acyclovir is
Today, the best drug for external use against herpes is Zovirax Duo-Active cream, which contains a combination of 5% acyclovir and 1% hydrocortisone. Acyclovir blocks the multiplication of the virus, and hydrocortisone reduces inflammation and swelling. Moreover, if the use of the cream begins even before the appearance of herpetic blisters, then hydrocortisone sometimes makes it possible to prevent their formation altogether. But if bubbles do form, their number and size will be smaller, which in itself will significantly speed up healing.
Disadvantages of acyclovir-based drugs - acyclovir is an outdated drug, but in principle it works well for most patients (with some exceptions). For example, in patients with good immunity, resistance of the herpes virus to acyclovir occurs on average in only 3% of cases, which is quite small. However, the problem is in patients with weakened immune systems + frequent courses of acyclovir use in the past - in such groups of patients, resistance to acyclovir can be observed in 10 to 27% of cases.
In addition, acyclovir molecules have a very low tropism for the herpes virus, which means that acyclovir usually simply does not find a certain percentage of viral particles in cells (for example, drugs based on penciclovir / famciclovir have a much higher tropism in the virus). In addition, acyclovir molecules tend to penetrate poorly through the skin, as well as through the resulting crusts (to the site of virus reproduction). In order to somehow reduce this problem, some manufacturers add propylene glycol and cetomacrogol to external products containing acyclovir.
Alternative external remedies for herpes -
First of all, this is the Fenistil-Pentivir cream, which contains the antiviral component Penciclovir. Compared to acyclovir, penciclovir is several times more effective (including due to the significantly greater tropism of penciclovir for the herpes virus, and due to better penetration into cells affected by the virus). It should also be noted that the resistance of the herpes virus to penciclovir is extremely low - it is no more than 0.2%.
The drug is applied to the lesion every 2 hours (8 times a day), but the course of use is usually only 4 days. Such a short course is due to the fact that after the last application of the cream, the clinically active concentration of penciclovir will remain in the cells for about 2 more days (i.e., the therapeutic effect after a 4-day course will last about 6 days). Clinical studies have also found that repeated outbreaks of herpes occur less frequently when using Fenistil-pencivir than when using other drugs. However, in recent months this drug has disappeared from Russian pharmacies, most likely due to the re-registration procedure.
We have already said above that patients with weakened immune systems often develop resistance of the herpes virus to acyclovir. What should such patients do? International recommendations in this case speak of the need to use courses of famciclovir in tablets - these are drugs such as Favirox or Famvir. Tablet preparations based on valacyclovir (if resistance to acyclovir is suspected) does not make sense to use, because valacyclovir is a precursor to acyclovir. The latter means that if there is resistance to acyclovir, there will be resistance to valacyclovir.
Cream Devirs for herpes –
Maybe there are some other topical products that would be effective against herpes and do not contain acyclovir? In pharmacies you can find such a prescription drug - Devirs cream (manufactured by Vertex, Russia), containing the antiviral component ribavirin. According to the instructions, this drug can be used in patients over 18 years of age - for genital herpes, for the treatment of labial herpes, herpes localized on the face and body.
Unfortunately, there are very few clinical studies on the effectiveness of local ribavirin-based products, and all of them, in our opinion, have a rather weak degree of evidence. Getting acquainted with the studies, we noticed that this drug was very rarely used in studies in the form of monotherapy (usually it was combined with either oral ribavirin or oral acyclovir), which already indicates the rather weak effectiveness of the cream. Therefore, our editors cannot recommend this drug for widespread use, especially for the treatment of herpes lips and small lesions on the face. But the drug may well be used as part of complex therapy, for example, for genital herpes.
Choosing tablets for herpes -
Herpes treatment in adults: drugs in tablets
- Acyclovir,
- Valaciclovir,
- Famciclovir.
Below we will compare the effectiveness of these antiviral tablets against the herpes simplex virus. It should be noted that Acyclovir tablets are approved for use from 0 years of age, and the drugs “Valacyclovir” and “Famciclovir” - only from 12 years of age. All these drugs are available only with a doctor's prescription.
Acyclovir in tablets of 200 and 400 mg –
Tablet acyclovir has the same disadvantages as creams: low tropism for the virus (i.e., acyclovir molecules do not find viral particles well); in patients with poor immunity + frequent courses of acyclovir use in the past - in 10-27% of cases the herpes virus may be resistant to acyclovir; plus low oral bioavailability. Pros: no age-related contraindications, affordable price, fairly few side effects.
We recommend choosing the original drug with acyclovir - Zovirax 200 mg tablets (instructions for use, see PDF). Moreover, its cost is not much higher than that of Russian generics.
Examples of drugs with acyclovir -
Acyclovir tablets certainly work, especially when it comes to patients with good immunity and rare relapses of herpes. If you have a weakened immune system, if you have taken acyclovir too often in the past, if you decide to start taking the drug more than 24-48 hours after the onset of herpetic rashes, acyclovir will not be particularly effective. In this case, it is better for you to immediately start taking the drug Famciclovir, which works better even at later dates of initiation of therapy, as well as in patients with immunodeficiency conditions.
The regimen of use - if you look at the official instructions, the standard regimen for adults and children over 2 years old - is to take acyclovir 200 mg 5 times a day (for 5 days). A single dosage of 400 mg is recommended in the official instructions - either only for severe herpes infection, or in patients with weakened immune systems. However, most clinical studies (source) show that a dosage of 200 mg has virtually no effect on either the duration of symptoms or the healing time of herpes.
Studies have shown that only 400 mg (respectively, 5 times a day, for 5 days) is an effective single dose. In children under 2 years of age, the dosage is reduced by exactly 2 times - from the adult dosage. In case of severe herpes infection, taking the drug can be extended to 7-10 days. By the way, abroad, at the moment, acyclovir is practically not used for chronic recurrent herpes, giving preference to valacyclovir and famciclovir.
Valacyclovir (Valtrex) tablets –
We have already said above that tableted acyclovir has poor bioavailability, i.e. only about 10-20% of its amount is absorbed in the intestine, which makes it difficult to achieve high concentrations of acyclovir in tissues. This problem is solved by Valacyclovir, which has a bioavailability of 50%. Valaciclovir is a precursor to acyclovir (i.e., it is converted to acyclovir once it enters the bloodstream). Taking tablets with valacyclovir allows you to create a concentration of acyclovir in tissues that can be achieved with traditional acyclovir - only through intravenous infusions of the latter.
The drug Valtrex is the original drug of Valaciclovir (we recommend this drug), but there are also a large number of cheaper generics. The cost of the original drug “Valtrex” (UK) is from 1350 rubles for 10 tablets. 500 mg each. There is a good Bulgarian generic “Valvir” - it costs from 750 rubles for a package of 10 tablets. 500 mg each. The cost of the Russian “Valacyclovir-Akos” will be from 450 rubles (for a package of 10 tablets of 500 mg).
Regimen: There is a short 1-day treatment regimen. Clinical studies have shown that taking high dosages of the drug for 1 day was the most effective for the treatment of herpes on the lips and facial skin, as well as herpetic stomatitis. In this case, the dosage regimen is 2000 mg 2 times a day, with an interval of 12 hours (1 day in total). But it should be noted that such a short regimen will be effective only if treatment begins no later than 12 hours from the moment the herpetic eruptions appear, and also in patients with satisfactory or good immunity.
If more than 12 hours have passed since the appearance of the rash, and also if you have a weakened immune system, it is optimal to use the standard treatment regimen of 500 mg 2 times a day for 3-5 days (for severe herpes infection - up to 10 days). When choosing a drug, keep in mind that if your herpes virus is resistant to acyclovir, taking valacyclovir will also be ineffective.
Famciclovir tablets (Favirox, Famvir) –
Famciclovir products are the most modern and effective tablets for herpes. Above we told you about the cream “Fenistil-pencivir” (based on penciclovir), which is used on the skin of the face and the red border of the lips. So, drugs with famciclovir are tablet analogues of penciclovir. Most often in pharmacies you can find drugs with famciclovir - under the trade names “Favirox” or “Famvir”.
The advantage of famciclovir drugs like Favirox is their rapid antiviral effect due to maximum bioavailability (for famciclovir it is about 74%, for example, for valacyclovir it is only 54%, and for acyclovir only 10-20%). Therefore, a package of three 500 mg tablets is enough for a short 1-day course of therapy to relieve the manifestations of herpes on the lip. Read more about this application scheme below.
→ Favirox instructions for use (view PDF)
Regimen for using famciclovir - there is a short 1-day treatment regimen: either take 1500 mg once, or 750 mg 2 times a day (with a 12-hour interval between doses) - our experience suggests that the second option is still better. This 1-day regimen is effective only if you start taking the drug before 12 hours from the moment the herpetic rash appears, and also if the patient’s immunity is normal. In case of weakened immunity, and/or if treatment is started later than 12 hours from the moment of the appearance of herpetic eruptions, the standard dosage regimen should be used.
The standard regimen according to the instructions is 250 mg 2 times a day for 5 days (however, in severe cases of herpes infection, dosage can be extended to 7-10 days). Here I would like to add that numerous clinical studies show the weak effectiveness of this standard regimen - especially in patients with poor immune system conditions. Studies have shown that the effectiveness of therapy increases significantly when famciclovir is prescribed in higher dosages. In patients with good immunity, a more effective regimen will be 500 mg 2 times a day (for 5 days). In immunocompromised patients - 500 mg 3 times a day (for 7 days).
Important: once again we draw your attention to the fact that short 1-day treatment regimens for herpes in adults (herpes on the lips and skin around the mouth, on the face) work well only if the following conditions are met. Firstly, only if you start taking medications no later than 12 hours from the moment the herpetic rash appears. Secondly, if you have a satisfactory or good immune system. If treatment is started later than 12 hours from the onset of the rash, as well as in patients with weakened immune systems, short 1-day courses of therapy are usually ineffective. Here we already need a standard regimen of administration.
Important : if more than 12 hours have passed since the first rash appeared (and even more so if more than 24 or 48 hours), it is better to opt for famciclovir, because the latter works better at later dates of initiation of therapy for herpetic infection.
Treatment with immunomodulators, prevention of herpes –
If you have a high frequency of relapses of herpes, or even rare, but severe outbreaks, it is very important for you to take up the prevention of outbreaks of herpes. And the point here is not only that the severe course of a herpetic infection and/or its frequent relapses themselves indicate problems with your immunity. The fact is that the herpes virus has an immunosuppressive effect on the entire immune system - both cellular and humoral immunity.
This means that the immune system under the influence of the herpes virus will continue to weaken, leading to a further increase in the frequency of relapses and the severity of outbreaks. At the moment, there are the following directions for preventing outbreaks of the herpes simplex virus (HSV-1, HSV-2), but you should choose one or another method only after consulting a doctor. All patients with a frequency of outbreaks of more than 6 during the year must be tested for the number of specific IgG and IgM antibodies to the herpes simplex virus, as well as consult an immunologist and have an immunogram (which evaluates the subpopulation composition of cells, NK activity, and also the levels of α- and γ-interferons).
Prevention methods:
- Prolonged use of antiviral drugs - in this case, Acyclovir tablets are prescribed 400 mg 2 times a day (but we do not recommend this option, since the use of acyclovir in patients with weakened immune systems very often leads to the development of resistance of the herpes virus to acyclovir ).
A preventive course of drugs from the list below should last about 9-12 months, and only on the recommendation of a doctor. The drug "Valacyclovir" - 500 mg 1 time per day (but for patients with a relapse rate of more than 9 times a year - 500 mg 2 times a day). The drug "Famciclovir" - 250 mg 2 times a day. Studies show that the preventive effect is more pronounced with Valacyclovir, but cross-resistance must also be taken into account (since if the herpes virus is resistant to acyclovir, it will also be resistant to valacyclovir). - Immunocorrective therapy – the immune system can be improved with special drugs “immunomodulators”. There are several drugs that have proven effective in preventing relapses of herpes, and for which this indication for use is directly stated in the instructions. The use of immunostimulating drugs allows - 1) to reduce the frequency of relapses by about 40-50%, 2) to reduce the duration of each outbreak, for example, complete healing will occur faster by about 2-3 days than usual.
Good drugs, the instructions for which specifically indicate “as part of the complex therapy of herpetic infection” are over-the-counter tablet drugs “Cycloferon”, “Polyoxidonium”, “Licopid” (you can look at the official instructions for treatment regimens). The first two drugs also have a release form as an injection solution, but this is only by prescription. By the way, Cycloferon, in addition to stimulating the immune system, also has its own antiviral activity against the herpes simplex virus (24stoma).Accordingly, if the patient has active manifestations of herpes, and the immunomodulator is used as part of complex therapy for herpes infection (together with antiviral drugs), Cycloferon will be the optimal choice. And, by the way, it can be used from 4 years old. If you use an immunomodulator between herpes outbreaks, i.e. in the absence of clinical manifestations, it is better to choose “Likopid” or “Polyoxidonium” (they can be used from 3 years of age).
Likopid" can be in tablets of 1 and 10 mg (tablets of 10 mg can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor, and tablets of 1 mg are available over the counter). Recommended use of Likopid 1 mg for adults – 2 tablets 3 times a day (orally or sublingually), course of treatment is 10 days. Scheme of use of Likopid 10 mg tablet for adults - 1 tablet 1 time per day, course of treatment for 6 days. For children over 3 years old, Likopid 1 mg tablets can be prescribed, and the regimen is as follows - 1 tablet 3 times a day (orally or sublingually), for a total of 10 days.
Important: taking immunomodulators is indicated not only for the prevention of relapses of herpes infection - in patients who are often and/or seriously ill with herpes. Immunomodulators should be used as part of the basic therapy of herpes infections (in addition to therapy with antiviral drugs) in patients with weakened immune systems.
Moreover, if the immunomodulator is used during an exacerbation of herpes, then it is best to use Cycloferon, because it also has a direct antiviral effect on the herpes simplex virus. If we are talking about taking immunomodulators in the period between outbreaks, then you can use Lykopid or Polyoxidonium. In the next section we will talk about the Vitagerpavac vaccine, which is nothing more than a real herpes vaccine.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of infections caused by herpes viruses is based on laboratory tests. They use polymerase chain reaction methods performed in real time.
PCR is the most accurate way to detect all types of herpes. It is also one of the fastest in production and allows identifying the pathogen at an early stage of the disease. To obtain the result, a small amount of the desired material is sufficient.
A special feature of the PRC method is the copying of a DNA region specific to the pathogen. It is reproduced a number of times that enlarges the sample to a size acceptable for diagnosis.
Any biological material is suitable as a sample:
- deoxygenated blood;
- seminal fluid;
- vaginal discharge;
- saliva;
- cerebrospinal fluid;
- biopsy and others.
Other methods for diagnosing herpes include molecular biological studies of skin biopsies for the diagnosis of Kaposi's Sarcoma. Hair follicles are examined to confirm or rule out HHV-6. The digital droplet PCR method helps to identify chromosomally integrated and inherited forms of type 6 virus. For tissue-invasive CMV, preference is given to histological and immunohistochemical studies.
When is a test for herpes viruses prescribed?
- In the presence of symptoms indicating diseases caused by herpes viruses.
- To differentiate herpesvirus and other infections.
- When planning pregnancy and in the presence of pregnancy pathology.
- For a comprehensive examination of HIV patients and people with immunodeficiency.
- Before immunosuppressive therapy.
- To monitor the effectiveness of therapeutic measures.
It is necessary to undergo a herpes test for patients with hematological malignancies and lymphoproliferative diseases. A study before and after transplantation is indicated.