Chickenpox in children is the most common disease after ARVI that parents have to deal with. The disease cannot be called dangerous, since most often it occurs in a mild form, and after recovery a stable immunity is formed. Diagnosing the pathology is not difficult, since the signs are clearly expressed.
Chickenpox - definition
Chickenpox (also known as varicella) is an infectious disease of Chickenpox (Varicella).
It is caused by the varicella zoster virus. By the way, a close relative of the herpes familiar to many. All herpes are contagious, but varicella is the coolest. Chickenpox spreads through airborne droplets, and does so very actively. To catch an infection, sometimes it’s enough to look into the patient’s room for a second.
It always seemed to people that the disease was literally carried through the air, by the wind. Hence the first part of the name - wind. It was named smallpox because of the numerous rashes in the form of fluid-filled vesicles (papules), similar to those that form in smallpox.
Fortunately, chickenpox is not as deadly.
Chickenpox symptoms
Chickenpox usually lasts about ten days. The main symptom of chickenpox is a typical rash. One to two days before the rash appears, the following nonspecific symptoms may occur:
- Fever
- Decreased appetite
- Headache
- Fatigue and general malaise
The chickenpox rash goes through three stages of development:
- Pink or red spots and bumps (papules), which appear in spurts, with each new wave of fever, 2-6 shocks per day, for 3-6 days.
- After a few hours, these papules turn into blisters filled with clear liquid (vesicles), they last for a day, after which they burst and the liquid flows out
- After the blisters burst, after a few hours weeping appears - in their place crusts form, which last from several days to several weeks until new tender skin forms under them, after which they fall off.
Causes and features of pathogen transmission
The disease spreads quickly and easily indoors, since the causative agent, the herpes virus, can be transmitted through coughing, sneezing, i.e. by air. A greater number of chickenpox cases occur in preschool children. Children staying in the same group room of a kindergarten get sick faster, although the virus is able to penetrate with air flow into neighboring rooms. Less commonly, the pathogen is transmitted through toys or third parties, since it is unstable in the external environment.
The peak of the disease occurs in spring/autumn, together with the peak of colds. The pathogen is transmitted by the bloodstream to the epithelial layers of the skin, where it begins to actively multiply. There are subjective signs of the onset of the disease: irritability, tearfulness of the child, the appearance of a common rash similar to hives. Due to the mobility of the virus in the blood, internal organs may be affected. The mucous membrane is an excellent “soil” for the virus; as a result, small hemorrhages form at the site of the papules. Immunity after the disease is stable (except for early infection by the virus).
Adults who did not have chickenpox as children may not get sick at all if they have a strong immune system. But when infected, adults become seriously ill, with a high rise in body temperature, and subsequently scars and visible dents form in place of the papules.
Features of the pathogen:
- papular fluid contains DNA;
- the virus is deactivated at a temperature of 45 to 50 degrees. It is enough to soak the patient’s clothes in hot water for half an hour to destroy the virus. Disinfectants should not be used when processing children's clothing; they can cause increased itching and rashes;
- the virus is not destroyed by freezing; after defrosting, the pathogen is still active. But it does not tolerate sunlight well, so when disinfecting a room, you can use ultraviolet lamps;
- the pathogen can be transmitted through the placenta from a sick pregnant woman to the fetus, as a result of which there may be damage to the fetus that does not threaten its life;
- in exceptional cases, chickenpox is contracted twice, if the first time occurred before the age of one year, when the child’s own immunity is not yet “working.”
Symptoms of the disease
On average, up to two weeks after the virus enters the body, the child feels normal. Then the body temperature rises sharply and quickly, and at the same time rashes appear on the head under the hair, cheeks, near the lips, and on the mucous membranes of the mouth. Due to the rash, the child becomes restless, the unpleasant tingling sensations in the papules a little later turn into severe itching, and the baby’s condition worsens.
Development of chickenpox
Initially, only a rash is visible on the skin, similar in appearance to miliaria. Then characteristic small spots become visible, in place of which bubbles with transparent contents - vesicles - form. There is always a small border around the bubble - a hyperemic halo. After a few hours, the liquid in the bubble becomes cloudy, and even later the bubble bursts and the liquid begins to flow out of it. If the vesicle is not touched, then after two or three days it begins to dry out. A dense crust forms from the center to the edges of the bubble, and after the crust has completely dried, the skin remains pink, but without scars, smooth to the touch. If a child actively scratches the rash, indentations may form, as after a BCG vaccination.
The bubbles do not appear all at once, but several days apart, so quarantine for chickenpox lasts up to three weeks. During this time, rashes in different stages of development may be visible on the skin - from spots to crusts. To treat chickenpox, doctors still recommend using a solution of brilliant green, which disinfects and dries watery blisters. Yes, it is ugly, the child will walk around with spots, but it is effective in preventing suppuration from scratching and the rapid healing of wounds.
If the course of the disease is severe, with a large amount of rash, the child is prescribed medications that lower the temperature and antihistamines. Acyclovir is effective only if used in a timely manner; if the disease is protracted, it should not be used. Sometimes doctors prescribe immunostimulants, for example, cycloferon liniment - it successfully replaces brilliant green. The drug facilitates the course of the disease and prevents the development of purulent infection when the blisters are scratched.
Chickenpox: course of the disease
Chickenpox is characterized by stages, which allows you to assess the course of the disease and navigate the quarantine period.
The incubation period of chickenpox is the time that elapses between the virus entering the body and the appearance of the first symptoms of the disease. It usually lasts 2 weeks, but can range from 10 to 21 days. The incubation period for chickenpox in adults and children is usually the same length.
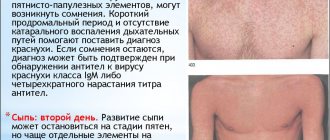
The prodromal period is the initial stage of chickenpox. It is short (1-2 days), and may be absent altogether. Its characteristic symptoms are poor health, fever, muscle and headaches, and catarrhal phenomena in the nasopharynx. The first symptoms of chickenpox in adults are usually more pronounced than in children.
The rash period lasts 3-10 days. Elements of the rash appear in waves, this is accompanied by an increase in body temperature and poor health. 1-2 days pass between “waves” of rashes. There are usually 2-5 of these “waves”, then new elements stop appearing and gradually heal. The next stage begins - healing.
The recovery period begins from the moment when new elements cease to form, and all that appear become covered with crusts.
The period of convalescence (recovery) after chickenpox can last up to 1 year. The varicella-zoster virus causes a serious blow to the human immune system, and the process of its recovery is usually quite long. During this period, the body's resistance to other viral infections, such as ARVI, decreases.
How many days chickenpox lasts depends on the individual characteristics of the disease, the patient’s age, and the state of his immunity. On average, from the moment the first signs of chickenpox appear in a child until the elements of the rash completely heal, 3 weeks pass; in adults it may be longer.
Prevention
{banner_banstat9}
It is almost impossible for a child to avoid infection with chickenpox, since he is constantly in contact with other people. The main method of prevention is strengthening the body’s protective functions and observing hygiene rules.
Important! Vaccination against chickenpox is not included in the list of mandatory vaccines for children; parents can vaccinate with Okavax and Varilrix for a fee - the average cost of the procedure is 2.5–4.5 thousand rubles.
Types of chickenpox (classification of chickenpox).
Chicken pox occurs in typical and atypical forms and in terms of severity is mild, moderate and severe. Chickenpox is also classified according to ICD-10 (with meningitis, encephalitis, pneumonia).
Atypical forms of chickenpox are divided into:
- Hemorrhagic form - a common consequence of this form is bleeding, and this form occurs in people with thrombocytopenia.
- Pustular form - develops when a bacterial agent is attached.
- Gangrenous form - can lead to the development of sepsis and occurs most often in patients with weakened immunity.
- The generalized (visceral) form of chickenpox is characterized by development in patients with immunodeficiency. It is very difficult, the symptoms are more pronounced and often ends in death for the sick person.
- The rudimentary form is found in children who received immunoglobulin during the incubation period. It flows quite easily.
The severity of chickenpox is directly determined by the degree of intoxication syndrome and its criteria, as well as the presence of specific vesicular rashes on the skin and mucous membranes. It should be noted that there are also so-called abortive (very mild) cases of the disease, which occur without the appearance of fever and are characterized by the appearance of single rashes on the skin of the abdomen and back. Such chickenpox is detected in kindergarten during examinations during outbreaks.
To the question “how long does chickenpox last?” It is difficult to answer unequivocally, since the duration of the disease directly depends on the form and course of chickenpox. On average, in the classical (typical) course, the duration of the disease is from 12 to 16 days.
Diagnosis of chickenpox
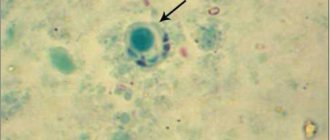
The basis for detecting herpes is a virological study - examination of media to detect the pathogen. In case of chickenpox, for diagnosis, liquid from vesicles is used, in which, when stained, accumulations of the pathogen, the Argan corpuscle, are isolated.
Chickenpox is usually distinguished from insect bites. The main difference is the lack of development of elements and bedding, as well as normal body temperature.
Also, the disease should be differentiated from:
- streptoderma - occurs without fever, the rash is different - cloudy, purulent contents, after involution leaving a yellow crust, in its place a red spot forms. The rash is located mainly behind the ears and on the extremities, never on the scalp (a hallmark of chickenpox).
- herpes zoster - the blisters are located strictly along the nerve trunk; they practically never occur on the legs and arms.
- vesicular rickettsiosis - a small scab forms at the site of the tick bite, followed by the formation of an ulcer (a scar forms in its place after healing). Enlargement of regional lymph nodes is typical.
When to see a doctor?
If you suspect that you or your child has chickenpox, consult your doctor. The doctor will be able to make a diagnosis simply by examining you, studying the elements of the rash and accompanying symptoms. Your doctor may also prescribe medications to reduce the severity of chickenpox and reduce the risk of complications, if necessary. Call the pediatrician in advance and warn that you suspect chickenpox - the doctor will see you in a separate room, without waiting in line, to avoid the risk of infecting other patients.
Also, be sure to tell your doctor if you have any of these complications:
- The rash has spread to one or both eyes.
- The skin around some parts of the rash becomes very red, hot, or painful, indicating a secondary bacterial skin infection.
- The rash is accompanied by dizziness, disorientation, rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, tremors (shaking hands), loss of muscle coordination, increasing cough, vomiting, difficulty bending the head forward, or a fever above 39.4 C.
- a history of any immunodeficiency, or age younger than 6 months.
How to treat chickenpox
Chickenpox is a virus. And, like most viruses, there is no specific treatment for it. Helping a sick person comes down to alleviating the main symptoms.
Fever and headache
Remember: paracetamol and nothing else! Popular painkillers and antipyretics based on ibuprofen should not be taken. The use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and the risk of serious skin and soft tissue complications in patients with chickenpox or herpes zoster have been reported to indicate that ibuprofen for chickenpox increases the incidence of complications such as skin infections.
Aspirin is completely contraindicated. In conjunction with the varicella-zoster virus, it has a powerful toxic effect on the liver and brain (the so-called Reye's syndrome).
Itching
To relieve itching, your doctor may recommend an antihistamine. Considering the insidiousness of the virus, under no circumstances prescribe it to yourself!
You can also treat your skin with calamine lotion according to the instructions.
Scratches and wounds
To avoid scratching the skin and causing infection in the wounds:
- Trim your nails as short as possible. If your baby is sick, put on thin protective gloves.
- Wear clean, loose clothing.
- Change your underwear and bed linen more often.
It is not necessary to smear the rashes with brilliant green: brilliant green will not speed up the maturation of the blisters. The color only helps to mark pimples in order to track the moment when new ones stop appearing.
Soreness in the mouth
If there are rashes on the oral mucosa, doctors recommend eating sugar-free popsicles. The cold will help relieve discomfort. Also try not to eat salty and spicy foods.
Care and treatment at home
Children with chickenpox can usually be cared for and treated at home. Because chickenpox is a virus, it cannot be treated with antibiotics. Treatment is to control the itching of the rash and other symptoms associated with viral illnesses. There are many medications and creams that can relieve itchy skin.
It is important to ensure that your child drinks enough fluids and does not become dehydrated. Give your child liquids in various forms: clean water, jellies, sorbets, soups and other liquids.
Children with chickenpox may have a fever and feel tired and irritable. Important to know: Aspirin is contraindicated for a child with chickenpox. Children with very severe infections or serious illnesses may receive additional antiviral medications as prescribed by their doctor.
What complications can occur with chickenpox?
The disease is usually mild, but complications may occur, including bacterial infections (eg, bacterial skin lesions, pneumonia) and neurological infections (eg, encephalitis, meningitis, myelitis), which can be fatal.
Secondary bacterial skin infections, which are caused by streptococcus or staphylococcus, are the most common cause of hospitalization and outpatient medical visits. Secondary infection with invasive group A streptococci can cause abscesses and cellulitis.
Pneumonia after chickenpox is usually viral, but can also be bacterial. Secondary bacterial pneumonia is more common in children under 1 year of age. It is characterized by an increase in temperature up to 40⁰C, an increase in pallor and cyanosis of the skin, the appearance of a substernal dry cough and shortness of breath. Patients can take a forced position in bed.
Damage to the central nervous system in chickenpox ranges from aseptic meningitis to encephalitis. Cerebellar involvement followed by cerebellar ataxia is the most common presentation of central nervous system disorders but usually has a positive outcome.
Encephalitis is one of the most dangerous complications of chickenpox (10-20% of cases are fatal). This complication manifests itself as headache, nausea, vomiting, convulsions and often leads to coma. Diffuse brain involvement is more common in adults than in children. Chickenpox meningitis may occur together with encephalitis or independently.
Rare complications of chickenpox include Guillain-Barré syndrome, thrombocytopenia, hemorrhagic and bullous chickenpox, glomerulonephritis, myocarditis, arthritis, orchitis, uveitis, iritis and hepatitis.
Once infected, the virus remains hidden in nerve cells and can be reactivated, causing a secondary infection, herpes zoster. It usually occurs in adults over the age of 50 or with a weakened immune system and is associated with a painful rash that can cause permanent nerve damage.
Possible consequences and complications
{banner_banstat8}
Negative consequences of chickenpox in children are rarely diagnosed; most often dermatological purulent complications occur - abscess, phlegmon, boils, which leave scars. If the disease is severe, the virus affects internal organs and dangerous concomitant diseases develop.
Possible consequences of chickenpox:
- Encephalitis - pathology manifests itself 7–12 days after the onset of the disease, characterized by frequent convulsions, severe headache, and impaired consciousness. In rare cases, idiocy develops.
- Myocarditis - the virus provokes the development of an inflammatory process in the heart muscle, shortness of breath occurs, the pulse rate is disturbed, and the child may complain of chest pain.
- Pneumonia – occurs in infants with neonatal chickenpox; the condition is dangerous and can be fatal.
- Nephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys that develops 10 days after the first signs of pathology appear; the disease goes away on its own and no specific treatment is required.
Since the virus can penetrate all tissues and mucous membranes, the consequences of chickenpox can be blurred vision, damage to the mucous membranes of the eyes, hepatitis, problems with the pancreas and spleen.
Chickenpox and pregnancy
A special type of complications from chickenpox can occur in pregnant women. Chickenpox in early pregnancy can lead to a variety of problems in the newborn, including low birth weight and birth defects such as limb abnormalities. A particularly great threat to the child occurs when the mother gets chickenpox a week before giving birth. In this situation, there is a high risk of infection that is life-threatening to the newborn (congenital chickenpox syndrome).
If you are pregnant and have been in contact with someone who has chickenpox, be sure to talk to your doctor about the risks to you and your unborn baby.
Is it worth getting vaccinated?
Doctors began vaccinating children against chickenpox relatively recently. The composition of the vaccine is represented by live but weakened pathogens. The first vaccination is usually given at 12–14 months. The chickenpox vaccine is re-administered after 3 to 5 years. Adolescents and adults who do not have natural immunity are vaccinated twice, with an interval of 1 month or more between injections.
Young children tolerate chickenpox vaccinations well, and pediatricians do not record any adverse reactions. However, if the child is part of a group of frequently ill children, it is necessary to consult with the local pediatrician about the advisability of vaccination. A weakened body may react to vaccination with unpredictable phenomena.
Is it possible to wash yourself if you have chickenpox?
“Is it possible to swim if you have chickenpox?” is an age-old question parents ask their pediatrician. The answer depends on the patient’s well-being. In general, bathing with chickenpox is not only safe, but even beneficial - keeping the skin clean reduces the risk of secondary infection and promotes faster healing. However, at high body temperatures, it is better to refrain from water treatments and limit yourself to treating the rash elements with antiseptics.
If you have chickenpox, you can bathe in a weak solution of potassium permanganate or with herbal decoctions, but it is better to refrain from using cosmetics (shower gels and even soap). It is also undesirable to use washcloths and towels, as they can injure the skin.
Advice from Doctor Komarovsky
The most common question that concerned parents ask their favorite doctor concerns the effects of brilliant green in children with chickenpox. Evgeniy Komarovsky’s answer is unequivocal - there is no therapeutic effect from such an action, brilliant green serves only as an indicator of the period of contagiousness. Lubricating the blisters with a colored solution every day, one day mommy notices that there are no new rashes. From this moment the countdown begins for the last five days, when the baby can pose a danger to others.
The doctor draws the attention of parents to the fact that the viral infection, which is chickenpox in children, is not susceptible to antibiotics and does not require special medications during the normal course of the disease. Only in adolescence, when the disease is too severe, do doctors prescribe antiherpetic drugs.
The main advice that Dr. Komarovsky gives for mothers of sick children:
- avoid overheating, which increases itching;
- cut your nails short, wear gloves if necessary, and do your best to distract the baby from combing the bubbles;
- do not give aspirin so as not to cause liver complications;
- scratching the blisters leads to bacterial infection and the likelihood of marks for life;
- chickenpox quite strongly suppresses the immune system, so after suffering from the disease you should refrain from visiting kindergarten and devote more time to walks.
Regarding vaccinations, Komarovsky believes, sensible parents should not have any discussions. However, he reminds that vaccination against chickenpox is voluntary, so mothers and fathers will have to take responsibility for its implementation.