What it is?
Staphylococci are a genus of anaerobic spherical bacteria that cause pneumonia, endocarditis, a number of skin infections, osteomyelitis, meningitis, septic arthritis, toxic shock syndrome and other diseases.
Bacteria constantly live on the skin of a healthy person, his nasopharynx and oropharynx. Infection occurs when immunity decreases. Particularly susceptible to staphylococcal infection are newborn children and nursing women, patients with reduced immunity, including those suffering from influenza, tumors, leukemia, chronic pulmonary diseases, those on dialysis, injection drug addicts, people with transplants and prostheses, with open wounds, burns, surgical incisions .
Most often, staphylococci are transmitted by airborne droplets or contact.
Staphylococcus aureus is the most pathogenic for humans, leading to inflammatory processes and suppuration of almost all human organs. It is called “golden” due to the formation of a golden pigment. However, this is not the only type of bacteria. In addition to it, patients experience:
- Staphylococcus epidermidis;
- saprophytic, leading to cystitis and urethritis;
- hemolytic, affecting the skin and often leading to sepsis.
What is staphylococcus
These are bacteria of the Staphylococcaceae family that attack various organs and systems of the body. The most common infection is staphylococcus in children. The infection enters the body through airborne droplets, through contact and through consumption of contaminated products.
Children are most often found to have one of the following three types of bacteria:
- Saprophytic. The most rare type in children. It attacks the organs of the excretory system and is fraught with acute inflammation of the urethra and bladder. This is the most harmless type for babies and can be cured in a few days.
- Epidermal. It multiplies on the skin and mucous membranes. Leads to conjunctivitis, purulent urinary tract infections and complications after operations. In the most severe cases, endocarditis and sepsis occur.
- Hemolytic. It makes itself felt by the development of purulent inflammation in the internal organs. If the child’s immunity is weakened and proper treatment is not provided, sepsis may develop.
- Golden. It is the most dangerous for humans. It can affect almost all organs, causing severe purulent inflammation in them. Staphylococcus aureus is characterized by high pathogenicity and causes the formation of boils, catarrhal tonsillitis, etc.
It must be said that pathogenic cocci of these bacteria are not always dangerous for a child. A body with a strong immune system can cope with them on its own. But for weakened children, staphylococcus threatens ENT diseases, digestive disorders, damage to bone tissue, pustular skin inflammation, etc.
Symptoms
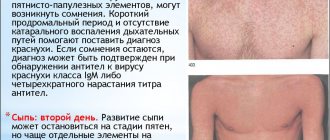
There are two forms of the disease - early and late. In the first case, signs of the disease appear within 24 hours. In the second - only after 48-120 hours.
How staphylococcus is treated is determined by a pediatrician or infectious disease specialist when the following symptoms appear:
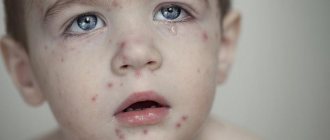
- pustules on the skin,
- furunculosis,
- rashes and pigmentation on the skin,
- stomatitis,
- conjunctivitis,
- temperature rise to 38° C,
- moodiness,
- general weakness,
- decreased appetite,
- bad dream,
- nausea,
- vomit,
- stomach ache,
- diarrhea.
In the worst cases, sepsis (general infection of the body) is possible.
Diagnosis of staphylococcus
Naturally, it is impossible to make a diagnosis and determine the type of pathogen at home. Therefore, if you suspect that your child has staphylococcus, symptoms and treatment should be correlated with the diagnosis and prescribed only by a qualified doctor. It is necessary to show the child to a pediatrician as soon as possible.
To diagnose the disease, a series of tests are prescribed. It includes:
- blood serology,
- throat and nasal swabs,
- urine or stool test
- endoscopic examination of the colon (in case of development of colitis),
- laryngoscopy (if the infection has “sank” below the throat and affected the larynx).
Additionally, PCR tests and analysis of the mother's expressed breast milk may be prescribed.
Symptoms of infection
Symptoms vary widely depending on the affected organ, the patient’s immunity, and his age. There are cases of asymptomatic bacteremia, when microorganisms are found in the blood, but do not cause concern and do not affect the functioning of organs.
However, the most common symptoms may include:
- formation of pustules and carbuncles on the skin;
- stomatitis, conjunctivitis and other local inflammations;
- the appearance of skin rashes accompanied by itching;
- increased body temperature, fever;
- loss of appetite, general weakness and apathy;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, flatulence, diarrhea;
- Redness of the throat and enlarged tonsils are symptoms of tonsillitis.
Since staphylococci can affect any organ, symptoms may also vary.
Classification of infection
In medicine, there are two forms of staphylococcal infection - generalized and focal. In the first case, we are talking about sepsis, when all systems and organs are infected with staphylococcus. Sepsis is a dangerous condition that often ends in death even with qualified medical care.
More often, a focal form of staphylococcal infection is diagnosed when diseases of the skin, bone tissue, and joints are detected. Separately, doctors identify food poisoning with toxins - with characteristic symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus in the intestines of adults.
Staphylococcal infection can occur in mild, moderate and severe, acute or chronic form.
Causes of staphylococcal infection
The main reason for the development of the disease is a decrease in immunity due to stress, illness, poor diet, vitamin deficiency or taking medications. A decrease in immunity, including seasonal ones, can provoke the proliferation of bacteria and subsequent infection.
There are other reasons:
- failure to follow doctor's recommendations when caring for wounds, abrasions and injuries;
- close interaction with a carrier of the infection, for example, with a family member suffering from a sore throat;
- eating poorly processed food - bacteria can be transmitted through food.
Infants become infected due to pathologies during pregnancy and childbirth, for example, a long anhydrous period, prematurity, and poor hygiene.
Due to the nature of its modes of transmission, staphylococcal bacteremia is relatively easy to prevent by observing basic hygiene requirements, not interacting with other people's personal belongings, following doctor's recommendations and, if possible, avoiding close contact with infected people.
About the disease
Staphylococcal infection combines a number of diseases that can manifest as purulent lesions of the child’s skin, pathology of the digestive tract, involvement of ENT organs or even bones in the process.
It is important to consider that the severity of the clinical picture and the danger of the pathology for the patient directly depends on the type of staphylococcus that caused the inflammation. The disease develops sporadically (unsystematically). The risk of infection largely depends on the baby's immune defense. Traditionally, there has been an increase in the number of episodes of staphylococcal infection in newborns. This is due to insufficient secretion of the natural factor IgA, which is responsible for protecting the mucous membranes throughout the human body.
The most common types of staphylococcal damage to the body are:
- digestive disorder caused by staphylococcus;
- septicemia (spread of bacteria in the blood);
- staphylococcal tonsillitis (angina);
- osteomyelitis.
The specialists of the SM-Doctor clinic have many years of experience in successfully treating children of any age who are faced with diseases caused by staphylococcus.
Treatment of staphylococcus
Treatment of staphylococcal infection is always individual and depends on the characteristics of each specific case.
SM-Doctor doctors have more than 10 years of experience working with such patients and know what remedies need to be used in each case. The clinic applies diagnostic and treatment standards approved by the global community of doctors. To combat the pathogen, the following are traditionally used:
- antibiotics (penicillins, cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones). Depending on the location of the pathological focus, the doctor may prescribe a remedy in the form of ointments, tablets, injections;
- antipyretic medications (paracetamol, ibuprofen) to combat fever above 38°C;
- local antiseptics (“zelenka”, hydrogen peroxide, furatsilin).
A little about VR
There is a part in the video where VR work is presented. To better understand what is where, please read the description below:
- For ease of viewing the internal processes occurring in a bacterial cell, the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane are made transparent.
- In the virus reproduction cycle, one type of bacteriophage is considered. This is staphylococcal bacteriophage 80α (alpha).
- The processes of replication, translation and transcription are simplified, and for a better visualization of these processes they are slightly separated in space.
How does the disease manifest itself?
The main manifestations of bacteria in the throat are:
- burning and soreness;
- coughing;
- soreness;
- need to swallow frequently.
Local symptoms of the pathology increase over several days, after which they acquire a pronounced form. Suppuration may occur - the formation of pustules, inflammation of the tonsils. The disease is always accompanied by an increase in temperature.
Signs of general intoxication are added - loss of appetite, nausea, weakness, headache, dizziness. The patient is almost always bothered by a cough.
About pathology
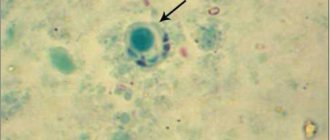
Colonies grow on a medium - blood agar. The bacterium got its name because of its golden color. In fact, approximately one-quarter of the world's population is carriers of this bacterium.
Staphylococcus aureus
Its favorite locations are the armpits, nasal cavity and groin area. But, despite its normal presence on the skin, it does not cause any diseases in humans. It is classified as normal skin flora.
It is worth noting that it does not cause any pathologies as long as it is in moderate quantities. As soon as its quantity exceeds the permissible norm, the development of the pathological process begins. As a rule, staphylococcus begins to penetrate into the deeper layers of the skin through the presence of scars, cracks and other damage. As a result, a skin infection or even an abscess develops.
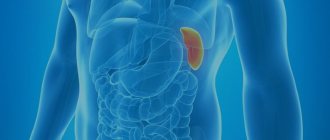
Basically, all body systems are damaged. First of all, the liver and spleen are affected. Then the musculoskeletal system. But that’s not all, because often the consequences are much more serious. Therefore, you should not neglect the first symptoms of the disease and immediately go to a specialist.
Staphylococcus aureus in the throat
It was Staphylococcus aureus that was recognized by doctors as the most dangerous type of bacteria, primarily due to the fact that it has high virulence and the ability to develop resistance to most antibacterial and antiseptic agents.
Settling in the throat, the bacterium becomes the cause of sore throats, laryngitis, and pharyngitis. Small ulcers and erosions are often observed on the mucous membrane of the throat. Staphylococcus aureus is especially dangerous for young children. Their immune system is weak enough to resist the toxins produced by the bacteria, and the infection process is particularly acute in them.
- Methods for treating Staphylococcus aureus in the nose in adults
In addition, the treatment of this particular type of bacterium is particularly difficult; often purulent deposits and necrotic areas must be surgically removed.
Another danger of the presence of Staphylococcus aureus in the throat is its ability to migrate throughout the body. It can settle on remote organs and joints, leading to meningitis, endocarditis, osteomyelitis, pneumonia, sepsis and infectious-toxic shock.
The bacterium is dangerous for the fetus, since the toxins it produces can lead to sepsis and pemphigus in newborns.
The bacteria can be identified using bacterial culture taken from purulent ulcers in the throat. At the same time, it is necessary to conduct an antibiotic sensitivity test. It is they who are prescribed to eliminate bacteria from the throat, often supplementing treatment with staphylococcal bacteriophage.
Prevention of staphylococcus
To prevent infections associated with staphylococcus, it is recommended:
- washing hands before eating and after going outside;
- treating any cuts, abrasions and wounds with antiseptics;
- strengthening the immune system through hardening, proper nutrition and exercise.
“SM-Doctor” is a clinic where real professionals work. If you detect the slightest signs of infectious processes in a child, you should immediately seek help. Timely initiation of proper treatment is the key to the health and well-being of every child. Contact us!
Competition “Bio/Mol/Text”-2020/2021
This work was published in the nomination “Visually about the beloved” of the competition “Bio/Mol/Text”-2020/2021.
The general partner of the competition is the annual biotechnology conference BiotechClub, organized by the international innovative biotechnology company BIOCAD.
The sponsor of the competition is SkyGen: a leading distributor of life science products on the Russian market.
Competition sponsor: the largest supplier of equipment, reagents and consumables for biological research and production.
"Book" sponsor of the competition - "Alpina Non-Fiction"
Diagnosis of staphylococcus
“SM-Doctor” is a multidisciplinary clinic, which is equipped following the example of leading clinics in Europe. Thanks to our own laboratory and modern equipment, our doctors can quickly and accurately identify the cause of deterioration in the condition of a child of any age and determine the strain of bacteria in order to select an effective treatment. Diagnosis of staphylococcal infections begins at the stage of the first consultation. Our specialists collect anamnesis, carefully analyze the complaints of the parents or the patient himself and conduct a comprehensive examination. This allows you to almost immediately decide on treatment tactics. To clarify the diagnosis, the following procedures are used:
- a set of standard laboratory tests (general and biochemical blood and urine tests);
- bacteriological examination of blood, skin scrapings, feces, urine;
- enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) - the technique allows you to identify specific antibodies to a specific pathogen;
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is one of the most effective diagnostic methods, which makes it possible to detect DNA or RNA particles of any bacterium in a minimal amount of test material.
In addition, all young patients are examined by related specialists.
In case of staphylococcal infection, consultation with a cardio-rheumatologist, sometimes a nephrologist, neurologist and other doctors is required. Our specialists pay special attention to the fact that in the absence of timely treatment of staphylococcal infection of any origin, it shows a tendency to generalize, which is fraught with septic conditions and death for the patient.