Microcephaly is a disease in which the size of the brain decreases by 25% or more, and as a result, the size of the head. The disorder can be primary or secondary, when its development is provoked by pathological processes.
One of the main symptoms of microcephaly is underdeveloped cerebral hemispheres. This disorder is often combined with other pathologies, such as aplasia of the corpus callosum, poor development of cranial nerves, and others.
When a child is born into a family with such a pathology, there is a need to conduct a medical genetic examination. This is necessary in order to assess the possible risk of having a second child with a similar disorder in this family.
If symptoms of microcephaly are detected, it is necessary to contact a pediatrician and neurologist, and the peculiarities of raising such children require the supervision of a defectologist and speech therapist.
Microcephaly in children and basic facts about it
But in reality, this rare birth defect is not so easy to spot.
I know what I'm talking about: my six-year-old son, Blake, was diagnosed when he was a year and a half old. Our journey began with an inspection. At one and a half years old, Blake still couldn't sit up or walk on his own and didn't speak much. So such a slight developmental delay did not seem like something terrible to me. Some are fighting for a better place in life, some with their fears, some for a position at work. I'm fighting for my life. For the life of your child. For his health. And in this fight, my son and I will be winners! VIDEO ON THE TOPIC: Diagnosis. Headlong / June 7 21:40 / announcement
- Causes
- What should the treatment be?
- Symptoms of microcephaly in children
- Deformation of the skull in a newborn
- Psychosocial adaptation
- What is microcephaly
- The difference between baby teeth and molars
- How is microcephaly different from hydrocephalus?
- “My son has microcephaly!”: the story of one mother
- Types of disease
- Description
- Why was the child’s skull deformed?
- Causes of microcephaly, classification
Folk remedies
Photo: avrorra.com
Traditional medicine is used as an additional measure in the treatment of microcephaly. For example, the well-known dark chocolate is not only a favorite treat for children and adults, but also, due to its richness in flavanols, has a beneficial effect on a person’s mental abilities and mood. The action is realized through the interaction of antioxidant molecules that stimulate brain perfusion.
The effects of ginseng have been known in Chinese medicine for a long time. This amazing plant affects almost all processes of brain activity. It is taken to improve short-term memory, improve attention, improve mood, and also reduce fatigue.
There is another unique plant - Rhodiola rosea. Thanks to research, it has become known that this plant can enhance performance by increasing the threshold of mental fatigue and fatigue caused by stress. In addition, actions such as strengthening associative thinking, improving short-term memory, and increasing the ability to concentrate on various objects and phenomena have been identified.
The diet should contain foods containing sufficient amounts of omega-3 fatty acids (walnuts, flax seeds, herbivore meat, legumes). In addition, you can buy fish oil capsules at the pharmacy that are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. This substance is considered absolutely deservedly useful, since increased mental activity is observed not only in people with reduced intellectual ability, but also numerous studies have led to the conclusion that healthy people also experience increased mental activity. You should also give preference to complex carbohydrates when choosing between simple and complex ones. The main source of complex carbohydrates is cereals. Moreover, it is worth noting that we are talking about whole grain products, and not about their processed products. That is, it is recommended to use oats, buckwheat, wheat, and brown rice. But oatmeal, buckwheat flakes, and semolina porridge can be excluded from the diet. Also, special attention is paid to the amount of vegetables eaten per day. Almost all vegetables are a source of complex carbohydrates. It should be remembered that to preserve the beneficial properties of vegetables, it is recommended to consume them raw.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.
SEARCH FOR TREATMENT AROUND THE WORLD WITH YELLMED
Causes
Most of the causes of microcephaly in children remain unknown. In some it is provoked by genetic abnormalities:
- Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18);
- Patau syndrome (trisomy 13);
- Absence of a fragment in the fifth chromosome (cry-cat syndrome);
- Prader–Willi syndrome (absence of a paternal copy of chromosome region 15q11-13).
Other risk factors include infectious diseases during pregnancy:
- Rubella;
- Toxoplasmosis;
- Cytomegalovirus;
- Zika virus.
Microcephaly can also be caused by severe maternal malnutrition and a lack of certain nutrients. This pathology is also affected by alcohol (provokes fetal alcohol syndrome), drug use or the ingestion of chemicals. Impaired blood supply to the child’s brain during its development after injury is another cause of the disease.
When planning a pregnancy, you should definitely consult your gynecologist on how to avoid serious malformations of the baby. In particular, doctors do not recommend that pregnant women travel abroad on vacation to tropical countries where the Zika virus is widespread.
The primary form occurs against the background of hereditary predisposition and genetic mutations. Causes of secondary microcephaly:
- Chronic and acute maternal intoxication, including alcohol and drugs.
- Infections (cytomegalovirus encephalitis, herpes, measles, chlamydia, toxoplasmosis) affecting the fetus during intrauterine development.
- Taking certain pharmacological drugs (Busulfan, Colchicine, other cytostatics) during pregnancy.
- Ionizing radiation.
- Adverse environmental factors.
Reasons for the development of the anomaly
Taking into account the causes and time of occurrence, primary microcephaly (true or hereditary) and secondary (syndromic) are distinguished.
Primary microcephaly in children is a manifestation of hereditary diseases; it accounts for about 7–34% of all types of this anomaly.
Primary microcephaly
The following diseases are independent forms.
Giacomini syndrome is a hereditary microcephaly, which is predominantly manifested by mental disorders in combination with the occurrence of convulsive conditions, as well as the progression of paralysis.
Payne's syndrome - this disease is also hereditary. It affects only boys and is manifested by constant convulsive conditions of the lower extremities, nervous disorders and abnormalities in the functioning of the heart.
Microcephaly can be a manifestation of the following pathologies:
- Down syndrome - the appearance of an extra chromosome in the XXI pair, clinically manifested by impaired mental development of the child, a decrease in the size of the brain and cerebellum, as well as other characteristic symptoms;
- Patau syndrome - the appearance of an extra chromosome in the XIII pair, characterized by low birth weight of the newborn, microcephaly and other anomalies of the skull and internal organs;
- Edwards syndrome - the appearance of an extra chromosome in the XVIII pair, while children have a small or long and narrow skull, low birth weight, underdeveloped brain and cerebellum, as well as developmental defects of the facial skeleton, legs (mainly feet) and internal organs;
- cat cry syndrome is a chromosome defect in the V pair, which is manifested by microcephaly, low body weight, retardation in physical and mental development, as well as a characteristic cry in a child, similar to the meowing of a cat (due to damage to the cartilage of the larynx);
- Prader-Willi syndrome - damage to chromosome XV, characterized by microcephaly, delayed psychomotor development and various anomalies of internal organs and skeletal bones;
- Miller-Dieker syndrome is a defect in the XVII chromosome, leading to disruption of the development of brain neurons in the embryo, as a result of which the brain of a newborn child is reduced and devoid of convolutions, in addition, there is severe muscle weakness, delayed physical and mental development and defects of internal organs;
- phenylketonuria is a hereditary disease characterized by impaired processing and use of one of the amino acids - phenylalanine; the resulting toxic substances have a damaging effect on the central nervous system of the pregnant woman, and also inhibit the development and growth of the fetal brain.
Secondary microcephaly develops due to the influence of unfavorable factors on the fetus in the embryonic period, when the formation and formation of all brain structures occurs. In this case, the genetic apparatus of the parents is not damaged.
Causes of secondary microcephaly
- viruses and infections (rubella, cytomegalovirus, measles, toxoplasmosis);
- alcohol abuse - ethanol almost freely penetrates from the mother’s blood through the placenta into the fetus’s body, the most severe manifestation is the so-called fetal alcohol syndrome, manifested by mental retardation and defects in the development of internal organs;
- drug abuse - they can also easily penetrate the placental barrier and adversely affect the fetus;
- taking certain medications that are contraindicated during pregnancy (for example, anticancer drugs such as colchicine or busulfan);
- intrauterine hypoxia - insufficient oxygen delivery to the tissues and organs of the fetus, which leads to a delay in its growth and development, as well as the occurrence of mental retardation and various anomalies;
- fasting - if the expectant mother fasts for a long time or does not take the required amount of protein food, then the fetal organs cannot form normally, which can be fraught with the development of congenital dystrophies and pathologies;
- mechanical injuries in the early stages of pregnancy can lead to disruption of the development of the brain and internal organs, often even incompatible with life;
- exposure to radiation - in the embryonic period, very intensive growth of all tissues occurs, therefore the damaging effects of radiation on the fetus lead to irreversible changes in the brain.
What should the treatment be?
Microcephaly is an incurable disease; it is impossible to restore normal brain activity, but there are ways to correct it.
Treatment of the disease involves an integrated approach, the activities of which are usually aimed at the physical and intellectual development of the child for his maximum adaptation in society.
Treatment takes place in three directions:
- Drug therapy. Used to stimulate metabolic processes in the brain. For these purposes, sedatives, dehydration and anticonvulsants are prescribed (Nootropil, Pyriditol, Cerebrolysin).
- Physiotherapeutic procedures, exercise therapy, massages.
- Therapeutic measures to correct the intellectual development of a child. In our country, there are special boarding schools for children with central nervous system lesions and a diagnosis of microcephaly. Photos of children studying in such institutions can be seen in this article.
Treatment of young patients with the primary form of the disease is sometimes successful. With properly selected therapy, the child will never be completely healthy, but will be able to lead a simplified social life.
As for the secondary form, things are much worse here. Many children, despite serious and persistent treatment, cannot master the most basic skills.
Treatment
Photo: medbooking.com
Children with microcephaly should visit a pediatrician more often than others, as regular monitoring of the child's weight gain and growth is required. Periodic examinations by a neurologist are also necessary, who adjusts the treatment depending on the current state of the child’s health. In addition, given the delayed formation of speech, the help of a speech therapist is required, classes with whom will not only help in the development of speech, but will also improve articulation and increase the child’s vocabulary. To combat spasticity, exercise therapy and massage are necessary. These classes should be regular, since the success of treatment depends on their frequency and quality of implementation.
Medicines used include drugs that improve metabolic processes in brain tissue. Their action is aimed at temporarily reducing the symptoms of the central nervous system, but, unfortunately, they are not able to get rid of the existing problem completely. Since microcephaly is often accompanied by epilepsy, anticonvulsants are prescribed. If necessary, sedatives are used that have a beneficial effect on the nervous system.
Symptoms of microcephaly in children
Symptoms of microcephaly necessarily include severe mental retardation, unclear articulation, speech dysfunction, or complete loss of speech. Violations and deviations from the norm are observed immediately after the birth of the child during a visual examination.
Microcephaly in children is manifested by a decrease in body weight and symptoms such as ataxia (impaired coordination during contraction of a muscle group), convulsions, paresis of the limbs, muscular dystonia (pathological, involuntary muscle contraction). Microcephaly in a child occurs with characteristic external signs:
- Narrow, sloping forehead.
- Predominance of the facial part of the skull over the cerebral part.
- Prominent brow ridges.
- Disproportionately developed body parts.
- Large teeth with large spaces between them.
- Folds of skin at the back of the head.
- Large ears with a low location relative to the physiological norm.
- Wide, short nose.
When diagnosed with microcephalic syndrome, the fontanels close at an accelerated pace, the cranial sutures are tightly closed. The large fontanel and cranial sutures become ossified in the first months of a newborn’s life. Often the pathology is accompanied by other disorders - cerebral palsy, epilepsy, autism, heart disease, renal hypoplasia, lissencephaly (smoothing of cerebral convolutions). Neurological signs in children with microcephaly:
- Muscle weakness.
- Impaired motor coordination.
- Spastic paresis.
- Convulsive syndrome.
- Strabismus (squint).
Babies begin to hold their heads, crawl, sit, walk, and pronounce words much later than their peers. Patients are characterized by a pronounced disturbance in the perception of external information (speech, gestures), a disorder of their own speech function, which is manifested by a limited vocabulary and unclear articulation.
Symptoms
Photo: clarenceplains.org.au
The main symptom indicating microcephaly is a decrease in the volume of the skull, including the predominance of the facial skull over the brain. There is also a lag in weight and height from age norms, and disproportionality of physique.
Considering that the brain with microcephaly does not have time to complete its development, there is a lag in the child’s intellectual and physical development. Therefore, speech is formed with a delay, articulation is characterized by its vagueness, the vocabulary is poor, and there is often a violation of the understanding of spoken speech. Such children begin to hold their heads up, crawl, sit, and walk late. Spastic paresis, muscular dystonia, and ataxia are also detected. Children with microcephaly often suffer from epilepsy and cerebral palsy. The degree of intellectual impairment varies; with mild mental retardation, children with microcephaly can be taught. They adapt to self-care and are also able to perform simple tasks. But, unfortunately, in most cases such people are not even capable of self-care, so they require care and supervision from adults. Such children are usually sedentary and indifferent to the environment, but at the same time they are good-natured and friendly. Less often, they are characterized by hyperactive behavior, which is accompanied by outbursts of aggression.
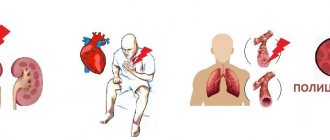
Microcephaly is often combined with other anomalies: cleft lip and palate, congenital cataracts, retinitis pigmentosa, congenital heart and lung defects, and renal hypoplasia. Such severe anomalies in various organ systems significantly complicate the condition of a person with microcephaly, which is why simultaneous medical assistance from specialists from different fields is required.
Deformation of the skull in a newborn
It is the mobility of the bones that allows them to connect, protecting the baby’s head from injury and helping to move along the birth canal. The shape of a newborn baby’s skull depends on the structure of the mother’s birth canal and can be:
- brachycephalic - in caesarean children, that is, round, with clearly visible frontal tubercles;
- elongated oval, that is, dolichocephalic - in children born naturally.
Due to the difficulties of passing along the mother's path, the baby may be born with asymmetry of the head, sometimes with a cephalohematoma. Deformation of the skull in infants is, to a greater extent, caused by this reason.
Within a few months, the shape of the newborn’s skull returns to normal.
Immediately after birth, the newborn’s skull is elongated in the anterior and posterior regions, after a few months it increases in the transverse region, and the shape of the head takes on its usual appearance. The normal size of a newborn's head is about 36 cm.
It is not dangerous if the size is larger. Sometimes a baby inherits this feature from its parents; with age, everything returns to normal. Indicators below the norm are found in premature babies, in children with compression, and Down syndrome.
Deviations from the norm
The main reason for deviations from the norm is birth trauma and congenital diseases. Injury can occur if the fetal head does not fit the size of the woman's tract or she suffers from diabetes. Many consequences can now be cured and the head can be straightened by the year.
For your information! Any deviations from the norm frighten adults; they do not know what to do. Doctors reassure: as long as the fontanel is not ossified, all the flaws can level out on their own.
Pathologies of the skull
It is much more difficult to cure congenital diseases, for example, hydrocephalus or hydrocephalus, which is a serious and dangerous disease. A symptom of another rare pathology, microcephaly, is a too small head, which indicates underdevelopment of the brain.
Such problems can be detected during pregnancy, with an x-ray, and then treatment can begin. There is also a pathological deformation of the head in a child:
- sloping and asymmetrical back of the head – plagiocephaly;
- acrocephaly or elongated form;
- curvature of the frontal or occipital areas - scaphocephaly.
Asymmetry of the skull in children can lead to neurological pathologies and retardation in mental or physical development.
The size of a newborn's head must correspond to certain parameters
Anatomy of the brain
The brain is the main organ of the human nervous system; its formation and development begin in the earliest stages of the embryonic period.
The first rudiments of nervous tissue are formed already on the 18th day of intrauterine development. They are a neural plate, which consists of a small number of neurons (nerve cells). As the embryo forms, their number increases, as a result of which the brain and spinal cord and other elements of the system are formed from the neural plate.
A neuron is a highly specialized cell that consists of a body and many processes through which it communicates with a huge number of other cells. Thanks to this structure, the main function of the nervous system is ensured, namely the reception and processing of information, including the regulation of the vital functions of the entire organism as a whole. Through some neurons (they are called afferent), information in the form of nerve impulses enters the brain, where it is processed and a response nerve impulse is formed, which is sent to organs and tissues through other neurons (they are called efferent).
The formation of nerve cells in the brain is completely completed only at the time of birth, on average reaching about 150 billion neurons. However, throughout a person’s life they are not able to reproduce (divide), and at the same time they gradually die due to so-called apoptosis (a genetically programmed process of death of malfunctioning or damaged cells).
The brain is anatomically divided into three sections.
- Large hemispheres of the brain (right and left). Being the higher parts of the brain, they consist of the cortex and subcortical structures (hypothalamus, thalamus, etc.). The cerebral cortex contains neurons that are responsible for the formation of personality, the processes of self-knowledge and learning (higher nervous activity of a person). Subcortical structures ensure the formation of instinctive and behavioral reactions (sexual, food, etc.). It is also worth noting that the cerebral cortex under normal conditions has an inhibitory effect on subcortical structures; in other words, a person’s consciousness can suppress his instinctive reactions.
- Brain stem. It includes the medulla oblongata, the pons, and the midbrain and diencephalon. They provide reflex activity of the human body, and also maintain communication between the brain and spinal cord. In addition, the trunk contains various nerve centers (for example, vasomotor, respiratory, etc.). They, in turn, ensure the performance of those physiological functions that are not controlled by consciousness (for example, a person breathes automatically, without thinking about it).
- The cerebellum is a small structural formation that is responsible for coordinating human movements, maintaining muscle tone and maintaining balance during complex movements (walking, running, etc.).
The human skull is divided into the brain and facial sections. The latter includes the bones of the face. The development of the skull comes from embryonic tissue called ectoderm. It surrounds the rudiments of the brain from the very beginning of their formation.
There are three stages in the formation of the skull bones:
- membranous - a layer of cells that surrounds the future brain, becomes soft membranous tissue, simultaneously increasing with the growth of brain tissue;
- cartilaginous - from about the sixth to seventh week of embryonic development, this tissue in the area of the base of the skull gradually turns into denser cartilaginous tissue;
- bone - already from the eighth to tenth week of the intrauterine period, ossification points are formed in various parts of the skull, which are zones of the beginning of the growth of bone tissue.
By the time of birth, some areas of membranous tissue (fontanelles) remain in the roof of the skull of a newborn child, which ensure bone mobility during childbirth or when the brain enlarges for any reason.
The large (anterior) fontanelle has a diamond shape and is located at the junction of the frontal and parietal bones. It completely ossifies and closes by the age of two years.
The small (posterior) fontanel has the shape of a triangle and is located in the occipital region at the junction of the parietal and occipital bones. As a rule, it becomes overgrown by the second month of life.
The lateral fontanels are paired and small in size, they are located on the side surface of the head, slightly in front and behind the ears, and are also completely overgrown by the second month of life.
The bones of the facial skull are formed from the so-called gill arches, which are derivatives of mesoderm (another embryonic tissue). Thus, the development of the brain and facial parts of the skull occurs independently of each other. In addition, the formation of the facial skull is practically independent of the development and growth of the brain; however, the size of the cerebral skull normally always corresponds to the volume of the cerebral hemispheres.
At the end of the 19th and beginning of the 20th centuries in Europe and North America, children with microcephaly were sold to the circus. There they took part in the so-called “freak show”.
Psychosocial adaptation
In the psychological and social adaptation of children with microcephaly, the main role is given to parents.
The child must take all prescribed medications in a timely manner, attend classes with speech therapists and other teachers, engage in physical therapy and receive a full-fledged massage.
Any interruptions in therapy can cause an exacerbation of the disease and accelerate its progression.
Recommendations for parents of children with this diagnosis:
- Raising children with microcephaly is accompanied by increased responsibility on the part of adults (parents must be aware of the scale of the problem).
- Psychological assistance should be provided not only to the child, but also to his parents.
- Slowing down the progression of the disease and the emergence of positive dynamics is only possible with constant training with the child and following the recommendations of doctors.
- Thanks to special classes, you can increase a child’s self-esteem and develop his individuality (such classes are in most cases conducted in a group form, children learn to communicate with each other, acquire basic skills and more easily adapt to external conditions).
- Children with a mild form of intellectual disability can attend remedial classes, but classes with a remedial teacher are mandatory.
What is microcephaly
Microcephaly of the brain is a pathology in which the growth and development of the child’s brain stops. Another name for this pathology is brain hypoplasia. This manifests itself in a decrease in its mass and slower growth of the skull.
The skull stops growing and is often severely deformed. All other organs of the child develop according to the norms of their age.
This pathology affects the further development of the child’s central nervous system. He stops developing mentally, and neurological abnormalities occur. Children with microcephaly are often diagnosed with imbecility, idiocy, and mental retardation.
Moreover, the severity of the disease can vary, from mild to very severe.
This is due to the fact that physical deformations of the skull cause disturbances in the structure of important brain centers that control mental processes such as memory, attention, intelligence, emotions and others. Doctors believe that it is impossible to fully restore the functionality of the brain of a child diagnosed with microcephaly
The main task is treatment aimed at the maximum possible adaptation of such a child to life in modern society
Doctors believe that it is impossible to fully restore the functionality of the brain of a child diagnosed with microcephaly. The main task is treatment aimed at the maximum possible adaptation of such a child to life in modern society.
This is achieved with the help of properly selected medications, physical therapy, massage, and a special development and training program.
Diagnostics
Prenatal diagnosis of microcephaly includes ultrasound examination (ultrasound). During this procedure, the doctor compares the data obtained on the size of the fetus's head and torso with normal values. The most reliable information can only be obtained if you know exactly the duration of pregnancy.
Determining mutations of genes and chromosomes is the so-called invasive diagnostics. This method is carried out with a puncture of the fetal bladder, because the material for research is fetal villi, amniotic fluid, and also particles of epithelium.
Prenatal screening also includes a biochemical blood test. In addition, the pregnant woman is asked to fill out a special form, which, among other questions, contains a column about the timing of pregnancy. All information received and test results are processed in a special computer program that shows the likelihood of developing brain microcephaly.
A newborn baby is examined by a neonatologist in the delivery room in the very first minutes of his life through an external examination. If the diagnosis is confirmed, then an additional comprehensive examination is required.
Children with microcephaly must be consulted by a geneticist to identify concomitant hereditary diseases. In order to determine the degree and prognosis, it is also important to conduct a full instrumental examination: ultrasound of the brain (neurosonography), electroencephalography (EEG), radiography of the skull, as well as computed and magnetic resonance imaging (CT and MRI).
In addition, in order to identify defects in the development of other organs and systems, the child should receive consultations from specialized specialists: otolaryngologist (ENT), ophthalmologist, cardiologist, neurologist, neurosurgeon, orthopedist.
The difference between baby teeth and molars
A child’s milk teeth differ from permanent teeth in their structure, shape and color. We strongly recommend that you look at numerous photos in which you can easily tell the difference. In addition, children's teeth have a thin layer of enamel, a small crown and dentin. In the photographs you can easily notice that such teeth have widely spaced roots that are located at an angle. This feature is explained by the need for the formation of permanent teeth. An X-ray of a child's jaw with baby teeth will help determine how much the new molars have formed. If you pull out children's teeth before the molars are formed, you are likely to encounter serious deficiencies. This usually causes a cosmetic defect in the form of a diastema, or a large gap between the teeth.
Babies grow 20 milk teeth, which are gradually replaced by molars (for more details, see the article: when do children change their milk teeth to molars?). Their rudiments are formed in the jaw at the stage of embryonic development of the child, so the skull of a newborn has a special structure. The chin is weakly expressed, the brain part is larger than the facial part. The lower jaw is located slightly further in relation to the upper. As temporary teeth appear, its position changes.
The formation of baby teeth begins at 5 weeks of pregnancy. From the 20th, the rudiments of permanent incisors and canines are formed. Premolars are formed after birth, and molars are formed closer to the year, usually at 10 months of life. The growth of the roots of permanent and temporary teeth lasts about 2 years, and begins only before their eruption.
Often, crooked molars grow in place of non-permanent teeth pulled out prematurely (see also: how molars grow in children: photo). They occupy an incorrect position in the dentition, which is not only a cosmetic defect, but also leads to dental problems. That is why, when the first signs of carious lesions are detected, doctors rush to fill temporary teeth.
The change in the skull with baby teeth takes place in 2 stages. Up to 3 years of age, the teeth are tightly packed, the enamel is not erased, and the lower jaw occupies a neutral position. The second period ends by age 7. It is characterized by the appearance of interdental spaces, changes in bite, and abrasion of the enamel.
The buds of permanent teeth put pressure on the roots of temporary teeth, which leads to their resorption (loss). When permanent teeth emerge, they have a size and shape that will last a lifetime. Eruption pathologies are often associated with inflammatory processes at the roots of temporary teeth. This can be seen on x-rays and corrected early.
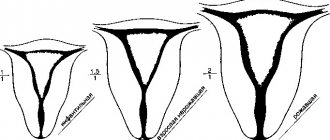
How is microcephaly different from hydrocephalus?
hydrocephalus CSF there are four in total - two lateral, the third and fourth subarachnoid In congenital hydrocephalus the amount of CSF can reach several liters Comparative characteristics of microcephaly and hydrocephalus
| Criterion | Microcephaly | Hydrocephalus |
| Appearance time | During the intrauterine period. Always appears at the birth of a child. | In the prenatal period or after the birth of the child. It can also occur in adults. |
| Causes |
|
|
| Changing the shape of the head |
|
|
| CSF pressure | Normal (130 millimeters of water column) or reduced. | Always elevated. |
| Intellectual impairment | Always present (from mild severity to idiocy and inability to self-care). | Intelligence depends on the time of development, severity and duration of compression of brain structures. |
| Treatment | The disease is incurable. Symptomatic therapy and education in special schools are prescribed. Manifestations of mental retardation will persist throughout the child’s life. | Timely surgical treatment (consisting of restoring the patency of the anatomical foramina or removing the choroid plexus papilloma) can lead to a complete cure (if irreversible changes in the brain tissue have not developed). |
“My son has microcephaly!”: the story of one mother
Microcephaly is a neonatal malformation in which the baby's head is much smaller than that of other babies of the same age and gender. When combined with improper brain development, children with microcephaly may develop developmental disorders.
The severity of microcephaly ranges from mild to severe. Microcephaly is a rare condition. The estimated prevalence of microcephaly varies considerably due to different definitions and depending on the target populations.
Scientists are studying a potential, although unproven, link between rising rates of microcephaly and Zika virus infection. Microcephaly can sometimes be diagnosed using fetal ultrasound. The most appropriate period for diagnosis is the end of the second trimester around 28 weeks or the third trimester of pregnancy. Head circumference of newborns should be measured at least 24 hours after birth and compared with WHO standard child development indicators.
The results are interpreted based on the baby's gestational age, height and weight. If there are suspicions, the child is referred for examination to a pediatrician and for a brain scan, the circumference of his head is measured once a month in early infancy and the data obtained are compared with standard indicators.
Doctors should also test for known causes of microcephaly. Microcephaly has many potential causes, but often the cause remains unknown. The most common reasons include:. Many babies born with microcephaly may have no other symptoms at birth but may later develop epilepsy, cerebral palsy, learning disabilities, hearing loss and vision problems. Some children with microcephaly develop completely normally. There is no specific treatment for microcephaly.
A multidisciplinary team is required to assess and treat newborns and children with microcephaly. Early stimulation and play programs can have a positive impact on development. Family counseling and parental support are also very important. Since mid-year, WHO has been working closely with the Americas to investigate and respond to the outbreak.
The Strategic Response Program and Collaborative Action Plan outlines the steps WHO and partners are taking to address the Zika virus and its potential complications:. Children's growth standards. Microcephaly February 16 Key Facts Microcephaly is a condition in which a baby is born with a small head or the head stops growing after birth. One child in several thousand is born with microcephaly. The most reliable way to determine microcephaly in a child is to measure his head circumference 24 hours after birth, compare this value with the WHO standard indicators for child development, and then measure head growth in early infancy.
Children born with microcephaly may suffer from seizures as they grow, as well as physical disabilities and learning problems. There is no specific test to detect microcephaly in a fetus, but an ultrasound scan in the third trimester of pregnancy can sometimes reveal the problem.
Guillain-Barré syndrome October 31 Zika virus July 20
Diagnostic features
Diagnosing microcephaly is not particularly difficult; it is based on determining morphological parameters and identifying signs of intellectual underdevelopment in a child.
Diagnosis is also carried out during pregnancy, this makes it possible to identify concomitant pathologies in fetal development and the risk of an anomaly such as microcephaly.
This is detected by obstetric ultrasound, when the biometric parameters of the fetus corresponding to a certain stage of pregnancy are compared. However, signs of an abnormality in the fetus can be detected only at 27-30 weeks of pregnancy.
In this regard, if there is a suspicion of the development of such a pathology due to genetic or chromosomal disorders, it is necessary to conduct additional examinations.
The degree of development of pathology can be determined using methods such as neurosonography, MRI of the brain area, EEG, and radiography.
Types of disease
There are primary and secondary forms of the disease. In the first case, we are talking about congenital microcephaly, which occurs due to hereditary factors or as a result of a gene mutation. Occurs with a frequency of up to 34% of cases. Giacomini and Payne syndromes are considered independent diseases. Both diseases are of hereditary etiology.
They manifest themselves as mental disorders, increasing convulsive states, and the progressive occurrence of paralysis. Payne's syndrome is additionally accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the heart. Microcephaly in a child is a pathology that is a sign of other syndromes: Patau, Down, Edwards, cat cry, Prader-Willi, Miller-Diecker, which in this case determines its secondary nature of origin.
All of these syndromes are associated with defects in certain chromosomes. The hereditary disease phenylketonuria, which occurs due to a violation of the metabolism of amino acids, especially phenylalanine, is the cause of the development of microcephaly in the fetus. As a result of insufficient utilization of phenylalanine, toxic products accumulate, which inhibit the growth of brain tissue.
Secondary microcephaly occurs against the background of diseases and injuries during the perinatal period or during childbirth. The causes of the secondary form are not related to genetic factors. There are 4 types of pathology, taking into account the nature of the postnatal course:
- Type 1. Symptoms do not increase, there are no convulsions or spasms of the limbs, motor activity is within normal limits. Intelligence quotient (IQ) is about 60.
- Type 2. Convulsive syndrome is observed with increasing intensity and strength of manifestation. The life expectancy of such children is about 10-12 years. Death usually occurs due to respiratory infections.
- Type 3. Characterized by a progressive convulsive syndrome with pronounced, predominant spasticity, impaired mental and motor functions.
- Type 4. Autosomal recessive form. It is characterized by the absence of convulsions and spasticity.
The quality of life of sick children depends on the degree of mental and physical impairment. Correct therapy in some cases can improve the patient's condition. There are stages of mental disorders:
- Moronism. Mild mental retardation. Children learn writing, reading, and self-care skills. Patients are not able to master the standard school curriculum, so they study in specialized schools and boarding schools. The prognosis is relatively favorable. Life expectancy can exceed 30 years; patients rarely live into old age.
- Imbecility. Mental retardation of moderate severity. The ability for self-care is often preserved. Intellectual functions are poorly developed. The child has difficulty learning. Life expectancy can reach 20 years. The cause of death is often pneumonia and other infectious lesions of the respiratory system, congenital malformations of organs.
- Idiocy. . The child cannot be taught and needs adult care. The prognosis is unfavorable. Death is possible during the first years of life. Main causes of death: concomitant pathologies, complications of infectious etiology, malfunctions of internal organs.
Depending on the nature of the course and temperament, patients with torpid and eretic forms are distinguished. In the first case, the child has an autistic syndrome (passivity, isolation, indifference, low mobility), in the second, motor restlessness, fussiness and emotional excitability predominate.
Medicines
Photo: pp.userapi.com
The main medications prescribed for microcephaly are aimed at improving metabolic processes in the brain. Due to this, a weakening of symptoms is achieved, which leads to a temporary improvement in the child’s condition.
Piracetam is a nootropic drug that has a beneficial effect on blood circulation and metabolic processes in the brain. According to researchers, the drug can have the following effects:
- stimulates intellectual activity;
- improves memory;
- facilitates the learning process;
- increases mental performance.
The drug is well tolerated and has virtually no contraindications for use. Side effects that occur while taking the drug include: dyspeptic symptoms, general weakness, dizziness, anxiety, sleep disturbance.
Gromecin (glycine) is also a nootropic drug. Capable of increasing mental performance, memory, concentration, normalizes mood, and regulates minor sleep disturbances. Side effects while taking the drug are rare. More often they are associated with individual intolerance and manifest themselves in the form of skin rashes and itching.
Cerebrolysin helps increase the rate of glucose penetration when the blood-brain barrier is disrupted, influencing the level of its consumption in damaged parts of the brain. In addition, this drug has a positive effect in cases of disruption of oxidative processes in the structure of brain metabolism and reduces the level of cerebral concentration of lactic acid. This leads to improved brain function.
B vitamins (neurobex, borivit) are also prescribed to improve the conduction of nerve impulses.
With microcephaly, epilepsy often develops, so an indispensable component of therapy is the prescription of anticonvulsants. The selection of a specific drug from this group, dosage and frequency of administration is made individually for each patient. This takes into account the type of seizures, the frequency of their occurrence and sensitivity to drug treatment. The most appropriate drug, prescribed by a qualified neurologist, is taken by the patient continuously. This is necessary to prevent the development of a seizure, during which the child may be injured. If an epileptic attack does occur, diazepam is immediately administered. This drug has many therapeutic effects, including being used to relieve seizures. It is important to understand that this drug is under no circumstances used as maintenance therapy, as there is a risk of developing addiction, as well as other undesirable effects.
Description
Microcephaly is a developmental defect of the central nervous system, characterized by a decrease in brain mass and skull circumference. Microcephaly is a cause of mental retardation and neurological abnormalities. It occurs with equal frequency among both boys and girls. It is believed that for every 10,000 newborns, there is 1 child with microcephaly. With microcephaly, a decrease in brain mass is detected (normally approximately 400 g), the circumference of the newborn’s head is reduced to 25–27 cm (normally 35–37 cm).
It is quite difficult to establish the exact cause of the formation of pathology. Possible factors are:
- alcohol, drug or nicotine addiction of the mother, leading to intoxication of the fetus;
- infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy (for example, toxoplasmosis);
- serious toxic poisoning of the mother during pregnancy;
- exposure to radiation;
- taking toxic doses of certain medications (for example, some antibiotics that have a teratogenic effect);
- various genetic defects.
Unfortunately, there are no effective treatments for microcephaly. The main treatment is aimed at reducing the severity of symptoms of the pathology. For this purpose, nootropic, sedatives, anticonvulsants and decongestants, therapeutic exercises, and manual therapy are used. Methods of upbringing, training and development of the child’s personality develop elementary self-care abilities and motor skills. Often children with a similar diagnosis attend a special boarding school. The outcome of the disease is unfavorable, the pathology cannot be completely cured. The average life expectancy of a child is 15 years; in rare cases, patients live up to 30 years.
Statistical information
The incidence of the defect ranges from approximately 1:2000 to 1:10000 among all newborns. As an independent disease, true microcephaly is much less common and is detected in one out of 50 thousand children, both girls and boys. If this pathology occurs as a manifestation of another hereditary disease, then its frequency in the population is determined by the frequency of the underlying disease.
Why was the child’s skull deformed?
Skull deformation in infants can occur not only at birth. Sometimes parents notice that during development, the child’s skull has changed unnaturally. What's happened?
Let's look at the most common cases:
Strongly elongated or sloping back of the head. In this case, the head may be uneven, flattened, and its size no longer corresponds to normal. What does this type of skull shape indicate? The problem most often is that the baby is in the same type of lying position for too long. Newborns have the peculiarity of tilting their head to a certain side. This leads to the development of skull deformation in children. The baby’s skull bones remain soft for a long time. This is provided by nature for a reason: this feature allows the brain to develop unhindered and protects the child himself from injury. Therefore, if he often turns his head in a certain direction, lies on one side, all this can affect the shape of his skull. Mothers always move the child from one position to another, placing him in different directions from the object of interest. Don't forget about the fontanel. This is an area on the head characterized by elastic soft tissues. While the fontanel is open and not closed, the shape of the child’s skull can sometimes change significantly. The head becomes lopsided or flat if the baby just lies in the same position for a long time
Therefore, parents should always pay attention to this fact so that in the future the adult child does not blame them for his disproportionate skull shape.
Causes of microcephaly, classification
There are several types of disease:
- primary: hereditary and true, occurs in 10-40% of all microcephaly;
- secondary: syndromic and embryopathic.
The first option occurs with chromosomal pathologies: autosomal recessive, recessive and sex-linked. These include Giacomini syndrome and Payne's syndrome. The second type of microcephaly is diagnosed when gene transformations occur, with enzyme pathologies, or disorders of intrauterine development of the fetus.
More than 125 chromosomal mutations occur with microcephaly, for example:
- Down's disease;
- Edwards syndrome;
- "Cry of the cat" syndrome;
- Patau syndrome.
Embryopathic microcephaly often develops against the background of infection of the fetus with cytomegalovirus, toxoplasmosis, syphilis, herpes, encephalitis, rubella, as well as with the systematic abuse of alcohol and drugs by the expectant mother, inhalation of toxic substances at work, and use of medications without a doctor’s prescription. In more rare cases, the causes of microcephaly are:
- ionizing radiation;
- asphyxia (oxygen starvation of the fetus);
- injuries during the rapid passage of the birth canal;
- thyrotoxicosis or diabetes mellitus in a pregnant woman.
Microcephaly is usually combined with other serious anomalies:
- "cleft lip";
- cataracts;
- skin pathologies;
- cardiomyopathies;
- malformations of internal organs.