This is an intrauterine syndrome accompanied by a complex of changes in the fetus, which are caused by insufficient oxygen supply to its organs and tissues. The pathology is characterized by the development of disorders in vital organs, especially the central nervous system.
Causes of fetal hypoxia
The pathology occurs in 10.5% of pregnant women and can develop at different stages of pregnancy. The main causes of fetal hypoxia are:
- gestational arterial hypertension;
- premature placental abruption;
- anemia in the expectant mother;
- infectious diseases;
- multiple pregnancy.
The likelihood of developing fetal hypoxia is increased by chronic diseases in the mother (heart defects, kidney disease, bronchitis, bronchial asthma, diabetes mellitus). As well as the use of alcohol and nicotine, disorders of the fetal-placental circulation caused by pathology of the umbilical cord, post-term pregnancy, threat of miscarriage, abnormalities of labor, etc.
Causes of fetal hypoxia
Acute form
Acute hypoxia can be caused by:
- rapid or prolonged labor - prolonged labor is dangerous due to prolonged compression of the head in the birth canal. A quick birth is dangerous because the baby does not have enough time to adapt and turn correctly in the birth canal;
- premature rupture of water - a prolonged period without water can cause hypoxia;
- impaired circulation of the umbilical cord - damage to the umbilical cord loops, the formation of knots, strong entanglement of the umbilical cord during childbirth, and separation of the umbilical cord contribute to the occurrence of hypoxia;
- weakness of labor - prolonged low-productive activity of the uterus prevents the advancement of the fetus along the birth canal, tires the female body and causes oxygen starvation of the fetus;
- premature placental abruption is a critical condition that poses a threat to mother and child. Part of the placenta separates from the uterus, and the feeding vessels rupture. The uterus cannot contract in the same way as the fetus is located in it. Acute hypoxia begins in the fetus and bleeding in the woman;
- Uterine rupture is an emergency condition that can lead to sudden death of the pregnant woman and fetus. The cause of the rupture may be thinning of the suture on the uterus.
- increased uterine tone;
- use of narcotic painkillers during childbirth;
- hypotension - low blood pressure in the mother impairs blood flow to the fetus and causes oxygen deficiency.
Chronic form
The causes of chronic oxygen deficiency of the fetus can be a variety of diseases and conditions of the pregnant woman:
- diseases of the respiratory system (asthma, bronchitis, pneumonia, etc.);
- diseases of the cardiovascular system (anemia, heart disease, hyper- or hypotension, heart failure, etc.);
- diabetes mellitus, thyroid dysfunction, hormonal imbalance;
- antiphospholipid syndrome. A pathology in which there is a high probability of infertility, pregnancy complications, or miscarriage;
- incompatibility of Rh factors in the blood of mother and fetus;
- gestosis (late toxicosis of pregnancy);
- dysfunction of the placenta, which is characterized by endocrine, nutritional, transport, metabolic dysfunction of the placenta;
- post-term pregnancy;
- multiple pregnancies may cause uneven blood flow to the fetuses and one of the fetuses may experience a lack of oxygen;
- infectious diseases of the reproductive, intestinal, urinary systems, as well as acute respiratory viral infections;
- drinking alcohol, smoking.
Degrees of hypoxia: acute and chronic
Our body cannot live without oxygen, so even a short oxygen deprivation leads to serious consequences. There are two types of hypoxia – acute and chronic.
What is the difference between them? A simple example: if a piece of food is blocked in the respiratory tract, this causes acute hypoxia. And if you live for months in a stuffy, poorly ventilated room, this causes chronic oxygen starvation.
Chronic hypoxia as a result of constant stuffiness is often the cause of malaise in adults - it leads to decreased immunity, deterioration in the quality of sleep, frequent headaches, constant fatigue and weakness.
Important! During pregnancy, prolonged stay in a stuffy room is dangerous precisely because of the risk of developing intrauterine fetal hypoxia. Therefore, doctors recommend being in the fresh air as often as possible, since they assume that all the windows in the apartment are closed and there is not enough fresh air.
The fruit is 100% dependent on the environment in which it is located. Therefore, expectant mothers need to avoid stuffiness, large crowds of people and regularly ventilate the apartment where they spend a lot of time. There is a myth that the room only needs to be ventilated for 15 minutes in the morning and evening. Ventilation should be constant, but this is not always possible due to the environment - dirt, noise, drafts, allergies.
Acute fetal hypoxia during pregnancy is the nightmare of any obstetrician. It can develop due to pathologies of intrauterine development (for example, placental abruption), or during childbirth - due to abnormalities in the birth act.
Signs and symptoms
At an early stage of pregnancy, pathology is quite difficult to identify; more often it appears in the second half of the baby’s gestation period. It is necessary to pay attention to the frequency and number of fetal movements. During the normal course of pregnancy, there should be at least ten fetal movements during the day for several minutes with breaks of 1-2 hours. A decrease in activity often signals developing hypoxia. In the second half of pregnancy, the baby's heartbeat should be heard.
Signs of developing fetal hypoxia:
- tachycardia, arrhythmia, bradycardia in the fetus;
- excessively active movement of the fetus - intense intrauterine movements can cause painful sensations to the mother and increase the tone of the uterus;
- too low fetal activity;
- greenish or brown color of waste water.
With fetal hypoxia, symptoms of pathology in a pregnant woman may also occur:
- severe toxicosis;
- depressive states;
- frequent fatigue, causeless fatigue;
- insomnia;
- changes in blood pressure;
- hearing and vision impairment.
Classification of asphyxia according to the Apgar scale
To assess the severity of asphyxia in a newborn, the Apgar scale is used. With its help, the doctor evaluates heart rate, breathing, muscle tone, skin color and reflexes, and then determines the severity of the pathological condition.
To give a rating, the doctor evaluates each of the five signs as 0, 1 or 2 points. Accordingly, the maximum and best score is 10 points. The assessment is determined taking into account the following criteria:
| Sign | 0 points | 1 point | 2 points |
| Pulse, beats per minute | No | Up to 100 | From 100 and above |
| Breath | No | Irregular, weak | Active, child screams and cries |
| Muscle tone | Arms and legs dangling | Weak flexion of arms and legs | Active movements |
| Reflexes | No | Weak | Present, well expressed |
| Color of the skin | Pale, cyanotic | Body – pink, arms and legs – bluish | Pink body, limbs |
The condition is assessed in the first and fifth minutes of life. Accordingly, the child receives two ratings: for example, 8/10. If the score is 7 or lower, the baby’s condition is assessed additionally at the 10th, 15th and 20th minutes.
Depending on the Apgar score, the degree of asphyxia is determined:
- 1-3 points – heavy;
- 4-5 points – average;
- 6-7 points – mild or moderate.
The Apgar score is not highly sensitive. Therefore, if a child has abnormalities, additional diagnostics are necessary to assess asphyxia.
Diagnosis of fetal hypoxia
If the intensity of fetal movements decreases or, conversely, if they become more active, the pregnant woman should immediately contact her gynecologist. Using a stethoscope, the doctor listens to the rhythm, frequency, and sonority of the heartbeat, and determines or excludes the presence of murmurs.
Ultrasound and Doppler measurements are performed. Cardiotocography is used to diagnose the condition of the child’s heart, the presence of fetal movements, and the activity of uterine contractions. Amniocentesis and amnioscopy are performed through the cervix and evaluate the amount, color, and biochemical composition of the amniotic fluid. A test of fetal blood from the presenting part is also performed. Additionally, a bimanual obstetric examination is prescribed for complaints of various types of discharge.
Types of newborn asphyxia
Classification is carried out according to several criteria. First of all, depending on the time of development of the pathological condition, the following are distinguished:
- primary, or intrauterine asphyxia - develops directly in the womb;
- secondary, or extrauterine asphyxia – occurs in the first hours of the baby’s life.
In turn, primary asphyxia is also divided into two subtypes:
- antenatal, or chronic - develops even before the onset of labor;
- intrapartum, or acute - occurs during the period of uterine dilation and fetal birth.
Consequences of fetal hypoxia
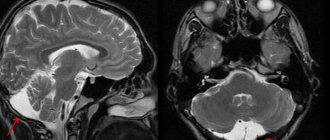
Fetal hypoxia is dangerous at any stage of pregnancy and childbirth and has serious adverse consequences. There is a delay in the development and growth of the fetus. A newborn baby may experience dysfunction or malfunction of many organs. The immune system weakens, the baby has low adaptive abilities. Disorders of the cardiovascular, respiratory, nervous systems, and psycho-speech abnormalities are often observed. High risk of various defects and development of cerebral palsy. Hypoxia can lead to asphyxia, a serious emergency condition.
To prevent fetal hypoxia, a woman must maintain a correct lifestyle throughout the entire pregnancy. Treatment of existing diseases, balanced nutrition, giving up bad habits, moderate physical activity, calmness, timely examination and monitoring of the health of the mother and fetus are required.
Consequences: why is this intrauterine syndrome dangerous?
Until the moment the child is born, he does not have independent breathing. He breathes liquid with oxygen dissolved in it, which entered it through the placenta from the mother’s blood. Simply put, the child breathes the air that his mother breathes, and if there are problems with O2 delivery at any stage, a threat of fetal hypoxia is created.
When oxygen deficiency occurs, the child’s body begins to redistribute it so that first O2 enters vital organs (brain, heart and adrenal glands), and only then goes to the skin, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract and lungs. Because of this, the first violations affect the development of those organs and systems that, during hypoxia, received oxygen according to the “residual principle.”
Problems with chronic hypoxia:
- difficulty in adapting to stimuli in a newborn (convulsions, problems with appetite and breathing);
- risk of developing epilepsy;
- cardiovascular disorders;
- risk of kidney failure;
- enterocolitis, frequent regurgitation;
- secondary immunodeficiency;
What could be the consequences for a child in the future due to acute hypoxia? In this case, the central nervous system is primarily affected. Acute oxygen deficiency in the fetus can cause the following disorders:
- mental retardation;
- DIC syndrome;
- neurological disorders;
- cerebral edema;
- pulmonary hypertension;
- necrosis and ischemia of various organs.
Osteopathic treatment of hypoxia during childbirth
Osteopathic treatment rightfully occupies one of the leading places in the rehabilitation of children who have suffered from hypoxia. Balancing the bones of the skull allows you to relieve tension from the dura mater and the cerebral hemispheres, thereby ensuring the most complete functioning of the central nervous system.
Osteopathic techniques allow for drainage of the venous sinuses, as a result of which cerebrospinal fluid resorption is improved and intracranial pressure is normalized. Freeing the cervical spine and eliminating torticollis promotes adequate blood supply to the brain.
Early osteopathic treatment in the first year of life allows children not only to keep up with their peers in development, but sometimes even to develop ahead of schedule. It is very important to carry out this treatment from the first months of life, as this will help get rid of long-term clinical pathological symptoms. Osteopathy sessions are conducted for children starting from the first month of life. Osteopathic treatment, creating optimal functioning of the central nervous system, stops the process of post-hypoxic changes in neurons, thereby somehow reprogramming the brain for full development.
There is no need to be afraid of hypoxia; you need to take the entire range of measures for rehabilitation after it. Moreover, modern medicine gives us many tools for this.
Treatment
Clinical recommendations for asphyxia include the provision of first aid to the newborn as a priority. This is the most important step, which, if carried out competently, reduces the severity of the consequences of the pathological condition and the risk of complications. The key goal of resuscitation measures for asphyxia is to achieve the highest possible Apgar score by 5-20 minutes of the newborn’s life.
The stages and principles of ABC resuscitation allow for consistent and effective resuscitation of a newborn born with asphyxia. Source: Carrying out therapeutic hypothermia in newborns born with asphyxia. K. B. Zhubanysheva, Z. D. Beisembaeva, R. A. Maykupova, T. Sh. Mustafazade. Science of Life and Health, 2021. p. 60-67:
- Principle A (“airway”) is to ensure a clear airway during the first stage of resuscitation. To do this, you need to create the correct position: tilt your head back, lower it 15 degrees. After this, suck out mucus and amniotic fluid from the nose, mouth, trachea, and lower respiratory tract.
- Principle B (“breath”) – create ventilation, provide breathing. To do this, a jet oxygen flow is created - artificial ventilation of the lungs is performed using a resuscitation bag. If the child does not cry, tactile stimulation is added: stroking along the back, patting the feet.
- Principle C (“cordial”) – restore heart function. Indirect cardiac massage helps with this. If necessary, adrenaline, glucose, hydrocortisone and other drugs are administered. In this case, the auxiliary ventilation from the previous stage cannot be stopped.
Care for a newborn child who has suffered asphyxia is carried out in a maternity hospital. Babies with a mild form are placed in a special tent with a high oxygen content. In cases of moderate or severe asphyxia, infants are placed in an incubator - a special box where oxygen is supplied. If necessary, the airways are re-cleaned and freed from mucus.
The scheme of further treatment, recovery and care is determined by the attending physician. General care recommendations include:
- maintaining normal body temperature, blood pressure, heart rate;
- creating maximum comfort: optimal ambient temperature, comfortable position;
- carrying out respiratory therapy;
- conducting infusion therapy - administering fluid to meet needs Source: Protocol for therapeutic hypothermia for children born with asphyxia. Ionov O.V., Balashova E.N., Kirtbaya A.R., Antonov A.G., Miroshnik E.V., Degtyarev D.N. Neonatology: News. Opinions. Training, 2014. p. 81-83.
During rehabilitation, regular monitoring :
- baby's weight (twice a day);
- neurological and somatic status;
- volume of fluid consumed;
- nutrition composition;
- basic vital signs: pulse, blood pressure, saturation, respiratory rate;
- laboratory characteristics of blood, urine;
- X-rays of the chest, abdominal cavity;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity;
- neurosonography;
- electrocardiograms, echocardiograms.
After discharge, the baby should be regularly monitored by a pediatrician or neurologist.