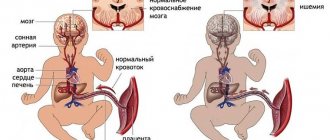
The causes and consequences of this negative condition are being studied by specialists from all countries to prevent the pathological situation and prevent the death of the fetus in the womb. Fetal development can stop at any stage, after which the woman’s body rejects the non-viable tissue.
According to global medical statistics, symptoms of frozen pregnancy are observed in 20% of women who decide to conceive. Those at risk are those who have crossed the threshold of 35 years of age and who have experienced a similar condition earlier.
Why does pregnancy stop?
Among the provocateurs of frozen pregnancy are:
1. Genetic factor or chromosomal abnormalities - mutations lead to the death of the embryo, due to the rules of natural selection of viable organisms. In most cases this occurs between 2 and 8 weeks, but it can happen later. The occurrence of a genomic abnormality is considered to be a mistake of nature, an accident. The disorder can be caused by a genetic deformation of one of the parents, which is inherited. To eliminate the risk of miscarriage, parents should undergo genetic counseling at the planning stage. If the pregnancy fails again, the supervising doctor issues a referral for a free genetic examination of the couple.
2. Infectious process - infections of a bacterial, viral, parasitic nature provoke fetal death in the early stages of development. Complications can be prevented by previous vaccination and timely visit to medical institutions to take adequate measures. Chronic infections of the female body lead to the formation of unfavorable conditions for the development of the fetus and can cause disturbances in the formation of the embryo that are incompatible with life. Much depends on the route of penetration of the provoking factor, the activity and type of pathogen. One of the main causes of missed pregnancy is TORCH infections - toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus infection and herpes, which cause up to 90% of disorders in the pregnancy program.
3. Fetal death is also provoked by disharmonious immune relationships . Deformation of a chromosomal nature leads in 60% of non-developing pregnancies in the first 6 weeks, in 20% - at 15 weeks, in 4% - up to 28 weeks. The older a woman is, the greater the likelihood of developing a chromosomal abnormality.
4. Of no small importance are thromboembolic complications caused by blood clotting disorders in the expectant mother.
5. Hormonal imbalance - the basis for testing is the study of progesterone, testosterone, 17-KS, DGAES. Lack of progesterone and excess of androgens often provoke missed abortion. It happens that the texture of the endometrium, damaged by previous abortions, does not allow the fertilized egg to take hold. This deficiency is neutralized with the help of hormone therapy.
6. Anembryony is the absence of an embryo inside the egg, in which tests for hCG levels in urine and blood give a positive result. The hormone continues to produce the fertilized sac. The situation ends in miscarriage when the egg leaves the inner cavity of the uterus.
7. Bad habits. Practice shows that in the question of why pregnancy falters, drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking are not the least important. The risk of developing pathology is higher in people with bad habits.
8. Weight – exceeding the normal body weight index provokes a stop in the development of pregnancy. Being underweight has a similar effect.
9. Anomalies in the development of the uterus - pathologies in the structure of the organ, neoplasms, tumors provoke miscarriage.
10. Aggressive drug therapy - taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, contraceptives, hormones in the early stages can stop the normal development of the embryo.
11. Intoxication of the mother with chemicals , other harmful factors - unfavorable working conditions with an increased risk to health.
12. Chronic diseases of the hematopoietic , cardiovascular systems, kidneys.
13. Carrying several embryos - the risk of fading is higher than when carrying one fetus.
14. Carrying out IVF - the mechanism of termination of pregnancy is poorly understood, but it is known that artificial insemination more often follows a negative scenario.
15. Unknown factors. Doctors in the emergency departments of gynecological hospitals note a strange trend - the admission of women with frozen pregnancies is wave-like. The reasons have not been definitively identified, but the fact forms the statistics of observations of the pathological syndrome.
Among the provocateurs of frozen pregnancy, one can also note diabetes mellitus, increased physical activity of the mother, stress and depression. The 8th week is considered the most dangerous, when the fetus acutely perceives any teratogenic effects.
Risk factors
There are risk factors, the presence of which increases the likelihood of miscarriage. They can be uncontrollable (that is, they cannot be eliminated) or controlled (they can be eliminated or compensated). Uncontrollable factors include:
- Age. The older the woman, the higher the risk of pregnancy not developing.
- Severe stress.
Among the controlled factors:
- Previous abortions, miscarriages, missed pregnancies. The more there are, the higher the likelihood of fetal death;
- Wrong lifestyle. Bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol, caffeine abuse) and an unbalanced diet during pregnancy can negatively affect the condition of the fetus;
- Chronic diseases of women, both gynecological and pathologies of internal organs and systems (severe diseases of the cardiovascular system, liver and kidneys, diabetes mellitus, polycystic ovary syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus);
- ECO. For reasons that have not yet been identified, among the frozen pregnancies there are more those that occurred as a result of in vitro fertilization. In this case, the fetus usually dies before the 12th week;
- Diseases of the reproductive system in men;
- Multiple pregnancy;
- Significant deviations of a woman’s body mass index from the norm (too little weight or severe obesity);
- Exposure of the expectant mother’s body to toxic substances (for example, inhalation of fumes from hazardous industries);
- Taking certain anti-inflammatory drugs in early pregnancy. An expectant mother should definitely consult a doctor about any medication she plans to take.
Often the fading of pregnancy is provoked by several factors at once.
Alcohol and frozen pregnancy
For a long time, doctors have been arguing about the use of alcohol during pregnancy. Some allow slight deviations from the recommended rules, others categorically prohibit the consumption of alcoholic beverages, even in small doses.
Large doses of alcohol during pregnancy threaten:
- freezing of the embryo, cessation of its development;
- abnormal defects of the fetal heart muscle, underdevelopment of the brain;
- miscarriage, spontaneous abortion;
- premature birth;
- birth of a child at term with low weight.
It is a mistake to believe that beer labeled “non-alcoholic” bypasses the taboo imposed on alcohol and does not cause adverse reactions. Each composition released by modern manufacturers contains an alcohol-containing formula. The safety of the product due to the low concentration of the dangerous substance has not been scientifically proven, so including the drink in the list of prohibited items is the right step towards the birth of a healthy child. Recent studies have shown that in addition to beer, you should also abstain from kvass, which contains up to 2.6% alcohol.
Oksana Igorevna
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
Abortion and contraception clinic in St. Petersburg - department of the medical gynecological association "Diana"
Make an appointment, tests or ultrasound via the contact form or by calling +8 (812) 62-962-77. We work seven days a week from 09:00 to 21:00.
We are located in the Krasnogvardeisky district, next to the Novocherkasskaya, Ploshchad Alexander Nevsky and Ladozhskaya metro stations.
The minimum cost of a medical abortion in our clinic is 4,500 rubles. The price includes all pills, an examination by a gynecologist and an ultrasound to determine the timing of pregnancy.
Psychological causes of frozen pregnancy
Experts include the following as the main provocateurs of the condition:
- emotional instability, psychological and intellectual overload;
- family quarrels, nervous atmosphere at work;
- personality traits of a pregnant woman;
- psychological immaturity for the birth of a child, unpreparedness or unwillingness to give birth, to bind oneself to obligations, the bonds of motherhood;
- state of chronic, incessant stress, depressive psychoses.
Signs of a frozen pregnancy
The first signs of a frozen pregnancy can be noticed by listening to your own health. The following symptoms should cause caution :
- An abrupt cessation of toxicosis , if previously nausea and dizziness appeared with any foreign smell or movement.
- Softening the mammary glands , stopping their enlargement. After swelling and soreness, the breasts become resistant to mechanical stress. Separately, these signs of a frozen pregnancy do not mean anything. Many women note that a similar condition often occurs during normal, uncomplicated gestation.
- Decrease in basal body temperature . A decreasing level of progesterone provokes similar symptoms. Measurements are taken immediately after waking up through the rectum. However, this method is not a panacea. Third-party factors and accompanying phenomena can affect the decrease in temperature - sexual contact the day before, taking certain medications, maternal illness.
Additional symptoms may include increased body temperature, pain in the lower abdomen, and spotting. If freezing occurs late in pregnancy, the pregnant woman ceases to feel fetal movements. Warning symptoms do not always appear clearly. They can occur during normal development of the embryo, as well as during an ectopic pregnancy. Only a doctor can make a diagnosis after an examination.
Non-developing pregnancy is a complex of pathological symptoms, including intrauterine death of the fetus (embryo), pathological inertia of the myometrium and disorders of the hemostatic system.
SYNONYMS Frozen pregnancy, failed miscarriage, missed abortion. ICD-10 CODE O02.1 Failed miscarriage.
EPIDEMIOLOGY The rate of miscarriage in the population is 20%. In the structure of miscarriage, the frequency of habitual miscarriage ranges from 5% to 20%, and of non-developing pregnancy - 45–88.6% of the number of spontaneous miscarriages in the early stages PREVENTION OF FROZEN PREGNANCY Prevention consists of correcting disorders of the body's immunoreactivity according to the ELIP Test, restoring vaginal eubiosis microflora. In case of a hyporeactive state of the body, treatment of chronic inflammation is carried out according to traditional regimens: increasing immunoreactivity (prodigiosan), prescribing immunomodulators and interferon inducers. In case of a hyperreactive state, immunomodulators and plasmapheresis are prescribed. In order to normalize the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian system and restore hormone reception of the damaged endometrium, it is advisable to carry out hormone-corrective therapy. It is recommended to prescribe microdoses of combined oral contraceptives from the first day of termination of pregnancy for 6 months. CLASSIFICATION Based on ultrasound results, two types of non-developing pregnancy are distinguished: anembryony and death of the embryo (fetus). Echographically, anembryonia types I and II are distinguished. In type I anembryonia, the embryo is not visualized, the average diameter of the ovum does not exceed 2.0–2.5 cm, the size of the uterus corresponds to the 5–7th week of pregnancy. Of decisive diagnostic importance is the lag in the size of the uterus and ovum from the gestational age, the cessation of their growth during dynamic observation. In type II anembryony, despite the absence of an embryo or the visualization of its remains (usually in the form of a vertebral fold), the fertilized egg grows at a normal rate. By the 10–11th week of pregnancy, the diameter of the fetal egg reaches 4.5–5.5 cm. In type II anembryonia, the formation of the villous chorion, which is normally detected already from the 8th week of pregnancy, is not clearly visible. ETIOLOGY (CAUSES) OF FROZEN PREGNANCY A non-developing pregnancy is a polyetiological complication of pregnancy, the most common cause is chronic endometritis with the persistence of opportunistic microorganisms and/or viruses. It is known that with primary infection in the early stages of pregnancy, damage to the embryo is possible that is incompatible with life, leading to sporadic spontaneous miscarriage. In the majority of women with frozen pregnancy and chronic endometritis, a prevalence of two or three or more types of obligate anaerobic microorganisms and viruses is noted in the endometrium. But there are other possible factors that contribute to a non-developing pregnancy: · anatomical abnormalities; · chromosomal defects; · disorders of the blood coagulation system. Currently, genetic, immune, and thrombophilic factors, which are the least studied, are of greatest interest. Thrombophilic factors are genetically determined. The fertilized egg and the maternal body are a functionally unified hormonal system. The ability of the fetus to take an active part in the synthesis and metabolism of progesterone has been proven. With threatening miscarriage, these processes are disrupted. Progesterone deficiency leads to pathology of decidualization of the endometrial stroma, weak cytotrophoblast invasion and, as a consequence, a decrease in uteroplacental blood circulation. In case of miscarriage of the frozen pregnancy type, the fetal metabolism of progesterone ceases - an important distinguishing sign of frozen pregnancy from spontaneous abortion. Genetic factors include chromosomal abnormalities of the embryo or fetus, formed by the fusion of two parental cells with the presence of point mutations in the chromosome set. When studying material from miscarriages, the majority of detected chromosomal abnormalities are quantitative (95%). The shorter the gestational age at the time of death of the fertilized egg, the higher the frequency of chromosomal aberrations. In the presence of chromosomal aberrations, embryogenesis is impossible or severely impaired in the early stages. It is suggested that developmental disorders due to chromosomal aberrations are associated with a reduced ability of cells to divide. In this case, a sharp desynchronization of the processes of embryo development, placental development, induction of differentiation and cell migration occurs. Causes of quantitative chromosomal aberrations. · Failures of meiotic division: cases of non-disjunction of paired chromosomes, this leads to the appearance of monosomy or trisomy. Chromosome nondisjunction in eggs and sperm can occur at any period of meiotic division. · Failures that occur during fertilization: cases of fertilization of an egg by two sperm (dispermia), resulting in a triploid embryo. · Failures that occur during the first mitotic divisions: complete tetraploidy, which occurs during the first division of mitosis, leads to the duplication of chromosomes and the absence of separation of the cytoplasm. Mosaics occur in the event of similar failures at the stage of subsequent divisions. PATHOGENESIS The leading place in the etiology of frozen pregnancy is occupied by persistent viral bacterial infection. The pathogenesis of frozen pregnancy is based on chronic endometritis. During acute or chronic viral infection, local and general immunity is activated in the body. Increased synthesis of damaging cytokines and decreased synthesis of growth factors contribute to abnormal invasion and damage to the trophoblast in early pregnancy. Some viruses, such as human papillomavirus (HPV), CMV, infect the trophoblast and vascular endothelium, causing increased production of prothrombinase, which contributes to further destruction of the endothelium. At the same time, the protective mechanisms that contribute to the maintenance of pregnancy are disrupted: the expression of HLA-trophoblasts decreases, the secretion of growth factors decreases, and the TH-2 pathway of lymphocyte differentiation does not activate. A study of the species and quantitative composition of the microcenosis of the vagina and cervical canal revealed a connection between the dysbiotic state of these microecosystems and the persistence of opportunistic microorganisms in the endometrium. Viral diseases of the female genital organs, which develop against the background of immunodeficiency states, contribute to the development of complications in secondary immunodeficiencies. That is why the presence of a chronic viral infection is considered an important provoking factor in the development of chronic endometritis. The main reason for the chronic course of the inflammatory process is considered to be the inadequacy of antibacterial treatment due to the change in the etiological structure of infectious morbidity in recent years. The inflammatory process can develop as a result of activation of the normal microflora of the vagina, for example, when general or local immunity is weakened. An important role in the pathogenesis of frozen pregnancy is assigned to the cytokine system. With excessive deposition of circulating immune complexes in tissues, immunopathological processes occur, accompanied by pronounced disturbances in the microvasculature. In patients with a non-developing pregnancy, insufficient activity of lymphocytes and an imbalance of the cytokines they produce are observed. A shift in the balance leads to an increase in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, excessive manifestations of the inflammatory process, even with the persistence of the infectious agent. This disrupts the interaction of cells, as a result, implantation becomes incomplete, the depth of penetration is insufficient or excessive. The frequency of structural chromosomal aberrations in miscarriage material reaches 80%. Approximately half of the cases of these anomalies are inherited from parents, the other half of the cases arose de novo. The integrin heterodimer aV;b-3, which appears on the 20th day of the menstrual cycle and opens the “implantation window,” is of greatest importance for the implantation process. The appearance of the aV;b-3 heterodimer is due to the activation of growth factors HB-E-F (heparin-bindin- - rowth factor) and E-F (epidermal - rowth factor). The connection of the aV;b-3 heterodimer with the ligand osteopontin indicates the beginning of the interaction between the embryo and the endometrium, i.e. the beginning of the invasion. Progesterone stimulates the synthesis of osteopontin and the production of endometrial calcitonin, which increases the intracellular content of calcium ions. Calcium potentiates trophoblast adhesion to the endometrium, redistributing receptor protein molecules and their ligands. During a frozen pregnancy, the structure of the endometrium is disrupted - the ratio of the components of the extracellular matrix (collagen of different types) changes. The consequence of the Leiden mutation is a disruption of the functioning of the protein C system, which represents the most important natural anticoagulant pathway: protein C, while inactivating factor Va, does not affect it; activated factor V, combining with factor Xa on the phospholipid surface, accelerates the thrombin formation reaction tens of thousands of times, this leads to the development of thrombophilia. With APS, the mother's body produces and circulates in the blood antibodies (I-A, I-, I-M) to the phospholipids of platelet cell membranes, resulting in an imbalance of the blood anticoagulant system. The main manifestations of APS: arterial and venous thrombosis; · miscarriage; · infertility. Mechanisms of thrombophilia in APS: · violation of the prostacyclin–thromboxane A2 ratio; · changes in the content and activity of antithrombin III; · expression of endothelial procoagulants (tissue factor, von Willebrand factor, platelet activating factor); · disruption of protein C activation and development of resistance to it. The retention of an undeveloped fertilized egg or a dead fetus in the uterus affects the maternal body. Absorption of autolysis products of fetal egg tissue into the mother's bloodstream (due to increased permeability of the fetal membranes) disrupts the intravascular conditions of hemostasis. The long stay of a dead fertilized egg in the uterus significantly reduces the hemocoagulation activity of tissue and vascular factors of the placenta; this is caused by degenerative changes in the placental tissue. Prolonged exposure of the uterus to autolysis products reduces the contractility of the myometrium. Inertness of the uterus in NB is explained by a disturbance in the “mother-placenta-fetus” system. The uterus is deprived of a universal inhibitor of the initiation of contractile activity and elimination of pregnancy - the fetal endocrine factor. Inhibition of the contractile function of the uterus in this pathology is associated with regressive changes in the functional bioenergetics of the myometrium due to the lack of hormonal reinforcement from the fetus. In the classical hormonal chain of labor induction, key fetal links are missing - oxytocin, DHEAS, cortisol. CLINICAL PICTURE (SYMPTOMS) OF FROZEN PREGNANCY The clinical picture of a failed miscarriage has characteristic features. The patient's subjective signs of pregnancy disappear, the mammary glands decrease in size and become soft. Menstruation does not return. Fetal movement is not observed at the expected time. However, if fetal movements appear, they stop. When a dead fetus is retained in the uterus for more than 3–4 weeks, 10% of women report general malaise, weakness, dizziness, and increased body temperature. The disappearance of nausea, vomiting, and salivation are characteristic subjective signs of the death of the fertilized egg in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. In the second half of pregnancy, the woman notices the cessation of fetal movement. The symptom of softening of the mammary glands occurs 3–6 days after the death of the fetus. Instead of colostrum, milk appears in the mammary glands. Engorgement of the mammary glands and the release of a significant amount of colostrum are observed in women with fetal death that occurs after 25 weeks of development. Clinical signs of frozen pregnancy (pain, bleeding from the genital tract, lag in the size of the uterus from the expected gestational age) appear 2–6 weeks after the cessation of embryo development. The stages of termination of a non-developing pregnancy correspond to the stages of spontaneous abortion: · threatened miscarriage; · beginning miscarriage; · abortion in progress; · incomplete abortion. Complete abortion in cases of frozen pregnancy is not isolated due to pathogenetic reasons. DIAGNOSIS OF FROZEN PREGNANCY Early diagnosis of a non-developing pregnancy is of great practical importance, since it helps to reduce the time required for examining patients and reduces the risk of complications associated with the long stay of a dead fertilized egg in the uterine cavity. The diagnosis of a non-developing pregnancy is established on the basis of echographic examination data, identifying the absence of an embryo in the cavity of the ovum after 7 weeks of pregnancy or the absence of a heartbeat of the embryo. ANAMNESIS Risk factors for chronic endometritis are identified: a history of two or more medical abortions; sexually transmitted diseases, inflammatory diseases of the genital organs. It is necessary to carry out an ultrasound, analysis of AFP proteins, hCG at the most informative time. PHYSICAL EXAMINATION A decrease in cyanosis of the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix occurs 4–5 weeks after fetal death for up to 16 weeks of pregnancy and 6–8 weeks for fetal death at a later date. A decrease or lag in the uterus from its proper size is detected when the fetus dies before 20 weeks and especially before 12 weeks. In the early stages of pregnancy, this occurs as a result of resorption of the fertilized egg. For long periods - due to the absorption of organic matter, maceration and wrinkling of the fruit. A change in the consistency of the uterus, its hardening or softening is not considered a reliable symptom of a frozen pregnancy. The opening of the cervical canal in nulliparous women by 1–1.5 cm, and in those who have given birth by 3 cm or more, is observed when the dead fetus is retained in the uterine cavity from 12 to 20 weeks. In the event of fetal death at a period of more than 14 weeks and its presence in the uterine cavity for more than 4 weeks, when examining the uterus with the help of mirrors, thick brown mucus is detected from the cervical canal. When the amniotic sac is opened, brown substances are released. If the death of the fetus occurred after 30 weeks and it was in the uterus for more than 2 weeks, using the third method of external obstetric examination, crepitus, which occurs as a result of friction of the skull bones with each other, is determined. INSTRUMENTAL STUDIES Ultrasound is considered the most informative method for diagnosing a non-developing pregnancy, which makes it possible to identify a frozen pregnancy long before the appearance of clinical symptoms. With anembryonia, an “empty” fertilized egg is found, its diameter does not exceed 2.0–2.5 cm, and the size of the uterus corresponds to 5–7 weeks. pregnancy (anembryonic type I), absence of an embryo or visualization of its remains, taking into account the normal growth rate of the fetal egg from 10–11 weeks of pregnancy (anembryonic type II). Ultrasound makes it possible to determine the death of the fetus immediately after its death in the second and third trimesters. Signs of intrauterine fetal death detected on ultrasonograms. · Changes in the fetal head. — Imbibile-like overlap of the edges of the skull bones. — Divergence of the edges of the skull bones. - Flattening of the cranial vaults. - Asymmetry of the contours of the skull. — Disappearance of the contours of the head. - Dropping of the lower jaw. — On the 4th–5th day after the death of the fetus, the disappearance of the midline structures of the brain is noted. An important sign of the length of stay of a dead fetus in the uterus is the figures of the cranial index (Y) characteristic of this pathology: the ratio of the biparietal size (BPR) of the fetal head to the fronto-occipital size (LOS) x 100. Normally, it exceeds 83. When the dead fetus is retained in the uterus up to At 3 weeks the cranial index is 74–64, with a delay of more than 3 weeks - 64. · Changes in the spine. — Deviation of the fetal head at an angle. - Abnormal rotation and flexion of the head. - Excessive curvature of the spine in the form of kyphosis. — Pathological curvature of individual parts of the spine in the form of an arc or angle. — Sagittal straightening of the spine and disappearance of physiological curvature. — Changes in the skeletal bones and limbs of the fetus. — Change in the shape of the fetal chest. - “Scattering” of limbs. - Indistinct and blurry contours of the fetal skeleton. — Atypical position of the fetus in relation to the center of the uterus. · Other symptoms. — Discrepancy between the size of the fetus and the expected period of pregnancy. - “Crown” around the cranial bones. — Shadows from free gas in large vessels, heart cavities and fetal skull. It has been established that the shorter the gestational age (the second half of pregnancy is considered) at the time of fetal death and the length of its stay in the uterine cavity, the more severely the individual parts of the skeleton are changed. The degree of transformation does not depend on the nature of post-mortem changes and the cause of fetal death. Ultrasound placentography is of diagnostic and prognostic value during a frozen pregnancy, allowing one to determine the location of the placenta, its size, premature detachment of individual sections, changes in the form of cysts, infarctions, necrosis, calcification, etc. During a frozen pregnancy, the placenta has a pronounced lobulated structure due to increased calcification of the outer surface of the mother part. Laboratory studies in complex diagnostics as additional tests use the determination in the blood serum AFP, hCG and trophoblastic b-1-glycoprotein. At the death of the fetus, a high content of AFP (2–4 times higher than regulatory indicators) and a decrease in the level of trophoblastic b-1-glycoprotein (6–18 times) and hCG (3–9 times) are noted. Before termination of pregnancy, it is necessary to carefully control the hemostasis system to correct possible disorders. Immunospores of gravid proteins in blood serum · trophoblastic B-1-glycoprotein. -The trophoblastic B-1-glycoprotein is considered a specific marker of the fruit part of the placenta, it is synthesized by the cells of cytrophoblast and syncytiotropoblast. The trophoblastic B-1-glycoprotein has the function of transport protein and pronounced immunosuppressive properties. The detection of trophoblastic b-1-glycoprotein in the serum of pregnant women is possible on the 7-14th day after ovulation. In case of uncomplicated pregnancy, the concentration of trophoblastic b-1-glycoprotein in the blood serum increases from 10.4 ± 1.1 μg/ml of 6–12 weeks to 281.1 ± 4.8 μg/ml in 33–40 weeks. A decrease in the level of trophoblastic b-1-glycoprotein occurs immediately after the death of the fetal egg. A sharp decrease (in 4.3–8.6 times) is observed in pregnant women after 3 weeks of stay of the deceased fetus in the uterus. · Placent-specific A-1-microglobulin. -Placent-specific A-1-microglobulin secrete the decidual membrane, it is considered a specific marker of the maternal part of the placenta. With an increase in pregnancy, the concentration of A-1-microglobulin gradually increases from 21–25 weeks of pregnancy (81.35 ± 14.31 ng/ml), to 31–35 weeks decreases (60.13 ± 9.91 ng/ml) and Subsequently, it reaches the maximum values to 40 weeks of pregnancy (111.19 ± 6.13 ng/ml). In women with a frozen pregnancy, the concentration of protein in the blood serum is 2.5 times higher than the norm. The appearance of a high level of serum A-1-microglobulin is associated with the destructive process in the mother (decidual) part of the placenta, this explains the increase in the level of protein in the blood plasma. · AFP. - Determination of AFP plays an insignificant role in the diagnosis of an undeveloped pregnancy. The high concentration of protein in the blood serum indicates the intrauterine death of the fetus (embryo). The highest serum level of embryonic protein is marked 3-4 days after the death of the fetus (embryo). The high content of AFP in the mother’s blood (1.5-3 times higher than during a physiological pregnancy) is associated with its diffusion in OV and the bloodstream of the mother from the deceased embryo or fetus. · HCG. - HCG - a specific hormone of pregnancy, reflecting its development. Hormone products serves as an indicator of the normal activity of the trophoblast, the criterion of its functional activity. In a physiological pregnancy, primitive trophoblast begins to produce hCG 1 day after implantation. The concentration of the hormone reaches a maximum of 6-10 weeks of a normal pregnancy (116.01 ± 16.12 IU/ml), then decreases and increases again by 31–35 weeks (34.91 ± 7.36 IU/ml). - HCG concentration in blood serum in patients with a frozen pregnancy, compared with physiological pregnancy, 6-12 weeks lower by 8.6 times, 13–26 weeks - 3.3 times, 28–30 weeks - 28–30 weeks - at 2 , 7 times. - note a decrease in the level of pl (1.8–2.7 times), but in general it remains high. In patients with an undeveloped pregnancy, the concentration of progesterone in the blood remains at a relatively high level, and the estradiol content decreases sharply. The diagnostic value of the study increases with repeated definitions. In a cytochemical examination, the peculiarity of the leukocyte formula in women with a frozen pregnancy is an increase in monocytes, a decrease in basophils and eosinophils, an increase in ESR. Disorders of hemostasis with an uninhabited pregnancy Laboratory diagnosis of thrombogenic blood activity (intravascular hemostasis mechanism) many authors believe that bleeding occurring during artificial termination of pregnancy in women with intrauterine death of the fetus are caused by impaired vascular and plasma -aging levels of hemostasis, violation of the system of fibrinization. The intravascular conditions of hemostasis, with an undeveloped pregnancy, are studied comprehensively: biochemical and electrocoagulographic methods, while determining the time of blood coagulation, plasma recalcification, the activity of the prothrombin complex, the concentration of fibrinogen, the fibrinolytic activity of the blood, the retraction of blood clot, and the chronometric and structural coagulation are evaluated. The express diagnosis of DIA syndrome according to E.P. Ivanov’s test tube, constantly warming in his hand, is turned over every 30 sec. As soon as the blood stops flowing on the walls, the clot is fixed on the anchor, the time of blood coagulation is noted. Norma: 5-11 min. Hypercoagulation phase of the DIC: 2-4 min. Hypocoagulation:> 11 min. When the clotting is formed, the tube is fixed in an upright position for 1 hour. If a reddish-yellow transparent fluid with a volume of not more than 1–1.2 ml is released from the clot in the first 30 minutes, normal fibrinolysis and retraction. If the serum does not emit, the processes of retraction (thrombocytopenia) are sharply disturbed in the blood. If the clot in the first 30 minutes has dissolved significantly (1-2 ml) and the liquid phase in color differs little from the color of the blood clot, then fibrinolysis is increased in the blood. With A-hypofibrinogenemia and an increase in the anticoagulant properties of the blood, the time of coagulation is significantly lengthened (more than 15 minutes). To clarify the causes of this phenomenon, to 1 ml of blood, dry thromboplastin and 0.1 ml of a 10% solution of calcium chloride, a dense clot, indicates anticoagulant activation, are added to the tip of the scalpel. If the blood in the test tube does not curl up for more than 1-3 minutes, they state A - or hypofibrinogenemia, less often - hypergeeparinemia. To exclude hypergeepanemia, 0.1 ml of a 1% solution ofemans sulfate is added to the test tube. If after 1-2 mines the blood is curled up, this indicates the presence of hypocoagulation due to hypergeepinemia, the patient must intravenously introduce indemnity sulfate (1 ml of protramine sulfate neutralizes 1000 CRPs). The pathogenetic basis for the prevention of coagulopathic bleeding is considered to be eliminated by the direct cause of the activation of the hemostasis system (dead fetal egg), the relief of thrombinemia, a deficiency of components of blood coagulation and their inhibitors. Differential diagnosis of differential diagnostics is carried out with a miscarriage that has begun, trophy disease, an ectopic pregnancy, and menstrual disorders against the background of inflammatory processes of the internal genital organs. Indications for consulting other experts consulting other specialists are necessary if the patient has extragenital diseases. With severe deviations of hemostasis - a consultation of a hemostasiologist. An example of the diagnosis formulation is an undeveloped pregnancy of 8 weeks. Treatment of frozen pregnancy is the treatment of an unheated pregnancy in the evacuation of the deceased fetal egg and prescribing anti -inflammatory therapy. The purpose of treatment is the purpose of treatment is a gentle evacuation of the fetal egg, the fight against endometritis. Indications for hospitalization of hospitalization are subject to all patients with an established frozen pregnancy as soon as possible. Non -drug treatment of non -human treatment does not exist. Surgical treatment with frozen pregnancy up to 14–16 weeks of evacuation of the fetal egg is carried out simultaneously with the help of instrumental emptying of the uterine cavity, with the expansion of the cervical canal and curettage, or the vacuum aspiration is used. In both cases, hysteroscopic control is necessary. With hysteroscopy, the localization of the fetal egg, the condition of the endometrium are evaluated, then the fetal egg is removed with aiming the histological material from the placental bed and washing the uterine cavity with an antiseptic solution (Fig. 24-4, see coloring). According to indications, antibiotics are introduced. Medication treatment during an interruption of an undeveloped pregnancy in the II trimester uses: · intra -amanial administration by transcrivical or transvaginal amniocentesis of a 20% sodium chloride or PG solution; · The use of anti -progestagen in combination with PG; · Isolated use of pg. One of the most effective methods for emptying the uterus with antenatal death of the fetus is the intraamnal administration of drugs that launch labor. Apply the introduction of 50 dinstr and transabdominal access. An alternative scheme is considered a transabdominal amniocentesis with a derived of about 10 ml of water for each week of pregnancy and the introduction of a 20% sodium chloride solution at 1 week of pregnancy +10% of the calculated volume. This algorithm is applicable with a normal amount of EV. In multi -screen, it is recommended to administer a smaller amount of hypertension, compared with the resulting amount of water by 10-15%. With inaccurate, the amount of the injected solution may exceed the volume of the output fluid, but to amount to 10 ml for every week of pregnancy. When opening the fetal bladder, this method is appropriate. Manipulation is performed under UZ control. Contraindication is a suspicion of the adhesive process in the pelvis. The cure of the uterine cavity after 14-16 weeks in the absence of the remains of the fetal egg and signs of a systemic inflammatory response is inappropriate. Indications for consulting other specialists consulting a specialist is necessary in the development of coagulopathic complications, the presence of severe extragenital diseases. The approximate terms of disability incapacity for work 10-14 days depends on the severity of endometritis and coagulopathic disorders. Further conducting the effectiveness of treatment is evaluated by echographically. When using hysteroscopic control during the emptying of the uterine cavity, complications develop extremely rarely. Despite the position of the uterine Retroflexio, the cavity is not expanded, the thickness of the M-echo 3 mm. The position of the uterus is anteflexio, the cavity is expanded, m-echo is unfinished, up to 1.0 cm. Information for the patient, taking into account the low sympomicity and latency of endometritis, it is necessary to conduct a standard examination even in the absence of complaints: · microscopic examination of strokes; · Bacteriological examination; · PCR Diagnostics STPP; · Study of hormone levels; · Determination of the immunoreactivity of the body; · Determination of hemostasiogram; · Ultrasound of the pelvic organs. Medical agencies are recommended to pairs with a repeat of NB. The prognosis during rehabilitation therapy in the postoperative period pregnancy occurs in approximately 85% of cases, childbirth - in 70% of cases. Without recovery therapy - in 83 and 18%, respectively.
Diagnostics
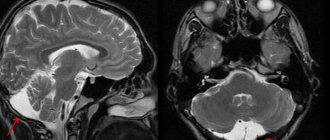
Tests after a frozen pregnancy should be taken with the mandatory inclusion of ultrasound in the list of studies - the most accurate diagnostic technology in this case. In addition to stating the fact of fetal death, the method will determine the period of developmental cessation.
Therapeutic treatment begins after diagnosis. If the pathology is confirmed, there are several response options:
- Expecting a miscarriage is a natural process for the body to rid itself of a foreign body. Ideally, the amniotic sac will be released completely with the embryo and amniotic fluid contained in it.
- Prescription of specialized drugs, the action of which is aimed at contracting the uterus and pushing out the dead fetus from the internal cavity. The method is applicable if the pregnancy did not last longer than 8 weeks.
- Surgery - intervention is carried out using different methods. These include gynecological cleansing and vacuum aspiration.
After the procedures, a control ultrasound is performed to assess whether the internal space of the uterus is completely cleared and whether there are any foreign tissues left in it that can cause inflammation and cause sepsis to develop.
Consequences
If a frozen pregnancy is detected in a timely manner, the risks to the woman’s health are minimal. Depending on the period, the patient may be referred for medical curettage or undergo drug therapy that causes uterine contractions and the birth of the fetus. This method (artificial birth) is used only in cases where the gestational age does not allow cleaning the uterine cavity.
It is mentally easier for a woman to endure the curettage procedure than giving birth to a stillborn child, but it is worth understanding that the second method is safer and allows you to minimize potential risks and maintain the health of the pelvic organs for carrying a new pregnancy.
Sometimes it happens that a woman carries a dead fetus for several weeks without even knowing it. In such situations, there is a high probability of severe intoxication, since the fetal body begins to decompose directly in the uterus, releasing toxins and dangerous substances. This condition can result in the death of a woman, so it is important to visit an obstetrician or gynecologist on time and not miss scheduled examinations.
The death of the patient can be caused by severe complications that occur if the dead fetus is inside for more than 3-4 weeks, for example:
- blood poisoning;
- infection of internal organs;
- disseminated intravascular coagulation;
- uterine bleeding.
Gynecological cleansing
Several weeks may pass from the moment the fetus dies until it is rejected by the uterus. The remaining traces of the deceased embryo provoke the development of the inflammatory process, bleeding and other complications. To eliminate risks, doctors recommend undergoing gynecological cleansing.
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia and usually takes about 15-20 minutes. In rare cases, complications may occur. The obtained tissue samples are sent to the laboratory for histological analysis. Genetic testing helps determine the cause of miscarriage. Histology determines the presence or absence of atypical cells in the uterus.
Vacuum aspiration
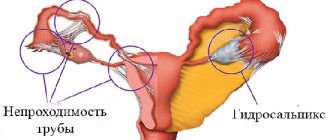
In addition to curettage, a vacuum aspiration method can be performed, which allows you to get rid of the remains of the embryo in a more delicate way. Indications for the procedure are:
- period no more than 12 weeks;
- confirmation of a frozen pregnancy using additional examination methods;
- incomplete exit of parts of the embryo from the uterus, the presence of foreign elements in the organ;
- threat to the mother's life or risk of developing fetal pathology;
- lag of placental tissue at the time of childbirth, when its remains are found in the uterine cavity;
- accumulation of blood clots or fluid in the uterus;
- the need for a biopsy.
The procedure is not relevant::
- with inflammatory processes developing in the uterus;
- to neutralize the risks of ectopic pregnancy;
- if there are changes in the uterus due to neoplasms or tumor.
The method is also not recommended if the period after the previous abortion does not exceed six months.
Aspiration is carried out in several ways:
- Under intravenous anesthesia with vacuum . The technology is not practiced beyond 4 weeks of pregnancy.
- Under local anesthesia with manual vacuum . Used up to 12 weeks of pregnancy.
Before aspiration, it is necessary to undergo a visual examination by a specialist, take recommended tests, and a smear to determine the microflora. Examination methods include ultrasound, blood and urine tests, tests for hidden infections in the body. Consultation with a therapist is mandatory.
The consequences of aspiration can be complicated by:
- menstrual irregularities;
- disruptions in the hormonal system;
- incomplete cleansing of the uterine cavity.
For a month after the procedure, you should refrain from sexual intercourse, visiting the bathhouse, and staying in the sun. It is not recommended to take a bath or go to the pool. Medicines should be taken in accordance with the schedule drawn up by a specialist.
Antispasmodics are prescribed to neutralize pain. You should not be active or engage in physical labor for 24 hours after surgery, as exertion may cause bleeding. Painful sensations in the lower abdomen and lumbar region may persist for several days.
Immediate consultation with a doctor is required if:
- a sharp increase in body temperature;
- continuous heavy discharge;
- pain, which even taking potent medications cannot relieve;
- unusual strong odor from the genitals.
Frozen pregnancy, the causes and consequences of which negatively affect the emotional background of the mother who has lost her child, also occurs in completely healthy couples. In the West, the practice of a thorough examination is recommended only after the third repetition of fetal growth arrest in the womb. As for the tests after an anomaly has occurred, the list is quite extensive: OBC, OAM, blood for hormone levels, smear for microflora, research for hidden sexually transmitted infections, tests for TORCH infections, transvaginal ultrasound. If necessary, the list can be supplemented with other diagnostic procedures. It is recommended to obtain advice from a geneticist, endocrinologist and immunologist.
What it is?
A frozen pregnancy is a pregnancy that initially complied with all medical standards, but at a certain period suddenly stopped developing. The cessation of progress in the development of the fetus leads to its death, but it remains in the uterine cavity. For this reason, this pathology is called a failed miscarriage.
In fact, at the very beginning everything happens, as in a normal pregnancy - the egg is fertilized, enters the uterus and is implanted for further development, but at one moment it stops. This pathology also includes “empty ovum” syndrome. It represents the development of membranes in which there is no embryo. With this syndrome, a pregnancy test is positive, as well as an hCG test.
Planning a new conception
The chances of a normal second pregnancy after the embryo died the previous time are high. The main thing is to listen to the doctor’s recommendations and follow the instructions given by the specialist. The majority of gynecologists have the same opinion - a new pregnancy should be planned no earlier than three to four months after the miscarriage. During this period, the woman’s body recovers, gains strength and accumulates positive potential. Hormonal levels are stabilized, and the stress factor from experienced unrest is reduced.
Before conception, the specialist advises the use of hormonal birth control pills, which prevent the risk of pregnancy at an unplanned period. By taking oral medications, a woman unloads the ovaries, giving them additional rest. Stopping OC increases the chances of egg fertilization. Three months after a frozen pregnancy, it is recommended to start taking folic acid.
The chances of successful delivery are also high if pregnancy occurs immediately after the fetus freezes in the womb. To reduce the risk of miscarriages in this situation, specialized therapy should be indicated based on the recommendations of a good specialist in the field of gynecology.
How to reduce the likelihood of fading?
Unfortunately, it is impossible to guarantee the absolute viability of the fetus, especially in the early stages. But it is possible to exclude factors that increase the likelihood of spontaneous abortions and death. To do this you need:
- prepare for conception in six months, strengthening the immune system, cleansing the body;
- quit smoking, taking alcohol, strong drugs;
- do not use medications for thrush containing introconazole), analgesics, cosmetics containing retinoids;
- take folic acid, iodine preparations and other vitamins.
Prevention of frozen pregnancy and other complications during pregnancy includes a targeted examination for the presence in the body of herpes, HPV, mycoplasma and other hidden infections that are dangerous to the embryo. Planning for the birth of a child, preparation and prevention greatly increases the chances of bearing and giving birth to a healthy child.
Along with risk factors, expectant mothers should know that for the fetus, if the pregnancy proceeds without deviations, air travel after 12 weeks, moderate physical activity, and sex with a spouse are not dangerous.
Folic acid (B9)
It has been proven that taking vitamin B9 a month before conception and the first three months after it reduces the risk of embryo development abnormalities by 50%. It is required at the planning stage of pregnancy and at the moment of its conception in the body. The daily dose of the drug should be 400-800 mcg. Some women limit themselves to taking multivitamins, forgetting to evaluate the folic acid content in them. The dosage is determined by the attending physician based on the situation, the health of the pregnant woman, and the characteristics of her body. Additionally, it is recommended to include spinach, citrus fruits, broccoli and cabbage, kiwi, and strawberries in your diet.
Do not be afraid of exceeding the dose of vitamin in the body. It has a water-soluble base, so it is easily excreted along with urine. However, cases of overdose were still noted in medical statistics.
A doctor’s prescription of an increased B9 standard is justified in the following cases:
- if the mother already has a child with an abnormality of the nervous system;
- if you are overweight;
- while taking anticonvulsants;
- with anemia detected as a result of blood tests, which is caused by a lack of folic acid in the body.
The dose of the drug in these cases can be increased to 5000 mcg.
How to prevent a frozen pregnancy - causes and consequences of the threat
Having analyzed the causes of the pathological condition and the threats it poses to health, the doctor draws up an individual observation protocol.
General recommendations include:
- Contacting a gynecologist at the planning stage, receiving consultations from a geneticist, endocrinologist, immunologist, taking tests and undergoing specialized examinations.
- Quitting bad habits, smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages.
- A balanced diet that includes healthy vitamins and microelements in the food you eat. Exclusion from the diet of semi-finished products, fast food, exotic cuisine, large amounts of coffee and strong tea.
- Exclusion from the list of certain categories of medicines that the doctor will tell you about. Among the prohibited drugs is aspirin, which can be painlessly replaced with paracetamol.
Summarizing the above, we should once again briefly dwell on the main postulates:
1. When does it occur? A frozen pregnancy can occur at any stage of embryo development, but most often in the first trimester.
2. Why is this happening? Disorders that occur in the early stages of fetal development include hormonal imbalance, infectious processes, menstrual irregularities, and genetic changes. This may be caused by chromosomal abnormalities or the fact of a blood connection, when the father and mother are related. Nature itself applies the filter of natural selection, rejecting non-viable fruit and provoking its death. The risk of embryo failure increases if a woman with a negative Rh factor has had several abortions before the desired pregnancy occurs. According to statistics, abortions often become a kind of harbinger of pathology. They grossly disrupt hormonal status and cause trauma to the uterus and infection of the cervix. At a later stage, frozen pregnancy often occurs due to a chronic illness of the mother, which occurs in a severe form - diabetes mellitus, heart muscle defect, kidney disease. The threat can be reduced if treatment is started at the planning stage.
3. What should you be wary of? Pain in the lower back and abdomen, spotting of blood, a decrease in basal temperature, and a lack of dynamics in the growth of hCG should cause concern for the child’s well-being. If during pregnancy you felt toxicosis, dizziness, nausea and other similar symptoms, followed by their rapid disappearance, this is a good reason to be wary and visit a gynecologist with complaints. The doctor will conduct an examination on a gynecological chair and, if necessary, send you for ultrasound diagnostics. Another symptom that characterizes a frozen pregnancy is the cessation of swelling of the mammary glands.
4. Why is a frozen pregnancy dangerous? If the female body “pushed” an embryo with a fertilized egg and waters through the birth canal after development had stopped, this is good. Soon the organs of the reproductive system will return to normal, gain strength and be ready for a new conception. If this does not happen, you should undergo an ultrasound to record the remaining material in the uterine cavity. To remove them, the method of curettage and vacuum aspiration is used. Waiting tactics can also be used, in which the body will miscarry some time after the pregnancy has died. To release the remains of the embryo and membranes, medications are also used, the action of which is aimed at contracting the walls of the uterus. Early consultation with a doctor eliminates the risk of complications. If the fetal sac remains in the uterus for a long time, blood loss may develop, caused by disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, when the blood stops clotting and excessive blood flow poses a threat to life.
5. What are the prospects? After what happened, it is important not to give up, but to do everything necessary to ensure that the next pregnancy ends in a successful birth. Visit a doctor, undergo the recommended examinations, eliminate dangerous factors, take care of yourself, get yourself in order physically and psychologically. Get advice from a geneticist, endocrinologist and immunologist. A powerful medical tandem will reduce the likelihood of errors when planning a new pregnancy.
Why is fetal freezing dangerous and what to do if it happens?
When diagnosing a frozen pregnancy, you cannot hesitate; the fetus must be removed as soon as possible. If this is not done, the following complications are guaranteed:
- Intoxication (severe poisoning)
. The tissues of the dead embryo begin to disintegrate, and the decay products are immediately absorbed into the woman’s blood. - Blood clotting disorder.
- Inflammation of the uterus and nearby organs.
Severe inflammation will lead to infertility, and if sepsis (purulent infection) begins, the uterus will have to be removed.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, you need to undergo a course of treatment to eliminate the missed abortion and undergo diagnostics to identify the causes of the pathology - this will protect against relapses in the future.