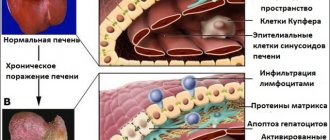
Hepatitis is an inflammatory disease that affects cells and liver tissue. The disease is caused by viruses and infections; all age categories of people are at risk of infection.
There are many forms of this liver pathology, which can be diagnosed using a blood test. Depending on the manifestation of symptoms and the nature of the disease, acute and chronic stages of hepatitis are distinguished. The first option, with proper treatment, can be cured quite quickly, but the chronic stage, without proper therapy, develops into cirrhosis of the liver.
Types of hepatitis
Not only viruses, but also parasitic microorganisms, pharmacological agents toxic to the liver, as well as a malfunction of the immune system can provoke the development of hepatitis. Depending on the nature of origin, renal anomalies are divided into five types.
Variations of hepatitis:
- Botkin's disease (A) is the most common type of disease. It is characterized by a long incubation period from 7 to 50 days. A patient who has recovered from this form of hepatitis develops immunity to all other types. B (HBV) - has a 10% permanent threshold. Symptoms may be similar to acute respiratory infections. The incubation period of the virus is about 2-3 months.
- C (HCV) – in 80% of cases the anomaly becomes chronic. Symptoms appear after a week, sometimes after 3 months. The disease can be combined with other types of hepatitis. There is no vaccine for this type of kidney pathology.
- D (HDV) – often develops simultaneously with hepatitis B, the disease severely affects the liver. The latency of the disease is up to 7 weeks.
- E (HEV) - this type of hepatitis is extremely dangerous for pregnant women. In most cases it is fatal. Residents of Africa and Central Asian countries are at risk.
Any variation of hepatitis is dangerous to health and requires proper treatment. Timely vaccination will help avoid the consequences of liver diseases.
Treatment
The infection is most difficult for the elderly and children under one year of age. The average duration of the disease is about 40 days, but this can be influenced by many factors, such as age, immune status, and following doctor’s recommendations. Chronic hepatitis A develops in 15% of cases, and then the disease can last up to 6-9 months. In addition, there is a small risk of death.
In fact, with a mild form of the disease, the body is able to fight the infection on its own. Treatment is carried out to provide liver cells with energy, materials for subsequent restoration and reduction of toxin levels. Vitamins, glucose, and detoxification solutions are administered to dilute the blood containing toxins; hepatoprotectors that protect liver cells. At the same time, symptomatic treatment of the disease is prescribed. During the acute phase of the disease, it is necessary to adhere to a special diet and be in a state of mental and physical rest.
Prevention of hepatitis A involves regular hand washing after caring for an infant, going to the bathroom or toilet, and before preparing and eating food. Vaccination of the population is of great importance.
Causes and methods of infection with hepatitis
Botkin's disease is transmitted through household contact with household items, dirty hands and unwashed foods; in general, it has a fecal-oral route of transmission. Hepatitis A goes away quickly and without noticeable consequences. Other variations of the disease belong to the parenteral group (C, D, and so on); they may not manifest themselves for a long time, but subsequently torment a person throughout his life, contributing to the development of cirrhosis or even liver cancer. Transmitted mainly through blood during transfusion.
Methods of infection with hepatitis:
- Intrauterine route - transmitted from mother to fetus.
- The use of one syringe by many people is the main way of infecting drug addicts.
- Sexual intercourse is how hepatitis B is mainly transmitted.
- If non-sterile instruments were used during ear piercing or tattooing.
- Impact of toxic substances on the body, etc.
The symptoms of each variant of hepatitis are different; almost always the patient feels fatigue, a headache may appear and the temperature may rise. During the progression of Botkin's disease and other types of illness, yellowness of the skin occurs. A blood test helps identify the disease.
How do you get infected with the hepatitis C virus?
The virus is transmitted through blood. You can become infected with the virus through tattooing, piercing, visiting a manicure salon, medical manipulations with blood, including blood transfusions, administering blood products, operations, or at a dentist appointment. Infection is also possible through shared use of toothbrushes, razors, and manicure accessories. Read more…
Sexual transmission is rare, as is transmission of the virus from the mother during pregnancy. Breastfeeding is not prohibited if you have hepatitis C, but you should be careful if blood appears on your nipples.
It is impossible to become infected with the hepatitis C virus through household contacts. The virus is not transmitted by airborne droplets, shaking hands, hugging or using shared utensils. Patients with viral hepatitis C do not need isolation and do not pose a danger to others. In Russia, however, they are exempt from military conscription.
up
Norms of blood tests for hepatitis
Diagnosis of hepatitis primarily consists of examining the patient’s blood; a general analysis and examination of the level of enzymes, antibodies and antigens are required.
Standards and deviations:
- Hepatitis A - blood is tested for the presence of IgG antibodies, the indicator should be less than 1 S/CO. Deviations from the norm indicate the presence of a virus or a previous illness.
- B – there should be no LgM virus antibodies in the blood; a positive result confirms the diagnosis of hepatitis.
- C – the ELISA method is used for diagnosis. If the results contain antibodies to the HCV virus, a repeat test is performed; if the test is positive, the diagnosis is confirmed.
- D – the algorithm for conducting a blood test is similar to the previous option.
During a blood test for non-viral hepatitis, an examination is carried out for bilirubin (normal 5-21 µmol/l), fibrinogen, total protein and other indicators.
To detect the disease you need to undergo special tests. For hepatitis B, this is the determination of surface antigen (HBsAg). For hepatitis C - for antibodies to the hepatitis C virus (anti-HCV). These tests are included in the compulsory medical insurance program and can be taken free of charge after receiving a referral from a local physician.
If a surface antigen (HBsAg) is detected in your blood, it means you have chronic viral hepatitis B.
If antibodies to the hepatitis C virus are found in your blood, it means that your body has once encountered the hepatitis C virus, but it does not yet know that you have chronic viral hepatitis C. To make a diagnosis, you need to take a qualitative test (PCR), which determines the presence of hepatitis C virus in the blood.
What are the symptoms of chronic hepatitis?
Chronic hepatitis has no specific symptoms. You can suffer from chronic viral hepatitis for years and not suspect it.
Therefore, it is important to get tested periodically.
How often should you be tested for hepatitis?
Since chronic viral hepatitis occurs with virtually no symptoms, it makes sense to get checked regularly.
Like many diseases, hepatitis has a so-called “incubation period,” so you need to get tested not immediately after a potentially dangerous event, but several weeks later.
What is the incubation period?
The incubation period is the time when the infection is already in the body, but the body has not yet responded to it. During the incubation period, an infected person not only has no specific symptoms of the disease, but even standard indicators for HBsAg and anti-HCV have not yet been determined.
The incubation period for various hepatitis lasts from 2 weeks to six months.
Is it possible to detect hepatitis during the incubation period?
Yes. There are tests that directly record the presence of the virus in the blood (RNA of the hepatitis C virus and DNA of the hepatitis B virus). But in clinics and antenatal clinics they are usually referred for standard tests included in compulsory medical insurance: HBsAg and anti-HCV, which appear in the blood later than the virus itself.
What should I do if I test positive for HBsAg and anti-HCV?
A positive HBsAg test indicates that you have hepatitis B.
The presence of anti-HCV in the blood indicates that your body has encountered the hepatitis C virus. But this does not mean that you are currently suffering from hepatitis C.
Further examination is required. It is best to immediately contact a hepatologist who will tell you what to do.
What is a false positive result?
Sometimes, if you violate the rules for taking tests (for example, if you were not tested on an empty stomach), during pregnancy, or with serious illnesses that affect the immune system, a hepatitis test may show a false result.
But there is no need to hope for a test error. It is better to immediately contact a specialist who will determine whether you had conditions for obtaining a false positive result and prescribe the correct tests for verification.
Further testing confirmed that I have hepatitis, but I don’t feel anything unusual...
Most often, the patient does not feel any special “symptoms of hepatitis”.
What are extrahepatic symptoms?
As a result of chronic hepatitis, not only the liver, but also other organs suffer. Most often - kidneys and skin, less often - muscles, heart, nervous tissue.
Extrahepatic symptoms appear quite rarely, but attract more attention as they greatly affect the quality of life. Unfortunately, their true cause - chronic viral hepatitis - may remain out of sight and without treatment.
| < Previous | Next > |
Preparing for and taking a blood test for hepatitis
A few days before the test, you need to give up alcohol, go on a diet, eliminating spicy, fatty, and fried foods from your diet. Blood is drawn from a vein strictly on an empty stomach; you can only drink clean still water. If the patient uses pharmacological drugs, he must notify the doctor about this.
To take a blood test for hepatitis, contact the President-Med medical centers in Moscow and Vidnoye
3. Examination to prescribe therapy for viral hepatitis B and C
Examination for prescribing antiviral therapy for viral hepatitis C
- Complete examination of the hepatitis C virus (genotype and viral load);
- Tests for hepatitis B virus in order to get vaccinated, if test results allow;
- Complete examination of the liver: biochemical tests reflecting the structural and functional state of the liver cells, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity with Dopplerography, assessment of the degree of fibrosis (Elastometry, FibroMax, fibrotest);
- Tests to exclude contraindications for prescribing therapy: clinical blood test, hormones and ultrasound of the thyroid gland, autoimmune antibodies;
- For patients over 40 years of age, examination of the heart, blood vessels and respiratory system is prescribed.
The cost of the examination is 30,000 rubles.
(may change if you have already had tests done, or if you need other tests in addition to the standard examination).
Examination for prescribing antiviral therapy for viral hepatitis B
- Complete examination of the hepatitis B virus: all enzyme-linked immunosorbent parameters, as well as PCR analysis with viral load;
- Delta virus analysis;
- Complete examination of the liver: biochemical tests reflecting the structural and functional state of the liver cells, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity with Dopplerography, assessment of the degree of fibrosis (Elastometry, FibroMax, fibrotest);
- Clinical blood test;
- Analysis for B virus mutation and drug resistance.
The cost of the examination is 28,500 rubles
. (may change if you have already had tests done, or if you need other tests in addition to the standard examination).
What is special about the hepatitis C virus?
After the virus enters the human body, it enters the liver through the bloodstream, infects liver cells and multiplies there.
The hepatitis C virus is characterized by genetic variability and the ability to mutate. There are 6 main genotypes of the virus and more than 40 subtypes. This is why the virus often manages to “deceive” the immune system, which leads to the development of chronic viral hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is one of the main reasons leading to liver transplantation, which is why it is better not to delay its treatment.
up