- What is viral hepatitis C
- Prevalence of viral hepatitis C
- How do you get infected with the hepatitis C virus?
- Hepatitis C virus testing
- What is special about the hepatitis C virus?
- How does hepatitis C occur?
- When do signs and symptoms of hepatitis C appear?
- What period after infection must pass for laboratory markers of viral hepatitis C to appear in tests?
- Can viral hepatitis C be cured?
- Where to start treatment?
- Which doctors treat hepatitis C?
- When to start treatment?
- Is it possible not to treat viral hepatitis C?
- Modern methods of treating viral hepatitis C
- Hepatitis S/C (Video - interview with B.L. Lurie)
What is viral hepatitis C, how does it manifest, why is it dangerous?
How is the virus transmitted and can hepatitis C be cured? Which doctors treat and where to start treatment? Hepatitis C
(
Hepatitis C Virus
) is an inflammatory liver disease caused by the HCV virus (Hepatitis C Virus). The disease can occur in both acute and chronic forms. Chronic viral hepatitis C, for many years, occurs without symptoms, which makes the disease especially dangerous. The HCV virus uses healthy liver cells to replicate, causing the cells to be destroyed and replaced with fibrous tissue. Without treatment for hepatitis C, the likelihood of developing the worst consequences, such as cirrhosis and liver cancer, increases dramatically. That is why it is so important to promptly identify the disease and begin therapy. Modern antiviral drugs can cure hepatitis C completely.
Symptoms of hepatitis C
The disease is most often asymptomatic, but some nonspecific manifestations are possible:
- fatigue, increased fatigue;
- nausea, loss of appetite.
- heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- joint pain;
- sleep disorders;
- skin itching.
up
How do you get infected with the hepatitis C virus?
The virus is transmitted through blood. You can become infected with the virus through tattooing, piercing, visiting a manicure salon, medical manipulations with blood, including blood transfusions, administering blood products, operations, or at a dentist appointment. Infection is also possible through shared use of toothbrushes, razors, and manicure accessories. Read more…
Sexual transmission is rare, as is transmission of the virus from the mother during pregnancy. Breastfeeding is not prohibited if you have hepatitis C, but you should be careful if blood appears on your nipples.
It is impossible to become infected with the hepatitis C virus through household contacts. The virus is not transmitted by airborne droplets, shaking hands, hugging or using shared utensils. Patients with viral hepatitis C do not need isolation and do not pose a danger to others. In Russia, however, they are exempt from military conscription.
up
Symptoms
The incubation period for hepatitis C can range from 2 weeks to 12 months. As noted above, the disease is often asymptomatic.
The disease may be accompanied by symptoms such as headache, decreased appetite, severe weakness and drowsiness. But most people perceive such symptoms as manifestations of physical or emotional stress, so they often go unnoticed.
Sometimes hepatitis is manifested by increased body temperature, yellowing of the skin, discoloration of stool, darkening of urine and digestive disorders.
Hepatitis C virus testing
To determine the hepatitis C virus in the blood, it is necessary to take an Anti-HCV antibody test, which shows whether there has ever been contact with the virus. The cost of analysis is 550 rubles
.
- Anti-HCV - negative - no contact
- Anti-HCV - positive - there was contact
The presence of antibodies does not mean the presence of the virus in the blood, and if the Anti-HCV result is positive, a PCR analysis of HCV-RNA is done
, based on the results of which we determine whether the hepatitis C virus is present in the blood.
The cost of the analysis is 750 rubles
.
Sign up for a free consultation to schedule an examination. ANONYMOUSLY.
You can get tested:
- from 9:00 to 17:30 on weekdays
- from 9:00 to 15:00 on Saturday
Sign up by phone
+7
Seven days a week from 9:00 to 21:00
Request a call back
up
Preventive actions
There is currently no vaccine against hepatitis C, so nonspecific prophylaxis is the only way to protect yourself from HVC infection. To prevent the development of such a disease, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- when visiting medical institutions and beauty salons, monitor the sterility of the instruments used;
- stop taking drugs;
- have one healthy sexual partner, otherwise use a condom (it must be taken into account that this contraceptive does not provide reliable protection against the penetration of HVC into the body);
- Do not use other people’s personal hygiene items - razors, combs, towels, etc.
In addition, it is necessary to carry out health education work so that people know almost everything about hepatitis, especially where you can get infected and how to protect yourself from the disease.
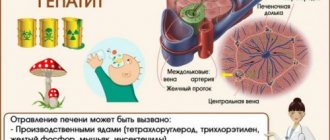
What is special about the hepatitis C virus?
After the virus enters the human body, it enters the liver through the bloodstream, infects liver cells and multiplies there.
The hepatitis C virus is characterized by genetic variability and the ability to mutate. There are 6 main genotypes of the virus and more than 40 subtypes. This is why the virus often manages to “deceive” the immune system, which leads to the development of chronic viral hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is one of the main reasons leading to liver transplantation, which is why it is better not to delay its treatment.
up
WHO activities
In May 2021, the World Health Assembly adopted the first Global Health Sector Strategy on Viral Hepatitis 2016–2021. It highlights the critical role of universal health coverage and aligns the strategy's objectives with those of the Sustainable Development Goals. The main goal of the strategy is to eliminate viral hepatitis as a public health problem. This is reflected in global targets to reduce the number of new cases of viral hepatitis infection by 90% and mortality from viral hepatitis by 65% by 2030. The strategy sets out the measures that countries and the WHO Secretariat must take to achieve these goals.
To support countries in achieving global hepatitis targets under the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, WHO is working in the following areas:
- raising awareness, facilitating partnerships and mobilizing resources;
- developing evidence-based policy and collecting data to inform action;
- improving health equity in the hepatitis response;
- prevention of transmission of infection;
- expanding coverage of screening, care and treatment services.
Since 2011, WHO has worked with countries, civil society and partners to organize annual events to mark World Hepatitis Day (one of the nine major annual health campaigns) to raise awareness and understanding of the virus. hepatitis A. This day is held on July 28 to honor the birthday of Nobel Prize-winning scientist Dr. Baruch Blumberg, who discovered the hepatitis B virus and developed a diagnostic test and vaccine against the virus.
In 2021, WHO is celebrating World Hepatitis Day under the theme “The fight against hepatitis can't wait” to highlight the urgency of eliminating hepatitis in order to achieve the goals by 2030. Key messages relate to the latest estimates of the burden of viral hepatitis and mortality from viral hepatitis at global and regional levels, and the need to ensure that hepatitis is certified as a public health threat by 2030. In addition, recommendations and guidance on self-testing for hepatitis C have recently been published and are expected to support increased testing coverage among key and vulnerable people. population groups, as well as groups with a high burden of HCV infection.
How does hepatitis C occur?
There are two forms of hepatitis C virus: acute and chronic. The acute form is most often asymptomatic and is diagnosed only by chance when markers of acute hepatitis C are detected in the blood - anti-HCV-IgM, which remains in the blood for no more than 6 months after infection with the virus.
After suffering from acute viral hepatitis C, there are three possible scenarios:
- About 20% of patients experience complete recovery;
- In 20% of patients, inactive chronic viral hepatitis C develops with the absence of laboratory markers of the inflammatory process in the liver;
- The remaining 60% have chronic hepatitis with clinical and laboratory manifestations of liver damage.
The transition of the disease to a chronic form occurs unnoticed. Liver damage increases over the years and the patient develops liver fibrosis with subsequent liver dysfunction. The disease progresses slowly over years. In patients with active hepatitis, the risk of developing cirrhosis within 20 years reaches 20%, of which 5% develop liver cancer.
up
How to legally import unregistered medicine into Russia
Polina Naydenkova lawyer in the field of pharmacology and medicine
There are two legal ways to buy the drug abroad: simple and complex.
Downtime is when the patient himself brings it in his luggage for his treatment. This option cannot be implemented by power of attorney; only legal representatives - parents and guardians - can transport medications. Obviously, not every patient and does not always have such an opportunity - this is a disadvantage of this method. In addition, this method is only suitable for drugs registered in the Russian Federation - you can check the availability of registration through the State Register of Medicines. However, if the drug is a prescription drug, you will need a prescription from your doctor to transport it.
The difficult way is to import it under a special permit issued by the Russian Ministry of Health. Under this permit, medications can be transported not only in person, but also by post.
To obtain such permission, you need to submit a package of documents to the Russian Ministry of Health:
- Protocol of the consultation of a federal specialized medical organization or institution of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences or an institution of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation in which medical care is provided to a specific patient. This protocol must indicate the need to prescribe the drug for health reasons, and such a need for which the prescription of a drug registered in the Russian Federation is impossible. The protocol is signed by the chief physician of the institution.
- An appeal from the regional health authority about the need to import an unregistered drug, accompanied by a copy of the council’s conclusion.
- An electronic copy of the passport or birth certificate of the patient who is prescribed the drug, certified not by a notary, but certainly by the medical institution providing medical care.
- Application for obtaining permission to import into the territory of the Russian Federation an unregistered medicinal product necessary to provide medical care for the vital indications of a particular patient. The application form was approved by the Russian Ministry of Health.
All this - both on paper and at the same time in the form of an electronic document - is submitted to the address and to the Russian Ministry of Health. The Russian Ministry of Health will review the documents and make a decision within one week. Such an application is not subject to state duty.
Violation of the rules for the import of drugs unregistered in the Russian Federation is subject to administrative and criminal liability. If a medicine is not registered in Russia, and there are no documents confirming the right of a specific individual to receive it, government agencies recognize it as falsified or of poor quality.
According to Art. 6.33 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, illegal import of unregistered medicines into the territory of the Russian Federation entails the imposition of an administrative fine on a citizen in the amount of 70,000 to 100,000 RUR.
If the state sees in the actions of an individual a sales goal - this depends on the size of the batch of imported drugs - liability is threatened in the form of imprisonment for a term of 3 to 5 years.
Where to start treatment?
From the examination.
A standard examination provides complete information about the virus, its genotype and viral load, as well as a detailed picture of the condition of the liver. For this purpose, biochemical blood tests are carried out to determine the structural and functional state of the liver cells, ultrasound, and assessment of the degree of fibrosis (using the Fibroscan, FibroMax, Fibrotest methods).
You can get tested:
- from 9:00 to 17:30 on weekdays
- from 9:00 to 15:00 on Saturday
Sign up by phone
+7
Seven days a week from 9:00 to 21:00
Request a call back
An important and necessary part of the examination is to exclude contraindications for prescribing therapy, since the instructions for antiviral drugs prohibit their use for a number of concomitant pathologies.
up
Where can you get infected?
Due to the specific nature of virus transmission, there are a number of establishments with an increased risk of infection.
- Cheap and mid-price catering establishments - blood is less likely to be saliva; infection through microcracks or wounds in conflict situations.
- Public toilets, showers - particles of blood, saliva, sweat from the wearer - microcracks, damaged nasopharyngeal mucosa, recipient's eye mucosa.
- Hairdressers, dental offices.
- Cosmetology salons.
- Production workshops – use of sharp objects.
- Medical institutions where preventive measures for the virus are neglected.
Modern methods of treating viral hepatitis C
The international standard for the treatment of viral hepatitis C is combination therapy with interferon and ribavirin. Doses of drugs and duration of treatment are selected by the doctor individually depending on many factors (see Treatment of viral hepatitis C).
Recently, new drugs with direct antiviral action have appeared, significantly increasing the possibility of complete recovery. Therapy with new drugs is prescribed according to individual regimens.
up
Side effects are possible but easily controlled.
Patients should be aware that the general health of most patients during treatment is somewhat worse than before treatment. This is due to the possibility of developing such side effects as increased temperature (at the beginning of treatment), decreased hemoglobin levels, changes in the state of the nervous system (irritability, insomnia, decreased mood), changes in thyroid function. Appetite decreases and, as a rule, there is a slight weight loss. Less common concerns include dry skin and rashes, dry mucous membranes, and cough. All side effects are monitored by a doctor and are not life-threatening. Some side effects may require additional medications, for example, drugs to regulate the function of the thyroid gland, the nervous system, and to increase hemoglobin levels. All side effects completely disappear in the first weeks after completion of treatment.
When there is a high risk of infection
They provoke a high risk of infection.
- Presence of cuts, microcracks, acne, boils, porous skin.
- Weak immunity.
- Drug addiction, especially with group use of 1 syringe.
- Tendency to collectively drink alcoholic beverages from one container.
- Blood transfusion 4% risk.
- Tendency to suppuration.
- Inflammatory diseases of the liver and gall bladder.
- Immune diseases.
- While taking toxic medications and 7 days after completion.
Watch a video about the modes of transmission of hepatitis C:
Is it possible for a child to become infected from his mother?
If a pregnant woman is a virus carrier, she can infect the baby during childbirth
According to statistics, transmission occurs in 5% of cases. The virus is transmitted only during childbirth if there is injury. Due to weak immunity in children, the likelihood of transmission is 50% higher than in adults.
Can you get infected through sexual contact?
There is a 50% chance of transmitting the virus.
- Acidity imbalance in the vagina.
- Unsanitary conditions and other conditions of the body that led to the appearance of microcracks in the anus and vagina.
- Frequent use of contraceptives, condoms with lubricants, flavorings – wounds – bleeding – acidity disorders – suppuration; 90% chance of developing cirrhosis.
Important! To date, no virus has been detected in semen. But until recently, it was not detected in saliva.
Risk group
The main risk group is laboratory assistants at medical institutions. Infection of drug users is not so widespread. There is a risk of infection when engaging in activities involving the use of cutting objects.
Alcoholism is not a risk factor for infection. Alcohol contributes to the rapid development of the disease and the rapid occurrence of cirrhosis.
People at risk should be tested for hepatitis first
Is it possible to become infected again?
If at the acute stage it was possible to cope with the disease, antibodies are produced to this genotype of the virus. The body does not have antibodies to other genotypes and subgenotypes.
If there are no other immune or inflammatory diseases, the chance of coping with genotype 1-4 virions increases to 40-50%. In case of weakened immunity or immune diseases, there is a high chance of the acute stage transitioning to autoimmune hepatitis C.
When another viral disease occurs simultaneously, the rate of hepatitis increases 3-5 times, regardless of the presence of antibodies to a similar hepatitis genotype.