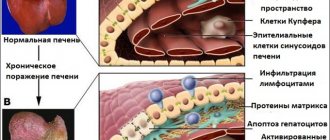
Liver fibrosis is the proliferation of connective tissue in the liver, which occurs when hepatocytes (liver cells) are damaged by hepatitis B, C, and D viruses, alcohol, toxic substances and other factors. Progression of liver fibrosis leads to cirrhosis, liver failure and portal hypertension.
Signs and symptoms of liver fibrosis
Early stage fibrosis is difficult to diagnose because it is often asymptomatic. Based on a blood test - the level of liver enzymes ALT and AST in the blood - one can judge the severity of fibrosis. AST levels are thought to have a stronger association with fibrosis than ALT levels. The AST/ALT ratio >1 is a reliable indicator of the severe stage of liver fibrosis (including liver cirrhosis).
The initial stage of liver damage due to fibrosis is characterized by an increase in liver size. Subsequently, the level of leukocytes, platelets and red blood cells decreases. As a result, the patient experiences anemia and thrombocytopenia. Signs that the disease is moving to the stage of cirrhosis are an enlarged spleen, varicose veins in the esophagus and hemorrhages from them.
Diagnosis of liver fibrosis
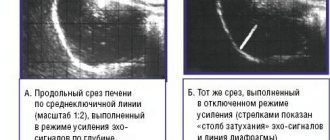
Elastometry (elastography, fibroscanning) replaces biopsy and is a modern, non-traumatic and most accurate examination method. It is carried out using a FibroScan ultrasound machine, which allows you to measure the density of liver tissue (hardness, elasticity). The procedure takes about 15 minutes, for the patient it resembles ultrasound diagnostics and has no restrictions. The measurement result is presented as the degree of liver fibrosis on the METAVIR scale from 0 to 4, where 4 is cirrhosis.
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs makes it possible to evaluate not only the size of the liver, which increases in the presence of an inflammatory process, but also the structure of the liver tissue, internal circulation (velocity and pressure in the portal vein, the width of the lumen of blood vessels, the size of the spleen). These are direct indicators of the condition of the liver - how far or close it is to cirrhosis.
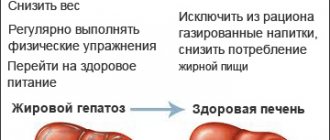
Determination of the exact degree of fatty liver (fatty hepatosis) using the Fibroscan device is prescribed if signs of fatty hepatosis are detected during ultrasound examination or based on the results of a biochemical blood test indicating signs of fatty hepatosis.
Liver elastometry - examination prices:
- Degree of fibrosis
3,500 rubles
- Degree of fatty hepatosis
2,500 rubles
- Consultation on results
for free!
on PROMOTION! (Moscow, Park Kultury metro station)
You can get tested:
- from 9:00 to 17:30 on weekdays
- from 9:00 to 15:00 on Saturday
Sign up by phone
+7
Seven days a week from 9:00 to 21:00
Request a call back
- Find out more about liver fibroscanning...
- Find out more about testing for the degree of fatty hepatosis...
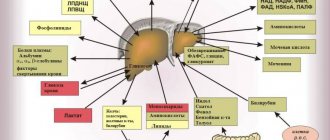
What is fibrous tissue?
Fibrous tissue is a type of connective tissue consisting primarily of collagen fibers and amorphous matter. It is produced by liver stellate cells, which are the main connective tissue cells in the liver and are activated during chronic inflammation.
Unlike connective tissue, fibrous tissue is rougher and more fibrous. It contains more collagen and amorphous intercellular substance. This tissue composition is unchanged and does not depend on the type of pathology developing in the liver.
Degrees of liver fibrosis
The severity of fibrosis in chronic liver disease reflects the long-term prognosis and, therefore, the need and urgency of treatment.
Liver fibrosis has 5 degrees (stages): F0, F1, F2, F3, F4 (cirrhosis). With viral hepatitis, for example, on average, it takes about 5 years from stage to stage. However, in later stages the rate of progression of fibrosis is higher. The rate of fibrosis development depends on the activity of the inflammatory process in the liver.
To determine the severity of fibrosis, there are various methods: biopsy, blood test, which measures biochemical markers of fibrosis formation ( FibroTest, FibroMax ). Currently, elastometry - direct ultrasound determination of the density of liver tissue using the Fibroscan device. The resulting density measurements at several points (10-20) in kiloPascals correspond to the degrees of fibrosis on the METAVIR scale from F0 - healthy liver, to F4 - cirrhosis.
A sufficient amount of scientific data has been obtained using this method and it has been proven that as the stage of fibrosis increases, the elasticity of the liver in kPa increases.
Legend:
- F 0-3 stages of fibrosis according to the METAVIR scale for chronic hepatitis,
- F 4 – cirrhosis of the liver,
- F 4+ URVP - cirrhosis of the liver with the presence of varicose veins of the esophagus,
- F 4+VRVP* - liver cirrhosis, portal hypertension, complicated by bleeding from varicose veins of the esophagus,
- HCC - hepatocellular carcinoma
Significance of differences p <0.05
Legend:
- F 0-3 stages of fibrosis according to the METAVIR scale for chronic hepatitis,
- F 4 – cirrhosis of the liver,
- F 4+ URVP - cirrhosis of the liver with the presence of varicose veins of the esophagus,
- F 4+VRVP* - liver cirrhosis, portal hypertension, complicated by bleeding from esophageal varices
The advantages of the method include simplicity, non-invasiveness, low cost, as well as clinical significance (prediction of complications of portal hypertension in liver cirrhosis, liver cancer formation). This determines broad indications for the method: initial examination, dynamics with and without treatment.
Limitations to the method are the presence of ascites, excess fatty tissue, and narrow intercostal spaces in the patient.
The results of Russian studies also confirmed high diagnostic accuracy (more than 80% for all groups) and reproducibility of the result by another operator.
The following elasticity thresholds are recommended for clinical use:
- 5.8 kPa to determine the boundary between stages F0 and F1 (METAVIR);
- 7.2 kPa to differentiate stages F1 and F2;
- 9.5 kPa – stages F2 and F3;
- 12.5 kPa to determine the boundary between severe fibrosis and cirrhosis of the liver - F4.
Factors influencing the diagnostic accuracy of elastometry:
- patient age >50 years,
- excess body weight,
- the presence of steatosis according to a morphological study of liver tissue.
Stages of the disease
Based on the results of a biopsy (histological examination of liver tissue under a microscope), the severity of fibrosis is assessed.
To do this, use a scale for assessing the severity of liver fibrosis - the Metavir5 system:
No fibrosis
Widening of the portal tracts, but without the formation of septa
Expansion of portal tracts with single porto-portal septa
Porto-portal and porto-central septa
Cirrhosis of the liver
However, this diagnostic method has a number of disadvantages5: it is an invasive method that is not indicated for every patient with liver fibrosis. Moreover, performing a biopsy is associated with a high risk of complications from bleeding to accidental damage to neighboring organs, such as the gallbladder, etc.
What methods of diagnosing fibrosis can be used in almost every patient?
Progression of fibrosis
The rate of progression of fibrosis varies markedly between patients. Among the known factors influencing the rate of development of fibrosis, the main ones can be identified - infection at an older age, male gender, alcohol abuse. At the same time, the connection between the viral load and the genotype of the virus and the rate of progression has not been established. The rate of fibrosis development is higher in immunocompromised patients. Fatty liver, obesity, and diabetes may also contribute to the faster development of fibrosis. To most accurately assess fibrosis progression, reassessment should be performed annually. In these cases, it is advisable to use methods for non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis - informative and accessible ( FibroTest, FibroMax, elastomery ). Experience with the use of serum tests for assessing fibrosis and ultrasound techniques indicates the need for their combination for greater diagnostic accuracy.
Treatment of liver fibrosis
The reversibility of liver fibrosis in patients has recently been convincingly demonstrated. This has prompted an active search for antifibrotic drugs. Antifibrotic therapy causes suppression of the accumulation of fibrogenic cells. It has been proven that drugs whose action is aimed at combating the cause of the disease have such an antifibrotic effect.
In viral hepatitis, treatment of liver fibrosis is aimed at eliminating the causes that caused it. Antiviral therapy can lead to a decrease in the degree of fibrosis when a stable virological response is achieved in the patient.
Reverse development of liver fibrosis as a result of etiological therapy:
- Hepatitis C - interferon-a + ribavirin.
- Hepatitis B - lamivudine, tenofovir, adefovir, interferon-a/g, entecavir.
- Hepatitis D - interferon-a.
- Alcoholic hepatitis - abstinence from alcohol.
- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis - weight loss, treatment of metabolic syndrome .
To improve the long-term prognosis, diagnosis and regular monitoring of the stage of liver fibrosis is necessary in the natural course of the disease or during therapy.
Delta Medical
Periarticular diseases of the shoulder joint are represented by several nosological forms:
1) isolated damage to the tendons of the muscles surrounding the joint (degeneration, inflammation, partial and complete ruptures): tendinitis of the rotator cuff muscles (indicating the specific muscle), tendonitis of the biceps brachii muscle, calcific tendinitis, rupture (partial or complete) of the tendons of the muscles of the shoulder joint ;
2) diffuse non-inflammatory damage to the capsule of the shoulder joint (retractile capsulitis); 3) subacromial syndrome (complex damage to the structures surrounding the subacromial bursa).
The ball-shaped structure of the shoulder joint allows for a variety of movements: flexion, extension, abduction, adduction and rotation. It should be remembered that the angle of movement in the shoulder joint without the participation of the scapula characterizes the true range of movements in it, and with their participation - the full range. When testing shoulder abduction, pain in the joint may occur when the abduction angle reaches 70-90°. This is due to the fact that the greater tubercle of the humerus rises close to the acromion process and can compress the structures passing through here (the supraspinatus tendon and the subacromial bursa). As you continue to raise your arm, the greater tubercle moves away from the acromion process and the pain decreases significantly. This painful arch is characteristic of supraspinatus tendinitis or subacromial bursitis. The appearance of pain at the moment of maximum abduction of the arm in the shoulder joint (up to 160-180°) indicates damage to the acromial clavicular joint. With an anterior dislocation, there is a displacement of the head of the humerus anteriorly and downward, which leads to a characteristic change in the contours of the shoulder and a sharp limitation of mobility due to pain (Table 1).
Table 1. Identification of symptoms when examining the affected structures of the shoulder joint area
| Pain, limitation of movement | Damage to structures |
| When the arm is abducted | Supraspinatus tendon, subacromial bursa |
| With the maximum lift of the arm up | Acromiocleidoclavicular joint |
| With external rotation (trying to comb your hair) | Infraspinatus and teres minor tendon |
| During internal rotation (trying to put your arm behind your back) | Subscapularis tendon |
| When bending the elbow joint and supination of the forearm (lifting weights, turning the key outward in the door) | Biceps tendon |
| All movements are impaired (painful and/or limited) | Damage to the capsule (or the shoulder joint itself) |
| Shoulder pain not associated with movement | Plexitis, thoracic outlet syndrome |
For tendonitis of the shoulder muscles
The following is recommended: