How does the disease manifest? Signs of liver problems
- External manifestations
- Internal manifestations
The liver is the largest gland in the human body, so its diseases have a serious impact on overall health. At the same time, it is very sensitive and extremely susceptible to various disorders. Doctors often hear the complaint “I have pain in the liver area.” But can the liver itself hurt and what sensations does a person experience when various diseases appear?
1.Common liver diseases
Liver diseases are a long list of diseases that are studied by a special branch of medicine - hepatology. Even though the liver is the only organ that is capable of complete regeneration, liver disease is very common and serious. Liver diseases can be either hereditary or result from various factors. Liver diseases can also be divided into temporary and chronic.
Here are just a few of the common liver diseases:
- Treatment of diffuse liver diseases;
- Functional hyperbilirubinemia;
- Primary biliary cirrhosis of the liver;
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis;
- Hepatolenticular degeneration;
- Chronic hepatitis;
- Liver tumors;
- Liver abscess;
- Acute hepatitis;
- Cirrhosis of the liver;
- Liver steatosis;
- Hemochromatosis;
- Liver cysts;
- Amyloidosis.
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is a general name for a group of inflammatory liver diseases of various etiologies. There are hepatitis A, B, C, D, E and F. Hepatitis, unlike other diseases, spreads to the entire organ, therefore it is considered especially dangerous.
Cirrhosis of the liver
Liver cirrhosis is a serious disease in which the liver becomes enlarged because... parenchymal tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue. Cirrhosis develops after prolonged alcohol abuse or as a result of viral hepatitis.
Liver cancer
Liver cancer is a malignant tumor in the organ. Typical symptoms of liver cancer:
- Jaundice;
- Heaviness and pain in the right side;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Fever;
- Hemorrhagic syndrome;
- Ascites;
- Cachexia.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Help the liver with Phosphogliv*
If liver problems are detected, the patient is prescribed diet and exercise; if this is not enough, therapy is supplemented with medications. It often includes the use of hepatoprotectors - drugs for treating the liver. One such drug is Phosphogliv*. Phosphogliv* is used as a means of pathogenetic therapy. This product contains 2 active ingredients: glycyrrhizic acid and essential phospholipids.
Glycyrrhizic acid has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and antifibrotic effects, which allows the drug to be used both at the stage of treating inflammation and for preventing its development, and essential phospholipids restore damaged liver cell membranes. The use of the drug Phosphogliv* ensures normalization of the patient’s general condition, relief of the inflammatory process in the liver - a decrease in ALT and AST enzymes, and also helps prevent the development of fibrosis and cirrhosis.
3.Risk factors
Risk factors that affect the likelihood of developing liver disease:
- Work in chemical laboratories conducting analyzes of body fluids;
- Increased levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood;
- Work involving chemicals and toxins;
- Some medicines;
- Alcohol abuse;
- Piercing and tattoos;
- Blood transfusion;
- Unsafe sex;
- Obesity;
- Diabetes.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Where does liver failure come from?
Chronic liver failure is most often caused by liver diseases such as hepatitis, including autoimmune hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and disorders of the bile ducts (for example, cholangitis).
There are slightly more reasons for the development of acute liver failure Acute Liver Failure.
Paracetamol overdose
In the United States, over-the-counter pain reliever abuse is the most common cause of an “acute” diagnosis. For liver failure, it is enough to take too much paracetamol once or take it for several days in a row in doses greater than the instructions recommend.
Side effect from taking certain prescription drugs
Antibiotics, antidepressants, antifungals and anticonvulsants can be “killers” of the liver.
Reaction to some herbal supplements
For example, kava-kava, ephedra, Chinese ephedra.
Poisoning
Let's say, poisonous mushrooms or toxins contained in refrigerants, varnish solvents and other chemicals used in everyday life.
Hepatitis and other viruses
Acute liver failure can be caused by hepatitis A, B, E, autoimmune, as well as Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus and herpes simplex virus.
Blood poisoning
Sepsis occurs when pathogenic bacteria enter the bloodstream.
Cancer
A malignant process that begins in the liver or spreads to it from other organs can lead to liver failure.
4. Diagnosis and treatment of liver diseases
Diagnosis of liver diseases
To diagnose liver diseases, the first step is to consult a general practitioner. He will take a history and ask you about your symptoms. If your GP decides that you have any liver disease, they will refer you to a hepatologist. The hepatologist, depending on the complaints and symptoms, will prescribe the following diagnostic methods:
- CT, MRI, ultrasound or any other research technique that allows you to see the organ;
- Various blood tests;
- Liver biopsy.
What are the symptoms of chronic liver failure
In the early stages, it is almost impossible to detect chronic liver failure. And if symptoms of Liver Failure Stages do appear, they are minor. In addition, they can easily be confused with ordinary malaise or fatigue.
- Fatigue, weakness.
- Decreased appetite.
- From time to time - causeless nausea or vomiting.
- Sometimes there is slight discomfort in the right upper abdomen.
Only as liver failure progresses do its symptoms become more noticeable. This:
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes;
- darkening of urine;
- bruises that occur even from weak blows;
- swelling of the arms, legs, and abdomen;
- noticeable and seemingly causeless itching of the skin.
Therefore, it is so important to consult a therapist even if there are minor changes in your health, especially if they are accompanied by abdominal discomfort. Only a qualified doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and possibly save your life.
What liver functions ensure a woman’s health?
The importance of normal liver function is the same for people of both sexes. This organ synthesizes a lot of necessary substances, is the largest depot of energy reserves, and utilizes biochemical processing methods toxins, poisons, and all waste products that the body receives from the external environment and produces during life.
It is impossible to replace the functions of the liver with another organ. A significant reserve supply of cells allows the work to be performed even with the loss of 1/3 of the parenchyma. Therefore, a person does not immediately detect the first signs of the disease.
The liver is involved in and controls all types of metabolism
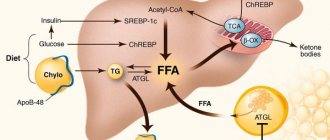
In protein metabolism - synthesizes essential amino acids, various types of protein components for building cell membranes, performing transport functions, immunoglobulins, blood clotting and anti-clotting factors. In fat metabolism - produces lipoproteins, cholesterol, triglycerides.
Carbohydrate metabolism is ensured by obtaining energy from incoming glucose and glycogen reserves. In the liver, if necessary, reactions can occur to “extract” calories from proteins and fats. To carry out such a synthesis, enzymes and coenzymes are needed. Their role is played by vitamins B, PP, C, K, E, D, and reserves of microelements cobalt, iron, and copper.
The liver is connected to other organs through the endocrine system. For the female body, its role as a producer of sex hormones, ensuring the functioning of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland is extremely important.
A “factory” for processing waste and toxins with a healthy liver does not allow the accumulation of products remaining after the absorption of food, medicines, alcohol, industrial and household harmful substances. They are disinfected and released into the intestines with bile. At the same time, the liver maintains the necessary composition and process of bile formation for digestion.
The load increases significantly during pregnancy. During this period, the woman’s liver ensures hematopoiesis of the fetus and cleanses the blood of the mother’s body.
Impaired metabolism in the liver leads to diseases of other organs
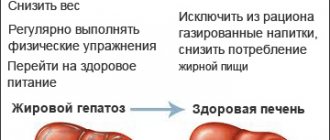
Nutritional features and diet for liver restoration
In the treatment of liver inflammation of any etiology (both chronic and acute viral), diet plays an important role. At least partial compliance with it would help many patients prevent the development of chronic hepatitis.
It is important to remember that diet for liver recovery is very important.
When treating a disease (especially viral forms with pronounced clinical manifestations), the diet must be strictly followed.
Otherwise, the liver will be under stress, making timely recovery impossible. “But untimely things will suit me!” - the patient will exclaim joyfully and go to empty the refrigerator full of fatty foods and alcohol. In this case, prolonged recovery threatens to transform into a chronic form of hepatitis, in which the above symptoms will accompany the patient for the rest of his life.
The basis of the diet for diet No. 5 includes the following products and dishes:
- vegetarian soups cooked in water;
- gray and bran bread;
- lean meat. Regardless of what type of meat (fish, poultry, beef) the patient eats, it should not contain a large amount of fat. Recommended for consumption are beef, lean pork, chicken, turkey, bream, mullet, pike, tuna, flounder, cod, pollock;
- dairy products: low-fat milk and cheese, kefir, cottage cheese. There is no need to worry about the fat content of the latter - in most cases, in cottage cheese it does not exceed 10%, which is at least three times less than the fat content of the lowest-fat cheese;
- boiled eggs, baked omelet, preferably no more than 2 yolks per day;
- It is preferable to use cereals as a side dish: wheat, oatmeal and buckwheat are best suited. At the same time, you should avoid all kinds of instant cereals - they do more harm than good;
- vegetables and fruits in any form - both raw and stewed (when cooking, it is important not to overdo it with adding oil). Sauerkraut is also allowed, with the only caveat that it should not be too sour.
Salted, fried, sour and smoked foods, meat broths, fatty meats and animal fats, baked goods and fresh white bread, sausages, frankfurters and other semi-finished products are contraindicated for consumption. In addition, it is not recommended to consume sweets (especially cream pies and cakes), strong black coffee, and chocolate. You should use radishes, sorrel, garlic and mushrooms with caution. It’s also better to forget about sour cream, fatty cheeses and ice cream.
Separately, I would like to note the need to give up alcoholic beverages. Very often, it is alcohol abuse that provokes the development of inflammatory processes and fatty liver disease.
The problem of alcohol abuse is primarily psychological, so at the very beginning of treatment you need to accustom yourself to the idea that you need to give up this bad habit. Otherwise, hepatitis has every chance of developing into alcoholic cirrhosis. After the condition improves, alcohol should also be treated with extreme caution - its use should not be systematic.
It is also advisable to refrain from smoking, since the liver is forced to process a number of toxic substances (for example, hydrocyanic acid) that enter the bloodstream along with tobacco smoke.
Liver Failure Symptoms
Signs of liver failure in humans are quite varied. They indicate damage not only to the hepatobiliary tract (gland, biliary tract), but also to other internal organs. This indicates the involvement of both the digestive and cardiovascular, nervous and circulatory systems in the pathological process.
Signs of liver failure include:
- jaundice;
- neuritis;
- hyperthermia up to 40 degrees;
- swelling of the limbs, ascites;
- encephalopathy;
- decreased libido;
- change in psycho-emotional state (irritability or apathy).
If the liver fails due to chronic glandular insufficiency, the person or his relatives may complain of:
- tremor of the limbs;
- disturbance of consciousness;
- disorientation;
- behavior change;
- slurred speech;
- inadequacy;
- severe swelling of the legs and abdomen;
- frequent nasal bleeding, prolonged menstruation;
- blurred vision.
If the pathology has an acute course, the following symptoms of liver failure in a person are observed:
- severe malaise;
- nausea, vomiting;
- hyperthermia;
- increased severity of jaundice;
- “liver” odor from the mouth;
- pain in the area of the right hypochondrium;
- lethargy;
- liver shrinkage.
What examination does the doctor prescribe?
Patients with even minimal symptoms should carefully approach the problem of examination, take all tests and undergo studies to determine the role and extent of liver damage.
The most common recommended tests: complete blood count, coagulation factors, protein, alanine and aspartic transaminases, bilirubin, glucose.
A urine test checks for the presence of excretion of bilirubin, protein, and glucose. Special tests are prescribed to detect viral hepatitis: viral markers, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for antibodies or antigens, immunoblotting, polymerase chain reaction method to detect RNA viruses.
A gynecologist-endocrinologist will advise you to check the hormonal composition of the blood and prescribe an ultrasound of the genital organs, thyroid gland, and adrenal glands.
To check the structure of the liver, size, and circulatory conditions of the organ, the following are used: ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. These methods are used to diagnose nodular formations and enlarged lobes. A cytological conclusion is obtained only after examining punctate material or liver tissue biopsy.
To decide on surgical intervention, you may first need to examine the surface of the organ using laparoscopy. Under anesthesia, a probe with an optical device at the end is inserted into the peritoneum through a small incision. It is possible to take samples of material from the damaged area. The diagnosis is made only after comparing all types of studies.
Consequences of liver failure
The number of complications depends on the underlying cause of liver failure. Undesirable consequences may include:
- generalization of infection, when pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the systemic bloodstream, settle in internal organs and form distant foci (abscess, pneumonia, peritonitis);
- profuse bleeding from the esophageal veins;
- hepatic coma. The first sign of toxic brain damage from ammonia and phenols is encephalopathy, which progresses rapidly if left untreated. In the precoma stage, a person becomes irritable, then apathetic, drowsy, and consciousness is gradually depressed. Convulsions, pathological reflexes and involuntary emptying of the bladder are also observed. The cause of coma is cerebral edema and cell hypoxia. It is characterized by a lack of consciousness, a lack of response to the action of an external stimulus, extinction of reflexes and dilation of the pupil.
In the terminal stage of the disease, treatment in the intensive care unit is required. The patient's death is due to deterioration of blood flow and compression of brain structures, which is accompanied by respiratory distress, vascular tone and disruption of the heart.
How to treat liver failure
It depends on the form and stage of the disease.
How is acute liver failure treated?
Only in the intensive care unit (resuscitation). Liver failure often leads to cerebral edema and massive internal bleeding, so the patient must be under the supervision of doctors.
Most often, treatment consists of keeping the person alive through supportive care, giving the liver time to recover. If the cause of deficiency is poisoning with paracetamol, mushrooms or other toxic substances, doctors prescribe an antidote (a medicine that stops the effect of the poison on the body). But supportive care and drug therapy do not always help.
Without a liver transplant, the overall mortality rate Acute liver failure - problems and prospects for their solution in acute liver failure is about 70%.
Transplantation—that is, removing a damaged organ and replacing it with a healthy donor one—may be the only way to save a person’s life.
How is chronic liver failure treated?
The main goal of Liver Failure Stages therapy in this case is to eliminate the factor that destroys the liver. If we are talking about hepatitis, the doctor will prescribe antiviral drugs. Or medications that suppress the immune system - they work if the inflammation of the organ is caused by autoimmune processes.
You can also improve your liver condition by changing your lifestyle. Here's what your doctor will recommend:
- Stop drinking alcohol.
- Get rid of extra pounds. Physical activity and a healthy diet will help with this.
- Eat a nutritious and balanced diet. You should get all the necessary vitamins, minerals and trace elements from food - they are important for liver health.
Treatment of hepatitis
For liver inflammation, treatment will largely depend on the etiology of the disease. If hepatitis is of viral origin, it is first necessary to carry out antiviral therapy. For this purpose, interferon preparations are used, which also have a good immunomodulatory effect. Detoxification of the body (magnesium sulfate, glutathione) also plays an important role. To restore liver tissue, courses of hepatoprotectors (Heptral, Essentiale, Ursohol, Karsil, Levasil) are prescribed.
Treatment of chronic hepatitis is also comprehensive and is primarily aimed at eliminating the harmful effects on the liver. For hepatitis caused by exposure to toxic substances on the liver, before treatment it is necessary to first stop the flow of toxins into the body by any means. The same applies to alcoholic hepatitis. Treatment of autoimmune hepatitis is based on the use of immunomodulatory and cytostatic agents. Then, as in the case of infectious hepatitis, hepatoprotectors are prescribed. Self-treatment of hepatitis is not advisable - all medications are prescribed by a doctor based on the results of the examination.
How long can a person live if the liver fails?
How long a patient can live with liver failure depends on the cause of the pathological condition. Considering the multifunctionality of the organ, when it is severely dysfunctional, not only the hepatobiliary system suffers, but the entire body. The prognosis depends on the severity of symptoms and treatment tactics. So, a person can live from a couple of days to several years.
Normal functioning of the body without the liver is impossible, therefore, if there is no chance of drug restoration of the functioning of the gland, its transplantation is performed. However, with continued exposure to the provoking factor, a relapse of the disease and repeated organ failure are possible.
How to prevent liver failure
Here are the most effective methods for preventing Acute Liver Failure from malfunctioning of this organ:
- If you take medications, follow the instructions strictly. Do not under any circumstances exceed the recommended dosage and duration of use.
- Don't self-prescribe. Even taking over-the-counter vitamins and herbal supplements must be approved by your doctor.
- Don't abuse alcohol.
- Consult your doctor about the need for vaccinations. Your doctor may recommend that you be vaccinated against hepatitis A, B, and other viruses that can potentially damage your liver.
- Avoid risky behavior. Sex with a partner whose health you are not sure about is only with a condom. Tattoos or piercings - only in a trusted salon that values its reputation. Sharing needles and using drugs is an absolute evil and a crime against your body.
- Do not share razors and toothbrushes with other people.
- Do not eat mushrooms that you are not sure are safe.
- Be careful when using household chemicals - aerosol cleaners, paint, solvents, insect repellents. Strictly follow the safety measures prescribed in the instructions.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Obesity can lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. And she, in turn, can lead to cirrhosis.