Do you quickly feel short of breath? This is not normal for a healthy person. Maybe lung disease is behind this.
In this article you will learn about what types of lung diseases exist and how to deal with them.
Take a very deep breath, then exhale quickly. It was easy? Congratulations, your lungs are likely healthy.
Do you hear wheezing in your lungs or have you had a coughing fit? Perhaps your breathing was heavier than usual?
Then you should read this article carefully because lung disease is usually a gradual process that you often only notice when it's too late.
What are the symptoms of lung disease?
Scientists say the signs are the same for most lung diseases: cough, shortness of breath and expectoration. Don't worry, a cough or cold is not always a reason to panic.
However, if symptoms persist for a long time, become unusually severe, develop a fever, or even cough up blood, you should definitely see a doctor.
In most cases, you can get a lung test, which will tell you if you have lung problems. The pulmonologist can then make a more extensive diagnosis by checking your lung capacity.
Diagnostics
The disease develops long before the onset of functional disorders, which can be recorded instrumentally. Therefore, unfortunately, early diagnosis of COPD is almost impossible.
When diagnosing, the following methods are used:
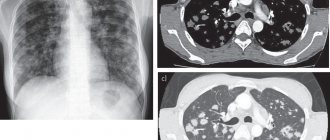
- X-ray and CT (computed tomography) of the chest;
- study of the function of the respiratory system using spirometry and other tests;
- sputum cultures for microflora;
- determining the level of alpha-1-antitrypsin;
- ECG and echocardiography to exclude cardiac causes of shortness of breath and identify cardiac complications.
When diagnosing, it is important to differentiate COPD from diseases with a similar clinical picture - asthma, heart failure.
Smoking:
“In our practice, the most common cause of lung disease is smoking,” the researchers say. Whether it's a cigarette, hookah or e-cigarette, many toxins from smoke enter the lungs and cause irreparable damage.
Burnt tobacco contains at least 100 substances that have been shown to be carcinogenic. Especially if you already have an affected lung, such as from asthma or just a cold, smoking can significantly complicate your symptoms or make your condition worse. Smoking a hookah is also very dangerous.
Tuberculosis
Many are still confident that tuberculosis is a thing of the past, in history and in Remarque’s novels, says Arkady Vertkin. Unfortunately, it is not. Russia is in third place in terms of the prevalence of this disease.
Another incorrect belief is that tuberculosis is a disease of people of special social status (people without a fixed place of residence, migrants released from prison, alcohol and drug abusers).
“These are indeed risk groups for infection with this disease, but, unfortunately, due to its widespread prevalence, tuberculosis can be contracted regardless of belonging to any social group - just look at the patients in TB departments,” the professor notes.
Symptoms:
- prolonged dry cough;
- constant low-grade fever (increase in temperature from 37.0 °C to 37.9 °C) or an increase in body temperature in the morning with the evening temperature curve returning to normal;
- sweating, especially at night;
- weight loss with preserved appetite;
- weakness, fatigue;
- generalized or limited enlargement of lymph nodes;
- hemoptysis.
Treatment is required; there should be no self-help, only examination and therapy prescribed by a doctor, so as not to aggravate the situation.
Why is he coughing? Three questions about bronchitis Read more
Infections:
If minor infections are not properly treated in time, they can become more serious illnesses. “If you do not treat a cold promptly, your weakened immune system becomes more vulnerable, which can lead to a chronic form of pneumonia,” warns a pulmonologist.
Although it is relatively rare, you should take every infection seriously and treat it completely. An annual flu shot and pneumococcal vaccine can help prevent the disease. This way you can quickly get rid of a cold.
What are the most common lung diseases?
Basically, the lungs consist of blood vessels and small sacs (alveoli), which allow gas exchange between carbon dioxide and oxygen, as well as air channels (bronchi). All these diseases can be acute or chronic.
At the beginning of the disease, the symptoms seem harmless, and you are unlikely to pay attention to it. But the longer you remain inactive, the more severe the disease becomes and can even be fatal. Therefore, you should know these 6 lung diseases:
Asthma
During an asthma attack, your bronchi suddenly constrict and you can't breathe. This happens most often at night, or when you are under stress, also during physical activity.
In case of an acute attack of asthma, an inhaler helps, thanks to the spray of which the bronchi expand again and you get air.
If you suffer from asthma, you need to always breathe clean air. Experts recommend strengthening your lungs with moderate physical activity, not smoking, and not living in big cities.
Heart failure
Every minute in Russia one person with chronic heart failure (CHF) dies. This complication is detected in many diseases and vascular accidents, notes Arkady Vertkin. According to statistics, more than 12 million people with this pathology are registered in Russia. 92% of patients in cardiology departments are hospitalized due to decompensation of chronic heart failure. It is important to note, the professor says, that cough and shortness of breath may be the first signs of CHF.
Symptoms:
- dry cough, combined with increasing shortness of breath;
- increased cough during physical activity, in a horizontal position, at night;
- “bubbling” breathing;
- symmetrical swelling of the lower extremities, palpitations, a feeling of interruptions in the functioning of the heart;
- orthopneic position.
A history of diseases of the cardiovascular system, including a previous myocardial infarction, coronary artery stenting, coronary artery bypass grafting, atrial fibrillation, as well as the presence of background pathology (arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus and obesity) will help recognize this complication, the specialist warns .
Not sparing your belly. Any pathology begins with problems in the stomach Read more
Lungs' cancer
Lung cancer is the third most common cancer in the world, and it is almost always malignant. Today, smoking (both active and passive) is the most common cause of lung cancer.
Toxic substances can even end up on clothing or hair and then end up in the air we breathe. You should also be especially vigilant if you have a history of lung cancer in your family, because then your own body is at greater risk.
When you find out you have cancer, it is often too late. Chemotherapy or radiation therapy can only extend your lifespan. Therefore, the most effective method of combating lung cancer is prevention, and most importantly, quit smoking.
Complications
The course of COPD is characterized by the following complications:
- Respiratory failure.
- Recurrent respiratory tract infections.
- Pulmonary hypertension (increased pressure in the pulmonary circulation).
- Failure of the right ventricle of the heart (cor pulmonale).
- Pneumothorax (accumulation of air in the pleural cavity).
- Lungs' cancer.
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Anxiety and depressive disorders.
- Weight loss.
The complicated course of the disease ends in death in 50% of cases within 10 years after diagnosis. The prognosis largely depends on whether the patient managed to quit smoking and how long he had as a smoker before.
Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is usually caused by infectious viruses or, less commonly, bacteria, which excite the bronchi and cause the typical cough. This may continue for several weeks until the tissue is completely restored.
If your cough doesn't go away, you may have chronic bronchitis. This can happen if you do not treat an acute infection properly. According to experts, the risk of the disease becoming chronic also increases if the bronchi are exposed to multiple pollutants. Thus, hand washing actually protects against infection.
What can help? You must definitely cure acute bronchitis, get plenty of rest, eat plenty of vitamins and drink as much fluid as possible. You usually don't need antibiotics unless you have bacteria in your lungs in addition to a viral infection.
For chronic bronchitis, your doctor may prescribe a cough suppressant or short-term, low-dose inhaled cortisone therapy to help the inflammation go away. However, it is important that you protect your lungs from environmental toxins and allow them to heal fully.
Otherwise, there is a risk that the disease will become acute chronic. Only an x-ray can provide a reliable diagnosis of lung diseases. Pneumonia can definitely be seen on an x-ray.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is characterized by constant and irreversible destruction of lung tissue. COPD often occurs due to bronchitis.
Smoking is by far the most common cause of this disease, with about 20 percent of smokers developing COPD. Exhalation is especially difficult for patients, because the cells of the bronchi are destroyed after exhalation.
What can help? The effects of COPD can only be reversed to a small extent. The sooner you learn about the disease, the sooner you can limit its further development. In addition, medications can relieve symptoms such as shortness of breath or coughing spells. You must avoid environmental toxins, smoking and infections, otherwise your quality of life and longevity will decline rapidly!
Treatment
The strategic goal in the treatment of stable obstructive disease is to prevent exacerbations and increase the functionality of the respiratory system.
For this purpose, a set of measures is used:
- Quitting smoking. Is crucial in therapy.
- Inhaled bronchodilators are drugs that dilate the bronchi.
- Inhaled corticosteroids – reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms.
- Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors have anti-inflammatory and bronchodilatory effects.
- Oxygen therapy is treatment with oxygen.
- Normalization of nutrition.
- Physiotherapy.
- In some cases, surgery is indicated.
Patients with COPD are advised to get vaccinated against influenza to avoid complications and sudden progression of the disease.
Pneumonia
In the case of pneumonia, it is not the airways or bronchi that are affected, but the lung tissue itself. Small bubbles in the lungs become inflamed and stick together, preventing oxygen from reaching the blood. Like bronchitis, pneumonia is caused by contagious germs in the air we breathe. When a doctor listens to a patient's lungs, he hears them cracking when he breathes because the nodes are coming off.
In this case, you need to act immediately because pneumonia is number 1 among deadly infectious diseases. How to fight pneumonia? If you act immediately, your chances of recovery are high. Most germs that cause pneumonia are easy to treat. It's even better if there is no infection at all. Therefore, strengthen your immune system through exercise and a balanced diet.
You can also protect yourself with vaccinations, since pneumococcus and influenza are the leading causes of pneumonia. Modern medicine has vaccines against both.
GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a disease in which inflammation of the walls of the lower esophagus occurs as a result of regular reflux of gastric or duodenal contents into it. “Many people are familiar with GERD by the appearance of heartburn. How are reflux related to coughing? It turns out that in 15 to 40% of patients, GERD is accompanied by a chronic cough, which is caused by acidic contents entering the upper and lower respiratory tract,” says Arkady Vertkin.
Symptoms:
- cough is prolonged, paroxysmal, dry, which often appears at night, in a horizontal position, and also 30-40 minutes after eating;
- The cough is accompanied by heartburn, sour belching and hoarseness.
Thus, despite the fact that all of these diseases have similar symptoms, knowledge of the characteristics of their manifestation, as well as combinations with other characteristic symptoms in various clinical situations, will help to carry out differential diagnosis and distinguish diseases from each other, the professor concludes.