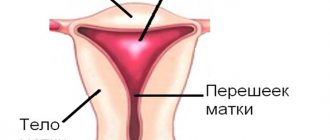
Inflammation of the vaginal cervix. Symptoms are nagging pain in the lower abdomen, purulent or mucous discharge, pain during urination and sexual intercourse. Inflammation of the cervix, or cervicitis, refers to inflammation of the narrow lower part of the organ. A healthy uterus is normally covered with epithelium that produces a mucous secretion. This substance plays a protective role and prevents infections from entering the internal cavity. When the secretory function of cells is disrupted, active growth of pathogenic microflora occurs, and symptoms of cervical inflammation develop.
According to statistics, cervicitis is diagnosed in 30% of women of childbearing age. The pathology can be in the cervical canal, then they talk about endocervicitis, or in the vaginal part of the cervix – exocervicitis. The peak incidence is recorded in the age group of 17-28 years, when a woman exhibits maximum sexual activity and rarely uses barrier contraception.
Treatment of cervical inflammation in the initial stage is carried out using conservative methods and does not require radical measures. The prognosis is favorable. But for this, a woman must undergo regular medical examinations and consult a gynecologist when the first symptoms of the disease appear.
You can get examined for signs of cervicitis in Moscow at the Alfa Health Center clinic.
Signs of cervical inflammation
Patient complaints are different for acute and chronic cervicitis.
The main symptoms of inflammation in the cervix:
- purulent or mucous discharge from the genitals;
- pain, heaviness in the uterine area;
- discomfort, burning in the genitourinary tract, aggravated by sex and urination;
- a slight rise in temperature to 37-37.2ºС.
In some cases, the inflammatory process occurs without pronounced clinical signs and is determined by the results of a gynecological smear.
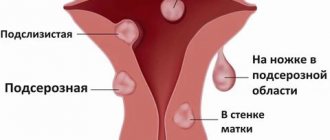
Diseases of the appendages
Diseases of the appendages include damage to the fallopian tubes and ovaries of the uterus.
Salpingitis, oophoritis, salpingoophoritis or adnexitis, pelvioperitonitis are the main inflammatory diseases of the uterine appendages in women.
The main symptoms of the disease may be pain in the pelvis and lower abdomen, bloody or purulent discharge with an unpleasant odor, pain during urination or sexual intercourse, changes in general health, and in severe conditions (pelvioperitonitis) clinical infectious shock.
Diseases of the appendages in women can cause adhesions in the pelvic area, obstruction of the fallopian tubes, and infertility.
Causes of cervicitis
Inflammation of the cervix and appendages can be caused by the following factors:
- sexually transmitted disease: gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia and other infections;
- microorganisms that are normally present on the vaginal mucosa;
- mechanical injuries during gynecological operations, conization, childbirth, from the use of the uterine ring, treatment with iodine, dimexide, and other means;
- hormonal disorders;
- antibiotic treatment, chemotherapy courses;
- allergy to latex or substances used in condoms;
- diseases of the female genitourinary system: colpitis, endometritis, cystitis, erosion and others.
A common cause of cervical inflammation is independent, uncontrolled use of antibiotics. Medicines inhibit the beneficial microflora of the vagina and reduce local immunity. Organisms resistant to antibiotics appear in a woman’s biota. These are the most complex cases of mixed infections that require an individual treatment plan.
Risk factors such as young age and frequent changes of sexual partners are also noted.
Endometritis and endometriosis: distinctive signs of disease
Quite often these two diseases are confused or considered the same. But these are different diseases. Endometritis is an inflammation caused by microbes and infections. The main current is located in the uterine zone.
Endometriosis is an overgrowth of the mucous membrane caused by intense cell proliferation. As the disease develops, these cells can spread throughout the body - that is, they collect not only in the genital area, but can also reach the lungs. And if with an inflammatory course the chances of cure are high, then with endometriosis everything is complicated, for example, the possibility of conceiving a baby sharply decreases.
prevention of endometritis
Types of cervicitis due to inflammation
- Purulent. Occurs when infected with a sexually transmitted disease. Purulent cervicitis is characterized by mucous discharge with an unpleasant odor and involvement of nearby organs and tissues in the process.
- Viral. The mucous membrane becomes inflamed when infected with cytomegalovirus, human papillomavirus or other pathogens. The disease may be accompanied by itching and the appearance of polyps.
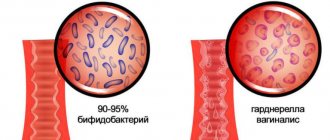
- Bacterial. Cervicitis develops from vaginosis, when active proliferation of pathogens of the natural microflora of the vagina occurs. Infection from a sexual partner is possible.
- Atrophic. The cause of the disease is thinning of the mucous membranes. Atrophic cervicitis often occurs in women during menopause.
When the uterus is inflamed. Endometritis: how to identify and treat
Endometritis is a disease of the female reproductive system that can lead to a woman being unable to have children in the future. Our questions about endometritis, its symptoms, diagnosis and treatment were answered by gynecologist, oncogynecologist at the Expert Clinic Tula Alexandra Alekseevna Dobrenko.
— Alexandra Alekseevna, what is endometritis?
— Endometritis is inflammation of the endometrium. The disease is quite common in women of childbearing age.
— What are the causes of endometritis? Why does it occur?
— As a rule, the cause of endometritis, i.e. inflammation, is an infectious agent. Any microorganism can act as an infectious agent: bacterial, fungal or viral. Combined causes of endometritis are very common. For example, a fungal component may be added to a bacterial infection.
Endometrial trauma, for example, as a result of an abortion, can also be a factor that provokes the development of endometritis.
— Among gynecological diseases there is a disease known as endometriosis. Tell me, are endometritis and endometriosis the same thing?
- No, these are two completely different diseases. What is the difference between endometritis and endometriosis? Their differences begin with the fact that the cause of endometritis is an infectious agent, and the cause of endometriosis (according to one of several theories) is a hormonal imbalance. These diseases should not be confused; they have completely different courses, clinical presentation and treatment.
To summarize: endometritis is inflammation of the endometrium. Endometriosis is an atypical arrangement of endometrial cells in other places, i.e. endometrial dystopia.
Read more about endometriosis in our article: Endometriosis: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
— What types of endometritis are there?
— Like any disease, endometritis has its own classification depending on various factors. Endometritis can be, for example, chronic and acute. The course of these two forms of the disease has significant differences. Symptoms in the chronic form are more blurred. Most often, the disease becomes chronic when acute endometritis is not treated.
Endometritis is also classified according to the nature of the pathogen (specific and nonspecific). Specific ones include infectious (viral, chlamydial, bacterial, protozoal, fungal) and parasitic endometritis. They can be provoked by pathogens such as herpes simplex viruses, chlamydia, mycobacterium tuberculosis, etc. With the nonspecific nature of endometritis, pathogenic flora is not detected in the uterus. A nonspecific form of endometritis can be caused by bacterial vaginosis, HIV infection, or the presence of an intrauterine device.
You might be interested:
Viruses and bacteria - what is the fundamental difference? Herpes: how to recognize and cure? I can't be seen. And I am! The hidden enemy – chlamydia Tuberculosis: a disease that knows no borders
— Please tell us about the signs of this disease. How does endometritis manifest?
— Clinical manifestations of endometritis depend on its form and are somewhat different. But if we summarize the general clinical manifestations, they include:
- discomfort in the lower abdomen,
- dyspareunia (pain during sexual intercourse),
- bleeding from the genital tract,
- discharge from the genital tract (purulent with an unpleasant odor or bloody),
- chronic pelvic pain syndrome,
- Irregular menstruation.
— How is endometritis diagnosed?
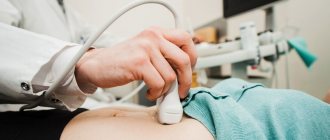
— When a woman comes in with the above complaints, the doctor may suspect endometritis. In order to make a diagnosis, a comprehensive examination is required: bimanual examination, examination of vaginal microflora, pelvic ultrasound.
The doctor may also suggest doing a hysteroscopy, i.e. an optical examination of the uterine cavity. Using a hysteroscope, you can see the condition of the endometrium and evaluate the nature of its pathological changes. In addition, material is taken (endometrial biopsy) for histological examination. Based on the result of an endometrial biopsy, a histologist can make a morphological diagnosis of “endometritis”, and then a gynecologist, accordingly, will be able to diagnose the patient.
Read materials on the topic:
What will a gynecological ultrasound show? Who can benefit from hysteroscopy? Histology: what kind of analysis is this?
— Alexandra Alekseevna, how is uterine endometritis treated? How effectively can doctors help a woman?
— Treatment of endometritis, like many other diseases, is complex and includes several parts. The main link, of course, is aimed at eliminating the infectious agent. This is antibacterial therapy. If endometritis is caused by several pathogens, then antibacterial therapy, antimycotics (antifungals), antiprotozoal and antiviral therapy are used. Plus, when the infectious agent is eliminated, it is imperative to help the body recover. For this purpose, drugs are prescribed that promote endometrial regeneration. And, as a rule, physiotherapy is used in the treatment of endometritis.
I repeat: the treatment is complex and is selected by the doctor for each patient individually.
— What could be the consequences if endometritis is not treated?
— Unfortunately, with a prolonged course, and also when the patient either does not fully comply with all the doctor’s recommendations or does not consult a doctor at all, endometritis can cause serious consequences in women of childbearing age, including infertility.
— Can endometritis turn into cancer?
— The mechanism of endometritis development itself excludes the degeneration of healthy cells into cancer cells. Therefore, according to statistics, we do not have such data. Endometritis is more of an infectious disease.
— Is it possible to get pregnant with chronic endometritis?
— Pregnancy with chronic endometritis is possible. And such cases are known. But I want to note that if a woman’s pregnancy is planned, then in any case she undergoes further examination. Additional examination may reveal endometritis. And before planning a pregnancy, it needs to be cured. I'll explain why. Chronic endometritis can cause miscarriages and other consequences of interruption of a planned and desired pregnancy. That is, it is possible to get pregnant, but problems during pregnancy and the occurrence of any pathologies cannot be ruled out.
— How can a woman protect herself from developing endometritis?
— Endometritis is an infectious disease that occurs, among other things, as a result of trauma to the endometrium. It occurs during abortive interventions, curettage of the uterine cavity. Accordingly, preventive measures include regular examinations by a gynecologist, the presence of one regular sexual partner, or contact only with a condom. And, of course, a woman who has an abortion has a higher risk of endometritis.
If you have the symptoms that we talked about earlier, you should definitely consult a doctor. Don't wait for it to go away on its own. Perhaps the woman currently has an acute form of the disease, and if it becomes chronic, the treatment will be more complex and protracted. Therefore, you need to monitor your health.
Interviewed by Marina Volovik
You can make an appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist here You can sign up for a pelvic ultrasound here ATTENTION: services are not available in all cities
The editors recommend:
Cytology smear: how to decipher correctly? What does an MRI of the pelvis show in women? Cervical polyp: why does it appear and what to do with it?
For reference:
Dobrenko Alexandra Alekseevna
In 2013, she graduated from the Faculty of Medicine at the Medical Institute of TULGU (Tula State University). 2013 – 2015 – residency in obstetrics and gynecology at the Federal State Budgetary Institution RNTsRR, Moscow. In 2016 – retraining in oncology at the TULGU Medical Institute. Currently, he is a gynecologist, gynecological oncologist at the Expert Clinic in Tula. Receives at the address: st. Boldina, 74.
Treatment of cervicitis
To select an adequate treatment regimen for cervical disease, the duration, severity of the disease, and cause are taken into account. If cervicitis is infectious, therapy will also be required for the sexual partner.
To treat acute inflammation of the cervix, your doctor may prescribe:
- Antibiotics of the fluoroquinolone or macrolide group. At the same time, it is recommended to take antifungal drugs that will prevent the development of candidiasis;
- Means for restoring microflora. A woman is prescribed medicinal suppositories, gels with lactobacilli;
- Immunomodulators. The drugs strengthen local immunity and help beneficial microflora resist the effects of antibiotics. Immunomodulators are taken in the form of powders or tablets;
- Hormonal medications with estrogens to regenerate the thinned mucous layer;
- Physiotherapy: endocervical electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, irradiation of the cervix with ultraviolet light, laser, microwaves, low-frequency ultrasound. Treatment is primarily aimed at restoring microcirculation of blood and lymph in the affected tissues. For chronic inflammation of the cervix, physiotherapy is carried out in courses several times a year to prevent exacerbation.
In rare cases, surgery is indicated. As a rule, the operation is performed in cases of severe and extensive inflammation, when the woman did not seek diagnosis at the onset of the disease. For treatment, the method of cryodestruction, diathermocoagulation or chemical coagulation of pathological areas is used.
Particular attention is paid to the treatment of exacerbation of cervicitis in pregnant women. The doctor carefully selects medications and calculates the dosage to eliminate risks to the fetus.
Diagnosis of inflammation in the appendages
During the consultation, a gynecologist examines a woman on a gynecological chair. Using a two-handed examination technique, the specialist identifies an increase in the area of the appendages. At this stage, they immediately take a smear for cytology and microflora in order to have a complete picture of the patient’s health status.
Next, you need to take laboratory tests: blood test, urine test, purulent discharge. It is important to identify the causative agent of the inflammatory process using microscopy and other techniques.
Basic instrumental research methods:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs, fallopian tubes. Shows the exact location and spread of the problem.
- Laparoscopy. Detects the condition of the internal tissues of the fallopian tubes. Thanks to the procedure, it is possible to immediately eliminate the purulent contents and excise the affected areas that are not suitable for restoration.
- X-ray examination with contrast agent. Indicates the patency of the pipes.
Diagnostics are carried out several times during the treatment period to evaluate the result of the chosen therapy program.
Why is cervical inflammation dangerous?
Self-medication risks complications, so only a doctor should decide how to treat a woman. If the patient does not seek help in a timely manner, acute cervicitis becomes chronic. A woman faces consequences such as erosion, miscarriage, and spread of the inflammatory process to the appendages. The risk of developing cancer increases. Chronic cervicitis leads to the formation of adhesions and infertility. Patients often experience chronic pelvic pain, menstrual irregularities and other manifestations that reduce quality of life.
Causes, symptoms and treatment of endometritis, video
Obstetrician-gynecologist Elena Koroleva about the treatment of endometritis.
Source - MC Juno Sources:
- CHRONIC ENDOMETRITIS AS ONE OF THE ACTUAL PROBLEMS IN MODERN GYNECOLOGY. Plyasunova M.P., Khlybova S.V. // Vyatka Medical Bulletin. – 2013. – https://cyberleninka.ru/article/v/hronicheskiy-endometrit-kak-odna-iz-aktualnyh-problem-v-sovremenno…
- CHRONIC ENDOMETRITIS AND PELVIC PAIN. Plyasunova M.P., Khlybova S.V. // Maltseva L.I., Smolina G.R., Yupatov E.Yu. // Obstetrics, gynecology and reproduction. – 2012. – No. 3. – pp. 23-27.
- Principles of individual hormonal preparation of the endometrium in patients with ineffective IVF attempts. E.V. Dyuzheva, E.A. Kogan, E.A. Kalinina, A.N. Kuzmichev // Akush. and gynecol. – 2011. – No. 7-2. – pp. 39-45.
- Cytokines and embrio implantation. C. Simon, C. Moreno, J. Remohi, A. Pellicer // J. Reprod. Immunol. – 1998. – Vol. 39. – pp. 117-31.
- Molecular and morphological aspects of endometrial receptivity disorders in chronic endometritis. E.A. Kogan, T.A. Demura, V.Ya. Vodyanoy, A.V. Shurshalina // Pathology Archives. – 2012. – Vol. 74(3). – P. 15-27.
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/endometritis
- https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/254169-overview
- https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article/file?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0088354&type=printable
- https://radiopaedia.org/articles/endometritis
Inflammation of the cervix during pregnancy
Cervicitis occurs in two out of three pregnant women at different stages of gestation. The disease is acute, not only the vaginal wall becomes inflamed, but also the labia. Women complain of burning, itching in the perineum, and discomfort. Inflammation of the cervix during pregnancy is one of the factors of miscarriage, so it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Cervicitis in this case is chronic. A woman may not be aware of inflammation until pregnancy, when the pathology manifests itself against the background of natural immunodeficiency.
Classification
Endometritis is classified according to stages:
- acute - occurs with severe general (intoxication) and local symptoms;
- subacute - occurs in the absence of treatment of endometritis in the acute phase against the background of weakened immune defense;
- chronic - characterized by an unexpressed clinical picture, involvement of the basal (deep) uterine layer, proliferation of the mucosa, disruption of its structure. Most often, it is chronic endometritis that leads to a woman’s infertility and miscarriage. Depending on changes in the endometrium, this stage can be hypertrophic (excessive growth of the membrane), atrophic (underdevelopment and insufficiency of glandular cells, proliferation of connective tissue). And cystic - the formation of intraendometrioid cysts.
Among patients experiencing problems with natural conception, from 12 to 68% suffer from chronic endometritis. Among women with unsuccessful attempts to use assisted reproductive technologies, the disease occurs in approximately 60%. 70% of patients with recurrent miscarriage have a diagnosis of chronic endometritis.
Doctor's recommendations
Every year, more and more women turn to us for treatment of chronic cervical inflammation. The reason is that the patient simply does not notice or ignores the first signs of cervicitis. We often detect inflammation when dealing with completely different complaints. This is dangerous for future motherhood. We recommend that couples with a history of stillbirth, frozen pregnancy, or intrauterine infection of the fetus undergo a thorough examination to identify hidden infectious agents. Only after treatment can you plan to conceive again. Miscarriages and premature births are a common consequence of cervical inflammation.
Small pelvis - risk factors
Factors that increase the risk of developing pelvic inflammatory diseases:
- unprotected sexual intercourse;
- women under 25 years of age have an active sexual life;
- sexual relations with many partners;
- procedure for inserting an intrauterine device;
- Regular vaginal douching, which disrupts the balance between “good” and “bad” bacteria in the vagina, can also mask obvious signs of infection;
- a problem with pelvic inflammatory disease or a sexually transmitted disease in the past.