Colpitis often develops in women during pregnancy. The disease is diagnosed in 75-80% of cases. The likelihood of developing inflammation does not depend on the duration of pregnancy. The high risk of infection persists throughout the entire period of gestation. The greatest danger to the unborn child is posed by a disease that occurs in the third trimester of pregnancy.
Colpitis during pregnancy due to weakened immunity is much more severe, and therefore poses a threat to the normal development of the fetus.
Toxins released by pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms cause inflammation that affects the uterus and birth canal. A child can get a “bad” disease not only in the womb, but also during delivery. The consequences of infectious infection are manifested by allergies, encephalopathy, and in the woman herself - endometritis, secondary infertility.
Causes of colpitis during pregnancy
The infection easily penetrates the mother's body, all of whose immune mechanisms are aimed at maintaining the life and development of the fetus. Due to hormonal changes, an alkaline environment is formed in the vagina, favorable for the proliferation and colonization of bacteria.
Predisposing factors to the development of infectious vaginitis in expectant mothers:
- early onset of sexual activity (14-16 years);
- chronic STIs;
- promiscuity;
- trauma to the vaginal mucosa (as a result of rough sex, medical procedures, surgical treatment);
- long-term antibiotic therapy.
If a woman leads a healthy lifestyle, lives with one partner, maintains intimate hygiene, and undergoes routine examinations with a gynecologist, then the risk of developing colpitis during pregnancy is minimal.
Any discomfort in the vagina, discomfort during sexual intercourse, or discharge should be a reason for a comprehensive diagnosis.
What is included in the examination for colpitis during pregnancy?
Causes of vaginosis, vaginitis and thrush
All three diseases are united by the fact that not only unprotected sexual intercourse can provoke the development of infection). The disease is also often associated with changes in hormonal levels, decreased immunity, and other reasons.
The essence of the process is this: every woman who has reached puberty has a unique microflora composition. It is not constant - the bioflora is formed by various factors, including ovulation, ARVI, stress, taking hormonal contraceptives, wearing tight-fitting trousers made of thick fabric, etc. All these processes cause a change in the conditions necessary for the life of certain bacteria. For example, when wearing synthetic panties, air access to the genitals is stopped, and the air temperature and humidity increase. As a result, anaerobic (air-hungry) beneficial bacteria die, and bacteria such as candida develop rapidly.
Getting thrush in an hour of being in a wet swimsuit in the sun is a piece of cake.
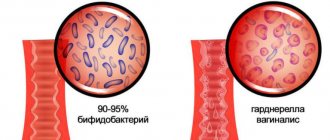
The microflora of a healthy woman is dominated by beneficial lactic acid bacteria (lacto- and bifidobacteria). When the quantitative and qualitative composition of the microflora shifts, beneficial bacteria give way to pathogenic anaerobic (able to live in the absence of oxygen) and facultative anaerobic (which oxygen does not have a destructive effect on).
The natural acidity level of 3.8-4.2 pH increases, and therefore lactic acid bacteria die (disintegrate), releasing ammonia. This is why vaginitis and vaginosis are characterized by an unpleasant smell of discharge.
Colpitis (vaginitis) most often occurs due to infection with an STD. This distinguishes it from vaginosis and thrush. Candidiasis (thrush) occurs without sexual intercourse. It is quite possible to pick it up in a pool or sauna if you sit on a bench without a towel. Thrush manifests itself when wearing neoprene shorts during fitness classes, tight-fitting trousers made of thick fabric, or playing sports in clothes not intended for this purpose. This disease worsens during adolescence, when rapid hormonal changes occur. It is rare that candidiasis is transmitted directly through sexual contact.
Symptoms of colpitis in pregnant women
Symptoms of colpitis differ depending on the type of pathogen and the stage of the disease. In the acute form, the clinical manifestations of the infection are pronounced, in the chronic form they are hidden, felt only during periods of relapse.
| Type of disease | Type of pathogen | Symptoms |
| Nonspecific colpitis | ||
| Candidiasis (thrush) | Candida fungus | Curdled white discharge, unbearable itching, redness of the genitals |
| Bacterial | Gardnerella, Escherichia coli, Proteus | Mucus discharge with an unpleasant odor, pain in the lower abdomen |
| Viral | Herpes, HPV | Foamy, foul-smelling discharge, erosions or “warts” on the vaginal mucosa |
| Specific colpitis | ||
| Gonorrhea | Gonococci | Discharge with pus, discomfort and pain in the vaginal area, pain during intercourse |
| Chlamydia | Chlamydia | Thick milky discharge, burning sensation in the vagina |
| Trichomoniasis | Trichomonas | Discharge with the smell of rotten fish, burning and pain when urinating |
The problem is that colpitis during pregnancy is caused not by one, but by several infectious agents. When examining a vaginal smear, an association of microorganisms is revealed, and in some of them, for example, in Candida fungi, more dangerous, pathogenic bacteria - ureaplasma and mycoplasma - can exist latently. In the early stages, this form of vaginitis is very dangerous for the child: hidden infections can cause miscarriage and affect the formation of the nervous system.
Clinic depending on the form of colpitis
In the acute form, the listed symptoms are noticeable for a long time and do not go away on their own. In addition to discharge with an unpleasant odor, the pregnant woman experiences discomfort when walking, constant burning and itching not only in the vagina, but also in the area of the inner thighs and buttocks.
In the chronic course of colpitis, the clinical signs are blurred, but even with a mild cold, a relapse can occur. The infection makes itself felt by redness of the genitals and scanty yellowish discharge.
During pregnancy, a woman, as a rule, especially carefully monitors her health and reacts with alarm to every unusual symptom.
Often the cause of panic for the expectant mother is unusual discharge and discomfort in the genital area. This set of symptoms most likely indicates the development of a pathological process, which in medicine is called vaginitis or colpitis. In pregnant women, this condition is observed especially often against the background of decreased immunity, hormonal changes in the body and high loads on all organs and systems of the woman.
Vaginitis during pregnancy is a good reason to immediately contact a gynecologist and begin treatment for this dangerous pathology. Qualified gynecologists will advise you to diagnose the disease and determine how to treat colpitis during pregnancy without harming the mother and baby.
Symptoms of colpitis during pregnancy
First of all, you should determine that vaginitis or colpitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the mucous membranes of the vagina. The inflamed walls of the vagina swell and become hyperemic. Also, isolated hemorrhages are observed on the surface of the vaginal tissues. If the inflammation does not spread beyond the vagina, the woman does not notice visual manifestations of the disease, while in some cases the pathological process affects the external genitalia. In this case, inflammation can be seen with the naked eye.
The characteristic signs of colpitis during pregnancy do not differ from the symptoms of a non-pregnant woman:
- itching and burning in the vaginal area
- the inflammatory process irritates the delicate mucous membranes, which causes discomfort and sometimes pain in the vaginal walls;
— lower abdominal pain
- this symptom is especially frightening for pregnant women, but it is not associated with the tone of the uterus, as many assume, but with tissue inflammation;
— the appearance of specific secretions
- discharge during colpitis during pregnancy is very abundant and can have a different color and consistency. Most often, a woman visually notices a white, cheesy discharge, reminiscent of a characteristic sign of thrush, but sometimes the vaginal discharge acquires a putrid odor and is greenish-yellow in color. This indicates the specific nature of the pathogen and requires immediate medical consultation;
— swelling and redness of the genitals
— patients often notice hyperemia and swelling of the labia and clitoris, which become more sensitive and cause discomfort to the woman.
Acute vaginitis during pregnancy is accompanied by severe symptoms, which should force the patient to seek professional help. This will help protect the child from possible negative consequences.
Causes and types of vaginitis during pregnancy
Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the vagina is usually of an infectious nature. This becomes possible due to vaginal dysbiosis, which often accompanies pregnancy. Hormonal changes and high loads on all organs of the expectant mother cause a decrease in the body's defenses, which provokes an infectious and inflammatory process. In this case, the causative agent of the pathology can be either bacterial flora that entered the body from the outside during sexual intercourse or through everyday life, or a component of the normal microflora of the vagina. The most likely infectious agents of colpitis in pregnant women include streptococci, fungi of the genus Candida, Escherichia coli, Trichomonas, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, etc.
It is interesting that depending on the cause of the development
of the disease, its symptoms and manifestations may differ:
- candidal colpitis
- accompanied by copious curdled discharge and severe itching of the genitals, which manifests itself even at rest;
— emphysematous colpitis
- a very common type of vaginitis in pregnant women. The pathology is accompanied by the formation of small watery blisters on the surface of the mucous membranes of the genital organs. This form of colpitis goes away on its own 2-3 weeks after birth;
— trichomonas colpitis
- a very dangerous form of pathology that develops when trichomonas enter the vaginal environment. Infection occurs during sexual intercourse or through the use of personal hygiene items shared with the carrier (towel, washcloth, etc.). It manifests itself as a characteristic putrefactive discharge with a strong unpleasant odor.
Concomitant conditions for the development of colpitis in a pregnant woman, in addition to decreased immunity, can be allergic reactions, microtrauma of the vagina, poor personal hygiene, and the presence of chronic diseases.
Colpitis during pregnancy: consequences for the child
Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the vagina poses a threat not only to the health of the expectant mother, but also to the baby. The ascending route of infection can lead to pregnancy abnormalities such as polyhydramnios, premature birth and contamination of amniotic fluid. Vaginitis is especially dangerous during childbirth, when the baby passes through the infected maternal birth canal. At
this moment, the likelihood of infection of the newborn is high.
Interestingly, colpitis after pregnancy can go away on its own, but this happens relatively rarely. The development of colpitis after childbirth is most often provoked by injury to the vaginal membranes during delivery. Due to this fact, doctors recommend abstaining from sexual activity in the first weeks after childbirth. By violating this prohibition, a woman increases the risk of developing colpitis after childbirth.
Treatment of colpitis during pregnancy
Diagnosis of the disease involves a standard gynecological examination and colposcopy.
This research method makes it possible to visualize the surface of the mucous membrane of the vaginal walls and assess their condition. During the examination, the doctor takes a smear for analysis. The study of biological material is carried out using bacterioscopic and bacteriological methods.
Treatment of colpitis in pregnant women requires a rational approach to the prescription of antibiotics.
The doctor selects an antibacterial drug that can suppress the pathogen identified in the smear, and at the same time does not have a negative effect on the fetus. Often preference is given to local forms of antibiotics - suppositories, ointments and tampons. Treatment is supplemented with restorative therapy and safe physiotherapeutic procedures.
Treatment methods for colpitis in expectant mothers
Treatment of the disease during pregnancy is somewhat difficult. The main method of destroying infectious agents is antibiotic therapy. Most antibacterial drugs have side effects on the fetus. Long-term use of antibiotics provokes the addiction of pathogenic microorganisms and the further spread of infection.
When choosing treatment tactics, the doctor’s primary task is not to harm the child, so the safest combination of medications is selected. If the disease is mild, then local procedures and medications are limited. You can make vaginal baths with medicinal herbs (chamomile, oak bark, calendula), put candles at night, for example, Terzhinan.
Systemic therapy
In the acute form, systemic therapy is carried out, aimed not only at destroying foreign microflora, but also at normalizing the protective environment of the vagina, eliminating pain, and relieving discomfort associated with inflammation of the genital organs.
The standard course during pregnancy is prescribed only from the 2nd trimester and includes several types of drugs:
- antifungal (for thrush) - Nystatin, Pimafucin;
- antiprotozoal (for trichomoniasis, chlamydia) – Metronidazole (topically);
- antibacterial (for nonspecific colpitis) – Erythromycin;
- to restore intestinal microflora - Bifidoback, Linex.
The combination of medications, dosage and duration are selected by the doctor. In this case, both partners must undergo a course of treatment for colpitis. To restore the natural microflora, it is useful for pregnant women to consume fermented milk products, eat lingonberries, and sour berries.
Read more about the treatment of colpitis during pregnancy
Diagnosis and treatment of colpitis at the Miracle Doctor clinic
First, they resort to a routine gynecological examination in the speculum. But the most effective diagnostic method is colposcopy, an endoscopic examination of the vagina. It allows you to clearly see the hyperemic (reddened) edematous mucosa with areas of hemorrhage and ulceration.
A gynecological smear for flora must be taken. Treatment of colpitis in women in the acute phase is carried out with anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and restorative agents in tablets, injections and topically in the form of vaginal suppositories and ointments. In the recovery phase, restorative therapy is continued; to restore normal microflora, probiotics are prescribed locally in suppositories and tablets.
Prevention of colpitis during pregnancy
To prevent colpitis, women planning pregnancy and after conception are advised to regularly visit a gynecologist and get tested for bacterial infections. Protected sex, following doctor's recommendations on nutrition and lifestyle, careful hygiene of the genital organs are measures that will help avoid conditions that are dangerous to the life of the unborn child.
To make an appointment or get advice, call the 24-hour number
+7
or fill out the form
Composition of a smear for microflora: norm and pathology
To identify the composition of the flora, you need to take a smear from a gynecologist. A smear on the flora is taken from the urethra (U), from the cervix (C) and the vaginal wall (V).
In a healthy woman, the composition of the microflora will look like this:
- Flat epithelium
. If it lines the walls of the vagina in layers, this indicates vaginitis, because normally there should be single digits of squamous epithelial cells. If there are no squamous epithelial cells at all, this indicates atrophic vaginitis. - Leukocytes
. They are designed to neutralize the causative agent of infection, therefore they are characteristic of inflammation. White blood cells are absent only in vaginosis. - Gram-positive rods
(staining blue during the Gram test). These are lactobacilli and Dederlein bacilli, which maintain optimal alkaline balance in the vagina. They feed on glycogen, a polysaccharide that gives life to beneficial microorganisms. When glycogen breaks down, lactic acid is formed, which prevents pathogenic bacteria from multiplying. With a decrease in immunity, gram-positive bacilli are reduced in quantity and are unable to resist infections. The more gram-positive rods in the composition, the better. - Slime
. It is needed to maintain a moist environment of the vaginal mucosa. Mucus is secreted by the glands of the cervical canal. Normally, the volume of mucus secreted is equal to the amount absorbed (about 5 ml), and an increase in the norm indicates inflammation of the cervix. - Key cells
. It is a squamous epithelial cell surrounded by bacteria. This only happens when the vaginal microflora is disrupted.
Treatment of vaginosis, vaginitis and candidiasis
Whether or not to treat these diseases is up to you to decide. All three pathologies may not give unpleasant signs for a long time and the woman may well come to terms with the state of affairs. Another option is to self-medicate, which, as you know, will definitely not lead to anything good.
Treatment of all three diseases is carried out with antiseptics in the form of suppositories, tablets or ointments. It is prescribed exclusively by a doctor and selected according to individual indications.
If you still made the right decision and chose treatment from a gynecologist, come to the Diana clinic in St. Petersburg. Here you can get tested inexpensively and be cured of any gynecological disease.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Comparative analysis of the results of a smear on microflora from the vagina
| Index | norm | vaginosis | vaginitis | candidiasis |
| leukocytes | 0-10 | 8-10 | over 30 | 5-100 |
| squamous epithelium | 5-10 | 5-10 | 25-40 | |
| gonococci | No | There is | a large amount (for gonorrheal vaginitis) | There is |
| key cells | No | There is | many cells surrounded by gardnerella | There is |
| yeast | No | There is | There is | over 104 CFU/ml |
| slime | moderately | above normal | a large number of | There is |
| microflora | Dederlein sticks | bacilli mobiluncus curtisii, Gardnerella vaginalis | low number of lactobacilli | Candida albicans |
| pH | 3,5-4,5 | 5-6,5 | 4-6 | 4-5 |
Leading specialists in the treatment of colpitis, vaginitis in the Southern Federal District
Ermolaeva Elvira Kadirovna is a well-known and recognized specialist in the North Caucasus in the treatment of colpitis, vaginitis in girls, adolescents and girls who have not been sexually active. Gynecologist, ultrasound doctor, physiotherapist-health resort specialist. Suffering women and women who want to improve aesthetics turn to Elvira Kadirovna genitals, shrink the vagina and refresh intimate relationships from all regions of Russia and foreign countries.
Ermolaev Oleg Yurievich Candidate of Medical Sciences, pediatric gynecologist with 25 years of successful experience in the treatment of colpitis and vaginitis. Able to see relationships that elude others.
Shchepkin Petr Sergeevich Gynecologist, specialist in the treatment of colpitis, vaginitis. Experienced ultrasound doctor.
About the doctors of the Clinic in detail...
| INTERNATIONAL RECOGNITION of the reputation and achievements of the Women's Health Resort Clinic in the development and implementation of effective and safe treatment methods and the quality of medical services provided is the AWARDING of the Women's Health Resort Clinic in Pyatigorsk with the SIQS International QUALITY CERTIFICATE in the field of medicine and healthcare. International Socratic Committee, Oxford, UK and Swiss Institute for Quality Standards, Zurich, SWITZERLAND. |
We work seven days a week and on holidays:
Monday - Friday from 8.00 to 20.00, Saturday, Sunday, holidays from 8.00 to 17.00.
Treatment of colpitis, vaginitis by appointment by multi-line phone 8 (800) 500-52-74 (toll-free within Russia), or +7.
| ONLINE information about the treatment of colpitis and vaginitis can be found at: REGISTER ONLINE for the treatment of colpitis and vaginitis here. REGISTER online for treatment of colpitis and vaginitis here. Buy coursework by phone +7 (928) 022-05-32 or here. |
Make an appointment with a gynecologist
We accept girls, young women and women from all cities of Russia, near and far abroad.
The spa clinic for women's health facilitates the accommodation and accommodation of women, women with children and couples during examination and treatment.
During the treatment period and after treatment of colpitis and vaginitis, contraception (protection) with a condom is necessary until “clean” results of a control smear examination are obtained for both spouses.
A control microscopic examination of a smear for vaginal flora is carried out 5 days after the end of local treatment. Service cost
With respect for the religion and different habits of our patients, we achieve high efficiency and comfort of treatment.
We are at your FULL DISPOSAL if you have any doubts or wishes.