Disease of the foreskin is a dangerous condition that is not only accompanied by pain, discomfort during urination and sexual intercourse, but can also lead to serious consequences - necrosis of the glans penis, genitourinary diseases, and precancerous conditions. Therefore, at the slightest symptoms, you should consult a urologist. Treatment in most cases requires surgery - circumcision of the foreskin. It is important not to waste time!
1
Consultation with a urologist in MedicCity
2 Consultation with a urologist in MedicCity
3 Consultation with a urologist in MedicCity
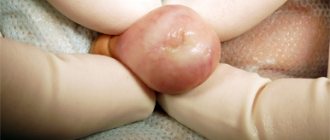
Phimosis
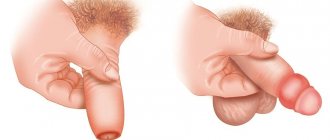
Phimosis is the inability to expose the head of the penis due to narrowing of the foreskin. Phimosis in men can be congenital (physiological) and pathological.
Physiological phimosis is caused by gluing of the inner layer of the foreskin to the head of the penis. Phimosis in very young boys is normal and is detected in 90% of cases. This condition becomes pathological if it does not go away by 6-7 years. Sometimes phimosis occurs due to a short frenulum connecting the head of the penis and the foreskin.
Physiological phimosis in boys does not require treatment if it does not cause any discomfort in the child. However, parents need to monitor the condition of the child’s external genitalia (for example, while bathing the baby). Swelling and redness of the foreskin, difficulty urinating, itching - this is a reason to urgently consult a urologist!
Pathological phimosis has 4 stages:
- Stage 1 - in the normal state, the head of the penis is exposed without difficulty, during an erection - with effort;
- Stage 2 - it is difficult to release the head of the penis even in a calm state, and during an erection it is impossible to do this;
- Stage 3 phimosis - the head is not exposed at all or is exposed only in a calm state and with considerable effort. However, there are no difficulties with urination;
- Stage 4 of phimosis – it is not even possible to slightly open the head, the patient experiences difficulty urinating.
The main complaints of patients with phimosis include pain when trying to expose the glans penis, during erection, hygienic problems associated with the accumulation of smegma in the preputial sac, as well as problems with urination.
It is not phimosis itself that is dangerous, but its complications. Excessive force when trying to free the head can lead to its pinching - paraphimosis. In this case, the head swells, turns blue, becomes sharply painful, and it is impossible to set it back on your own. If the patient is not provided with emergency medical care, he may develop necrosis of the head, which threatens its amputation.
Causes of phimosis:
- genetic predisposition (pathologically low elasticity) of the connective tissue of the genital organ);
- trauma to the penis with the formation of scar tissue, which leads to narrowing of the foreskin (cicatricial phimosis);
- inflammation of the foreskin of the penis (balanoposthitis), leading to scarring, phimosis;
- inflammation of the foreskin resulting from various infections;
- gluing of the glans penis and the inner layer of the foreskin in children.
The presence of phimosis is a factor in the development of further narrowing of the foreskin and the formation of microtears (and, accordingly, the formation of scar tissue) when the glans penis is exposed or during an erection. Phimosis progresses, so it must be treated.
How to treat phimosis?
Treatment of phimosis in children
Many parents are concerned about whether something needs to be done if their children have phimosis? What treatment is needed for phimosis? Is it possible for children diagnosed with phimosis to be treated without surgery? For children under 3 years of age, if the baby does not experience difficulty urinating, pain or discomfort, treatment for phimosis is not required.
After 3 years, the boy begins to develop an erection in the morning, and the body itself will carefully push the boundaries of the foreskin, removing the consequences of phimosis.
Treatment of phimosis in adults
One of the effective non-drug methods for treating phimosis is the method of exposing the foreskin. This should be done daily for 15 minutes.
Non-surgical treatment involves the use of ointments containing corticosteroids, which are applied to the foreskin and glans penis. Reviews about the treatment of phimosis on the Internet indicate that applying ointments is not always effective. Therefore, it is better not to self-medicate, but to turn to specialists.
1 Surgery for phimosis
2 Surgery for phimosis
3 Surgery for phimosis
Phimosis is treated using the following surgical techniques:
- conservative surgery;
- circumcision of the foreskin;
- laser treatment;
- Plastic surgery.
After phimosis, patients may experience some pain and decreased sensitivity of the glans penis. Sutures after surgery for phimosis are removed after a week, during this period the patient is prescribed dressings and follow-up examinations by a specialist.
Diagnostics
A urologist-andrologist determines the nature of the pathology. The doctor collects anamnesis, establishes when and under what circumstances the pain syndrome appeared, what other symptoms it was accompanied by, and how the disease developed. Important information is the presence of injuries, unprotected sexual intercourse, the use of spermicides, the connection of pain with erection, rough sexual intercourse, homosexual contact, attempts to prolong an erection using improvised means. The examination program includes the following diagnostic measures:
- Visual inspection
. The specialist evaluates the appearance of the external genitalia, identifies deformations, swelling, discoloration, tumor-like formations, examines the sensitivity of the penis, and palpates the inguinal lymph nodes. - Ultrasound of the penis.
Informative for hematomas, Peyronie's disease, tumors, inflammatory processes. It can be performed separately or in combination with ultrasound examination of blood vessels. Detects foci of fibrosis, tumor-like formations, thickening of the tunica albuginea, changes in the lumen of blood vessels, signs of atherosclerosis of the arteries, and vein thrombosis. - MRI of the penis.
It is carried out in diagnostically difficult cases when cancer or penile fracture is suspected. To increase information content, it can be performed using a contrast agent. - Lab tests
. In case of an inflammatory process, smear microscopy is performed; in case of leukocytosis, PCR, RIF, ELISA, and microbiological examination are prescribed. For patients with space-occupying formations and fibrous changes, a histological examination of the biopsy specimen is indicated.
Balanoposthitis
Balanoposthitis in men is two diseases that usually accompany each other. Balanitis (or balanoposthitis of the glans) is manifested by inflammation of the head of the penis. Posthitis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the foreskin.
Balanoposthitis is characterized by inflammation and various rashes throughout the male genital organ.
According to medical statistics, children suffer from balanoposthitis more often than adults. Only balanoposthitis in men is more often caused by non-compliance with hygiene rules, and in children it is caused by phimosis. The disease can be caused by various infections, including sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Like any disease, balanoposthitis has acute and chronic forms. If there is no appropriate treatment for balanoposthitis, then balanoposthitis from the acute form can turn into chronic balanoposthitis.
Acute balanoposthitis
Balanoposthitis in acute form comes in the following varieties:
- simple ( catarrhal balanoposthitis ). Itching of the skin, burning, tissue swelling, and hyperemia appear. The skin becomes wrinkled, discolored and swells, erosions of different sizes appear on it, sometimes they merge with each other. Ulcers with purulent discharge form;
- erosive balanoposthitis . Large, bright red erosions appear on the affected area, the area of the inguinal lymph nodes is extremely painful, and the patient may develop a fever;
- gangrenous balanoposthitis . The ulcers become deep and become covered with a purulent coating of a dirty yellow color, swelling of the glans penis and the entire foreskin, phimosis occurs. In severe cases, penile gangrene may develop.
After curing the simple and erosive form, there are no scars left. After pustular-ulcerative and gangrenous balanoposthitis, deep scars appear, and deformation of the penis may appear.
Chronic balanoposthitis
Balanoposthitis of the penis in chronic form is characterized by pain, hyperemia and swelling, whitish deposits in the foreskin, difficulty exposing the head, discharge with pus during urination and pain during intimate contacts. The chronic course of balanoposthitis manifests itself in viral, venereal and fungal diseases.
The disease continues for months, periods of exacerbation alternate with periods of improvement. Chronic balanoposthitis can provoke the development of urethritis, prostatitis, pyelonephritis and infertility.
Quite often in men, candidiasis balanoposthitis occurs, which is associated with the ingestion of the yeast-like fungus Candida.
The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- redness, irritation and swelling;
- the appearance of red spots of different sizes;
- the appearance of a constant cheesy white discharge on the head of the penis;
- the occurrence of itching, burning, and unpleasant odor.
Balanoposthitis does not occur in women. Candida fungi, which provoke balanoposthitis in men, cause vulvovaginal candidiasis in women.
1 Diagnosis of balanoposthitis
2 Diagnosis of balanoposthitis
3 Diagnosis of balanoposthitis
Causes of balanoposthitis
There may be several reasons for the development of balanoposthitis:
- weak immunity, which is the “culprit” for the appearance of various pathogenic microflora in the body;
- mechanical or chemical damage to the skin;
- poor hygiene;
- sexually transmitted diseases: gonorrhea, syphilis, viral herpes, mycoplasma, trichomoniasis;
- intimate relations with a woman who has vaginal dysbiosis;
- diabetes mellitus (an infection can also occur as a result of improper metabolism).
Symptoms of balanoposthitis
Symptoms of the disease may be the following:
- painful sensations in the penis area, accompanied by itching, pain, premature ejaculation and decreased duration of sexual intercourse;
- the appearance of red spots, cracks and ulcers on the head of the penis and foreskin;
- copious discharge from the head of the penis, discharge can completely wet underwear, so hygiene procedures must be carried out several times a day.
Treatment of balanoposthitis
Many men are concerned about the question: how to treat balanoposthitis?
Treatment of balanoposthitis is complex, it includes maintaining hygiene and treating the diseased organ with an antiseptic solution of furatsilin.
Drugs for the treatment of balanoposthitis are used as prescribed by a doctor; these can be antibiotics or antiviral drugs.
Prevention of Perioni's disease
Since the exact causes of the disease are still unknown, it is difficult to offer specific prevention of Peyronie’s disease. However, men are advised to adhere to a certain lifestyle to minimize the occurrence of the disease.
- Healthy lifestyle (healthy diet, exercise, regular checkups).
- Wear comfortable underwear and loose pants.
Article information
| Last update | April 21, 2021 |
| Next update | April 21, 2022 |
| Author | Potapov S.A. |
| Medical editor | Doctor Plekhanov A.Yu. |
Bibliography
- Guidelines on Penile Curvature; European Association of Urology (2015)
- Bilgutay AN, Pastuszak AW; Peyronie's Disease: a Review of Etiology, Diagnosis and Management. Curr Sex Health Rep. 2015 Jun 17(2):117-131. doi: 10.1007/s11930-015-0045-y.
- Gelbard MK, et al. The natural history of Peyronie's disease. J Urol 1990 144(6): p. 1376-9.
- Jarow JP, et al. Penile trauma: an etiologic factor in Peyronie's disease and erectile dysfunction. J Urol 1997 158(4): p. 1388-90.
Lichen sclerosus
Lichen sclerosus is considered a precancerous skin disease and requires constant monitoring by a specialist. The manifestation of the disease is white atrophic plaques on the genitals. The affected tissues have a pearly-whitish color (secondary vitiligo) and are characterized by increased dryness, which can lead to phimosis. Patients complain of itching, burning, urination problems and painful sexual intercourse. As a rule, surgical treatment (circumcision) is recommended for this disease.
You can see the cost of surgery for phimosis and other urological procedures here.
Contact Medixity! Our specialists know how to cure balanoposthitis and a wide range of other urological diseases.
Classification
Peyronie's disease is classified according to stage, cause and degree of deformity.
Taking into account the cause of occurrence, the following are distinguished:
- acquired form – developed as a result of hormonal imbalance or injury;
- congenital – formed as a result of intrauterine disorders.
According to the degree of progression, Peyronie's disease is divided into:
- pain – severe pain is observed at rest and during erection;
- functional - apart from pain, with the disease it is impossible to lead a normal sex life.
According to the degree of deformation, the disease is divided into several types:
- dorsal – the penis is directed upward;
- ventral – the genital organ is tilted down;
- lateral - the penis is directed to the side.
Peyronie's disease is not a disease that poses a threat to human life, but has a high social significance, since it has a direct impact on sexual communication, and, therefore, the quality of life of men of active working age.
Pimples on the penis in a child
This alarming symptom in a child may indicate simple heat rash. During the hot season, due to increased sweating, children's delicate skin becomes irritated, causing small pimples to appear.
A more dangerous cause is intestinal mycosis. This manifestation is also characteristic of a very contagious disease - frequency. Only a doctor can identify the specific cause, so first of all the child must be shown to a specialist.