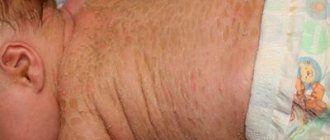
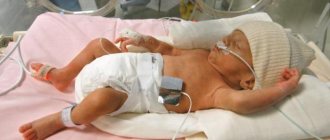
Harlequin ichthyosis (harlequin fetus, Latin ichthyosis fetalis) is a rare genetic disease belonging to the group of genodermatoses and inherited in an autosomon-recessive manner. This is the most severe form of congenital ichthyosis, which is characterized by the presence of rhomboid and polygonal hyperkeratotic plates in newborns. They cover the entire body in a geometric pattern reminiscent of a harlequin costume (hence the name of the disease). In addition, other changes are observed that pose a direct threat to life. Babies with harlequin ichthyosis have low birth weight. Previously, they quickly died due to the addition of a systemic infection or as a result of thermoregulation disorders. Modern medicine has made progress in combating the symptoms of this disease, so there is a chance to save the life of a newborn.
It is difficult to calculate the exact frequency of occurrence; doctors believe that it is 1:1000,000 cases. In closed communities (for example, in tribes), ichthyosis of the harlequin type is diagnosed more often, because there is a higher likelihood of marriages in which both partners are carriers of the mutant gene. The pathology equally affects female and male infants.
Signs and symptoms
The skin of babies with Harlequin ichthyosis is covered with thick, scaly, diamond-shaped plates (see photo above). The tightness of the skin stretches around the eyes and mouth, causing the eyelids and lips to turn inside out, exposing the red inner lining. The baby's chest and abdomen may be severely restricted due to tight skin, making breathing and feeding difficult. The arms and legs may be small, swollen, and partially bent. The ears may appear misshapen or missing, but are actually fused to the head due to thick skin. Children born with Harlequin ichthyosis may also have:
- flat nose (depressed nasal bridge);
- hearing impairment;
- frequent respiratory infections;
- decreased joint mobility.
Premature birth is common, leaving babies at risk for complications during early labor. These infants are also at high risk for low body temperature, dehydration, and hypernatremia (high levels of sodium in the blood). Narrowing and swelling of the mouth may interfere with absorption, and infants may require tube feeding. The infant's corneas need to be lubricated and protected if the eyelids open under the pressure of tight skin.
Diagnosis of Harlequin ichthyosis
Most often, diagnosis is carried out after birth, based on the clinical picture. If the parents have a genetic predisposition to this mutation (there were similar cases in the family), it is advisable to look for signs during an ultrasound that may indicate fetal ichthyosis:
- flat face profile;
- flat nose;
- wide “fish” mouth, macroglossia (large tongue);
- flat ears or no ears;
- swelling of the thighs and legs;
- slowing of fetal growth.
The symptoms listed are not specific and may indicate other health problems. Therefore, if the doctor is in doubt, he may order a skin biopsy.
The symptoms listed are not specific and may indicate other health problems. Therefore, if the doctor is in doubt, he may order a skin biopsy.
Causes
Harlequin ichthyosis is caused by changes (mutations) in the ABCA12 gene, which provides instructions for making a protein necessary for normal skin cell development. The ABCA12 gene plays a key role in transporting fats (lipids) to the most superficial layer of the skin (epidermis), creating an effective skin barrier. When this gene mutates, the skin barrier is destroyed.
Harlequin ichthyosis is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. Recessive genetic disorders occur when a person inherits an abnormal gene from each parent. If a person receives one normal gene and one abnormal gene for a disease, the person will be a carrier of the disease, but usually asymptomatic. The risk that two carrier parents will both pass on the abnormal gene and therefore conceive an affected child is 25% in each pregnancy. The risk of having a child who is a carrier like the parents is 50% with each pregnancy. The chance for a child to receive normal genes from both parents is 25%. The risk is the same for men and women.
Can it be cured?
At the current stage of development, medicine is not yet able to cope with genetic diseases, so modern treatment of ichthyosis is aimed at reducing clinical manifestations and alleviating the patient’s condition. For this purpose they prescribe:
- vitamin complexes, iron-containing compounds, immunoglobulin;
- blood plasma transfusions;
- hormone therapy (in difficult cases);
- baths with the addition of various drugs, emollient ointments and creams;
- physiotherapy, spa treatment according to indications.
The choice of treatment methods depends on the degree of skin damage and the characteristics of the disease.
Standard Treatments
Once a baby with Harlequin ichthyosis is born, a multidisciplinary team of doctors will be involved in the baby's care. It has been shown to improve outcomes and reduce complications such as respiratory distress, dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, thermoregulation, systemic bacterial infections and nutritional difficulties. Early treatment with oral retinoids is thought to improve outcomes. However, they are only used in severe cases due to their known toxicity and side effects.
The thick, scaly, lamellar skin of Harlequin ichthyosis will gradually split and peel off over several weeks. Antibiotic treatment may be necessary at this time to prevent infection. Administration of oral acitretin may accelerate the release of thick scales. Most babies with Harlequin ichthyosis will require one-on-one care in the first few weeks of life.
After the thick scaly plates peel off, the skin remains dry and red and may be covered with large thin scales. Skin symptoms are treated with skin emollients. This can be especially effective after swimming while the skin is still damp. Many patients with severe ichthyosis are exfoliated by hand, using special exfoliating gloves with a rough surface to rub off the thick scales.
Skin barrier repair formulas containing ceramides or cholesterol, moisturizers with petrolatum or lanolin, and mild keratolytics (products containing alpha hydroxy acids or urea) can help keep skin hydrated and elastic, and prevent cracking and cracking that can lead to infection. . To avoid loss of circulation, it may be necessary to remove damaged tissue (debridement) from the fingers if they are compressed by strips of skin.
Prognosis and complications of Harlequin ichthyosis
The prognosis is unfavorable: 50% of newborns die in the first few days after birth. Those who survive a critical moment may later struggle with:
- ocular complications (as a result of persistent eyelid inversion);
- slower growth;
- motor impairments;
- psychological problems and lack of social skills.
Long-term use of retinoids can cause complications in the liver, kidneys, and cardiovascular system. Unfortunately, the life of people with such a diagnosis is generally associated with enormous suffering, but medicine does not stand still, and every day new techniques appear that significantly improve the patient’s condition.
Forecast
The mortality rate from Harlequin ichthyosis is high, with rates approaching 50% worldwide. A review of 45 cases by Dr Rajpopat et al identified 25 survivors (56%) ranging in age from 10 months to 25 years. Twenty deaths (44%) occurred from days 1 to 52 and were as likely to cause respiratory failure as fulminant sepsis. A Japanese survey of 16 patients reported a survival rate of 81.3% (13 of 16 patients). Respiratory failure, fulminant sepsis, or a combination of both are the most common causes of death in newborns.
Possibilities of early diagnosis
Even at the stage of planning a child, future parents need to visit a geneticist.
To reduce the risk of genetic diseases, the doctor carefully collects family history, analyzes existing diseases in the family, including cases of various skin diseases. Couples with a high risk of developing genetic pathologies in the baby may be recommended to undergo in vitro fertilization with preimplantation genetic diagnosis. This method allows for genetic research of embryos before transplantation into the uterine mucosa. If pregnancy does occur, for early detection of harlequin ichthyosis, doctors may prescribe:
- electron microscopy of fetal skin particles (sampling of material for research is carried out under ultrasound or fetoscope control);
- diagnosis based on chorionic villi (this study is carried out at a period of 7-16 weeks under ultrasound control);
- amniocentesis (analysis of amniotic fluid);
- 3D or 4D ultrasound examination.
If Harlequin ichthyosis is confirmed in the fetus, the woman is clearly indicated for artificial termination of pregnancy. To date, doctors cannot offer any alternative for parents of children with this disease.
Lamellar ichthyosis: photo with description, treatment, causes, symptoms
A severe skin disease, lamellar ichthyosis, is inherited. For many years, doctors from different countries have been searching for a cure. The disease is one of the incurable diseases, but scientists still hope to find a treatment for lamellar ichthyosis.
Lamellar ichthyosis in newborns
It is diagnosed immediately at birth, since the skin is covered with a specific film. It is possible to predict the disease before birth, but the biopsy that is used can harm the fetus.
When the newborn is in a kind of cocoon of a yellowish-brown color. It is not immediately possible for doctors to accurately determine the type of disease.
When the film comes off, the entire skin becomes covered with scales, which may disappear over time. There are cases when the dermis is completely cleansed and becomes healthy. But as the disease progresses, areas similar to fish scales remain on the body.
Varieties of the disease
The disease is classified according to severity.
- Hystrixoid form (extremely severe) - symptoms are pronounced, often occurs in premature babies. They live for several months.
- Moderate form - newborns survive.
- Late form - appears several months after the baby is born.
Care
For external care that provides nutrition and softening of the dermis, you can use Vaseline immediately after water procedures. The affected skin must be protected from various types of infections, since the immunity of those suffering is reduced. In this case, in the first aid kit it is necessary to protect patients from infections and fungi. For this they can use
special ointments. Doctors can prescribe keratolytic agents that help exfoliate scales and cleanse the dermis. Also, for this disease, creams are used that can reduce the manifestations of keratosis.
The drugs are used with caution, as there is a real danger of intoxication
A good result is obtained by using vitamins of group A internally. Also, other groups of vitamins can be prescribed by doctors. Under no circumstances should you resort to self-medication. The disease is very complex, and a whole group of doctors helps to cope with it. Support from family and friends is necessary for those suffering; they may have low self-esteem.
Maintaining immunity
For the purpose of prevention and improvement of general condition, patients are prescribed other drugs:
- Sedatives.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes.
- Hormonal drugs (during exacerbations, in severe cases).
- Immunostimulating drugs (immunoglobulin, others).
- Zinc courses.
To improve the functioning of other organs
Due to the fact that the endocrine system of patients suffers, doctors prescribe drugs to improve the functioning of the thyroid gland. The liver also needs to be supported, since it bears a large load. And the kidneys may need support.
Physiotherapy
With this disease, it is necessary to maintain a certain temperature in the house where the patient lives throughout his life. It is necessary to protect those suffering from heat, hypothermia, and physical exertion. If the patient is overheated, he is wrapped in a wet sheet and doused with cool water.
Physiotherapy is also considered as one of the treatment options. Doctors recommend:
- take baths with bischofite salt;
- do underwater massage;
- apply mud applications;
- irradiate the skin with a UV lamp;
- use thalassotherapy (sea bathing, smearing with mud, seafood, sea air);
- use heliotherapy (solar therapy. Infrared rays are collected in a beam and directed to diseased areas. For this, a special mirror reflector is used, which you can prepare yourself).
Climatotherapy refers to homeopathic, alternative treatment.
Treatment of lamellar ichthyosis with traditional methods
Compresses, homemade ointments, and herbal preparations have a softening effect. The most used and easily accessible include:
- honey with aloe (biologically active mixture, suitable for internal and external use);
- Kombucha (used only internally. Improves well-being);
- sea buckthorn oil (lubricate rough areas, cracks);
- unsalted lard with buckthorn leaves (an ointment is prepared from the ingredients).
Traditional treatment produces results, but they are not stable. Therefore, this type of treatment can only be used in combination with other methods.
Ichthyosis in children
As a rule, the disease manifests itself at birth. In severe cases (for example, harlequin ichthyosis), the child is born prematurely and dies in the first days. However, the pathology can manifest itself in the second or third month of life, and sometimes the first manifestations occur at the age of 5 years. With moderate severity, this pathology is compatible with life.
If we talk about the gender of patients, it is worth noting that girls are carriers of the mutated gene, but mostly boys suffer from this pathology. Girls get sick in rare cases - for this to happen, two X chromosomes with the affected genes from both the mother and the father must match. In this case, the disease is very severe and can lead to the death of the child.
Against the background of the disease, pathological changes in other organs and systems are observed. These children are often diagnosed with:
- corneal clouding.
- epilepsy,
- disruption of the development of the skeleton and other organs,
- mental retardation.
Frequently asked questions about ichthyosis
How is ichthyosis inherited from sick parents?
The disease ichthyosis is hereditary. Pathology is caused by mutation of genes on the X chromosome, so girls are carriers, and boys are most often affected.
Is ichthyosis transmitted during contact with a sick person?
No. Ichthyosis is not an infectious disease. They cannot be contracted through contact with sick people. The pathology is caused by gene mutation.
How do people with ichthyosis live?
The disease requires constant skin care. The main tasks are to reduce moisture loss, intensively moisturize the skin, and control the thickness of the stratum corneum. Due to impaired thermoregulation in such patients, it is important to avoid overheating and prolonged stay in rooms with dry air.
History and clinic
The onset of the disease, that is, pathological thickening of the skin and its cracking with the formation of deep defects, is observed already at birth.
The characteristic symptoms of this syndrome are spots that can completely cover one half of the body, while the baby’s legs and arms are only partially covered with such spots. In case of hyperthermia or overheating of the baby, the spots acquire a bright burgundy hue, and in case of hypothermia, they turn blue. When the child is in normal condition, they are practically invisible.
Local symptoms. Skin manifestations of Harlequin syndrome manifest as thick and rigid skin with the appearance of triangular/hexagonal/polygonal plaques that form when the affected skin cracks. In this case, the skin has a yellow or gray color with plaques and bright red deep cracks on the surface.
In addition, there is pronounced ectropion (that is, eversion) of the eyelids, eclabion (deformation in the form of a fish mouth), flat deformed ears and, in some cases, microcephaly.
General symptoms. The majority of babies with Harlequin syndrome are stillborn or die immediately after birth. Such infants are malnourished and suffer from electrolyte imbalance and heat exchange disorders. Due to skin rigidity, breathing and movement difficulties are noted.
Deep fissures often become infected, which leads to the development of sepsis.