December 06, 2020
Seasickness, kinetosis or motion sickness - a feeling of nausea and due to monotonous vibrations (people first encountered this phenomenon during sea travel, hence the name)
Seasickness, kinetosis or motion sickness is a feeling of nausea due to monotonous vibrations (people first encountered this phenomenon during sea travel, hence the name). Seasickness can occur not only on water transport, but also in a car, bus, train, or plane.
Women are more likely to suffer from seasickness than men. But children from 2 to 12 years old suffer most from seasickness (81% of children suffer from seasickness at this age). Approximately 5-15% of the population suffers from motion sickness throughout their lifetime. Although in particularly unfavorable conditions (with strong pitching), anyone, even an experienced sailor, can get motion sickness.
Onset is often subtle, with drowsiness, yawning and decreased alertness, and symptoms progress through cold sweats and pallor, salivation and sometimes headache, to nausea and vomiting. Once the triggering movement stops, symptoms usually disappear completely within 24 hours. Seasickness isn't actually life-threatening, but it can ruin your travel experience.
General information
About 30% of adults and 60% of children do not tolerate travel in transport due to motion sickness.
Motion sickness syndrome (synonymous with kinetosis and motion sickness) is a pathological reaction to unusual movement in the form of vestibular disorders, which is manifested by dizziness, nausea, vomiting, decreased blood pressure, and pallor. Symptoms of kinetosis are associated with the effect of acceleration on vision, the vestibular apparatus and on the receptors of the mucous membranes of the internal organs. Most often, this condition occurs when the vestibular apparatus is irritated while traveling in various types of transport. Varieties of kinetosis are sea, air, automobile and carriage sickness. Less common and less well known are riding sickness, elevator and swing sickness, as well as motion sickness in a 3D movie theater when watching movies.
The most common forms are car sickness and motion sickness. The predisposition to them is higher in women, children and young people, less in men and the elderly. Why does this happen and why do only some people get motion sickness? Movement in transport in the form of monotonous vibrations irritates the vestibular organ and the organ of vision differently, but the organ of vision and the vestibular apparatus are interconnected. When traveling, a person is motionless, and the eyes look at moving objects, and the vestibular apparatus and muscles do not feel body movements, as a result the brain receives conflicting signals. The resulting imbalance between information from these analyzers is transmitted to the brain as an impulse about a stressful situation, in response to which pathological reactions occur. The intensity of nausea and dizziness is proportional to the severity of the sensory mismatch.
The susceptibility of individuals to motion sickness depends on the individual characteristics of the vestibular apparatus - our organ of balance. In some people, the manifestations are so pronounced that it limits their work activity, reduces their quality of life and causes social maladaptation.
The functional immaturity in children and the slight excitability of their vestibular apparatus lead to the fact that they predominantly suffer from this pathology. Usually, unpleasant symptoms in children disappear with age (by 12-14 years), when the vestibular analyzer finally matures. Manifestations of kinetosis are also expressed in people with increased excitability of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system. In the elderly and people with congenital deaf-muteness, the sensitivity of the vestibular apparatus is reduced, so they usually have mild or no symptoms. Children under two years of age do not use their vision to orient themselves in space, so they are less susceptible to motion sickness.
What is the cause of motion sickness?
Unfortunately, there is no clear and precise reason for this reaction of the body to movement.
There are currently several theories.
The theory of inconsistency between visual, vestibular and somatosensory afferentation has received the greatest recognition in the world. (Reason, 1978; Dichgans and Brandt, 1978) According to this theory, signals coming from different sensory systems, or expected and actual sensory signals, contradict each other.
Pathogenesis
The science of pathological physiology studies the general patterns and mechanisms (pathogenesis) of the occurrence of all diseases and pathological conditions. How does pathological physiology explain kinetosis? If we consider typical pathological processes of kinetosis, their pathophysiology lies in the reflex effect of movement on:
- vestibular apparatus;
- visual receptors;
- skin and muscle receptors;
- veceroceptors (receptors of internal organs).
Of primary importance in the development of motion sickness are the receptors of the vestibular apparatus, which respond to acceleration, and the visual receptors, which transmit information about the rapid movement of objects. Activated vestibular and visual receptors cause excitation of the sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic (nucleus of the vagus nerve).
Afferent pathways, which include the vestibular, optic and vagus nerves, reach the cerebellum, hypothalamus and the centers of the internal organs and blood vessels, which causes the development of characteristic symptoms. Radial acceleration causes vibrations of the endolymph in the vestibular apparatus, and this excites the vestibular nerve, which transmits excitation to the vestibular nuclei (located in the medulla oblongata).
Then the excitation is transmitted to the cerebellum (dizziness occurs and the patient’s coordination is impaired), to the nuclei of the oculomotor nerves ( nystagmus - rhythmic twitching of the eyes), to the nuclei of the vagus nerve. The latter also receive impulses from the abdominal organs (this explains nausea, vomiting, sweating, slow pulse and low blood pressure). In addition, the vomiting center is stimulated by the vestibular apparatus, which perceives a change in position. Kinetoses also occur with irritation (flashing objects) of the visual analyzer. Excitation from the retina is transmitted to the cerebellum, visual cortex, medulla oblongata to the vestibular nuclei and characteristic symptoms develop.
What to feed your guinea pig?
The problem of feeding a guinea pig worries everyone who brings the animal home. Guinea pigs eat constantly in small portions, so the food should be available to them constantly, but it needs to be refreshed 3 times a day. Grain feeds increase excess weight and lead to obesity, so they are limited to the norm. Be sure to have a piece of well-dried dry grass, branches of fruit trees, and willow in the cage. A guinea pig's teeth grow throughout their life, and hard foods help to wear them down in captivity. To prevent the pig from getting sick, there should always be food in the cage.
Give succulent food to pigs in the morning. You should not give potatoes that the body cannot digest. Carrots, celery, cabbage, beets, pumpkin, and sweet peppers should be given by cutting them into pieces. The norm is 160 grams. For pregnant, lactating and Skinny women, the dose is doubled and divided into two doses: one in the morning, the other in the evening.
The volume of the animal's drinking bowl should be 250 ml. Vitamin C is added to the water in an amount of 2.5-5 mg per glass of water. In summer a minimal dose is sufficient, in winter a larger dose is sufficient. If the animal receives a premix of vitamins in the finished feed, then this is enough.
Berries and fruits are given as a treat in small quantities in the first half of the day. These could be apples, pears, dry rose hips.
Herbs such as red clover, dandelion, plantain, nettle, chamomile, and yarrow are very beneficial for the animal and can be dried for the winter. Parsley, dill, leaf celery - these herbs are not given to pregnant animals. Spinach and lettuce are only those that grew in the open ground in the summer. An excess of fertilizers in greenhouses leads to the accumulation of harmful substances in plants, which can poison the animal. Salt is given to young animals per 1 animal 0.5 g, to adults - 1 - 2 g.
Classification
According to clinical manifestations, the following forms of kinetosis are distinguished:
- Nervous.
- Cardiovascular.
- Gastrointestinal.
- Mixed.
According to mental manifestations of the disease:
- Asthenic form. The person becomes apathetic, lethargic and very inhibited, feeling overwhelmed and tired.
- Agitated. Manifested by excitement (motor and speech). The person is very emotional, fussing, constantly moving and talking.
- Mixed. In this form, excitement alternates with apathy and depression.
Sea travel is more likely than other types of travel to cause motion sickness. This is due to prolonged and pronounced exposure to irritating factors. Seasickness occurs from various types of pitching and their combination: roll, transverse, longitudinal, pitching and vertical. For many people, even the sea outside of a storm causes motion sickness.
Air sickness ranks second after sea sickness. The smaller the aircraft and the lower it flies, the higher the likelihood of passengers experiencing motion sickness. Air sickness occurs when the plane moves up and down, when swinging along the longitudinal axis, and when it hits air pockets.
Cases of motion sickness are much less common in modern large aircraft that fly at high altitudes. The least kinetosis occurs on the train. But with the spread of high-speed trains, the frequency of kinetosis in this type of transport has increased. This is explained by the accelerations that occur when turning at high speeds (more than 200 km/h).
Thus, physiological dizziness and motion sickness develops with strong irritation of the vestibular apparatus - a sharp change in the speed of movement, prolonged rotation, observation of moving objects. Dizziness and other unpleasant symptoms disappear quickly when the unusual exposure to the normal state stops. However, you need to know that symptoms of motion sickness can be a manifestation of neurological diseases: Meniere's disease , otosclerosis , vestibular form of migraine , multiple sclerosis , tumors of the cerebellum or brain stem, cerebrovascular accidents, infectious lesions of the central nervous system, vestibular neuronitis . Therefore, this will require additional examinations. If kinetosis is accompanied by hearing loss or severe ringing in the ears, you should consult a doctor.
Diseases caused by vitamin deficiency and viruses
- Vitamin deficiency in guinea pigs causes diseases such as scurvy, focal baldness, allergic reaction, itchy skin, decreased immunity and colds.
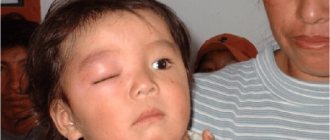
- Conjunctivitis is a purulent inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyelids, which often accompanies excessive growth of molars, keeping the animal in a dusty room, due to chemical irritants. First, the animal's eyes become swollen and red, then the appearance of pus causes the eyelashes to stick together and tearing increases. Then the eyelids completely stick together from pus and if the disease is not treated, the mumps will go blind. It is advisable not to self-medicate for conjunctivitis because it may be an indirect sign of a cold that will turn into pneumonia or an indirect sign of overgrown teeth. Remember to practice good personal hygiene and wash your hands after treating your pet.
- Rickets occurs due to a lack of calcium and vitamin D. It usually occurs in young pigs in winter. They recommend a trivitamin, irradiation with a quartz lamp, and adding salt to the diet. With rickets, the limbs are twisted, the joints are thickened, the animal is depressed and stunted.
- Paratyphoid fever is an infectious disease that begins due to damage to the pig's body by microorganisms that enter with drinking water and feed. A sick animal refuses food, its fur becomes sticky, and its eyes become dull. Antibiotic treatment is prescribed only by a doctor.
- Pasteurellosis causes a runny nose. The disease begins with moistening of the hairs around the nostrils, then sneezing appears. The nose itches and the animal rubs it with its paws. Then mucus appears from the nose, turning into pus. The pig's breathing becomes heavy and wheezing. All this is accompanied by decreased appetite and lethargy. The disease is chronic and lasts a long time. During an exacerbation, ulcers appear on the body, high fever and convulsions rise. Pasteurellosis cannot be cured. Animals with severe symptoms of the disease are euthanized. At the beginning of the disease, when the symptoms are not clear, they are treated with antibiotics and sulfa drugs.
- Wounds can occur in the event of a fight with a relative or an attack on an animal by a cat or dog. The hair around the wounds is cut off, the wound is washed and dried using hydrogen peroxide or a solution of potassium permanganate in a ratio of 1:1000. Then it is lubricated with Levomekol, synthomycin or streptocyte ointment until it is completely cured.
- Fractures and cracks in bones occur during a fall. Swelling occurs at the site of injury, and there may be muscle damage with an open fracture. There is always severe pain. The animal will limp for the rest of its life. The fracture must be treated in a clinic.
- Diseases of the digestive system are associated with the structural features of the intestines. In rodents it is very long, and food takes a long time to digest in it. Changing feeds and an excess of juicy vegetables leads to intestinal upset and diarrhea. The owner of a rodent should know that the introduction of new food should begin with minimal portions, in the morning, with a gradual increase and replacement of the usual diet. This is done when absolutely necessary. Or with the change of season, when you need to introduce fresh grass into your diet. To correct nutritional errors, give activated carbon and a weak pink solution of potassium permanganate instead of drinking.
- Flatulence requires examination by a veterinarian. The formation of gases in the colon area often causes disturbances in the functioning of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. In rodents, this disease leads to death from suffocation or cardiac arrest. You can relieve flatulence with massage or gymnastics. The animal must be released to run around.
- Infection of the salivary gland with cytomegalovirus and herpes virus occurs through water. In some cases, guinea pigs develop a fever and increased drooling. After some time, the immune system expels the virus and the disease goes away. Re-infection is excluded, since antibodies against these viruses have appeared in the body.
- Enteritis is accompanied by diarrhea, bloating and loud rumbling in the intestines; with these signs, the rodent should be urgently taken to the veterinarian. The cause may be moldy feed. A urine test is taken, which shows the presence of ketone bodies. Treatment of enterocolitis involves restoring the intestinal microflora. To do this, exclude all feed except high-quality hay. In summer, you can collect yarrow, chamomile, red clover, plantain, nettle, dry the herbs on an iron tray and feed this to the animal for 3 days. Glucose is added to the water, dissolved feces from healthy pigs are given, which improves the intestinal microflora. It is diluted in water and injected into the oral cavity through a syringe once a day. There is no need to prevent pigs from eating their own droppings. This will only benefit them. The list of diseases can be kept endlessly, but only a veterinarian can make the correct diagnosis.
Any disease with fever, accompanied by pain and discharge requires the attention of a veterinarian. Call the phone number listed on the website and ask all your questions.
Causes of seasickness
Why do some people get motion sickness when traveling in public transport? The exact cause is not known, but in some cases there are several causes. The main reasons can be named:
- Immaturity of the vestibular apparatus.
- Vegetovascular dystonia.
- Cervical spine instability.
- Various ENT diseases.
Why do you feel sick in the car and factors that contribute to it:
- childhood and immaturity of the vestibular analyzer - this explains why the child gets sick in the car;
- many people note that they started getting motion sickness in the car during pregnancy ;
- pathology of the cardiovascular system in old age;
- taking medications (antibiotics and antidepressants);
- alcohol consumption;
- motion sickness in transport for women taking oral contraceptives and on menstrual periods;
- eye diseases (for example, astigmatism and strabismus );
- otitis media suffered in childhood ;
- emotional stress;
- the smell of tobacco smoke in the car interior and the strong smells of air fresheners and perfumes;
- heat and stuffiness in the cabin;
- overwork.
Why do guinea pigs get sick?
Diseases in guinea pigs are associated with poor diet, infections and lack of vitamins. These can be infectious diseases that affect the animal’s body, getting to it with food and water. Another cause of disease lies in improper feeding. Some foods can cause intestinal upset, and its long-term manifestations result in the death of the animal. The third reason is the structural features of her body, which should be taken into account during care. Treatment by a veterinarian prolongs the life of your pet.
The peculiarity of these rodents is their long intestines, which become upset after a change in diet, and teeth, which grow throughout their lives and require constant grinding. They need to be fed hay every day to keep their teeth and intestines normal. The body of these animals does not absorb vitamins well, so special attention should be paid to the food. These ancient animals cannot tolerate penicillin, which becomes a deadly poison for them. Therefore, moldy food is not suitable for them. Guinea pigs need to chew something constantly to keep their digestive system healthy. These rodents live up to seven years, and those who live in a pack live longer than solitary individuals.
Symptoms of seasickness
The main symptoms of kinetosis are nausea, repeated vomiting, pallor, sweating , decreased blood pressure, rapid or slow heartbeat. Symptoms develop gradually. Precursors may include yawning , drooling, cold sweat, paleness , drowsiness , headache and fatigue . Then the symptoms increase like an avalanche, nausea intensifies, vomiting appears and coordination is impaired. An unventilated room, heat and human emotional factors (fear and anxiety) aggravate kinetosis. The weakening and growth of symptoms can continue for a long time. Thus, when traveling by sea, the period of unsatisfactory health lasts several days.
The course of the disease depends on the intensity of the stimulus and the person’s sensitivity to it. The duration of these disorders varies for each patient - from hours to days. Some people have minor symptoms before vomiting develops, while others feel unwell for a long time without vomiting. Some people who experience severe motion sickness and severe kinetosis experience sleep disturbances , apathy , or depression .
Depending on the predominant symptoms, motion sickness is divided into main forms:
- Gastrointestinal, in which dyspeptic disorders - nausea, vomiting and lack of appetite. There is a special sensitivity to tobacco smoke, exhaust fumes and food odors. The taste sensations of familiar foods may also be distorted or the taste of soap, blood or metal may appear.
- A nervous form in which the leading symptoms are dizziness , heaviness in the head, headache, loss of coordination, drowsiness , lethargy, severe weakness, and disorders of consciousness are also possible. Sometimes these symptoms appear in a person on the eve of a trip. Some patients develop mental disorders - depression , memory and concentration problems, asthenic and apathetic-abulic syndrome (inactivity, passivity, lack of initiative).
- Cardiovascular form, which first manifests itself as increased heart rate and increased blood pressure, and as it becomes heavier, the pulse slows down, blood pressure drops, and breathing becomes shallow. This form is very dangerous for people who suffer from cardiovascular pathology.
- Mixed form. It occurs most often and with it the above symptoms occur in various combinations.
With prolonged exposure to the provoking factor, the majority experience a gradual decrease in the symptoms of motion sickness, which is associated with adaptation of the vestibular apparatus. The speed of adaptation depends on individual characteristics. Most often it occurs after three days. This happens because new control over motor acts is established. After returning to normal conditions, the central nervous system is rebuilt again (readaptation) and unexpressed symptoms of motion sickness may appear.
What are the symptoms of motion sickness?
Motion sickness
There are a number of symptoms associated with motion sickness, some more severe than others. However, symptoms may vary from person to person, and people with motion sickness may experience some or all of the following:
- nausea
- vomit
- dizziness
- sweating
- excessive salivation (may drool)
- uneven breathing
- feeling of discomfort
- headache
- belching attack
All this is very unpleasant. However, the most serious side effect of motion sickness is vomiting, as it can lead to dehydration. Dehydration can also be aggravated by the fact that, when experiencing the urge to vomit, a person often refuses any food or drinks at all, as they can cause additional discomfort and nausea.
Tests and diagnostics
The following studies will help exclude pathologies of the central nervous system and vestibular apparatus:
- Doppler ultrasound.
- Rheoencephalography (diagnosis of cerebral vessels, study of cerebral circulation by passing a weak electric current through tissue).
- Electroencephalography (registration of brain biocurrents).
- MRI.
- Nystagmography (recording the movement of the eyeballs).
- Vestibulometry is a series of tests to determine the function of the vestibular analyzer.
- Caloric test - study of the duration of nystagmus that occurs when water of a certain temperature (warm and cold) is poured into the ear canal. Each irrigation causes short-term dizziness and nystagmus. Caloric nystagmus is an indicator of the state of the vestibular apparatus.
- Videooculography (synonymous with videonystagmography) is a recording of eye movements during vestibular tests. The study allows us to identify hidden nystagmus in pathology of the labyrinth.
Alcohol
There is a version that alcohol helps with motion sickness, and this is true. But this assumption only applies to strong drinks, so before going to sea you can drink a shot of strong alcohol. But there is also a side effect - you will have to become a real pirate - in order not to get motion sickness, the level of alcohol in the blood must be constantly maintained. This may be unsafe for swimming. There is a risk of falling overboard or not remembering your trip.
However, drinking alcohol is not prohibited. It is only important to remember that you need to moderate yourself in the evening so that there is no hangover in the morning, which, on the contrary, will increase seasickness. Dizziness may appear without it, but in the morning it will be aggravated by the motion.
In children
A child's tendency to get motion sickness depends on many factors. Genetic characteristics (if the baby’s parents suffer from this pathology, then the child will also have motion sickness), the general health of the child, his age and the state of the vestibular system are affected. Motion sickness appears in children after 2 years of age and with age, as the vestibular apparatus develops, the motion sickness goes away (after 12-13 years) or becomes less pronounced. Children often experience motion sickness: they can tolerate long flights and bus rides, but symptoms appear in the car. Motion sickness in it depends on the way the driver drives; if the car accelerates sharply and suddenly brakes, or makes sharp turns, then this will undoubtedly affect the condition of the vestibular apparatus.
With the issue of motion sickness of a child in transport, they often turn to doctor Komarovsky. Komarovsky believes that if an infant is actively engaged - turned, laid on his stomach, doing gymnastics, placed on his legs early and led by the arms from an early age - then his balance apparatus is trained. If a child is treated like a crystal vessel, he is more likely to develop motion sickness at a certain age. After suffering from otitis media , the likelihood that he will get motion sickness also increases. If a child gets carsick, the doctor advises:
- Provide fresh air in the cabin.
- Do not overheat the child and do not dry out the oral mucosa, so the child should constantly drink a cold drink in small sips (decoction of raisins, dried apricots with mint and lemon, after cooling, add ice cubes to the thermos).
- When traveling, the child should make swallowing movements more often, which prevent motion sickness.
- Therefore, lollipops (mint or ginger, sour lollipops) are effective in this regard; when sucking on them, the child will constantly make swallowing movements.
- Do not overfeed your child before traveling. Light foods (cottage cheese, banana, omelet, oatmeal, yogurt, a piece of cheese) that do not have strong odors and do not irritate the stomach are desirable.
- You need to try to put the child to sleep.
- Children benefit from acupressure and elements of suggestion.
As for motion sickness tablets for children, the doctor recommends their use in extreme cases when other measures are ineffective. In such cases, Komarovsky recommends homeopathic remedies or the drug Dramamine .
At home, you need to organize a gym corner, a swing for training, and introduce your child to sports in any way. Strengthening the vestibular system will help eliminate or minimize the manifestations of motion sickness syndrome.
4.Medicines for motion sickness
There are also medicines for motion sickness
. Some of them are sold without a prescription, others can be prescribed by a doctor. These anti-motion sickness medications will help reduce nausea and prevent vomiting. Moreover, most drugs help better if they are taken in advance, some time before the trip. The way motion sickness medications work varies. Some drugs are sedative and minimize the effect of movement. Others simply help with nausea.
Some people recommend non-medical remedies for motion sickness - capsules with powdered ginger, special bracelets for motion sickness. In fact, all these methods are safe, and you can try them out. But there is no medical evidence that all these remedies for motion sickness really help.
Preventing seasickness
Prevention for kinetosis includes:
- Take care of your tickets in advance in order to choose seats with the smallest swing amplitude and located in the direction of travel.
- If possible, choose night flights, which are easier to handle.
- The day before the trip, calm down and have a good rest.
- On the day of your trip, avoid alcoholic drinks.
- Do not overeat before the trip, but during the trip, have light snacks of fruit, yogurt, cheese and drink cold, acidified still water.
- While traveling, limit your head movements. To do this, you need to take a comfortable reclining position, fix your head with a collar or a special pillow, and do not move or make sudden movements.
- It is optimal to travel with your eyes closed. If you can’t fall asleep, fix your gaze on the horizon, and not look around for flashing objects.
- Avoid overheating and hypothermia.
- Not recommended reading.
- Periodically dissolve sour candy, since sucking and swallowing movements reduce the symptoms of kinetosis.
What to do during a trip to avoid nausea
Just before and during travel, avoid large meals, caffeine and alcohol, but at the same time it is important to drink enough water. The “black list” of a passenger prone to motion sickness includes fatty, spicy, difficult-to-digest foods, as well as foods with a strong odor. Coffee and other caffeinated drinks irritate the lining of the stomach, which also increases the risk of nausea. However, you should remember that you should not hit the road hungry. The best solution is to have a light snack a few hours before your trip.- Get plenty of rest before your trip. Remember: overwork is one of the triggers for seasickness.
- If possible, travel at night. This way, you are more likely to fall asleep and the trip will be less painful for you.
- Choose places in transport where shaking is minimal. If it is a car, then the place is near the driver. On an airplane, take the seats above the wing - this is the quietest area in the cabin. On a ship, movement is less noticeable in lower level cabins closer to the center of the ship. Motion sickness is most common on deck and in the cabins on the upper level.
- Do not sit with your back to the direction of travel.
- If possible, drive. Many are sure that only someone who does not get sick on the road can be a driver. Meanwhile, experts are of the opinion that, on the contrary, driving reduces the risk of motion sickness [3]. The driver uses motor skills while driving, thereby gaining the opportunity to control the situation and predict his movements. That is, taking control of the situation helps fight seasickness. If it is impossible to get behind the wheel of a vehicle, take a seat as close to the driver as possible. In the front seat there is a feeling of at least partial control. The most dangerous places for people prone to motion sickness are at the back of the bus.
- Don't read on the go or watch videos. Instead, try to distract yourself by listening to music.
- Stabilize your sensory signals. People with seasickness may feel more comfortable in a horizontal position, focusing their gaze on the horizon or a static point. Focus your gaze on a stationary object in the distance. The main thing is to look to the side in the direction of travel of the vehicle. This helps to reorient the internal sense of balance and gain visual confirmation of movement. But it’s better not to look out the side windows of your car: rapidly changing pictures only aggravate motion sickness.
- Relax and find something to focus your attention on. For example, count from 100 to 0 and vice versa. You can also close your eyes during the countdown. A good way to avoid motion sickness is to take a nap on the road. This helps eliminate the conflict between the perception of the inner ear and the visual information received by the eyes.
- The vestibular apparatus can sometimes be deceived. During the trip, use your feet to imitate walking. In this way, it will be possible to reduce the number of inconsistencies in the signals received by the brain.
- A few deep breaths taken in the fresh air often help to overcome a mild attack of nausea. You can also apply cold to the back of your head or forehead - this will invigorate the body a little.
- During the trip, try to breathe more fresh air (for example, open a window), do not smoke yourself and avoid smoky places.