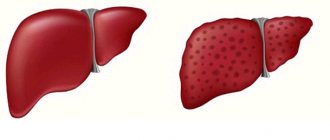
Choleretic drugs are often perceived by consumers as light health-improving drugs. But in fact, things are much more complicated - such drugs seriously affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and experimenting with them may be unsafe for health. That is why it is important for the pharmacy worker at the first table to have a clear understanding of how choleretic drugs work and to be able to convey information to the consumer in a simple and understandable form. Let's look at everything in order - from physiological basics to specific questions that should be asked to a pharmacy visitor during a consultation.
Types of choleretic drugs
{banner_banstat0}
Medicines that increase the outflow of bile are divided into 2 groups according to their mechanism of action - choleretics and cholekinetics.
Classification:
1. Choleretics. They increase the volume of bile secreted and the concentration of acids.
- True choleretics - Allohol, Liobil. The products contain liver enzymes, animal bile, and extracts from medicinal herbs.
- synthetic choleretics - Nicodin, Cyclalon. They have a choleretic effect, relieve inflammation, eliminate spasms, and fight pathogenic bacteria;
- choleretics of plant origin - Cholagol, Chofitol. Contains extracts from herbs and plants. Helps improve bile movement, reduce secretion viscosity, improve liver function;
- natural bile acids, often of animal origin – Cholenzyme. Active substances – crushed mucous membrane of the small intestine, pancreas, animal bile.
- Hydrocholeretics. Mineral medicinal waters – Essentuki, Smirnovskaya, Slavyanskaya. Salts improve the production of bile and dilute it.
- 2. Cholekinetics – promotes the passage of bile into the intestines.
- Cholekinetic agents. Atropine, Magnesia. They relax the bile ducts by stimulating the contractile functions of the gallbladder, eliminate congestion, and prevent their occurrence.
- Cholespasmolytics. Relaxes smooth muscles, eliminates pain.
- Synthetic – Drotaverine, Papaverine;
- Natural – St. John's wort tincture.
Preparations to prevent the formation of gallstones with ursodeoxycholic acid - Ursosan.
The classification of drugs that have a choleretic effect is conditional; many drugs have a complex effect.
Indications for the use of drugs for the secretion of bile
{banner_banstat1}
General indications for taking medications with a choleretic effect:
- cholecystitis;
- cholangitis;
- hepatitis B, C, D, pathological processes in the bile ducts of a chronic course;
- cholestasis;
- biliary dyskinesia;
- inflection of the gallbladder;
- prolonged, frequent problems with bowel movements;
- after removal of the gallbladder in order to prevent the development of gallstone disease.
The need to take choleretic medications is indicated by a bitter taste, a coating on the tongue, pain, a feeling of heaviness under the right ribs, and belching. All these signs may indicate disturbances in the functioning of the biliary system and liver.
Important! General contraindications for taking medications for bile stagnation are hepatitis in the acute stage, cirrhosis, acute and subacute dystrophic liver pathologies, obstructive jaundice, erosions of the gastrointestinal tract, pancreatitis, diarrhea.
Part 2. The most important things about cholekinetics
Cholekinetics are also divided into two groups:
- Actually, cholekinetics, which include:
- magnesium sulfate;
- polyhydric alcohols (sorbitol, mannitol, xylitol);
- sunflower, olive oils, essential oils;
- herbs and plants containing bitterness;
- juices of lingonberries, cranberries, etc.
- Cholespasmolytics:
- hyoscine butyl bromide;
- papaverine;
- drotaverine
Indications for the use of cholekinetics:
- atony of the gallbladder with stagnation of bile;
- gallbladder dyskinesia;
- chronic cholecystitis;
- chronic hepatitis;
- anacid and strong hypoacid gastritis;
- carrying out duodenal sounding.
Cholespasmolytics are prescribed for the hyperkinetic form of biliary dyskinesia and for cholelithiasis. They are used to relieve pain of moderate intensity, often accompanying pathology of the biliary tract [6, 7].
Such drugs are contraindicated
in acute liver diseases, with exacerbation of hyperacid gastritis and peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. In this case, taking cholespasmolytics will only worsen the situation.
Review of the best choleretic drugs
{banner_banstat2}
The list of good choleretic drugs is extensive. These medications quickly cope with the manifestations of diseases, have few restrictions on use and side effects. Before starting therapy, read the instructions and follow the recommended dosages.
Allohol
A medicine with choleretic and cholekinetic properties. Ingredients: extract of bile, garlic, nettle, activated carbon. The tablets enhance the process of bile formation and activate the motor and secretory functions of the gastrointestinal tract.
Additionally, Allochol has a mild laxative effect and improves the process of breaking down fatty foods.
When to take Allohol:
- chronic hepatitis;
- inflammatory processes in the gallbladder, bile ducts;
- constipation caused by intestinal atony;
- with the gallbladder removed for normal bile movement.
Dosage for adults – 2 tablets with an interval of 8 hours after meals, with an exacerbation, 1. Duration of treatment – 3-6 weeks. The break between courses is 3 months. Improvement in the condition occurs on days 5-8 of taking the medicine - pain decreases, dyspeptic disorders disappear.
Children under 7 years of age are prescribed 1 tablet in the morning, afternoon and evening. For children over 7 years old – adult dosages.
During treatment, adverse reactions rarely occur. Mostly allergic manifestations and stool disorders are observed.
Contraindications – acute form of hepatitis and pancreatitis, liver dystrophy, stones in the gall bladder or ducts, peptic ulcer of the gastrointestinal tract.
Price – 70-115 rub.
Hofitol
{banner_banstat3}
Plant choleretic with field artichoke leaf extract. Release form: tablets, suspension, syrup for oral administration.
A drug with hepatoprotective, choleretic effect, normalizes metabolic processes. The medicine activates the process of formation and movement of bile, prevents the development of atherosclerosis.
Indications:
- nausea, bloating, discomfort in the central abdominal area;
- chronic non-calculous cholecystitis, hepatitis;
- slowing down the outflow of liver secretions with biliary dyskinesia;
- cirrhosis;
- renal failure, chronic form of nephritis.
Hofitol is prescribed as an auxiliary drug for intoxication with salts of heavy metals or alkaloids, obesity, anorexia, atherosclerosis, and urolithiasis.
Directions for use: drink three times a day before meals. Dosages – adults and children over 12 years old – 2-3 tablets. Course – 2-3 weeks. Dosage regimen for children 6-12 years old – 1-2 tablets.
Single dosages of medication in liquid form for children:
- Up to a year. Dilute 5-10 drops of the drug in 5 ml of water.
- 1-5 years. 10-20 drops, dissolve in 15 ml of water.
- Over 6 years old. Dissolve 2-3 ml or 40-60 drops in 15 minutes of water.
The container with the suspension must be thoroughly shaken before use; the artichoke extract will settle to the bottom.
Side effects occur with long-term use of the drug in high dosages. Possible negative reactions are abdominal cramps, heartburn, upset stool, nausea. Rarely, hypersensitivity reactions occur - rash, itching, skin hyperemia.
The drug is not prescribed for individual intolerance, bile duct obstruction, cholelithiasis, or diseases of the urinary system in the acute stage. Hofitol tablets are contraindicated in children under 6 years of age.
Price – 470-580 rub.
Holosas
{banner_banstat4}
Effective natural remedy, contains rosehip extract. It has a complex effect - improves the flow of bile, promotes the restoration of liver cells, eliminates manifestations of the inflammatory process, strengthens the immune system. Holosas reduces the permeability of small blood vessels, accelerates the regeneration process and the synthesis of hormones, and is involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates.
Indications for use:
- viral hepatitis;
- cholecystitis, cholangitis;
- deficiency of vitamin C, P;
- poisoning with drugs, alcoholic beverages;
- increased physical and mental stress.
Dosage for children over 12 years of age and adults – 5 ml 2-3 times a day half an hour before meals. The average duration of therapy is 15-30 days.
The medicine should not be taken if there is intolerance to the components, cholelithiasis, and should be taken with caution if you have diabetes. The syrup is contraindicated for children under 12 years of age, pregnant and lactating women. Possible side effects are allergic manifestations, stool upset, bloating, flatulence.
Average price – 100-200 rubles.
Holenzym
{banner_banstat5}
Combined choleretic tablets from the group of natural bile acids.
Practiced with:
- gastrointestinal pathologies;
- chronic hepatitis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis;
- gastritis;
- colitis;
- bloating;
- diarrhea of non-infectious origin.
Dosage: 1 tablet after meals at intervals of 8-24 hours.
Possible adverse reactions are caused by allergic manifestations:
- sneezing;
- lacrimation;
- redness and swelling of the skin;
- rashes.
It is strictly forbidden to take when:
- acute pancreatitis or exacerbation of the chronic form of the disease;
- obstructive jaundice;
- hypersensitivity to components.
The price of tablets No. 50 is 250-300 rubles.
Papaverine
{banner_banstat6}
Synthetic antispasmodic, active ingredient – papaverine hydrochloride. The drug has a relaxing effect on smooth muscles.
Papaverine will help cope with spasms and pain due to cholecystitis and spastic colitis. The medicine is prescribed before surgical interventions on the gallbladder.
Tablet dosage regimen:
- children from 1 year to 12 years – maximum single dose 200-300 mcg/kg;
- adults - 0.04-0.06 g orally, dosage frequency 3-5 times a day.
Possible side effects are tachycardia, decreased blood pressure, dyspeptic disorders, drowsiness.
Contraindications:
- individual intolerance;
- violation of intracardiac conduction;
- glaucoma;
- severe forms of renal failure;
- less than 6 months old.
The medicine is prescribed with caution for chronic renal failure, shock, hypothyroidism, and malfunction of the adrenal glands.
Price – 35-90 rub.
Odeston
{banner_banstat7}
Synthetic choleretic agent, the main ingredient is hymecromone. A complex action medicine – improves the synthesis and movement of bile, relaxes the bile ducts, analgesic, antispasmodic.
Odeston's indications:
- chronic form of non-calculous cholecystitis, cholangitis, cholelithiasis;
- impaired motility of the biliary tract, sphincter of Oddi;
- after surgical interventions on the organs of the biliary system;
- lack of appetite, problems with defecation, vomiting caused by bile hyposecretion.
Take the medicine 30 minutes before meals. Dosage regimen for adults – 1-2 tablets every 8 hours. Duration of therapy is 14-21 days.
The recommended dosage for children over 7 years old is 1 tablet 1-3 times a day. The treatment course is 2-3 weeks.
The medicine sometimes provokes the development of allergies, dyspeptic disorders, ulcers of the mucous organs of the gastrointestinal tract, migraine attacks and dizziness.
Odeston should not be taken if you have kidney or liver failure, blockage of the bile ducts, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, or hemophilia. The drug is not prescribed to children under 7 years of age.
Price – 430-880 rub.
Flamin
{banner_banstat8}
Herbal preparation with extract of immortelle flowers. Cholekinetic, choleretic, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antispasmodic.
Tablets or granules help with inflammation of the gallbladder, ducts, and liver.
Take the medicine before meals. Dosage for tablets – 1-3 times a day. Duration of treatment is 1.5-6 weeks.
Children are prescribed the drug in granules, from which a suspension is prepared.
Single dosage for children:
- 1-12 months – 2.5 ml;
- 1-3 years – 5 ml;
- 4-5 years – 7.5 ml;
- over 5 years – 10 ml.
Course duration is 10-14 days.
Allergic reactions may occur during treatment. With hypertension, blood pressure may increase.
The medicine should not be taken if you have hypersensitivity, cholelithiasis, or obstructive jaundice.
Price – 170-300 rubles.
Magnesia
Magnesium sulfate, when taken orally, has a choleretic, laxative, and antispasmodic effect.
The medicine will help with cholangitis, cholecystitis, constipation, and gallbladder dyskinesia. The drug is effective before duodenal intubation to obtain a cystic portion of bile.
As a choleretic agent, dissolve 20-25 g of powder in 100 ml of water. Drink 15 ml solution 3 times a day before meals.
Contraindications:
- hypertension;
- bradycardia, AV block;
- severe forms of chronic renal failure;
- depression of the respiratory center.
The price of 1 sachet is 20-28 rubles.
Ursosan
{banner_banstat9}
The drug contains ursodeoxycholic acid. Hepatoprotector with choleretic, immunomodulatory effects.
Indications:
- uncomplicated forms of cholelithiasis;
- prevention of stone formation when the gallbladder is removed;
- biliary dyskinesia;
- acute, chronic active hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis.
The Ursosan treatment regimen is selected individually, depending on the type and severity of the disease. The standard dosage is 2-5 capsules per day. The duration of therapy ranges from 2-3 months to several years.
Contraindications:
- chronic hepatitis, pancreatitis;
- disabled gallbladder;
- acute form of cholecystitis, cholangitis;
- decompensated cirrhosis of the liver;
- acute infectious pathologies of the gallbladder;
- renal, liver failure;
- pregnancy, breastfeeding period.
Possible adverse reactions are vomiting, diarrhea, exacerbation of psoriasis, back pain, allergies, alopecia.
Price for 10 capsules – 180-190 rubles.
Bile acids
Bile acids
- monocarboxylic hydroxy acids from the class of steroids, derivatives of cholanic acid C23H39COOH.
Synonyms: bile acids, cholic acids
,
cholic acids
or
cholenic acids
.
The main types of bile acids circulating in the human body are the so-called primary bile acids
, which are primarily produced by the liver, cholic and chenodeoxycholic, as well as
secondary ones
, formed from primary bile acids in the colon under the influence of intestinal microflora: deoxycholic, lithocholic, allocholic and ursodeoxycholic .
Of the secondary acids, only deoxycholic acid, which is absorbed into the blood and then secreted by the liver as part of bile, participates in noticeable quantities in the enterohepatic circulation. In the bile of the human gallbladder, bile acids are found in the form of conjugates of cholic, deoxycholic and chenodeoxycholic acids with glycine and taurine: glycocholic, glycodeoxycholic, glycochenodeoxycholic, taurocholic, taurodeoxycholic and taurochenodeoxycholic acid - compounds also called paired acids
. Different mammals have different sets of bile acids.
Bile acids in drugs
Bile acids, chenodeoxycholic and ursodeoxycholic, are the basis of drugs used in the treatment of gallbladder diseases.
Recently, ursodeoxycholic acid has been recognized as an effective treatment for bile reflux. In April 2015, the FDA approved Kybella, a drug containing synthetic deoxycholic acid, for the non-surgical treatment of double chins.
At the end of May 2021, the FDA approved the use of the obeticholic acid drug Ocaliva for the treatment of primary biliary cholangitis in adults.
In the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification (ATC), bile acids are assigned the following codes:
- in section "A. Drugs affecting the digestive tract and metabolism”, a separate group “A05AA Bile acid preparations” is allocated, which contains the codes:
- A05AA01 Chenodeoxycholic acid
- A05AA02 Ursodeoxycholic acid
- A05AA03 Cholic acid
- A05AA04 Obeticholic acid
- D11AX24 Deoxycholic acid
Bile acid metabolism
In a healthy person with a gallbladder, primary bile acids synthesized in hepatocytes are excreted into bile conjugated with glycine or taurine and enter the gallbladder through the biliary tract, where they accumulate. A small amount of bile acids (approximately 1.3%) is absorbed in the walls of the gallbladder. Normally, the main pool of bile acids is located in the gallbladder, and only after stimulation by food does the gallbladder reflexively contract and bile acids enter the duodenum. Secondary bile acids (deoxycholic and lithocholic) are formed from primary (cholic and chenodeoxycholic, respectively) under the influence of anaerobic bacteria of the colon (see figure below, Lyalukova E.A., Livzan M.A.):
Metabolism of bile acids
After reabsorption of secondary bile acids, they are conjugated with glycine or taurine, from which they also become components of bile. Ursodeoxycholic acid is a tertiary bile acid that is also formed under the action of microbial enzymes. From the intestine, bile acids with the portal blood flow again enter the liver, which absorbs almost all bile acids from the portal blood (approximately 99%); a very small amount (about 1%) enters the peripheral blood (see figure below, Lyalukova E.A., Livzan M.A.):
Metabolism of bile acids with the participation of intestinal microflora
Bile acids and esophageal diseases
In addition to hydrochloric acid and pepsin secreted in the stomach, components of the duodenal contents: bile acids, lysolecithin and trypsin can have a damaging effect on the mucous membrane of the esophagus when they enter it.
Of these, the most well studied is the role of bile acids, which apparently play a major role in the pathogenesis of esophageal damage during duodenogastric esophageal reflux. It has been established that conjugated bile acids (primarily taurine conjugates) and lysolecithin have a more pronounced damaging effect on the esophageal mucosa in acidic conditions, which determines their synergy with hydrochloric acid in the pathogenesis of esophagitis. Unconjugated bile acids and trypsin are more toxic at neutral and slightly alkaline pH, i.e. their damaging effect in the presence of duodenogastroesophageal reflux is enhanced by drug suppression of acid reflux. The toxicity of unconjugated bile acids is primarily due to their ionized forms, which more easily penetrate the esophageal mucosa. These data may explain the lack of an adequate clinical response to monotherapy with antisecretory drugs in 15-20% of patients. Moreover, long-term maintenance of esophageal pH close to neutral values can act as a pathogenetic factor for epithelial metaplasia and dysplasia (Bueverov A.O., Lapina T.L.). When treating esophagitis caused by reflux in which bile is present, it is recommended, in addition to proton pump inhibitors, to prescribe ursodeoxycholic acid drugs in parallel. Their use is justified by the fact that under its influence the bile acids contained in the refluxate are converted into a water-soluble form, which is less irritating to the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus. Ursodeoxycholic acid has the property of changing the pool of bile acids from toxic to non-toxic. When treated with ursodeoxycholic acid, in most cases, symptoms such as bitter belching, abdominal discomfort, and vomiting of bile disappear or become less intense. Research in recent years has shown that for bile reflux, the optimal dose should be 500 mg per day, divided into 2 doses. The duration of treatment is at least 2 months (Chernyavsky V.V.).
Patient Materials
The GastroScan.ru website contains materials for patients on various aspects of gastroenterology:
- “Advice from doctors” in the “Patients” section of the site
- “Popular gastroenterology” in the “Literature” section
- “Popular gastroenterology” in the “Video” section
Materials for healthcare professionals addressing the issue of bile acids in pathogenesis and their use in the treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
Articles
- Lyalukova E.A., Livzan M.A. Dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi and the syndrome of bacterial overgrowth in the intestine // Attending physician. 2013. No. 1.
- Maev I.V., Dicheva D.T., Andreev D.N. and others. Differentiated tactics of treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease // Current problems of gastroenterology. 2012 November 28. Moscow. pp. 71–79.
- Bueverov A.O., Lapina T.L. Duodenogastroesophageal reflux as a cause of reflux esophagitis // Farmateka. 2006. – No. 1. - With. 1–5.
- Evsyutina Yu.V., Trukhmanov A.S. The role of motor disorders of the esophagus and stomach in the pathogenesis of gastroesophageal reflux disease // RZHGGK. 2015. No. 5. pp. 10–15.
- Lapina T.L., Kartavenko I.M., Ivashkin V.T. Pathogenetic and therapeutic significance of bile acids in reflux gastritis // RZHGGK. 2015. No. 1. pp. 86–93.
- Uspensky Yu. P., Fominykh Yu. A., Gnutov A. A. Duodenogastroesophageal reflux: current state of the problem. Medical alphabet. 2020; (37): 11–16.
On the website GastroScan.ru in the “Literature” section there is a subsection “Diseases of the hepatopancreatobiliary system”, containing publications for healthcare professionals on this topic.
Video
Still from video Minushkin O.N., Zverkov I.V., Skibina Yu.S. Chronic reflux gastritis (biliary): diagnosis, some treatment approaches.
Still from video by E.S. Vyuchnova Tactics for managing patients with duodenogastric/biliary reflux
On the website GastroScan.ru in the “Video” section there is a subsection “For Doctors”, containing video recordings of reports, lectures, webinars in various areas of gastroenterology for healthcare professionals.
Back to section