12 April 2021
35120
0
3.3 out of 5
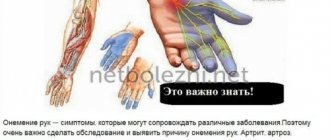
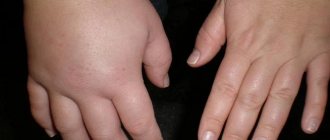
Numbness or hypoesthesia of the fingers is a rather unpleasant situation, which can be either a consequence of physiological reasons or a sign of various types of diseases. Therefore, if this symptom persists for an hour or more, and there is no improvement in rubbing your hands, clenching and unclenching your fists, you should consult a doctor. He will help you understand the reasons for its appearance and, if necessary, prescribe the necessary treatment. This will be the key to detecting pathology at an early stage of development and the success of therapy, and will also help to avoid aggravation of the situation and eliminate the risk of complications. After all, it is not so much the numbness of the fingers that is dangerous, although it can cause significant difficulties in performing everyday tasks, but the consequences of the lack of treatment for the diseases that provoked its occurrence.
Why do my fingers go numb?
Numbness and decreased sensitivity in the fingers may be a consequence of the development of neurological disorders and changes in their blood supply, which is caused by vascular pathologies. However, this can also occur as a result of such harmless factors as prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position, which compresses the blood vessels supplying the fingers. This is often observed in the morning when a person has just woken up, especially if during sleep he put his hand under his head or threw them behind it. In such situations, numbness is usually combined with tingling in the fingers of varying strength, as well as a feeling of loss of control over the hands. But all these symptoms go away on their own with the restoration of normal quality of blood circulation in the hands, which takes no more than 10-15 minutes.
Also, one of the physiological causes of numbness in the fingers is prolonged exposure to the cold. As a result of prolonged exposure to low temperatures, blood vessels reflexively contract. This leads to a decrease in the rate of blood circulation in the fingers and the occurrence of characteristic numbness, and sometimes aching pain. This is no longer as harmless as sleeping in an uncomfortable position, since this already indicates the possibility of frostbite on the fingers. Therefore, in such situations, it is necessary to take measures to warm your hands.
But, if your fingers often go numb and this feeling persists for a long time, you should look for the reason in:
- neurological disorders (tunnel syndrome, polyneuropathy, plexitis, etc.);
- traumatic injuries;
- vascular disorders, etc.
Sometimes fingers go numb while taking medications such as Isoniazid, Vincristine, Metronidazole.
Neuropathy, carpal tunnel syndrome and polyneuropathy
As for neurological disorders, a fairly large number of different diseases can manifest themselves in a similar way. First of all, these are neuropathies of various origins. This term refers to damage or compression of one or more nerves of the peripheral nervous system, one of the first symptoms of which is the occurrence of a crawling sensation and numbness. But if in the early stages of development this is observed only periodically, then as the pathology progresses, the fingers become numb more often and longer, pain occurs, changes in the condition of the skin are observed, and the muscles lose tone.
With inflammation of the nerve, bruise, prolonged compression of the arm, for example, with the habit of leaning on the elbows at work, or the action of other isolated factors, local neuropathies or tunnel syndromes may occur. In such cases, in addition to numbness, pain, weakness or awkwardness may be observed when moving or grasping objects with your fingers. The nature of their manifestation directly depends on which of the nerve trunks is damaged. So:
- numbness in the 1st, 2nd and partially in the 3rd fingers is characteristic of damage to the radial nerve;
- numbness of the little finger and ring finger up to half on the palm side and the 4th, 5th and part of the 3rd fingers on the back side is observed with damage to the ulnar nerve;
- numbness of the 1st, 2nd, 3rd and half of the 4th finger on the side of the palm and nails of 2-5 fingers is caused by damage to the median nerve;
- Numbness of 1-3 fingers and weakness when abducting the thumb are characteristic of the most common syndrome of the carpal or carpal tunnel, in which the median nerve is pinched in the flexor muscles of the wrist joint.
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs in 1% of people and often occurs in those who have to work with a computer for long periods of time.
Fingers can also go numb as a result of the development of polyneuropathies, i.e., with simultaneous damage to a large number of nerves of the peripheral nervous system as a result of the development of certain systemic diseases. In such situations, numbness of the fingers on both hands is observed, and other symptoms characteristic of these pathologies may also appear.
This may be a consequence of diabetes mellitus, in which constantly high blood sugar levels lead to damage to nerve fibers, i.e. the development of diabetic neuropathy. But diabetes is more likely to affect the toes, although the hands can also suffer.
Fingers also become numb during development:
- chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy;
- Roussy-Lévy syndrome;
- alcoholism, which led to the emergence of so-called alcoholic polyneuropathy;
- Refsum's disease;
- amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS);
- Guillain-Barre syndrome;
- poisoning with chemicals and heavy metals.
Other neurological disorders
Some diseases can indirectly cause numbness in the fingers, but they are also characterized by a number of other symptoms, which makes it possible to differentiate them from neuropathies. These include:
- Cervical plexitis is a disorder that occurs when the nerves entering the cervical plexus are compressed by enlarged lymph nodes, cervical ribs or spinal structures as a result of the development of spondylosis, osteochondrosis, protrusion or intervertebral disc herniation of the cervical spine. It may also be the result of a birth injury or other damage to the cervical spine.
- Brachial plexitis is a neurological disorder that develops when the nerves that form the brachial plexus are pinched. It can occur as a result of injury to the collarbone, shoulder joint, the formation of an aneurysm (protrusion of the wall of a blood vessel), or a tumor. Sometimes brachial plexitis is observed in people against the background of dysmetabolic or infectious pathologies.
- Horner's syndrome is a neurological disorder that develops in response to damage to the sympathetic nerve fibers of the brachial plexus as a result of tumor formation, aortic aneurysm, thyroid dysfunction, and the development of multiple sclerosis.
Spinal diseases, in particular spondylosis, osteochondrosis, and intervertebral hernias, are among the most common causes of numbness in the fingers.
Injuries
Any bruises, fractures or other injuries to the hands, accompanied by severe swelling, can lead to short-term numbness of the fingers. This is a consequence of compression of the blood vessels by edematous tissue, which temporarily disrupts the blood supply. This can also be observed in the first days after applying a plaster cast to immobilize the injured arm and requires its prompt loosening.
It is extremely rare to observe the occurrence of myofascial compartment syndrome, which is characterized by numbness of the fingers and hands, severe pain that cannot be relieved with traditional non-narcotic drugs. This is a dangerous complication that requires immediate qualified medical care.
Also, numbness in the fingers immediately occurs after open wounds, during which the nerve trunks were damaged. But this is usually combined with noticeable limitations in mobility.
Patients who have suffered traumatic brain or spinal cord injuries often complain that their fingers go numb. At the same time, they have numbness constantly.
Vascular disorders
One of the possible causes of numbness may be hypertension, especially if it occurs without treatment. In such situations, the fingers usually go numb due to the development of swelling of the hands, which is combined with:
- redness of the face;
- increased sweating;
- long-term pain in the heart area.
Another cause of hypoesthesia can be anemia, i.e. a condition in which the number of red blood cells in the blood sharply decreases, and therefore the level of hemoglobin drops. Since this compound is responsible for transporting oxygen to cells, when it is deficient, signs of oxygen starvation are observed:
- feeling of weakness;
- increased fatigue;
- headache;
- decreased appetite;
- increased heart rate;
- shortness of breath even with minor physical exertion;
- decreased concentration;
- dizziness up to loss of consciousness.
Also, numbness in the fingers can be a consequence of a stroke.
Numbness in the fingers is also characteristic of Raynaud's syndrome. This is the name for a disorder in which there is a violation of arterial circulation in the 2nd and 4th fingers under the influence of cold or stress. It is characterized by a paroxysmal course with the initial appearance of a feeling of numbness, coldness and blueness of the fingers, which indicates a decrease in the intensity of blood circulation in them. Then these sensations are replaced by distension, aching pain and burning. When blood circulation is restored and, accordingly, the attack ends, a strong feeling of heat appears in the fingers, and they turn sharply red.
Raynaud's syndrome may be a sign of the development of diseases such as:
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- scleroderma;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- damage to the sympathetic ganglia or neurovascular bundles;
- some endocrine diseases;
- blood pathologies.
Less commonly, it occurs against the background of vibration disease and frequent hypothermia.
Diagnostics
Thus, there are quite a lot of diseases that can provoke hypoesthesia of the fingers. Therefore, if this symptom occurs regularly and persists for a long time, you should definitely consult a neurologist. The doctor will conduct a survey and examination of the patient, during which he will assess the condition of the skin, pulse strength, reflexes and conduct certain neurological tests to detect possible motor disorders. But to make an accurate diagnosis, this data is not enough. Therefore, depending on the detected signs, patients may be prescribed one or another diagnostic procedure from the following:
- electromyography and electroneurography - used to assess the degree and extent of damage to nerve trunks;
- X-ray or CT - used to detect deformities of the bones of the hands, tumors;
- angiography is a method used to assess the quality of blood circulation in the area of interest, in particular for diagnosing Raynaud's syndrome;
- Dopplerography of the vessels of the neck and head - is prescribed to detect cerebral circulation disorders and vascular pathologies;
- MRI is used to detect minute changes in soft tissue structures, the brain, and intervertebral discs.
A set of laboratory tests is also often prescribed, the results of which help to identify systemic diseases, for example, diabetes mellitus, anemia, endocrine disorders, rheumatoid diseases, etc.
Treatment
For each patient, treatment is developed individually based on diagnostic results and detected diseases. In most cases, they begin by prescribing conservative therapy appropriate to the situation. It may include medication, physical therapy and exercise therapy.
Drug treatment may include drugs from different groups. They are selected based on the causes of numbness in the fingers, but they must take into account concomitant diseases, age and other characteristics of the patient. Typically used:
- NSAIDs - prescribed during an exacerbation of neuropathy to reduce the intensity of pain and eliminate swelling of soft tissues;
- corticosteroids - indicated for severe inflammatory processes, as well as complex neuropathy;
- B vitamins - used to improve the transmission of bioelectric impulses along nerve trunks;
- antiplatelet agents - prescribed to reduce blood viscosity and improve blood circulation;
- calcium antagonists - used to increase the lumen of blood vessels, which is indicated for Raynaud's syndrome;
To increase the effectiveness of drug treatment, physiotherapeutic procedures are often used. The most effective for neurological disorders are:
- electrophoresis;
- phonophoresis;
- laser therapy;
- UHF;
- electromyostimulation;
- applications with paraffin;
- ozocrete treatment;
- mud therapy.
To eliminate numbness, an individually developed complex of exercise therapy must be prescribed. It helps to develop the joints of the hands, activate blood circulation and relieve muscle tension. As a result, tissue trophism and innervation of the fingers improves. But exercise therapy should be done systematically, devoting the proper amount of time to gymnastics every day.
Physiological causes of numbness
Numbness occurs with prolonged immobility. Whatever position we are in, some vessels become pinched, and we risk that the nerve endings, which do not receive proper nutrition, will lose sensitivity. Our body must move, changing the areas that have been subjected to compression, and then we will not be in danger of numbness. This usually happens during the day. But during deep sleep, we can lie in the same position for quite a long time without changing posture. And then, when we wake up, we notice that we have rested some part of our body, for example, a hand placed under our head.
Numbness is caused by exposure to cold. When in contact with cold air, the skin loses sensitivity. Local blood circulation is disrupted, and we cease to feel the nerve endings. If this situation lasts longer, frostbite is possible, but in most cases it is enough to rub the area of skin that has lost sensitivity or return to warmth, blood circulation will be restored and the numbness will go away.
If numbness occurs without an obvious connection with a specific situation, then it probably has a pathological cause.
When is surgery needed?
There are a number of situations when conservative therapy does not allow one to get rid of the numbness in the fingers and other symptoms that bothers the patient, or the disease that provokes it poses a serious threat to the life and health of a person. In such cases, patients are recommended to undergo surgical intervention, the nature of which directly depends on the type of pathology detected.
So, the operation could consist of:
- removal of peripheral nerve tumors;
- neurolysis;
- decompression of compressed nerve structures;
- performing nerve plastic surgery for traumatic injuries;
- removal of cervical ribs;
- removal of aneurysms;
- removal of intervertebral hernias, etc.
Peripheral nerve tumor removal
This operation is required when benign or malignant tumors are detected that compress the peripheral nerve trunks. In the first case, it can be carried out by blunt desquamation from a capsule formed by connective tissue. Sometimes it becomes necessary to remove the damaged nerve fragment, after which it is repaired or sutured.
If fingers become numb as a result of the formation of neurofibromas, especially with multiple neurofibromatosis, surgical intervention is indicated only in cases where this benign neoplasm compresses the nerve trunk. This is due to the fact that the removal of one of the tumors can become an impetus for the formation of others, which can complicate the patient’s condition.
When diagnosing cancerous tumors, the operation involves removing the entire tumor, including healthy tissue and nearby lymph nodes. After this, patients are prescribed radiation therapy.
Neurolysis
Neurolysis or release of the nerve from the surrounding connective tissue scar tissue is used for:
- injuries of various types that caused nerve damage;
- compression of the nerve trunk by scar tissue;
- compression of the nerve by an aneurysm;
- failure of the nerve suture.
The goal of the operation is to restore normal nerve conduction. Therefore, it can act as a separate type of surgical intervention, or be only one of its stages.
Decompression of nerve trunks
This operation is performed when carpal tunnel syndrome develops as a result of compression of the nerve in the musculoskeletal canal of the wrist, etc. It is used when pain in the hand persists and there is a significant risk of developing muscle atrophy. The essence of this type of surgical intervention is to dissect the tissue that is compressing the nerve, and sometimes to move the nerve itself, followed by restoration of the anatomy of the musculoskeletal canal.
Plastic surgery and suture of nerve trunks
A nerve suture or neurorhaphy is required when the nerve trunk is ruptured as a result of a traumatic factor or after resection of its fragment during surgery. The essence of the method is the precise comparison of cross sections of the dissected nerve, followed by suturing its sheath or individual bundles.
Nerve repair is indicated when it is impossible to apply a suture due to the remote location of the remaining ends. It consists of using grafts taken from the patient’s other superficial nerves innervating the skin and using them to connect the remaining fragments of the injured nerve trunk. The autograft is fixed with sutures.
Removal of cervical ribs
If the fingers become numb due to the presence of an additional rib at the cervical vertebra, it is recommended to remove it in parts, but entirely along with the periosteum. For this purpose special forceps are used.
Aneurysm removal
The operation can be performed using different techniques, the choice of which directly depends on the location of the aneurysm:
- installation of a vascular stent or coil;
- applying a clip at the base of the aneurysm neck.
Removal of intervertebral hernias
Operations of this type are performed when fingers become numb as a result of the formation of protrusions or hernias in the intervertebral discs of the cervical spine. They can be carried out in different ways, including by:
- hydroplastics;
- nucleoplasty;
- endoscopic hernia removal;
- microsurgical operation.
In all cases, by removing the protrusion of the disc, decompression of the spinal root responsible for the innervation of the arm and fingers is carried out.
Thus, numbness of the fingers can be either a harmless situation, or be a consequence of an injury, or indicate the development of quite dangerous diseases, including the spine. Therefore, when this symptom appears, it is important not to hesitate and immediately contact a neurologist or spinal surgeon.
In what cases should you consult a doctor if you have numbness?
If the numbness has a physiological cause, that is, caused by a temporary disruption of the local blood supply, then it is enough to change the position and rub the numb area, and sensitivity will be restored. If the numbness does not go away, then the cause is more serious and you should consult a doctor.
It is necessary to get emergency medical help if numbness is accompanied by symptoms of damage to the central nervous system:
- headache, dizziness, attacks of weakness, double vision, loss of coordination;
- unexpected bowel movements or sudden urination;
- speech problems.
These symptoms may occur after a head, neck, or back injury.
You should also consult a doctor if:
- numbness occurs periodically and without an obvious reason;
- thermal perception is impaired (for example, the ability to distinguish between warm and cold water is impaired);
- Numbness is preceded by pain and loss of range of motion in one of the joints.