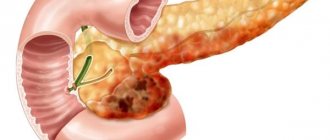
Schmorl's intervertebral hernia is a vertical defect in which the intervertebral disc penetrates the bone body of a nearby vertebra. Schmorl's hernias differ from other types in the absence of intense symptoms, so for a long time the patient may not be aware of the existing problem.
Yusupov Hospital is a modern multidisciplinary medical institution where patients have access to a wide range of services. Thus, for patients diagnosed with Schmorl's hernia, treatment is developed and carried out by highly qualified specialists in accordance with international standards.
General information about the disease
The intervertebral disc consists of an elastic core surrounded by a durable fibrous membrane. Under the influence of certain pathological factors, the shell becomes thinner and breaks, and the core begins to form a small cavity in the vertebral bone, simultaneously filling it. This disease is asymptomatic for a long time and is often detected accidentally during examination for one reason or another. Only with significant volumes of the formation does it begin to bulge beyond the boundaries of the vertebra, causing symptoms of compression of the nerve roots, similar to a classic intervertebral hernia.
Formations often occur in adolescents against the background of rapid skeletal growth. In this case, the most typical location is the thoracic region. Adults are more likely to experience Schmorl's hernias, which have formed in the lumbar spine due to increased load on the musculoskeletal system.
Make an appointment
Pathogenesis
Depending on the etiology, disorders of the vertebral structure can develop in different ways:
- the pathogenesis of congenital Schmorl's hernia is based on weakness and inferiority of cartilage tissue, impaired blood supply to the growing disc;
- in old and senile age, osteoarthritis or osteoporosis causes degenerative changes in cartilage tissues, disrupts their structure, which leads to loss of strength and elasticity, and further formation of a knot;
- injuries can cause disc defects, breakthrough of tissues of the nucleus pulposus, formed under the influence of large and sudden mechanical force, for example, due to an impact, fracture, dislocation, subluxation.
What is Schmorl's hernia?
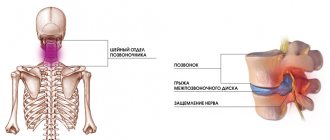
Schmorl's nodes in the spine are simply a herniated intervertebral disc, formed by pushing through the intervertebral endplates of the body of an adjacent vertebra (upper or lower) by cartilage tissue. They can be congenital or acquired - as a result of degenerative processes or injuries of the thoracic or lumbar spine.
Schmorl's cartilaginous nodes extend beyond the fibrous ring and can have a median, paramedian, foraminal and extraforaminal location.
On x-rays, Schmorl's nodes appear in the form of narrowing of the intervertebral spaces, uneven contours of the end plates and slight beak-like growths along the edges, while signs of calcification of the nucleus pulposus or annulus fibrosus are revealed, as well as the “vacuum phenomenon” - slit-like clearing in the anterior parts of the intervertebral discs.
Causes
The reasons contributing to the appearance of Schmorl's hernia include:
- hereditary predisposition: often the pathology is congenital or develops in the first years of life;
- uneven growth, in which bones lag behind cartilage in development;
- intense physical activity and accompanying microtraumas of the spinal column (weight lifting, some sports, excess body weight, pregnancy);
- single intense physical activity: falling, lifting a heavy object in the wrong position;
- vertebral deformation due to osteoporosis or spondyloarthrosis (in old age);
- impaired blood supply to the spinal column;
- lack of microelements: calcium, vitamin D;
- metabolic disorders;
- postural disorders, scoliosis, thoracic kyphosis;
- osteochondrosis;
- sedentary lifestyle.
Consequences
Despite the fact that in the first stages of development, Schmorl’s hernia does not manifest itself with the appearance of unpleasant symptoms, in the future the following serious complications are possible:
If a Schmorl's hernia is not treated, then the pathology gradually develops into an intervertebral hernia. The formation of a Schmorl's nodule gradually develops into an intervertebral hernia.- The body has a special predisposition to compression fractures, in which the thinning of the vertebrae occurs so severely that they begin to break under physical stress.
- Tendency to develop the pathology of arthritis or arthrosis of the intervertebral joints due to increased loads on them.
- Disease of Scheuermann-Mau pathology, or childhood dorsal kyphosis.
- Partial or complete loss of the ability to move (disability), resulting from impaired mobility of the spinal column.
Such complications pose a great threat to a person’s health and ability to work ; for this reason, it is important to remember that treatment for the disease should begin as early as possible.
Find out more about the consequences of Schmorl's hernia in the following articles:
- You can read more about the treatment and symptoms of Schmorl's hernia in the thoracic region here
- You can find out what intervertebral hernias are on the page
- What can be the consequences of a herniated disc?
Symptoms
Schmorl's hernia is asymptomatic for a long time, since it does not extend beyond the contours of the vertebra. Regardless of the location of the protrusion, a person periodically notices slight pain in the affected area. They intensify when lifting weights, bending, turning the body, as well as staying in the same position for a long time. In a lying position, discomfort decreases.
The second typical symptom of Schmorl's hernia is a feeling of fatigue in the spine, which increases with prolonged stay in an upright position.
Significant pain occurs even with a significant increase in the size of the formation, as a result of which it can cause a typical picture of radiculopathy with pain and signs of irritation or compression of the nerve root: numbness of the limbs, paresthesia, decreased muscle strength and reflexes. With the development of pathology in the cervical spine, the growth of the protrusion can provoke headaches, dizziness and other signs of insufficient blood flow to the brain.
Forecast
The asymptomatic course of the disease does not have a negative impact on a person’s activity and well-being. Pain syndrome requires complex treatment, combining drug therapy and physiotherapy. This will stabilize the condition and lead to remission.
In the absence of therapy, the protrusion progresses, acquires large sizes, and begins to compress important structures of the spinal canal. This is dangerous by the development of complications up to complete paralysis, that is, immobilization of the patient.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of Schmorl's hernia is not difficult. At the first visit, the neurologist interviews the patient, finding out details about the main complaints, the timing and circumstances of their occurrence. At the same time, data is collected on chronic diseases, past infections, and injuries. If we are talking about a child or teenager, the developmental characteristics of the body are taken into account.
After the interview, the doctor performs a neurological examination to assess the function of the central nervous system and peripheral nerves. The diagnosis is confirmed using modern techniques for visualizing internal structures. Depending on the situation, the following may be used:
- X-ray;
- computed tomography (CT);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
These examinations allow you to see characteristic changes in the bone tissue of one or more vertebrae and make an accurate diagnosis. If necessary, laboratory diagnostics are prescribed (general blood and urine tests, biochemical blood tests), instrumental and functional examinations, as well as consultations with specialists. They are necessary to exclude another cause of symptoms.
Proper nutrition
Products recommended for cervical hernia include:
- dishes containing gelatin (jelly, pudding, aspic);
- fish (mackerel, salmon, herring);
- low-fat dairy products (sour cream, milk);
- fruits (berries, apples, pears);
- nuts (hazelnuts, walnuts, almonds);
- foods rich in fiber (cabbage, pumpkin, beans);
- dried fruits, raisins;
- porridge, bran;
- wholemeal bread.
Alcohol, spreads, margarine, tomatoes, white rice, flour products, sweets, and ice cream are prohibited. It is necessary to sharply limit the consumption of fatty, fried, spicy, smoked and pickled foods.
Treatment of Schmorl's hernia
Treatment is based on a combination of methods of unloading the spine, strengthening the muscle corset, drug support and physiotherapy. An integrated approach allows not only to relieve the patient from pain and discomfort, but also to eliminate the consequences of compression of the roots.
Drug treatment is prescribed if the patient has pain and other signs of damage to nerve fibers. Depending on the situation, the following are used:
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), necessary to relieve inflammation and pain (diclofenac, nimesulide, meloxicam, ibuprofen, etc.); Both local and tablet forms are used, as well as injections;
- muscle relaxants (baclofen, mydocalm): aimed at relieving reflex muscle spasms that occur in response to irritation;
- chondroprotectors (chondroitin, glucosamine and drugs based on them): necessary for concomitant osteochondrosis, promote the regeneration of cartilage tissue;
- B vitamins (milgamma): stimulate the restoration of nervous tissue;
- calcium and vitamin D supplements: necessary if there are signs of osteoporosis.
The type of drugs, their combinations, dosages, and regimen are determined by the doctor in accordance with the specific clinical situation.
Physiotherapy is aimed at improving blood supply to affected areas and eliminating inflammation. Depending on the indications and concomitant diseases, the following are prescribed:
- electrophoresis: delivery of drugs to the site of inflammation by electrical impulses;
- phonophoresis: administration of drugs into the pathological focus using ultrasonic waves;
- magnetic therapy: stimulation of blood circulation in the affected area using electromagnetic waves;
- electrical stimulation: improving blood circulation and metabolism through stimulation with weak electrical discharges
To enhance the effect of therapy, auxiliary techniques are used:
- massage: improves blood circulation, prevents stagnation of lymph in the affected areas;
- physical therapy: training is aimed at strengthening the back muscles and forming a natural corset, as well as stretching the spine;
- underwater and classic traction: helps unload the spinal column;
- manual therapy: helps remove muscle blocks, improve blood circulation, reduces the load on the spine;
- acupuncture: relieves muscle and vascular spasms, reduces pain.
When hernias are large and conservative therapy is ineffective, doctors resort to surgical treatment. Operations are indicated for severe pain, severe pinching of a nerve root, as well as for a fracture of the affected vertebra.
In this case, the following is carried out:
- percutaneous fluoroscopic vertebroplasty: a procedure for restoring vertebral bone tissue;
- removal of fragments with the subsequent installation of prostheses or the introduction of special fillers to eliminate compression of the spinal cord or roots.
Specific treatment methods are selected depending on the size and location of hernias, as well as their number.
Make an appointment
What it is
Schmorl's hernia is a deformation of the structure of the intervertebral discs throughout their entire mass . This happens due to the daily colossal loads that the spine of almost any person experiences. Most often, it is this reason that leads to the development of pathologies of varying severity.
Schmorl's hernia is characterized by the introduction of expanding cartilaginous tissue of the intervertebral discs into the vertebral cavity, which is a spongy substance. In this case, deformation of the obturator plate located between them occurs.
A concavity appears on the endplates of one or a row of vertebrae . In some cases, experts even note the presence of microfractures. The difference between this pathology is its formation exclusively within the spinal segment. In this case, there is no prolapse into the lumen of the spinal canal or beyond its edge.
In Schmorl's hernia, the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc is pressed into the vertebra
Compression of the spinal cord, nerve processes and spinal roots also does not occur , which is the reason for the absence of signs of pain or serious restrictions on movement.
Clinical picture
The development of this disease is characterized by the application of extremely strong pressure from the cartilage of the intervertebral disc . If such a load becomes constant and dynamic, the deformation of the obturator plate begins to grow, forming a dent. It is this that is gradually filled with cartilaginous tissue of the disc, which in this case is called Schmorl’s node.
Classification
Classification of Schmorl's hernia is carried out according to a number of characteristics.
By localization:
- central single in the cervical region;
- anterior multiple in the thoracic region;
- posterior shallow in the lumbar region;
- lateral intracorporeal;
- deep cartilaginous hernia of the endplate;
- caudal hernia.
By location they distinguish:
- central hernia , in which the pathology is located between the vertebral bodies. It can be accidentally detected during diagnosis, while no special symptoms are observed. With a significant increase in size, it can become a source of symptoms similar to osteochondrosis: lower back pain that radiates to the legs, a feeling of back fatigue, reduced mobility in the area of pathology, pain when moving;
- anterior hernia developing on the anterior part of the vertebral body. It manifests itself as back pain, both during and without physical activity, and provokes limited mobility of the spine;
- posterior hernia , located in the posterior part of the vertebral body;
- lateral hernia without pain symptoms.
Schmorl's hernia may be:
Sometimes a patient may develop several multiple hernias, which occur in children and adolescents and are asymptomatic;- single, formed in mature and elderly people in the thoracic or lumbosacral region, respectively. It also occurs without any special symptoms;
- small, resulting from destructive phenomena in the intervertebral discs;
- intracorporeal, formed directly inside the vertebra, when the jelly-like core of the intervertebral discs penetrates into the bone tissue;
- deep, developing with strong penetration of cartilage tissue deep into the vertebrae, often occur in those who suffer from osteoporosis and its consequence is often compression fractures of the spine, failures in the intervertebral discs.
Prevalence and significance
As a rule, Schmorl's hernia develops in certain groups of people : children and adolescents; elderly people; professional athletes who often experience back injuries.
In most cases, Schmorl's hernias do not cause much concern. They do not require surgical intervention. Such neoplasms pose a danger when they noticeably increase in size, which increases the risk of compression fractures.
Prevention
Preventive measures are relevant both for patients who have already started treatment, and for those who do not want to allow its formation. These include:
- eliminating physical inactivity, regular exercise and walking;
- reducing the load on the spine by normalizing body weight;
- proper nutrition with a sufficient amount of nutrients, vitamins, microelements (especially calcium and vitamin D);
- eliminating situations that require heavy lifting;
- compliance with the work and rest regime;
- a full night's sleep.
Stages of the disease
- Initial stage. A crack appears in the fibrous ring and the contents come out, the nucleus gradually protrudes, and shooting pain appears.
- Partial prolapse. At this stage, the pain is already constant, swelling occurs near the nerve root, and blood supply to the disc area is disrupted.
- Complete prolapse. The pain becomes intense and radiates to the lower extremities. Possible loss of ability to work.
- Sequestration. Pieces of the disc are displaced, several nerve roots begin to suffer at once, which leads to throbbing and debilitating pain.
Treatment at the Health Energy Clinic
Neurologists at the Energy of Health clinic offer a full range of services for the diagnosis and treatment of Schmorl’s hernias of any size and location:
- thorough diagnosis excluding other possible diseases;
- individual selection of drug treatment using effective combinations of drugs;
- massage, physical therapy, physiotherapy to quickly achieve results;
- services of an osteopath and chiropractor;
- selection and organization of sanatorium-resort treatment.
Advantages of the clinic
Multidisciplinary medical is:
- experienced staff;
- comfortable conditions;
- affordable prices;
- high-precision diagnostic equipment;
- all types of laboratory tests;
- individual approach to the selection of therapy;
- auxiliary treatment methods: exercise therapy, massage, manual therapy, acupuncture;
- own day hospital;
- organization of rehabilitation and sanatorium-resort treatment;
- issuance of certificates, conclusions, certificates of incapacity for work.
A Schmorl's hernia may not manifest itself for a long time, but sooner or later the formation will make itself felt. Don’t delay contacting a neurologist; sign up for an examination at Health Energy.
Will Schmorl with a hernia be accepted into the army?
The question is ambiguous. Pathology itself is not a contraindication for conscription; it can also be applied to military institutions. But a complicated Schmorl's hernia (this is especially typical for multiple types) is accompanied by a limitation of sensitivity and motor functions, and a conscript with such a diagnosis is not fit for service. To make a decision regarding the suitability of a conscript with Schmorl's pathology, additional examinations are carried out, and the verdict is made by a commission.
Get diagnosed at the Consultative Diagnostic Center (formerly the National Diagnostic Center) and receive professional medical care. Make an appointment for a FREE appointment with a neurologist by calling the numbers listed on the website, or click the APPLY button.