Mite
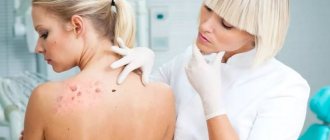
The subcutaneous mite causes skin lesions in humans and animals - demodicosis. The mite settles in the hair follicles of the head, eyelashes and eyebrows, in the ducts and secretions of the sebaceous glands of the facial skin. A subcutaneous mite is a normal phenomenon, and for the time being it does not pose a danger, since it feeds on waste cells. But if the body’s defenses weaken, the mite begins to actively multiply, penetrates into the deeper layers of the skin and causes inflammation. According to the observations of researchers, women are more often affected by this disease.
FACT:
It is believed that more than 20% of people are carriers of demodicosis, but no clinical signs are detected.
Diagnosis of demodicosis
To diagnose the disease, there is a special laboratory test, which is called a demodex test. For analysis, material is taken from the affected areas. The following can be used as biomaterial:
- Pieces of skin (they are taken with a scalpel, painlessly for the patient).
- Contents of ulcers.
- Eyelashes.
Next, the biomaterial is studied under a microscope. A demodex test is considered positive if at least 5 parasites are detected per 1 square centimeter of skin. These must be adults or larvae. If only egg shells are detected, a new study is prescribed.
Since Demodex “hides” from ultraviolet radiation, it is advisable to take the test in the afternoon, preferably after 18.00. If you conduct a test in the morning or afternoon, the tick may be under the skin, and the result will be unreliable.
Simple preparation is required for the analysis:
- Avoid alkaline cosmetics (with a pH above 7) a week before the procedure.
- Avoid any cosmetics at least one day before the test.
- Stop taking antibiotics and other antibacterial drugs the day before the test.
- Refusal to wash your face during the day before the test.
To confirm the diagnosis, a histological examination of tissue taken from the affected area can be performed. When examined under a microscope you can see:
- Thickening of blood vessels.
- Overgrowth of the sebaceous glands.
- Destruction of hair follicle cells.
All of the above signs indicate the presence of demodicosis.
Reference! The disease has similar clinical manifestations to such pathologies as lupus erythematosus, perioral dermatitis, and acne vulgaris. Therefore, it is important to carry out differential diagnosis.
The patient may need to consult an endocrinologist or other specialist.
Signs of illness
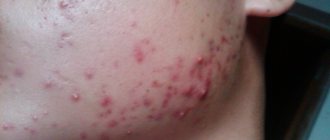
In its manifestations, damage to the subcutaneous mite is very similar to rosacea or acne. Peeling of the skin and its redness are noted, itching may occur, constant or worsening after using tonics or washing with cold water. Sometimes there is a combination of demodicosis caused by subcutaneous mites and the above-mentioned skin diseases. And this is not surprising, because the occurrence of demodicosis is influenced by negative changes in the skin. Thus, both acne vulgaris and rosacea weaken the skin’s natural defenses. When affected by skin mites, the following parts of the face are most often affected: eyelids, forehead, chin, nasolabial folds and brow ridges. Exacerbations of demodicosis occur in autumn and spring.
Such different demodicosis: symptoms and manifestations
Depending on the nature of the clinical manifestations, the following forms of demodicosis are distinguished:
- Erythematous - swelling and redness are observed in the affected areas of the skin, acne is rare.
- Papular - multiple pink pimples appear.
- Pustular - pustules and purulent acne appear.
- Combined – signs of several forms are present.
The disease can manifest itself in different ways, depending on the form of the pathology, the number of parasites on the skin and the condition of the body. The main sign of demodicosis is skin inflammatory reactions: pimples, ulcers, redness that do not go away with the use of anti-acne cosmetics. Skin manifestations are usually accompanied by itching.
As the disease progresses, the face becomes dull and sallow. Another characteristic sign of pathology in the later stages is increased oiliness of the skin, combined with peeling.
General list of symptoms of demodicosis:
- Rashes: pink pimples, purulent acne.
- Itching, worse at night, after washing, using cosmetics and being in the cold.
- Redness, swelling, bumpiness, peeling of the skin.
- Deterioration of complexion: becomes sallow.
- When the scalp becomes infected, hair loss occurs.
- The presence of clearly visible dilated blood vessels on the face.
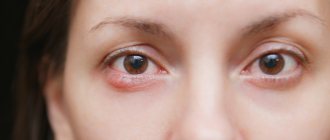
- If there are parasites on the eyelids, lacrimation, redness of the eyes and eyelids, scales on the eyelids at the roots of the eyelashes.
- Painful sensations when facial muscles are tense.
- Active loss of eyelashes and eyebrows.
Risk factors
As mentioned above, what is unpleasant is not the presence of a subcutaneous mite as such - in itself it cannot harm a healthy person - but demodicosis, which is caused by a mite. If the body is weakened and there are additional risk factors, the tick can settle in the skin for a long time and cause considerable mental and physical damage to its “breadwinner”. Risk factors include:
- dysfunction of the sebaceous glands, changes in the composition of sebum, vascular changes;
- some skin diseases (rosacea, acne, seborrhea);
- long-term use of hormonal corticosteroid ointments;
- adolescence;
- pregnancy;
- stress.
Unfortunately, non-specialists react with unacceptable ease to the appearance of acne on the face and body. The appearance of such problems is attributed to age and ordinary acne, which sooner or later should disappear on their own. We have to disappoint you: demodicosis caused by subcutaneous mites will not go away on its own. The disease can travel from one area of the skin to another, existing for years and ruining the life of its “donor”.
IMPORTANT:
squeezing out acne when infected with a subcutaneous mite only leads to an exacerbation of the infection, since during this process the mites are pressed into healthy areas of the skin and infect them.
Make an appointment
Complications
Demodicosis can be accompanied by the following complications:
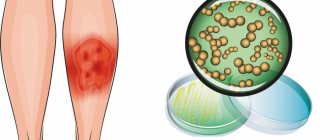
- Attachment of a secondary bacterial infection due to scratching of itchy skin, spreading to other areas of the body.
- Development of other dermatological pathologies: dermatitis, rosacea, conjunctivitis, blepharitis.
- Abscess of the skin, subcutaneous fat.
- Scar formation.
The most common complication of the disease is psychological discomfort, which can provoke the development of psychoses and psychoneuroses. The affected face looks unaesthetic, the patient begins to feel embarrassed to communicate with other people, withdraws into himself, becomes nervous and irritable. The quality of life is significantly reduced.
Treatment
Treatment of demodicosis caused by subcutaneous mites is a long and difficult process. Its complexity is that often this disease develops against the background of a decrease in the body’s defenses and has accompanying skin problems. Therapy tactics include suppressing the parasite, treating underlying diseases and increasing immunity.
The most commonly used local therapy is lotions and special ointments. In more severe cases, the doctor prescribes a course of antibiotics in combination with external therapy. Sometimes plasmapheresis procedures are recommended. In special cases, even surgical intervention is possible.
An important point in the course of treatment is diet. It is necessary to exclude hot, spicy and salty foods, foods rich in carbohydrates and fats from the diet. Those who are being treated for subcutaneous mite infestation are recommended to consume large amounts of fruits, vegetables, microelements, fiber, and dairy products. During treatment, you should not use face masks, especially those containing honey. You need to limit your exposure to the sun. You should also wait until better times to visit the bathhouse and sauna.
What to do if you have a Demodex mite: treatment of the disease
To eliminate the pathology, complex therapy is necessary. Its components depend on the characteristics of the course of the disease and the condition of the patient’s body, however, in all cases, the main goal of all measures is to eliminate parasites and create unsuitable conditions for his life. To eradicate Demodex, treatment should include:
- Drugs that reduce sebum production.
- Antifungal, antiparasitic medications (ointments, gels).
- Elimination of background diseases (endocrinological, gynecological, etc.).
- Increasing immunity: prescribing immunomodulators, vitamins, antihistamines.
During remission, physiotherapeutic and cosmetic procedures are also often prescribed, for example, electrophoresis (combined with moisturizers), microdermabrasion (exfoliation).
During the treatment period, it is important to follow a diet aimed at reducing the activity of the sebaceous glands:
- Limit your intake of fats and carbohydrates.
- Avoid spicy foods, alcohol, sweets, and pickles.
- Pay attention to foods rich in proteins, vitamins and minerals. The best foods during this period are vegetables, fruits, lean meat, and lean fish.
- Food must be boiled or steamed. Allowed to bake.
During the treatment period, decorative cosmetics should be abandoned. Those products that were used before the start of treatment (both decorative and caring) should be disposed of, since they are already infected with demodex and can no longer be used. Tools for applying makeup: brushes, sponges, etc. should also be thrown away.
To moisturize the skin during the treatment period, it is recommended to use products in bottles with a dispenser or in disposable packaging. Regarding the selection of caring cosmetics, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Demodex does not tolerate high temperatures. Therefore, during treatment, it is necessary to change bed linen daily, and after washing at high temperature, iron it on both sides. It is also recommended to wash pillows and blankets frequently.
The prognosis depends on the severity of the pathology. If therapy is started in a timely manner, complete cure can be achieved. If the disease is advanced, it will be much more difficult to treat, and scars may also remain on the skin.
Prevention of demodicosis
There are no specific preventive measures, but the risk of developing pathology can be significantly reduced. First of all, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system, since, as already mentioned, the disease is dangerous only for people with reduced immunity. To do this, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle: give up bad habits, eat healthy foods rich in vitamins and minerals, sleep at least 7-8 hours a day, and devote time to physical activity.
To avoid becoming infected with demodex from other people, you should never use other people’s things and hygiene items:
- cosmetics;
- towels;
- hygiene products.
It is also necessary to carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene.
Classification
In dermatology, there are several forms of the disease, which are based on the characteristic clinical manifestations of demodicosis:
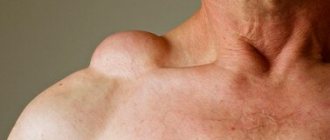
1. Erythematous . It occurs with the formation of areas with pronounced redness (erythema) on the body. Around them, the subcutaneous tissue is pasty and easily injured. Typically, such formations have clear boundaries and are clearly visible on the face, in the area of the nose, eyes, and cheeks. 2. Papular-pustular . It is characterized by the spread of compactions in the form of pimples from 0.5 to 2 mm throughout the body. (papules and pustules), their surface is inflamed and painful, and the color varies from pale pink to dark red or burgundy.
Photo of demodectic lumps on the face
The mechanism for the appearance of these pathological formations is due to the blocking of the sebaceous glands by the bodies of the mites, due to which the normal metabolic processes in the skin are disrupted and there is a continuous process of accumulation of excess sebum in the pores and hair follicles. 3. Hypertrophied . It occurs in advanced demodicosis, with pathological thickening and discoloration of the skin, and disruption of normal nutrition and respiration of the epidermis in these areas. 4. Demodectic mange of the eyelids . It is characterized by the development of inflammation of the edge of the eyelids or conjunctiva of the eyes, blepharitis, the appearance of a bright white stripe at the base of the eyelashes, their thinning and loss. Hypertrophy (thickening of the eyelids) may also develop, then persistent discomfort occurs when blinking and difficulty closing the eyelids during rest and sleep. 5. Demodicosis of the head . It occurs with the formation of small compactions under the hair, which are detected when combing or washing the hair.
BIBLIOGRAPHY _
Akbulatova L.H. The pathogenic role of the Demodex mite and clinical forms of demodicosis in humans. // Bulletin of Dermatology, 1996, 2, pp. 57-61.
Akilov, O.E., Vlasova I.A., Kazantseva S.V., Features of the immune response in patients with dermatoses complicated by severe infestation of anthropophilic mites of the genus // Immunology. 2002. - No. 1. P.43-47
Ambartsum, AM Treating demodicosis / AM Ambartsum // New pharmacy. 2007. -№7. — P.32-35
Beridze, L.R. Changes in immune parameters in primary and secondary demodicosis of the skin // Georg. Med. News. 2004. - No. 6 - P.43-45
Bobrov V.M. Rosacea of the nose, complicated by demodicosis. Bulletin of Dermatology and Venereology 1994; 4:43-44
Butov, Yu.S., Akilov O.E. Clinical features and issues of classification of demodicosis of the skin // Ros. magazine skin and venereal diseases. 2003. - No. 2. — P.53-58
Vartapetov A.Ya. Follicular demodex in skin pathology. // Abstract report at a scientific-practical conference, Moscow Research Institute of Cosmetology of the Ministry of Health of the RSFSR. M., 1972, pp. 38-39
Vasilyeva M.S., Lange A.B. Iron mite populations in perioral dermatitis and rosacea. M: 2006; 135
Vasilyeva M.S., Shif L.V., Vardoyants S.A., Kanbarova L.I. About some clinical manifestations of demodicosis: New cosmetic preparations and treatment of diseases and cosmetic defects. Sat. scientific works of the hospital named after. Y.M.Sverdlova. L 1970; 45-48
Verkhoglyad I.V. Modern antiparasitic therapy of demodicosis // Clinical. dermatology and venereology. 2006. - No. 4. — P.89-90
Vostroknutova T.M. , Mokronosova M.A., Iron mites and problematic facial skin // Attending physician. -2007. No. 9. — pp. 10-12
Zhsltikova, T.M. Is demodicosis a diagnosis or a symptom? // Medical Bulletin. - 2006. - No. 38. — P. 16
Clinical recommendations, Dermatovenereology /edited by A.A. Kubanova// M.: DEX-Press, 2010.-206-209, 230-233
Kogan B.G., Gorgol V.T. Specificity of Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis mites, the causative agents of human demodicosis. // Ukrainian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology, Cosmetology, 2001, 21, pp. 37-41.
Kogan, B.G., Gorgol V.T. Diagnosis of demodicosis // Dermatology. Cosmetology. Sexopathology, - 2008. No. 1-2 (11).- P. 286-287
Koshevenko, Yu.N. Demodicosis pseudo-problem of dermatocosmetology // Ros. magazine skin and venereal diseases. - 2004. - No. 4. — P. 6469
Loshakova, V.I. Demodicosis is an urgent problem of modern dermatocosmetology // Vestn. postgraduate honey. education. — 2001. -№1. - pp. 79-80
Petrosyan E.A., Petrosyan V.A. Treatment of rosacea complicated by demodicosis with blood extracorporeally modified with sodium hypochlorite. Vestn Dermatol 1996;2:42-44.
Polunin G.S., Kasparova E.A., Polunina E.G.: Clinical effectiveness of blepharogels in the prevention and treatment of blepharitis. New in ophthalmology No. 1, 2004, pp. 44-47
Akilov OE, Mumcuoglu KY Immune response in demodicosis. //J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol., 2004, v.18, N4, p.440-444
Aylesworth R., Vance JC Demodex foliculorum and Demodex brevis in cutaneous biopsies. //J.American Academy of Dermatology, 1982, v. 7, n. 5, p. 583-589
Ayres J, Ayres S (1961) Demodecidosis in the human. Arch Dermatol 83:816–27
Bassiouni SO, Ahmed JA, Younis AL, Ismail MA, Saadawi AN, Bassiouni SO A study on Demodex folliculorum mite density and immune response in patients facial dermatoses. // J. Egypt Soc. Parasitol., 2005, v.35, N3, p.899-910
Forton F., Cermaux M.A., Brasser T. Et al. Demadecosis and rosacea: epidermiology and significance in daily dermatologie practice. J Am Acad Dermatol 2005; 1:74-87
Forton F., Seys B. Density of Demodex follicolorum in rosacea: a case-control study using standardized skin-surface biopsy. // British J. of Dermotology, 1993, v.128, p.650-659
Kligman AM, Christensen MS Demodex folliculorum: Requirements for Understanding Its Role in Human Skin Disease. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 2011; 131:8–10
Kogan BG, Stepanenko VI, Gorgol VT, Pavlyshin AV Role of Demodex mites and Helicobacter infection in etiopathogenesis of rosacea, demodicoses, perioral dermatitis and acne disease. Eur Acad Dermatol Venerol 2003; 15(3): 165.
Lacey N, Kavanagh K, Tseng SC. Under the lash: Demodex mites in human diseases. Biochem (Lond). 2009; 31(4): 2-6
Nutting WB Pathogenesis associated with hair follicle mites (Acari: Demodicidae) // Acarologia, 1975, V.17, p.493-507
Rodriguez AE, Ferer C, Alio JL Chronic blepharitis and Demodex. //Arch. Soc. Esp. Oftalmol, 2005, v; 80, N11, p. 635-42
Rufli T., Mumcuogly Y. Tile hair follicle mites Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis: biology and medical importance // Dermatolog., 1981, p.162
Diet
Not only skin care for demodicosis, but also nutritional recommendations that are aimed at reducing sebum secretion will help cope with the manifestations of the disease.
To do this you need:
- exclude, for the duration of therapy, alcohol, confectionery, fatty, smoked, hot, salty, spicy dishes;
- eat food warm, hot food is not recommended;
- limit your intake of sugar, spices and salt;
- quit smoking or reduce the number of cigarettes consumed per day;
- eat more fresh vegetables, berries, fruits, cereals and wholemeal bread (foods rich in fiber, which can remove toxic substances accumulated from the activity of parasites);
- drink and eat fermented milk products, which improve intestinal activity and metabolic processes throughout the body.
A specially selected diet is one of the methods that can help cure chronic forms of demodicosis
How the disease develops
Demodectic mange on the face can develop in several stages. Characteristic symptoms appear as follows:
- The skin on the face turns red. At the same time, the person feels irritation on the skin and heat. At first, the redness is temporary, intensifying in bright sun, after exercise, or drinking hot drinks.
- The redness becomes persistent and permanent. The face is red, especially on the cheeks, chin, nose, and in some cases on the forehead.
- Blood vessels dilate , spider veins appear on the face.
- Papules and pustules develop. These are painful ulcers, acne. They are painful, do not last long, and scars form in their place.
- Rhinophymas appear on the nose - these are compactions, small tumors on the skin. The blood vessels and sebaceous glands become inflamed, the nose enlarges and becomes shapeless. More often, this symptom is characteristic of men with demodicosis on the face.
All this is accompanied by increased sebum secretion or dryness. The skin becomes rough. The person feels burning and itching. There is a tingling sensation on the face and the skin hurts. The face becomes noticeably swollen and swollen due to impaired lymphatic drainage.
Demodicosis of the face is often, but not always, accompanied by demodicosis of the eyelids. Symptoms of eyelid damage include redness, irritation, dryness, and a feeling of a foreign object in the eyes. The eyelids become inflamed and blepharitis appears. Eyelashes stick together and fall out. The eyes are constantly inflamed and tired.