Last update: 02/21/2021
Author of the article: pediatrician Valentina Razheva
One of the effective ways to combat skin diseases is to follow the basics of proper nutrition. We invite you to familiarize yourself with the diet for eczema. Along with medical treatment prescribed by a doctor and physiotherapeutic procedures, adjusted nutrition for eczema can significantly reduce the manifestations of the disease. Thanks to the tips below, as well as a summary table of prohibited and permitted products, it will be much easier for you to avoid exacerbations of the disease and prolong periods of remission.
Hypoallergenic diet for eczema in adults and children: what can you eat?
The list of products allowed for skin diseases should be announced by the doctor, focusing on the intensity of eczema, its nature, symptoms and general health. Each case is individual, so a dish that causes an exacerbation of the disease in one patient may be completely safe for another. However, there are a number of general restrictions that most people suffering from itchy skin, redness and rashes should adhere to.
What should be the diet for eczema on the arms, legs and other parts of the body?
First of all, you need to note the optimal method of preparing food. You'll have to give up fried foods. In some cases, such a refusal may be temporary and come into force only during exacerbations of the disease. However, the patient will significantly improve his health if he eliminates fried foods altogether. As an alternative, you can eat baked foods, and in some cases, grilled ones (however, this aspect should definitely be discussed with your doctor).
It is recommended to boil or steam dishes that are included in the diet menu for eczema. As for fresh vegetables and fruits, in most cases they are consumed raw (the exception may be apples and pears - they are often baked). Vegetable and fruit juices should not contain sugar or preservatives. If the juices are concentrated, it is better to dilute them with water.
In most cases, exacerbation of eczema is caused by protein foods, dishes high in starch and sugar, as well as vegetables, berries and fruits of red, black, yellow and orange. However, since the diet must be balanced and complete, you cannot blindly give up all types of protein foods and sweets in order to completely switch to safe plant-based foods. That is why it is not recommended to create your own diet: this should be done by a qualified allergist, dermatologist or nutritionist. At the same time, the patient himself must be sufficiently familiar with permitted and prohibited products in order to find an appropriate replacement for potentially dangerous dishes.
What foods are suitable for creating a diet menu for eczema, and which ones should you avoid? You will find the answer in the table:
| Most allergenic foods | Products of medium and low allergenicity |
| Cow's milk protein and products prepared from it. | Ghee, dairy products. |
| Citrus. | Bananas. |
| Caviar, shrimp, shellfish, lobster, red fish, squid. | River fish. |
| Cocoa, coffee, chocolate, nuts. | Dried fruits. |
| Cakes, pastries, muffins with rich cream, chips. | Rough bread. |
| Chicken eggs. | Vegetable oils. |
| Fatty pork, duck, goose, smoked meat. | Lamb, horse meat, beef, rabbit. |
| Wheat and gluten. | Rice, oats, peas, unroasted buckwheat. |
| Some spices. | |
| Tomatoes and other brightly colored vegetables. | Cabbage, zucchini, green bell pepper, potatoes. |
| Red fruits and berries. | Rose hips, cherries, pears, green and white apples, gooseberries, white currants. |
Despite the fact that the list of prohibited foods is quite extensive, you can find a more suitable alternative to a dangerous product. Nutrition for dry and weeping eczema can be varied through the following substitutions:
| Potentially Hazardous Products | Safe Alternative |
| Milk, cheese, cottage cheese and other products based on milk. | Coconut and rice milk can be consumed occasionally. In addition, consume low-fat fermented milk: in most cases, bifidobacteria contained in lactic acid products have a positive effect on the condition of the intestines, and therefore damaged skin. |
Alternative Foods for Eczema: Almond Milk
| Red apples. | Green and white varieties of apples (Semerenko, Antonovka). |
| Wheat flour products (with gluten). | Gluten-free products (crackers, cookies, pasta), whole grain breads and crisps. |
| Sweets (chocolate, candies, cakes). | Carob, dried fruits. When choosing dried fruits, pay attention to the method of processing: a quality product should be obtained naturally (drying in the sun or in the shade), and not by processing with chemical compounds. |
| Fatty meat (pork, duck). | Lean varieties of beef, horse meat, rabbit and turkey. You need to be careful with chicken meat: in rare cases, it can cause an exacerbation of the symptoms of the disease. In such cases, it is recommended to abandon it completely or consume it occasionally (and only the dietary part - the breast). You can also eat specialized canned food for children (pureeed meat). |
| Meat broths. | Vegetable broths. |
| Seafood. | In some cases, you can replace sea fish with lean river fish. |
| Carbonated drinks with dyes. | Rose hip decoction. |
| Tomatoes, spinach, red bell pepper, beets. | All varieties of cabbage, except red cabbage (Savoy, Peking, white cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower), zucchini, squash, asparagus, young green peas. |
| Butter, margarine, lard. | Vegetable oils (olive, sunflower, rapeseed). |
| Artificial (chemical) food additives. | In very small quantities: black pepper, ginger, curry. |
In conclusion
In addition to the course of action prescribed by your dermatologist, you can add another valuable component to your treatment regimen by adding an eczema-friendly diet to reduce the frequency and intensity of flare-ups.
An eczema-friendly diet is similar to the Mediterranean diet in that it focuses on fruits and vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts and fatty fish. Make sure you drink plenty of water every day to keep your skin hydrated and your body balanced.
Summarize and exclude those foods that cause aggravation. Include foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, flavonoids, vitamins C, D and E, and the minerals selenium and zinc. These foods can support a healthy immune system and skin barrier, and are effective in reducing inflammation.
Diet for eczema on hands
In addition to aesthetic disadvantages, eczema on the hands causes a number of inconveniences to a person while performing everyday household duties - cooking, laundry, washing dishes. The diet for eczema of the hands, palms and areas of skin between the fingers must be strictly followed if you want to cope with the disease.
Sources
- Carrasco P., Estarlich M., Iñiguez C., Ferrero A., Murcia M., Esplugues A., Vioque J., Marina LS., Zabaleta C., Iriarte G., Fernández-Somoano A., Tardon A., Vrijheid M., Sunyer J., Ballester F., Llop S. Pre and postnatal exposure to mercury and respiratory health in preschool children from the Spanish INMA Birth Cohort Study. // Sci Total Environ - 2021 - Vol782 - NNULL - p.146654; PMID:33838378
- Zarini GG., Masters J., McLean MA., Strobel CT. Clinical and Anthropometric Improvements with a Tailored Dietary Approach in Pediatric Crohn's Disease. // Altern Ther Health Med - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33711815
- Logan CD., Norton SA. At the dinner table with Adam and Eve. // Pediatr Dermatol - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33656169
- Trikamjee T., Comberiati P., D'Auria E., Peroni D., Zuccotti G.V. Nutritional Factors in the Prevention of Atopic Dermatitis in Children. // Front Pediatr - 2021 - Vol8 - NNULL - p.577413; PMID:33585361
- No authors found Correction: Ethnic differences in maternal diet in pregnancy and infant eczema. // PLoS One - 2021 - Vol16 - N1 - p.e0246481; PMID:33508000
- Ogawa K., Pak K., Yamamoto-Hanada K., Ishitsuka K., Sasaki H., Mezawa H., Saito-Abe M., Sato M., Yang L., Nishizato M., Konishi M., Sago H ., Ohya Y. Association between maternal vegetable intake during pregnancy and allergy in offspring: Japan Environment and Children's Study. // PLoS One - 2021 - Vol16 - N1 - p.e0245782; PMID:33507986
- Ross AB., Barman M., Hartvigsson O., Lundell AC., Savolainen O., Hesselmar B., Wold AE., Sandberg AS. Umbilical cord blood metabolome differs in relation to delivery mode, birth order and sex, maternal diet and possibly future allergy development in rural children. // PLoS One - 2021 - Vol16 - N1 - p.e0242978; PMID:33493154
- Ballart M.J., Monrroy H., Iruretagoyena M., Parada A., Torres J., Espino A. . // Rev Med Chil - 2021 - Vol148 - N6 - p.831-841; PMID:33480383
- Tanaka K., Okubo H., Sasaki S., Arakawa M., Miyake Y. Maternal caffeine intake during pregnancy and risk of food allergy in young Japanese children. // J Paediatr Child Health - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33464698
- Chan CWH., Leung TF., Choi KC., Tsui SKW., Wong CL., Chow KM., Chan JYW. Association of early-life gut microbiome and lifestyle factors in the development of eczema in Hong Kong infants. // Exp Dermatol - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33433023
Diet for eczema: menu for one day
One of the main requirements in relation to nutrition (diet) for eczema is to eat small portions, but often. There should be 4-5 meals a day: breakfast, lunch, dinner, afternoon snack (optional) and dinner. Below is a sample menu for the day:
| Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner |
| Oatmeal cooked in water. Weak tea. | Fruits from the list of permitted. | Soup with vegetable or beef broth. Vegetable stew. | Homemade yogurt or low-fat kefir. | Salad of permitted vegetables with vegetable oil. Steamed turkey cutlet. |
The dishes proposed above can be replaced with others at your discretion: the main thing is that they are prepared from permitted products. Also, remember to consume the required amount of fluid. It can be clean water, still mineral water, weak tea.
Disease triggers
Researchers believe that eczema is the result of an interaction between an overactive immune system and certain triggers. One of these triggers has been identified as food, so following an eczema-friendly diet may play a role in treating symptoms.
Eating certain foods does not cause eczema, but instead causes a flare-up if you already have the condition. It is also important to note that you may have food sensitivities or food allergies. Food sensitivities are triggered by the digestive system, which is triggered by the immune system.
Identifying foods that cause symptoms can be challenging and is often a process of eliminating and reintroducing those foods into your diet, one food at a time.
Removing known food triggers from your diet may not completely eliminate flare-ups, but it will reduce them.
What remedies help with eczema besides diet?
Proper nutrition is an important component of the treatment and prevention of the disease. However, treatment should consist not only of observing a number of rules and restrictions regarding food, but also of using emollients for damaged areas of the skin. La Cree products are excellent for this purpose.
Intensive cream "La-Cri" is well suited for dry eczema, accompanied by severe itching and flaking of the skin. The product contains natural ingredients: violet and licorice extracts, wheat germ oils, jojoba and shea butter, lecithin, bisabolol and allantoin.
Eczema - symptoms and treatment
During the course of the disease the following stages :
- Erythematous - skin redness, swelling and itching appear.
- Papular - red papules (nodules) form.
- Vesicular - grouped bubbles with liquid appear, reminiscent of air bubbles when water boils.
- Weeping - the covers of the bubbles open and weeping and erosion are formed.
- Cortical - areas of weeping dry out and become covered with crusts.
- Peeling – exfoliation of crusts and restoration of the skin surface [2].
As eczema enters the chronic stage, the skin undergoes changes: it becomes rougher and drier, as a result, it flakes and pigmentation appears.
Forms of eczema depending on the clinical picture and causes of occurrence [5]:
- true;
- seborrheic;
- microbial;
- nummular;
- mycotic;
- intertriginous;
- varicose;
- sycosiform;
- nipple eczema;
- children's;
- professional.
True eczema
True eczema most often affects the face and limbs. Areas of healthy and affected skin alternate. Other areas may be involved in the process, including erythroderma (generalization of the inflammatory reaction and fever). The process is usually symmetrical. In the acute stage, the disease manifests itself in the form of blisters (vesicles), redness of the skin, erosions with weeping, crusts, excoriations (mechanical damage to the skin when scratching), there may be papules and pustules. Eczematous lesions have uneven boundaries. When the disease enters the chronic stage, redness becomes stagnant, areas of cracks and lichenification (thickening of the skin with increased skin pattern as a result of prolonged scratching) appear, the skin becomes rough and dry. Often the process is complicated by the appearance of ulcers caused by the addition of an infection: beta-hemolytic streptococcus or Staphylococcus aureus [1].
Monetoid (nummular) eczema
Nummular eczema occurs mainly in adults. Men get sick more often than women. The highest incidence occurs between 50 and 65 years of age, in both sexes. In women, the first peak occurs between the ages of 15 and 25, when puberty passes and the woman reaches adult height and weight. But in children, nummular eczema is extremely rare. The lesions are often located in the elbows and behind the knees, with the arms being affected more often than the legs.
The pathogenesis of the disease is still unclear. In some patients, foci of chronic infection are detected, including in the oral cavity and respiratory tract. Allergens, such as house dust mites, play an important role in the development of nummular eczema. With the disease, clearly defined coin-shaped plaques of papules and vesicles appear. Characteristic signs include pinpoint weeping and crusting. Crusts can cover the entire area of the plaque, the diameter of which varies from 1 to 3 cm. Itching can be either minimal or severe. In ring-shaped forms of the disease, the manifestation decreases in the central part. Chronic plaques become dry, flaky, and the skin thickens.
Microbial eczema
Microbial eczema is a polyetiological disease. In the pathogenesis of microbial eczema, the skin barrier plays an important role, because one of its main functions is protection. Itching provokes scratching of the skin, damaging the integrity of the skin, and this, in turn, forms an entry point for infection. Exudation (the release of the liquid part of the blood into the inflamed tissue through the vascular wall) creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of microbes.
An important component of pathogenesis is the skin microbiota. In scrapings from the affected skin of patients with microbial eczema, Staphylococcus aureus and hemolytic staphylococcus, yeast fungi, mainly of the genus Candida, are found. Microbial eczema can also be caused by external physical or mechanical irritants. Often, foci of microbial eczema appear around purulent wounds and in places of long-term pyoderma (a purulent skin disease resulting from the penetration of bacteria).
In microbial eczema, the lesions are round or irregular in shape, with clear boundaries, located asymmetrically and limited by a border of exfoliating epidermis. In the center of the lesions, purulent and serous crusts can be seen; after their removal, weeping, reminiscent of “wells,” is discovered. The rash is characterized by intense itching [2].
Seborrheic eczema
Inflammation begins on the scalp and is localized in areas of the skin with the largest number of sebaceous glands. In this way, seborrheic eczema is similar to seborrheic dermatitis. The lesions are localized behind the ears, on the chest, neck, between the shoulder blades, and on the flexor surface of the limbs. The skin within the lesion is hyperemic, edematous, on its surface there are small yellowish-pink papules and greasy yellowish scales and crusts [2].
Varicose eczema
Varicose eczema, as the name suggests, occurs when the patient has varicose veins. The skin of the legs next to varicose ulcers is predominantly affected. The development of this type of eczema is caused by irrational and untimely treatment of varicose ulcers, skin maceration (wrinkling of the skin during prolonged contact with water), and trauma. Varicose eczema causes severe itching. Differential diagnosis, first of all, must be made with myxedema and erysipelas [3].
Sycozyform eczema
The disease occurs against the background of vulgar sycosis - inflammation of the hair follicles as a result of the penetration of staphylococci into them. The pathological process can go beyond the boundaries of hair growth; as a rule, lesions can be found on the upper lip, armpits, chin and pubis. Clinically, sycosiform eczema is manifested by serous wells, severe itching and weeping, and later areas of skin thickening appear [2].
Childhood eczema
The first symptoms can be noticed at the age of 3-6 months. Eczematous areas are symmetrical, the skin within the lesions is brightly hyperemic, swollen, hot to the touch, has a shiny smooth surface, there is weeping, layering and milky crusts. Eczema primarily affects the cheeks, forehead, scalp, ears, buttocks and extremities (usually extensor surfaces). It is characteristic that eczema does not affect the skin of the nasolabial triangle. When sick, children complain of itching and insomnia. Eczema often transforms into atopic dermatitis[5][10].
Eczema of the nipples
Skin breakdown occurs after nipple trauma during breastfeeding. Externally, eczema manifests itself as slight redness, weeping, crusts of blood collections, and in some cases pustules and cracks, usually without hardening of the nipples. As a rule, the eczematous process spreads to both breasts [5].
Occupational eczema
Occurs under the influence of various industrial allergens. The disease can be caused by mercury, various metal alloys, penicillin and semi-synthetic antibiotics, resins and synthetic adhesives. Occupational eczema is more common among workers in various industries, people who deal with various chemicals (chemists and biologists), as well as those whose work involves constantly immersing their hands in water (for example, cleaners and orderlies). Under the influence of allergens, a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction develops. Clinically, occupational eczema occurs like ordinary eczema. The lesions are located mainly in the area of contact with allergens and on open areas of the skin. Occupational eczema is characterized by rapid recovery when the cause disappears [6].
Paratraumatic eczema
Occurs in the area of postoperative scars or with incorrectly applied plaster casts. Manifests itself in the form of acute inflammatory erythema (redness), pustules or papules, and crusting. Hemosiderin, a yellow pigment formed during the breakdown of hemoglobin, can be deposited in the affected tissues [5].
Clinical researches
Conducted clinical studies prove the high efficiency, safety and tolerability of the products. The cream for sensitive skin is suitable for daily care of adult and children's skin with mild to moderate forms of atopic dermatitis and during remission. As a result of therapy, a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process, a decrease in dryness, itching and flaking was noted.
Many remedies are recommended by the Union of Pediatricians of Russia.
Sources:
- Ratner Desiri, Avram M.R., Avram M.M., Procedures in Dermatology. Clinical cosmetology, GEOTAR-Media, 2021.
- Sukolin Gennady Ivanovich, Clinical dermatology. A short guide to the diagnosis and treatment of dermatoses, Notabene, 2017.
- Sukolin Gennady Ivanovich, Illustrated clinical dermatology. Brief alphabetical reference book, Lux Print publishing house, 2010.
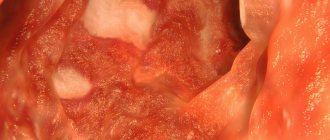
Photos of eczema
Photo album on the diseaseDiagnosis of microbial eczema
Due to the lack of obvious symptoms, diagnosing microbial eczema can be somewhat difficult, but qualified dermatologists can handle it without problems.
First of all, the doctor pays attention to provoking factors, such as varicose veins, previous injuries or fungal diseases. To clarify the result, some tests may be required, first of all, bacterial culture from the erosion surface
Difficulties may also arise with the treatment of this disease. It rarely heals spontaneously, but has a tendency to relapse, returning after suffering stress or illness. Therefore, in each case, the dermatologist develops an individual treatment regimen:
- Treatment of the lesion with antiseptic, anti-inflammatory solutions and ointments.
- General strengthening of the body, improvement of immunity, vitamin therapy.
- Treatment of the underlying disease and elimination of provoking factors.
- Allergen-free gentle diet, antihistamine therapy.
- Physiotherapy and spa treatment.
In most cases, correctly selected therapy and timely treatment can help get rid of microbial eczema for a long time and prevent its reappearance.
Is microbial eczema contagious?
This type of bacterial disease cannot be transmitted by shaking hands or kissing. This disease is not considered one hundred percent contagious. It can occur in the body of a healthy person only with the simultaneous occurrence of infections of a bacterial or fungal nature.
| Appointment with a dermatologist at the clinic. Call a dermatologist at home. | Reception is strictly by appointment, make an appointment by phone: +7 | Prices for services | Reviews about the clinic |
Types of microbial eczema
In medicine, five types of microbial eczema are defined:
- Coin-shaped or plaque-shaped;
- Varicose;
- Sycosiform;
- Post-traumatic;
- Nipple.
In the first type of disease, small round plaques appear in the area of the upper extremities. The boundaries of the inflammation focus are clear. The patient feels a strong blood flow. Swelling and purulent formations appear on the surface of the skin.
The second type is accompanied by varicose veins or venous insufficiency. Swelling appears around the formed ulcer. The body is itchy and itchy, especially at the end of the day. In the third form, the follicles become inflamed. On the body you can see weeping spots of a bright red hue. Lesions are most often found in the chin area and on the lip.
If the healing process of a wound after surgery or an abrasion is disrupted, then the fourth form of the disease occurs. The latter type is most common in women. The nipples become inflamed and itchy. The lesion becomes wet, its boundaries are clearly defined. The disease is very painful.
Common symptoms and manipulations in dermatology:
- Skin rashes
- Calling a dermatologist to your home
- Itching in the urethra
- Itchy skin
- Skin rash
- Prevention of casual sex
- Skin neoplasms
- Pyoderma
- Pityriasis rosea
- Streptoderma
- Scabies
- Peeling skin
- Fungal infections
- Skin infection
- Pus on the skin
- Blisters on the skin
- Papillomas on the foreskin
- Sexually transmitted diseases
- Skin structure