In this article we will tell you:
- Barley classification
- External stye
- Symptoms of external styes
- Internal stye
- Symptoms of internal stye
- Causes of stye on the eye
- How to treat stye on the eye
- How not to treat stye
- Prevention of eye stye
When the immune system is weakened, the opportunistic flora, which has peacefully existed for years on the surface of the skin, mucous membranes or inside the human body, is activated and can lead to various diseases. Among them is barley - or, scientifically, hordeolum: a condition familiar to many, which in more than 90% of cases is caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
The bacterial pathogen is not the only culprit of the disease. The appearance of stye can be caused by a fungus or the microscopic parasitic mite demodex, which likes to settle in or near the hair follicles.
According to statistics, most often barley is diagnosed in the age range from 20 to 50 years, but its manifestations are also common in childhood. The pathology manifested itself at least once in 90 people out of 1000.
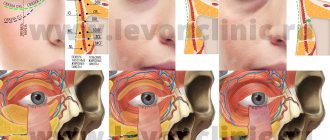
Barley - (lat. hordeolum) - an acute inflammatory process affecting - depending on the location - one or more ciliary follicles or glands of the cartilage of the eyelids.
Barley classification
Typically, barley in adults and children is divided into external and internal - according to the location of the inflammatory process.
External stye
External stye occurs much more often than its internal “brother”. The location is the outer, visible surface of the eyelid.
External stye occurs due to infection of the eyelash follicles or glands that are located at the edge of the eyelids. It usually affects the Zeiss gland and the Moll gland. Zeiss' sebaceous glands are located in pairs around each follicle, into which they secrete their secretion. Moll's sweat glands are located there; their function is still not fully understood.
With external styes, an abscess with a white abscess on the top forms on the outside of the upper or lower eyelid. Over time, the abscess matures and opens. After this, tissue regeneration begins: most often, within a few days, not a trace of inflammation remains.
Symptoms of external styes
Usually the disease has a mild onset: a person may not even notice that a health problem has arisen. The primary symptoms of stye on the eye include:
- hyperemia of the eyelid;
- swelling;
- pain, tingling in the affected area;
- lacrimation;
After 2-4 days, the infiltrate bursts and the purulent contents come out. After this, the pain subsides and the healing process begins.
The symptoms of stye on the upper eyelid are no different from stye on the lower eyelid.
Internal stye
As for the internal styes, the zone of its destruction is the lobules of the meibomian glands located in the cartilaginous plate of the eyelid. These glands are named after Professor Meibom, who discovered them, and they belong to the sebaceous group. Their secretion is involved in the formation of the lipid layer of the tear film that lines the surface of the eyeball and the inside of the eyelids.
Symptoms of internal stye
The initial symptoms of internal and external stye are similar: the patient is plagued by pain, swelling, increased lacrimation, and a sensation of a foreign body. On the inside of the eyelid you can notice a hyperemic area with a yellowish center. Internal stye is usually more painful than external stye, and it takes longer to ripen.
The ripened internal barley opens into the conjunctival sac. If the course of the disease is unfavorable, a chalazion may form at the site of the stye - a chronic inflammation of the cartilage and gland, in which the gland duct is clogged and the secretion cannot come out. A chalazion looks like a dense, hyperemic ball the size of a millet grain to a pea. This condition requires mandatory treatment under the supervision of an ophthalmologist.
In rare cases, the formation of stye - both internal and external - may be accompanied by general malaise, fever, aching joints, muscle and headache, and enlarged lymph nodes located next to the affected eye. Typically, such a reaction of the body indicates a complicated course of the disease. Consult a doctor: you may need more serious treatment for stye or additional diagnostics.
Diagnosis and treatment
To quickly and effectively treat the disease, you should seek medical help as soon as possible. Before choosing the appropriate therapy, the ophthalmologist at the First Clinic Orekhovo will prescribe tests to determine the nature of the inflammation and the sensitivity of pathogenic bacteria to antibiotics. Based on the results of laboratory tests, a treatment plan is drawn up, which includes not only the use of antibacterial drugs, but also the external use of appropriate drops and gels.
Will it go away on its own?
In many cases, the abscess goes away on its own and does not require special treatment, but you should not neglect visiting a specialist. The doctor will give the necessary recommendations and ensure that the recovery process proceeds safely and quickly. However, it happens that over time the barley remains intact and the abscess does not open. Such inflammation on the eyelid can persist for more than one month and can often be eliminated only through surgery.
Causes of stye on the eye
The reasons leading to the occurrence of the disease include:
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- using someone else’s or expired cosmetics, dirty brushes and applicators;
- untreated demodex;
- long stay in a dusty, dirty room;
- lack of vitamins;
- colds, hypothermia, decreased immunity;
- constant stress;
- diabetes;
- obesity.
Stages of development of stye on the eye
Possible complications
Incorrect or untimely treatment can lead to serious complications:
- Sepsis is a very serious complication that requires immediate hospitalization. It can occur due to chronic stye or as a result of pus getting inside the eye. Symptoms of sepsis are fever, weakness, and severe headache.
- Meningitis is a deadly disease in which the lining of the brain or spinal cord becomes inflamed. It can develop if an infection gets inside the eye socket, which the blood spreads throughout the body.
- Multiple abscesses occur when infection affects adjacent tissue. Often the cause of this complication is low immunity or improper therapy.
- A chalazion is a thickened tumor-type formation that is formed as a result of blockage of the sebaceous gland. If the stye is not treated at an early stage, there is a risk that it will turn into such a dense “nodule” that can only be removed surgically.
- Phlegmon of the eye is a purulent inflammation of fatty tissue and occurs when the infection spreads to the eye orbit. This complication negatively affects vision, and in the most severe cases can lead to irreversible damage to the optic nerve and loss of the eye.
- Chronic infection manifests itself as constant relapses of the disease and can occur against the background of reduced immunity, ARVI. As a rule, it is a consequence of untreated primary barley.
If you value your health and do not want to lead to complications, then you need to visit a doctor at the first signs of illness. And it is important to remember that under no circumstances should you try to open the abscess yourself. This is fraught with the entry of pus into the bloodstream and subsequent sepsis, even death.
How to treat stye on the eye
Typically, barley ripens and opens on its own within a week. A disease without complications does not require medical intervention. To quickly get rid of the disease, you can resort to warming compresses: apply a towel soaked in warm water or a heated towel to the inflamed area 3-4 times a day. Compresses with aloe juice, a decoction of St. John's wort, and chamomile can also help. In addition, careful hygiene of the eyelids is important: if the discharge increases, you should clean the eyes of crusts and pus using sterile wipes and boiled water.
If there is severe pain, general malaise, or suspicion that the disease has become complicated, it is better to consult a specialist. The doctor may prescribe:
- a course of antibiotics (for the treatment of chalazion, phlegmon, or in case of frequent occurrence and severe course of the disease;
- local anesthetics, antiseptics, glucocorticoids;
- ultra-high frequency therapy;
- removal of the eyelash around which barley has formed;
- surgical removal of barley under local anesthesia. If the inflammation is too severe and treatment is ineffective, the surgeon will open the abscess and clean it of accumulated pus.
Folk remedies: effective or dangerous?
Many patients do not take a disease such as stye seriously and do not consider it necessary to consult a doctor. These people prefer to be treated with traditional methods, of which there are a huge number. What are these methods and how safe are they?
A popular method of folk treatment is to apply an alcohol compress, for example, a piece of cotton wool soaked in vodka, to the reddened area. It is believed that this method will help warm the barley and speed up its ripening. However, doctors categorically do not recommend resorting to this method, because alcohol can leave a serious burn not only on the eyelid, but also on the mucous membrane of the eye. Other warming options using a boiled egg or warm flaxseed should also not be used without consulting an ophthalmologist. If heating is applied during a purulent process, this can lead to serious complications. Other popular methods of folk treatment are various lotions based on herbal infusions. To get rid of barley, traditional healers recommend using herbs with anti-inflammatory, wound-healing, antimicrobial effects (plantain, aloe, calendula, etc.). At best, such pseudo-treatment will be ineffective; at worst, it can cause an allergic reaction, damage the mucous membranes of the eyes, and provoke complications of the disease.
On the Internet you can find completely ridiculous advice on treating barley. For example, tie your fingers with red woolen thread in the shape of a figure eight and swallow tansy flowers. Apply garlic to your eyelids or rub them with a gold chain that you wear. Such advice has nothing to do with adequate treatment of barley. The only correct answer to the question of what to do when barley appears is this: immediately go to see an ophthalmologist, who will prescribe an effective and safe treatment that can help you as soon as possible. Hoping to cure stye using traditional methods, you are wasting precious time and can cause yourself even more harm.
Prevention of eye stye
Prevention of the disease consists of simple rules, the main one of which is hygiene. Not worth it:
- leave makeup on eyelashes and eyelids overnight;
- rub your eyes, comb them;
- use someone else's brushes to apply makeup;
- overwork, hypothermia;
- neglect the rules of wearing and caring for contact lenses.
By following these recommendations, you will not protect yourself from the appearance of barley 100%, but you will significantly reduce the likelihood of its occurrence.
Risk factors
Barley appears in people of different ages and lifestyles. But there are factors contributing to the development of pathology:
- Reduced immunity. In this case, eye stye may be multiple.
- Oily skin.
- Diabetes.
- Adolescence is usually caused not by hormonal changes, but by the lack of proper hygiene, lack of vitamins and fresh air.
- Chronic eye diseases: blepharitis (inflammation of the edge of the eyelids), conjunctivitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane).
- Prolonged or frequent exposure to low temperatures, severe hypothermia.
- Diseases and pathologies of the endocrine system.
- Chronic diseases of the digestive system.
- Allergic reactions.
- Impaired metabolism.
- Avitaminosis.
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules.
- Injuries to the eyelid, including from ordinary scratching.
- Cheap or simply low-quality cosmetics, the use of dirty cosmetic tools.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions.
An internal stye or an external stye can develop due to one of these reasons or a combination of them.
Symptoms
The first signs of stye include itching, burning and swelling of the edge of the eyelid. Then additional symptoms develop:
- Redness of the skin of the eyelid;
- Edema;
- Pain;
- Formation of an abscess;
- Redness of the sclera;
- Tearing.
General health, as a rule, does not suffer, that is, the person feels the same as usual, only noticeable discomfort occurs in the area of the affected eye. However, with a severe course of the process, an increase in temperature and a general deterioration in well-being are possible.