Traumatologist-orthopedist
Shelepov
Alexander Sergeevich
12 years of experience
Doctor
Make an appointment
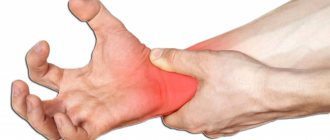
An accumulation of clots or liquid blood in the soft tissues of the body, formed due to rupture of blood vessels, is called a hematoma. The most common type of pathology is an ordinary bruise. However, this concept includes much more severe and complex cases that cannot be left without qualified medical care. Blood flowing from the vessel irritates the tissues surrounding it, resulting in pain, tissue swelling and other signs of developing inflammation. In addition, the hematoma compresses the tissues or organs located next to it, which can lead to the development of complications.
Causes
Hemorrhage usually occurs after injury. This could be a bruise of the skin, internal organs, a concussion or bruise of the brain, an injection with thin (sharp) objects. Sometimes blood leaves the vessels and pours into the skin and internal organs as a result of infections, autoimmune diseases, and poisoning. The occurrence of hemorrhages and bruises is promoted by increased fragility of blood vessels, fasting, lack of vitamins in food, high blood pressure, and congenital bleeding disorders.
At CELT you can get a consultation with a traumatologist-orthopedic specialist.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
Pathogenesis
The provoking factor may be damage to the vascular wall as a result of a bruise, incomplete cessation of bleeding, disruption of the thrombus formation process, which leads to the outflow of blood from the vessels into the surrounding soft tissue and the formation of a cavity (hematoma). Bleeding from a hematoma in most cases stops on its own, which is caused by an increase in blood pressure in the cavity of the resulting hematoma, which exceeds the pressure in the damaged vessel and mechanical compression of the lumen of the bleeding vessel by loose fiber infiltrated with blood, and the resulting clots of coagulating blood quickly close the wall of the damaged vessel. At the same time, under the influence of tissue thrombokinase, some of the blood in the hematoma cavity also coagulates. Bleeding stops especially quickly in cases of venous hematomas.
Resorption of the hematoma occurs in stages. The resulting blood clots gradually become dense and decrease in volume due to the reabsorption of blood serum. Dead leukocytes, disintegrating, release various proteolytic enzymes, which soften and dilute the fibrin of the blood clot and destroy the red blood cells contained in it. Then the red blood cells become discolored and they disintegrate into lumps and grains, which, together with other products of cellular decay, undergo a process of phagocytosis by the structures of the reticuloendothelial system, which proliferate in the circumference of the hematoma.
Hemoglobin from erythrocytes gradually dissolves in tissue fluid and gradually turns into methemoglobin , which gradually transforms into verdohemoglobin (green) and, when disintegrating, turns into hemosiderin (yellow pigment), which is visually manifested by a change in tissue color, which is especially pronounced on non-pigmented skin with a superficial hematoma ( the so-called “bruise bloom”).
Color palette of superficial hematoma at different stages of the healing cycle
Initially, the superficial hematoma becomes red in color as oxygen-rich blood accumulates under the skin. After 1-2 days, the blood, gradually losing hemoglobin, changes color to blue-violet. After 5-10 days, the color of the skin changes to yellow or green, this is due to biliverdin / bilirubin , which are formed during the breakdown of hemoglobin . After 10-14 days, the color of the skin over the hematoma will acquire a light brown tint and begin to disappear. The whole process takes about 15 days.
The vast majority of hemoglobin is secreted by the liver and kidneys. Normally, the bulk of the blood in the hematoma is absorbed back during the coagulation process, enhanced regeneration of connective tissue cells occurs and the hematoma cavity is gradually filled with newly formed connective tissue.
In cases of insufficient absorption of blood accumulated in the hematoma, the process of fibrin formation intensifies, which leads to fibrous degeneration, hyalinization of the hematoma wall, compaction of the newly formed tissue and its adhesion to surrounding tissues, ultimately forming an encysted hematoma. an abscess / cellulitis may develop .
Symptoms
A bruise on the skin is always clearly visible. At first it has a purplish-blue color, and then begins to “bloom”, acquiring yellow and green colors. If a sufficiently large amount of blood accumulates under the skin, a protruding lump forms. At first it is very painful to feel, but later the pain goes away.
The outpouring of blood into the internal organs and into the substance of the brain is preceded by trauma. The main symptom is pain. In this case, the hematoma is not visible externally. If bleeding continues, the victim becomes pale, weak, and dizzy. With chronic internal bleeding, anemia comes to the fore. Bleeding in the brain is especially dangerous. Compression of brain structures may occur, sometimes leading to death.
General information
Hematoma is a post-traumatic hemorrhage in a limited volume into soft tissue with the formation of a cavity filled with blood.
Habitual hemorrhages in the upper layers of soft tissues are often called “bruises” in everyday vocabulary, which is due to the bluish-purple color of the skin at the sites of hemorrhage. Most often, a bruise is a consequence of the rupture of several small capillaries resulting from a bruise. By bruise we mean injury to various soft tissues (skin, subcutaneous fat, muscle tissue and blood vessels) without violating the integrity of the skin. Most often, a hematoma is one of the clinical signs of a bruise resulting from domestic trauma. In most cases, hematomas go away on their own within 10-15 days and no medical help is required. With more extensive and deep hematomas (subfascial, intermuscular, subperiosteal), the function of the limb may suffer and their appearance may be accompanied by pain and swelling, which requires consultation with a traumatologist, and in cases of infection and suppuration of the hematoma, surgical treatment.
Hematomas appear especially often in children. In most cases, bruises on a child’s legs appear due to increased physical activity and frequent trauma to soft tissues. Much less often, bruises in a child are a manifestation of pathology. Also, frequent hematomas are typical for athletes due to high physical activity and for elderly people, the walls of blood vessels in which lose their elasticity and the connective tissue becomes thinner. In addition, even insufficient intake of vitamins C , D , and K .
Predisposing factors
The formation of hematomas occurs after injuries, including pinching, blows, squeezing, and bruises. Subarachnoid hemorrhage does not fall into this category, since it does not appear due to trauma, but due to damage to an unchanged vessel. Often small hematomas appear due to eating large quantities of food or drinking alcoholic beverages. This is due to stretching of the gastrointestinal tract and the appearance of cracks.
The development of pathology is influenced by vascular weakness and problems with blood clotting. Often due to a weakened immune system due to infections or age-related changes, the likelihood of pus accumulating in the affected area increases.
First aid for injury
If you bruise your leg with subsequent formation of a hematoma, you must do the following:
- during the first 15-20 minutes. after injuring an area of a limb, it is advisable to cool the damaged area, ideally with an ice compress or a special medical cold pack intended for use for bruises (if there is no damage to the integrity of the skin);
- if there is no tendency to allergic reactions, apply a thin layer to the bruised area with medical products containing heparin;
- limit the load placed on the injured leg by fixing it in a comfortable position for a while.
Qualified specialists do not recommend using anti-inflammatory absorbable ointments and gels earlier than 3 days from the moment of injury, due to the warming effect they have.
If there is an open wound, it is advisable to immediately show the leg to a doctor who can not only identify the presence of a real danger to the victim, but also provide assistance directly in stopping the bleeding.
Classification of hematomas
In modern medicine, when classifying hematomas, the following are taken into account:
- Relation to the vessel - pulsating and non-pulsating hematomas.
- Localization - in the cranial cavity, internal organs, under the skin or mucous membrane.
- The state of the blood in the affected area is suppurated, clotted, fresh, infected.
- Symptoms – limited, encysted, diffuse.
There are hematomas that do not fall into this classification. For example, intracerebral, intracranial, intraventricular. They are of the epidural or subdural type and cause serious complications.
List of sources
- Urakov A.L. DIAGNOSTICS OF SOFT TISSUE DAMAGE DURING BLEEDING//Advances of modern natural science. – 2015. – No. 1-6. – pp. 951-957.
- Gumanenko E.K. Military field surgery. 2nd ed., rev. and additional 2012. - 768 p.: ill.
- Kornilov N.V. Traumatology and orthopedics: textbook. Ed. N.V. Kornilova. — 3rd ed., add. and p First Aid: Textbook/Under the general editorship of Doctor of Medical Sciences. Professor Vartanyan F.E. – M.: Russian Society of the Red Cross, 1997, – 215 p. reworked - 2011. - 592 p.: ill.
Soft tissue hematomas
Soft tissue hematomas are divided into 3 types:
- Lungs - appear 24 hours after injury and are accompanied by mild pain. No special treatment is required.
- Medium - appear within 5-6 hours and are accompanied by pain and swelling. The motor function of the limb deteriorates. Consultation with a traumatologist is required.
- Heavy - formed within 2 hours after tissue damage. The function of the limb is impaired, acute pain and diffuse swelling are observed. You should immediately consult a doctor to determine a treatment strategy.
Immediately after the injury, swelling appears, and the skin acquires a purplish-bluish tint. After 5 days, the skin takes on a green tint as hemoglobin breaks down. Gradually, the hematoma resolves and “flows” down.
If there are no complications, the hematoma will resolve on its own. In the worst case, a hard area appears that causes discomfort and impairs motor function. When an intramuscular lump forms, external symptoms are rarely observed, but the limb swells significantly and an area forms inside, the touch of which causes severe pain.
Note! For chronic intramuscular hematomas, an MRI is prescribed to determine the location and extent of tissue damage.
When large lumps form, surgical intervention is required. Treatment is carried out by a traumatologist. The opening of infected seals is performed by a surgeon after a comprehensive diagnosis. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis, but for large hematomas hospitalization is required. An autopsy is performed, during which blood clots are removed and washing is carried out. Drainage and suturing are required. Sutures are not applied only for infected hematomas. Antibiotics are often prescribed in combination to eliminate the infection.
Treatment of hematoma on the leg after a bruise
A hematoma on the leg after a bruise, the treatment of which in the vast majority of cases is determined by a doctor, can have a different nature. Thus, bruises of mild and moderate severity, as a rule, resolve on their own as soon as possible after their formation.
The only thing the victim can do is to use special ointments that promote this process or resort to traditional medicine.
Only in case of ineffectiveness of drug and “natural” therapy of this kind, as well as in case of hematomas formed as a result of severe bruises or serious injuries, can doctors prescribe physical procedures or surgical intervention.
Ointments: names of drugs, description, instructions
The most effective drugs for eliminating swelling, relieving pain, and restoring the skin of the limb are several ointments.
They are as follows:
- Heparin ointment , the main active substances of which (heparin and anesthesin) have antimicrobial and analgesic properties. By expanding the blood vessels located on the surface under the skin itself, the components of the product in question are quickly absorbed and immediately begin their action. The manufacturer recommends applying a thin layer of ointment to the damaged area of skin 2-3 times a day for no more than a week.
- Lyoton is a gel for external use with a pronounced analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. The only active substance included in its composition is sodium heparin. To achieve maximum effectiveness of the product, it is necessary to apply a thin layer of gel to the affected area of the skin 1-3 times a day, gently rubbing.
- Troxerutin (gel ) is an effective remedy for getting rid of hematomas that occur after a bruise, in particular on the legs. Due to the high concentration of the active substance of the same name (troxerutin), the drug in question has a tonic effect on the venous system, and also strengthens and promotes the restoration of damaged blood vessels. It is recommended to apply the product externally no more than 5-6 times a day, without rubbing it into the surface of the skin.
Traditional methods of treatment: recipes for remedies for bruises, injuries, hematomas
A hematoma on the leg after a bruise (treatment can be not only medicinal) also resolves in the shortest possible time when using traditional methods.
The most common and proven ones include:
- urine therapy (compresses with urine);
- vodka compress, which needs to be changed at least once every 15 minutes (recommended for use after 3 days from the moment of injury; moisten a small piece of cloth in hot vodka (60 degrees) and apply to the injured area, covering with cling film and a woolen product);
- onion ointment (grate the onion and squeeze the juice out of the resulting pulp; mix with a small amount of olive oil and apply to the damaged area of the skin, gently rubbing the resulting mixture into the injured area);
- compress with clay (mix 2 tablespoons of cosmetic clay (preferably blue) with 1 raw egg and 1 tablespoon of honey; you need to change such a compress to a cooled one as it warms up to room temperature without any restrictions on the number of times).
Physiotherapy: effective methods, duration of treatment
In addition to “natural” treatment methods, as well as special medications, physiotherapy also contributes to the resorption of hematomas on the leg.
The most effective methods in this case include:
- lymphatic drainage procedures (usually a hardware massage);
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- IR irradiation;
- Ultrasound therapy;
- UHF therapy;
- water procedures (for example, taking hydromassage baths).
The duration of physical treatment depends on the type of hematoma formed, as well as its location. Traditionally, when the “victim” first approaches, the doctor prescribes a course consisting of 10 procedures. After completing the first stage of treatment, the specialist at a follow-up appointment assesses the dynamics of changes in the condition of the injured area.
If swelling, pain, and the dark color of the skin at the site of the injury persist, the patient may be prescribed a second course of physiotherapy until positive changes occur in the appearance and functioning of the limb.
Surgical methods of treatment: when is surgery necessary?
If you do not contact a medical facility for assistance in a timely manner, the victim may require surgical intervention followed by a long recovery period.
The operation is prescribed when there is a significant increase in the size of the area of damaged vessels, as well as when swelling and pain persist for a long time or the general condition of the “victim” worsens, indicating the development of a purulent inflammatory process in the human body.
If the primary surgical intervention does not bring positive changes, the doctor may prescribe a repeat operation. It is important to understand that in the presence of secondary circumstances, for example, diabetes, the rehabilitation period may be delayed. If the effectiveness of multiple surgical treatment is low, amputation of the limb is a further indication.
Intracranial hematomas
Intracranial hematomas are divided into the following types:
- Epidural.
- Subdural.
- Intracerebral.
- Intraventricular.
Epidurals appear in 1-3% of cases and are due to injury to the middle meningeal artery. Pathology is often observed with skull fractures or depressed fractures. A hematoma develops in 2-3 hours or within 24 hours. Lack of treatment leads to coma. The first symptoms are confusion and weakness. Children rarely lose consciousness after a severe blow. Significant swelling of the brain does not lead to the detection of a light gap (which is rare in adults).
Subdurals appear in 1-7% of cases and pose a threat to human life, since death occurs in 60% of cases. There is an acute, subacute and chronic form of the pathology. Bleeding occurs due to a rupture of a vein or artery in the damaged area. People report nausea and severe headaches. Symptoms characteristic of compression of the brain stem are often observed. Lack of treatment and worsening symptoms lead to coma.
Intracerebral are observed extremely rarely with severe traumatic brain injuries. The light gap is not visible, the development of pathology occurs quickly. Hemiplegia or hemiparesis often occurs, as well as extrapyramidal symptoms.
Intraventricular diseases are rarely diagnosed due to the serious condition of patients. There are acute disturbances of consciousness, an increase in body temperature, a decrease in heart rate, and an increase in blood pressure. To establish a diagnosis, a survey of close people is carried out, since the patient is unconscious. To establish the location of the hematoma, MRI is used. In the most severe cases, lombal puncture is used.
Diagnosis: when is medical help needed?
In order to avoid situations where traditional methods of treatment are useless and we are talking exclusively about surgical intervention, it is important to promptly determine the severity of a hematoma found on the leg after a bruise.
The most common signs of the need to immediately consult a doctor to prescribe an additional examination in order to establish a diagnosis and determine the correct treatment should be some factors:
They are as follows:
- impossibility or difficulty changing the position of the leg;
- severe pain when trying to touch the affected area;
- rapid spread of swelling over the area of the limb;
- the occurrence of weakness and elevated body temperature;
- loss of consciousness due to pain;
Treatment of a hematoma on the leg after a bruise should begin immediately if the pain leads to fainting. - lack of positive dynamics in the external state of the hematoma after 3-5 days.
The circumstances listed above should be the reason for prescribing an ultrasound, x-ray, MRI or CT scan, a general blood and urine test in order to identify the development of a purulent process in the victim’s body.
Diagnostics
A hematoma is diagnosed by visual examination. If the hemorrhage is located deep under the skin, in internal organs, or in a joint, it is often very difficult to assess its size and possible consequences.
Patients are prescribed an examination, which may include:
- Ultrasound of internal organs, joints;
- computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging;
- puncture (puncture with a needle): for example, a puncture of the knee joint is often done if there is a suspicion that blood has accumulated in it after an injury.
Treatment
Minor bruises can be treated conservatively: physiotherapeutic procedures and medications are prescribed.
In case of large accumulations of blood, the hematoma is treated surgically: it is opened, the blood or pus is evacuated, washed with antiseptics and drainage is installed. Antibiotics are prescribed if necessary.
When hemorrhaging into internal organs, it is often necessary to perform surgical intervention, during which it is necessary not only to remove the spilled blood, but also to stop the bleeding.
The multidisciplinary CELT clinic employs experienced traumatologists and surgeons who perform operations on hematomas of various locations. Modern techniques used in our clinic help provide effective treatment and minimize the risk of complications.
Orthopedics and traumatology services at CELT
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Appointment with a surgical doctor (primary, for complex programs) | 3 000 |
| X-ray of the chest organs (survey) | 2 500 |
| Ultrasound of soft tissues, lymph nodes (one anatomical zone) | 2 300 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions