There is no such disease as sand in the kidneys or bladder in the International Register of Diseases. It refers to the pathological formation of calculi, stone-like formations that impede the passage of urine from the kidneys or bladder.
Cost of urologist services in our clinic
| Initial consultation with a doctor with the highest category | 1000 rub. |
| Consultative appointment with a doctor based on test results and ultrasound results | 500 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the kidneys in standard mode and using Doppler techniques | 1200 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the bladder | 500 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the pelvis using Doppler techniques | 1200 rub. |
| Make an appointment by phone: 8-800-707-15-60 (toll-free) | |
| *The clinic is licensed to remove tumors |
In fact, stone is a later stage of stone formation, which is preceded by so-called sand. However, the sand has not yet completely hardened, so it is easier to remove from the body. But in terms of their composition, these are the same elements, only they differ in size and shape.
What is sand
The content of the article
Both sand and stones are a mixture of various salts with proteins, but sand is a mixture that has not yet acquired a rocky structure. The sand particles have a diameter of no more than 8-9 mm, and the largest stone discovered was 17 cm wide.
Sand is more often found in the bladder, and stones in the kidneys. From there, small particles of stones descend down the urinary tract and enter the bladder.
At the initial stage, neither stones nor sand show themselves in any way, so a person may not be aware of the problem. Treatment in the initial stages is quite quick and effective, while large stones can sometimes only be removed surgically. For this reason, you should definitely visit a urologist once a year and undergo an ultrasound examination of the urinary system.
Indications
Phytolysin can be used as a symptomatic, complementary to complex therapy, medicine, independent treatment, to prevent the recurrent course of the disease, the development of acute inflammation or its chronicity.
The drug is prescribed:
- for cystitis, urethritis;
- inflammation of the kidneys and urinary tract, including: chronic calculous pyelonephritis;
- for loosening large stones, removing sludge from urolithiasis;
- with insufficient diuresis;
- for disorders of uric acid metabolism;
- for the prevention of inflammatory processes, re-formation of sand, deposition of oxalate stones after surgical treatment.
What are stones
Stones are concretions, i.e. stones formed as a result of metabolic disorders in the body. Depending on the reasons for their formation, they are divided into groups:
Alkaline stones . They were formed as a result of the creation of an alkaline environment in the body. This is directly related to the diet, the products of which create this or that environment. The optimal pH level is 6.5-7.4, and any decrease or increase creates an environment favorable for the formation of stones.
When food is processed and broken down, uric and lactic acid are formed. They are neutralized by reaction with lymph and bile, which have an alkaline environment. When there is an excess of foods that also give an alkaline reaction, the body experiences a lack of acid.
As a result, phosphoric acid salts are deposited in the kidneys or bladder, which, when interacting with proteins, crystallize and turn into stones.
Phosphates. These are stones formed when there is an excess of phosphoric acid. Seemingly healthy and harmless foods such as vegetables and fruits give an alkaline reaction. The “champions” for alkalizing the body are citrus fruits, in particular lemon.
During the off-season, people try to strengthen their immune system and prevent the spread of infection by eating lemons, oranges, apples, onions and garlic. Strict adherence to fasting or a new-fangled diet is also fraught with the onset of stone formation. Phosphate stones grow quickly and provoke the development of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system. Ultrasound shows smooth stones with a clear contour and low echo structure.
Acid stones. The consumption of certain foods leads to acidosis - a shift in pH to an acidic environment. Oxidation corrodes body tissue, promotes the accumulation of water in cells, causes premature aging and the development of cancer. Also, the acidic environment provokes the leaching of calcium from the bones, which becomes the cause of osteoporosis with age.
Products that create an acidic environment in the body include sugar and everything connected with it (sweets, pastries, cakes, chocolates), flour products (pasta, rolls, pies, loaves), except black bread made from rye flour, meat and dairy products (sausages, yoghurts, milk, sausages, cottage cheese), alcohol, sweet carbonated drinks, fast food. In addition, the acidic environment is favorable for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria that feed on glucose. Along with the formation of stones in the kidneys or bladder, inflammatory processes occur caused by the activity of microorganisms.
Oxalates. These are salts of oxalic acid, secreted by the kidneys independently during biochemical reactions, as well as with the consumption of certain foods. The formation of oxalates is stimulated by sorrel, rhubarb, asparagus, spinach - almost all greens.
This does not mean that they need to be excluded from the diet, but long-term “herbal” diets should be avoided and be sure to compensate with alkaline foods. In hot climates, the formation of oxalates is significantly accelerated.
Also provocateurs are poor-quality drinking water, excessive intake of vitamin D and excess meat and products made from it. Oxalates are clearly visible on ultrasound because they are quite large, but not dense, and therefore do not have an increased echo structure. They are removed from the body in a difficult and time-consuming manner, and when carried forward they cause renal colic.
Urats . This is a combination of uric acid crystals and proteins. They are formed during metabolism and are always present in small quantities without causing harm to health. They are mainly found in the bladder because urates are formed when there is an excess concentration of uric acid in the urine.
Unlike phosphates or oxalates, urates are not affected by diet. They most often form in people who consume insufficient amounts of fluid (the norm is 2 liters in the summer and 1.5-2 liters during the rest of the period).
When there is a lack of water, uric acid salts settle on the walls of the bladder in the form of a sediment of dense texture. The formation of urates can be triggered by taking analgesics, a sedentary lifestyle, lack of vitamin B, and excess food of animal origin. On ultrasound, urates are visualized as round formations of increased echostructure ranging in size from 1-2 mm.
Struvite-carbonate and phosphate-ammonium-magnesium stones. They are formed on the basis of crystals of magnesium ammonium phosphate or carboapatite. Unlike other types of stones, struvite has the appearance of coral-shaped growths.
They are caused by pathogenic bacteria that break down uric acid and produce urease, an enzyme that breaks down uric acid into ammonia and carbon dioxide. A prerequisite for stone formation is the presence of pathogenic microflora.
Inside each calculus there is a dead bacterium surrounded by a crystal. On ultrasound they appear as coral-shaped formations with a soft echostructure. In 50% of cases, damage to the kidney of this type of stones leads to loss of the organ.
Stones formed as a result of genetic disorders and congenital defects. Stones are formed regardless of diet and lifestyle, but only due to metabolic disorders in the kidneys.
Cystine stones . They are the result of the development of cystinuria, an autosomal recessive pathology consisting in impaired reabsorption of the amino acids arginine, ornithine and cysteine.
They are not absorbed by the small intestine and remain in the urine. Cystine is practically insoluble in water, therefore it forms crystals, which, when interacting with acids, turn into stones.
On ultrasound they are smooth, round, not layered. People suffering from cystinuria have a high probability of inheriting the disease.
Xanthine stones also form as a result of a genetic abnormality involving a lack of the enzyme xanthine oxidase, a precursor to uric acid. Unprocessed xanthine settles in the kidneys in the form of crystals, from which stones are formed.
Protein stones . Fibrin is a protein that is formed during the blood clotting process. When the kidneys malfunction, it reacts with uric acid and forms a calculus. The process is facilitated by inflammation of the kidney caused by infection (pyelonephritis). On ultrasound, protein stones have a flat shape and a soft echostructure.
Cholesterol stones rarely form in the kidneys, mainly in the gallbladder. But when lipid metabolism is disrupted, cholesterol is oxidized in the kidneys, and stones form from it. They crumble easily and can damage the kidney parenchyma. They have a low echostructure.
Form and composition of the drug
Phytolysin is a medicinal concentrate in the form of a viscous gel-like paste intended for oral use. The product has a greenish-brown color and a characteristic balsamic herbaceous odor. It is packaged in metal tubes, from which it is very convenient to squeeze it out in sufficient volume. One aluminum package contains 100 g of the drug.
The medicinal substrate contains 67% of an alcohol-based extract of 9 medicinal plants:
- horsetail;
- goldenrod;
- birch leaves;
- lovage rhizomes;
- fenugreek seeds;
- knotweed;
- parsley roots;
- wheatgrass;
- onion peel.
Among the auxiliary components are essential oils: pine, peppermint, orange and sage. Binders and stabilizers:
- gelling agar;
- glycerol;
- ethyl parahydroxybenzoate;
- wheat starch;
- vanillin;
- distilled water.
Symptoms of kidney stones and sand in the bladder
Sand in the bladder is more difficult to detect because its symptoms are not very pronounced. This disease occurs more often in women because their urinary tract is shorter than that of men.
Basically, a person is concerned about the following symptoms:
- discomfort in the abdominal area, especially after exercise, when bending forward, or sitting in a car. The pain sometimes spreads to the vagina;
- pain when urinating, feeling of a full bladder, frequent urge to go to the toilet;
- blood clots in the urine, pinkish color of the liquid;
- a large amount of mucus in the urine;
- inflammation of the walls of the vagina, labia;
- pain when pressing on the anterior wall of the abdomen.
The symptoms of kidney stones are more pronounced, especially if the stone moves through the urinary tract. These include:
- renal colic (severe stabbing pain in the side, back), spreading to neighboring organs;
- nausea and vomiting during an attack;
- frequent urination, weak stream;
- frequent urge to go to the toilet;
- temperature increase;
- cold sweat on forehead;
- increased blood pressure;
- bloating;
- blood in urine.
Stones less than 5 mm in size pass on their own, from 5 to 10 mm - only in 50% of cases. Stones larger than 10 mm require surgical intervention.
Causes of urolithiasis
Kidney stones appear both after inflammation and without it. The reasons leading to the formation of stones include:
- Genetic predisposition. Metabolic disorders lead to impaired absorption of certain amino acids by the small intestine, so they remain in the urine and crystallize.
- Wrong diet. When consuming meat and dairy products, pickles and smoked meats, smoking and drinking alcohol with a lack of vegetables and fruits leads to oxidation of the body and increased urine acidity. Vegetarianism, lack of protein foods, and passion for fruit diets lead to alkalization of the body and a decrease in acidity. All this leads to the formation of stones.
- Lack of vitamins and sunlight. Vitamin D levels also affect the formation of stones, both a deficiency and an excess of the vitamin.
- Urogenital infections. Very often, after removing stones, bacteria are found inside them, which have become a capsule around which a calculus has formed.
- Hot climate. People living in countries with tropical climates are much more likely to suffer from urolithiasis.
- Thyroid diseases. Hypothyroidism, or insufficient production of the hormones T3 and T4, impairs the kidney's blood flow and reduces its ability to filter.
Contrary to popular belief, water quality has less of an impact on stone deposition. In order for stones to be deposited due to poor drinking water, it must be a truly undrinkable, poorly purified liquid that a person takes due to the development of an infection.
Correct drinking regime
To wash sand out of the kidneys, you need a high-liquid drinking regimen. During the day, you must drink at least 1.7-3.0 liters of pure non-carbonated water (not tea, coffee, juice, etc.), preferably warm, regularly between meals. You can drink alkaline mineral water, which prevents the formation of salts. Essentuki, Narzan, Borjomi are suitable. By increasing the volume of daily urine and decreasing its concentration, good conditions are created for removing existing sand and preventing its formation in the future.
Kidney stones in pregnant women
There is a high risk of developing urolithiasis in pregnant women. This is due to changes in hormonal levels, in particular, an increase in progesterone levels. It prevents embryo rejection, but at the same time relaxes smooth muscles, causing urinary stagnation.
Also, during pregnancy, the immune system weakens, which causes microflora to change. Often a woman expecting a baby is tormented by thrush. Pathogenic microflora easily reaches the bladder through the short urinary tract, and from there to the kidneys. Stagnant urine is an excellent environment for the development of pathogens. All this contributes to the formation of stones or sand.
Also, the expectant mother needs to carefully monitor her diet. You should reduce your consumption of meat, but not give it up altogether. On the one hand, protein is a building material for the growing fetus, on the other hand, it helps to increase the acidity of urine.
Pregnant women also move less and limit themselves to fluids. Hormonal levels change taste preferences, and women, who have been limiting themselves to sweets and starchy foods throughout their lives, relax during pregnancy and indulge in sweets, pizza, carbonated drinks, and smoked sausages. In a word, a pregnant woman automatically falls into the risk group.
Kidney stones are dangerous for pregnancy because in the initial stages, a stone passing through the ureter causes a spasm of smooth muscles, which can provoke rejection of the fertilized egg from the uterine wall. At later stages, stagnation of urine and the infection developing in it can spread to the placenta.
A pregnant woman should definitely see a doctor. A high-precision ultrasound machine will show the position of the stone, and if there is a threat of its movement, measures will be taken to reduce the risk for the mother and the unborn baby.
Millet
When discussing how you can remove sand yourself at home using folk remedies, it is also necessary to mention a recipe using millet. To do this, rinse the raw material well in half a glass, pour one liter of water over the millet and simmer over low heat for 4 minutes. Remove the broth from the heat and let it brew until a white foam forms. Strain the broth and drink the resulting water in several small sips throughout the day. In this case, the millet can be cooked and then simply eaten as porridge.
Diagnosis of urolithiasis
Diagnosing the presence of kidney stones or sand in the bladder is complicated by the fact that at an early stage the problem does not manifest itself in any way. Typically, the patient consults a doctor only when the stone has formed and began to move through the urinary tract. In this case, the person is taken to the hospital with a diagnosis of renal colic and often undergoes surgical treatment.
To prevent this from happening, the functioning of the kidneys and bladder should be monitored, and if a problem is detected, the doctor will prescribe treatment to prevent the formation of stones.
The most difficult thing to identify is sand in the bladder or kidneys. The stones are no more than 1 mm in size, so even with the most advanced ultrasound machine they are difficult to detect. Therefore, the most informative will be a urine test. Based on its result, the doctor judges the patient’s health status.
The following symptoms should alert you:
- Protein in the urine (proteinuria) . It indicates a violation of the filtering ability of the kidneys and possible mechanical damage to the parenchyma. Normally, the amount of protein should not exceed 0.033 g/liter, but in some cases, increased protein is not a deviation, in particular, after an acute respiratory viral infection or flu, after any inflammation, increased physical activity, or on a protein diet. Also, increased protein indicates the development of diseases such as pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, cystitis, prostatitis in men, vulvovaginitis, adnexitis, etc.
- Red blood cells . Normally, they are visualized individually, but if the walls of the parenchyma, ureter or bladder are damaged, the number of red blood cells increases.
- Acidity . If the acidity is above 7, this indicates the development of infection or the formation of struvite stones. If the value is below 5, then there is not enough acidity to dissolve the crystals, and phosphates, oxalates and urethates accumulate in it. They should not be found in urine because they are a component of stones. If the salt level in the urine is elevated, but no stones are detected on ultrasound, the patient is prescribed a therapeutic diet.
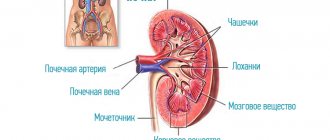
If a kidney stone is present, then using a kidney ultrasound, the doctor will see the following picture:
- bud size: width 5-6 cm, length 10-20 cm, thickness 3-5 cm;
- capsule size up to 15 mm;
- the contours are clear and even;
- the location of the kidneys, both standing and sitting, is normal;
- homogeneous structure;
- medium echogenicity;
- parenchyma thickness on the right is 17-25 mm;
- parenchyma thickness on the left is 18-25 mm;
- the allocation system is not expanded;
- in one of the kidneys an echo signal of up to 1 cm with an acoustic shadow is visualized.
Kidney stones are similar in echo structure to air bubbles, but the latter actively move when the patient’s body position changes. They have increased echogenicity, but ultrasound shows only large stones measuring 8 mm or more, as well as small stones blocking the urinary tract.
Normally, the parenchyma is heterogeneous in structure and loose. This is due to the function of the parenchyma to cleanse the blood of various impurities, which is why the tissue has a spongy structure. The inner part of the parenchyma adjacent to the renal calyces is denser, therefore it appears dark on ultrasound.
The outer fabric has a less dense structure and therefore appears in a light color. For this reason, the ultrasound picture of the parenchyma is heterogeneous and combines light and dark colored foci. The loose structure makes the parenchyma prone to various cysts, fibrosis and other neoplasms. They are clearly visible on ultrasound and indicate the development of some process.
Normally, the contours should be smooth and clear. If they are blurry and have an uneven surface, this indicates an inflammatory process or the presence of echogenic formations. It is also possible to see the following medical terms:
- Echoten . This is a dark area behind the stone, so the ultrasound does not pass through the stone, and it is followed by an acoustic shadow in the form of a dark path on the ultrasound screen.
- Echogenic formation . Echogenicity is the degree of reflection of ultrasound. Lumps surrounded by softer tissue reflect it well, and this is called increased echogenicity. Loose structures, glands, and areas of inflammation have reduced echogenicity because they transmit ultrasound less well. Cysts filled with fluid that does not reflect ultrasound are anechoic, i.e. have no echogenicity.
- Microcalculosis. These are small stones with a diameter of up to 10 mm, as well as sand.
- Volumetric formations . These are lesions with a changed structure. Benign formations have a clear structure, and when connecting the Doppler function, it is clear that the blood supply to the tumor site is poor.
With an oncological tumor, the contours are uneven and blurred, and during Doppler scanning, the red color predominates, indicating good blood circulation of the tumor.
Sand is observed mainly in the renal pelvis or bladder. The pelvis is where urine collects and is then directed to the bladder. If metabolic processes are disrupted, small stones measuring 1-2 mm in size are observed in the pelvis, which enter the bladder through the ureter.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter