Compound
| Capsules | 1 caps. |
| active substance: | |
| St. John's wort herb dry extract, standardized to hypericin ND company (from 0.75 to 1.3 mg) | 425 mg |
| excipients: lactose monohydrate - 18.7 mg; cellulose, powdered - 6.2 mg; calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate - 40.5 mg; colloidal silicon dioxide - 26 mg; magnesium stearate - 5 mg; talc - 10 mg | |
| capsule shell: gelatin - 80.465 mg; sodium lauryl sulfate - 0.194 mg; titanium dioxide (E171) - 1.229 mg; chlorophyll-copper complex (E141) - 0.233 mg; purified water - 14.065 mg |
In the structure of general morbidity in Ukraine, mental disorders account for 0.88% (522 per 100 thousand). The prevalence of mental disorders when visiting medical institutions is 4555.1 per 100 thousand population (3.7% of the prevalence of all diseases).
Over the last decade (1990–1999), the incidence of mental and behavioral disorders in Ukraine has increased by 7% (from 248.0 per 100,000 population in 1990 to 265.8 per 100,000 population in 1999). In the structure of mental morbidity in 1999, the group of mental disorders of a non-psychotic nature accounted for 71.1%, and disorders of a psychotic nature accounted for 15.6% of the total mental morbidity [1].
The current stage of social development of Ukraine is characterized by an extremely high level of psycho-emotional stress of the population. This has led to a significant deterioration in the level of mental health in the population.
The level and structure of neuropsychic morbidity are determined by the action of powerful destructive and destabilizing factors.
In conditions of socio-political, economic and ideological instability of society, the loss of old guidelines and the absence of new ones lead to mass neuroticism of the population.
The structure of changes in morbidity indicates that in Ukraine in recent years there has been a significant increase in psychogenic in origin, somatized, psychosomatic and neurosomatic diseases with a chronic course, borderline conditions [2].
Traditional therapeutic approaches to these conditions require activation of the individual, restructuring of life orientation and categories of self-esteem, which sometimes causes psychological resistance and personal rejection on the part of patients.
This occurs against the backdrop of the traditional orientation of the population towards inpatient medical care, as well as the absence in the general somatic network of psychosomatic and neurosomatic departments for the treatment of borderline conditions, post-traumatic stress disorders, etc.
A certain negative role is also played by the distancing of psychiatric services from other social structures with a concentration on the contingent of patients with psychotic disorders, the lack of preventive focus of the activities of dispensaries and non-dispensary forms of psychiatric care, in particular consultative and diagnostic centers.
It is also impossible not to note the crisis of biological methods of treatment, primarily psychopharmacology. Against the background of the overwhelming predominance of drugs with neuroleptic, tranquilizing and sedative effects, drugs with psychostimulant effects are rare.
The nature and severity of the side effects of traditional antidepressants, partly used as psychoenergizing drugs, potentiate the constant search for new, more specialized and effective drugs [3].
In this regard, a new medicinal product of plant origin deserves attention - deprim (Lek, Slovenia). Deprim contains St. John's wort extract, the main active ingredients: hypericin, hyperforin, quercetin, essential oils, xanthones. In its therapeutic spectrum of action, hypericin is similar to reversible selective inhibitors of MAO (its A-isoenzyme), and hyperforin is a serotonin reuptaker. In general, the drug has a balanced energizing, thymoanaleptic and sedative effect.
Over the past 20 years, the results of many studies, including placebo-controlled ones, have been published, which especially emphasize the good tolerability of deprim [4]. In the UK, 23 randomized, double-blind trials compared hypericin extract with placebo and standard antidepressants in the treatment of mild to moderate depressive disorders in 1,757 outpatients. The results showed that its antidepressant activity in these groups was similar to that of standard antidepressants, and side effects were almost 3 times less common [5].
The purpose of our study was to study the effectiveness of the use and spectrum of action of deprim in neurotic and somatoform disorders and to develop criteria for its further use in psychiatric and general somatic practice.
Materials and methods
We conducted a comparative randomized study of the drug Deprim in psychiatric practice, which involved 42 patients (28 women and 14 men aged 22 to 65 years) with the presence of various psychopathological disorders of the neurotic register. The study was conducted at the Department of Psychotherapy of the Kharkov Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education and Central Clinical Hospital No. 5.
Examination technique. The drug was prescribed according to a single regimen: 1 tablet of Deprim (0.3 mg hypericin) three times a day - morning, afternoon and evening before meals. The course of treatment lasted 6 weeks. Prescription of concomitant psychotropic medications was not allowed. Only for insomnia were sleeping pills (short-acting tranquilizers) prescribed occasionally.
Patients were examined once a week. For the purpose of clinical diagnosis of the mental state of patients, a clinical-psychopathological method of studying patients was used. In addition to the clinical study, the Hamilton scale was used to assess the severity of depression from the day the treatment began at weekly intervals until the end of the course; General clinical condition scale. Data were assessed and entered into a questionnaire once a week.
Information about adverse events was recorded on the patient's record form weekly. Their possible connection with taking the drug was carefully analyzed.
Routine clinical and laboratory tests were performed.
Blood pressure and heart rate were determined three times - before the start of treatment, in the middle of the course and at the end of treatment. Clinical blood and urine tests - before and after treatment.
After 6 weeks, the therapeutic effectiveness of the drug was assessed in four grades (from “4” - a significant improvement to “1”, when the condition remained virtually unchanged or worsened). In addition, its tolerability and safety (based on the number of side effects) were assessed.
The duration of mental disorders in the examined patients ranged from several months to 3 years.
Data on the nosological and syndromological representation of mental disorders in patients, according to ICD-10, are presented in Table. 12.
Table 1
Distribution of patients by nature of mental disorders
| Mental disorders | Number of patients |
| Dysthymia (F34.4) | 2 |
| Panic disorder (F41.0) | 3 |
| Obsessive-compulsive disorder (F42.0) | 2 |
| Prolonged depressive reaction (F43.1) | 1 |
| Mixed anxiety-depressive reaction (F43.22) | 6 |
| Somatization disorder (F45.0) | 4 |
| Hypochondriacal disorder (F45.2) | 3 |
| Somatoform autonomic dysfunction of the cardiovascular system (F45.30) | 7 |
| Somatoform autonomic dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract (F45.32) | 2 |
| Chronic somatoform pain disorder (F45.4) | 4 |
| Neurasthenia (F48.0) | 8 |
| Total | 42 |
table 2
Distribution of leading psychopathological syndromes
| Leading psychopathological syndrome | Number of patients |
| Astheno-depressive | 15 |
| Anxious-depressive | 5 |
| Astheno-hypochondriacal | 7 |
| Anxious-asthenic | 4 |
| Obsessive-depressive | 2 |
| Depressive | 3 |
| Anxious-phobic | 4 |
| Dissociative-conversion | 2 |
| Total | 42 |
All patients had asthenic syndrome as a baseline. Mild (hypothymic, dysthymic) severity of depressive syndrome was diagnosed in 21 patients, moderate (cyclothymic) - in 13.
Results and discussion
An assessment of the dynamics of the psychopathological state of patients using the clinical-psychopathological method revealed the following: in patients receiving Deprim, by the 7th day of the study there was a significant improvement in the subjective range of sensations, their mood and activity increased. By the 14th day of therapy, a pronounced decrease in asthenic, anxious and depressive symptoms was recorded, in particular, the vital components of depression and anxiety, fatigue, tearfulness, irritability, hyperesthesia, unreasonable fears or specific concerns about the state of one’s health. In the majority of patients, dyssomnic disorders and anti-vital experiences were relieved. By the end of the 3-week course of using Deprim, the somatized manifestations of depression almost completely disappeared: pain and somatovegetative dysfunctions were relieved. The isolated cases of fragmentary elements of depression that remained at the end of the course were characteristic of patients with hypochondriacal symptoms and in cases of prolonged depressive reaction, which was due to specific manifestations of pathopsychological personality development.
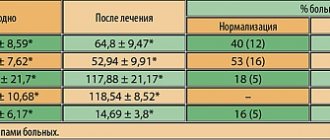
An objective assessment of the dynamics of psychopathological disorders during deprim therapy according to the Hamilton scale revealed a significant significant decrease in the level of anxiety and depressive disorders by the 14th day according to all criteria in the main group of patients. By the end of the course (by the 21st day of the study), the level of depressive mood decreased by 53.25%; feelings of guilt - by 36%; anti-vital experiences - by 33%; dissomnia disorders decreased by an average of 25.8%; the level of somato-vegetative dysfunction - by 29.1%.
During the clinical trial, minor side effects of the therapy were discovered. Manifestations of photosensitivity were recorded in 3 patients and in 1 patient - a decrease in the duration of night sleep without somato-depersonalization disorders.
conclusions
- Deprim has a balanced effect, the main components of which are psychoenergizing, antidepressant and tranquilizing effects.
- The results of the study show that Deprim is an effective antiasthenic drug and a “mild” antidepressant in the treatment of neurotic and somatoform disorders of various etiologies.
- The effect of the drug appears quickly, already by the beginning of the second week of treatment.
- Deprim is practically free of side effects, is safe to use, and does not reduce the quality of life of patients. Therefore, it can be recommended for the treatment of neurotic and somatoform disorders in pediatric practice, in geriatric, somatically weakened patients.
- Deprim can be used both in inpatient and outpatient settings, not only in psychiatric, but also in general somatic practice.
Literature
- Tabachnikov S. I., Voloshin P. V. Until the World Day of Health, dedicated to the protection of mental health // Archives of Psychiatry. - 2001. - No. 1–2. — P. 5–6.
- Mikhailov B.V., Kozidubova V.M., Maruta N.A. et al. Current problems of social psychiatry, psychotherapy and medical psychology in Ukraine // Bulletin of Mental Health. - 1999. - No. 1. -S. 6–8.
- Linde K., Ramirez G. et al. St. John work for depression - an overview and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. - British Medical Journal. - 1996. - Vol. 313. - P. 252–258.
- Volz HP Controlled clinical trials of Hypericum extracts in depressed patients - an overview.
- Tochilov V. A. Experience in treating depression with deprim // Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry named after. S. S. Korsakova. - 2000. - T. 100, No. 5. - P. 63.
Directions for use and doses
Inside, with water. Capsules must not be opened!
Adults and adolescents over 12 years of age: 1 capsule. Once a day, regularly at the same time. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 2 caps. per day - 1 capsule. in the morning and in the evening. The greatest effect of the drug is achieved with regular use for several weeks.
The therapeutic effect of the drug appears 10–14 days after the start of administration.
If your condition does not improve within 4–6 weeks after starting treatment, you should stop taking Deprim® forte and consult your doctor.
The patient must inform his doctor that he is taking Deprim® forte.
If you miss one dose of Deprim® forte:
- you should take the medicine as soon as possible;
- if it is time to take the next dose of the drug, do not take an additional dose to compensate for the missed dose;
- do not take 2 doses of the drug at the same time.
Interactions of the drug Deprim
Deprim should be taken with caution during simultaneous treatment with drugs containing digoxin, theophylline, as well as oral contraceptives, anticonvulsants and antidepressants, triptates. Preparations containing St. John's wort extract may increase the activity of certain enzymes that take part in the metabolism of the drug. These interactions may reduce the effectiveness of some drugs, such as warfarin, cyclosporine, theophylline, indinavir, digoxin, and birth control medications. Deprim can interact with drugs whose metabolism occurs with the participation of cytochrome enzymes, as well as if their transport occurs using p-glycoprotein. The effect on enzymes may continue after treatment is stopped. In this regard, interaction of Deprim with other drugs may occur for another two weeks after stopping its use. Due to the pharmacodynamic interactions of the drug Deprim with triptan derivatives (sumatriptan, naratriptan, zolmitriptan), antidepressants (especially selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, for example citalopram, fluvoxamine, fluoxetine, sertraline, paroxetine), the side effects of serotonin may increase.