Indications
The irrigoscopy method is used to diagnose the following diseases:
- Fistulas;
- Tumors in the large intestine;
- Megacolon;
- Spikes;
- Scarring;
- Diverticula;
- Inflammation in the colon (chronicle).
Irrigoscopy is prescribed when:
- The functioning of the intestines (large) is impaired;
- There are difficulties with defecation;
- There are abdominal pains, but the causes are unclear;
- An inflammatory process in the intestinal area is suspected;
- There are substances of a different color in the feces;
- There are recurrent formations;
- They want to assess the consistency of anastomoses in the intestines.
When is the procedure indicated?
Intestinal irrigoscopy is a complex examination that requires professional performance in a special diagnostic center with appropriate equipment. In addition, many patients find this x-ray procedure not the most pleasant, so only a doctor prescribes it if there is a justified need.
Discomfort and pain in the anal area
These symptoms can be caused by inflammation, as well as the presence of polyps and diverticula. Irrigoscopy of the intestines allows you to identify their dislocation and understand the causes of pain.
Bleeding from the rectum (hemorrhoids)
Hemorrhoids in themselves are not difficult to diagnose, but irrigoscopy allows you to identify the dislocation and size of hemorrhoids inside the rectum. This is the only way to find a complication of hemorrhoids in the form of thrombophlebitis. In the future, this will be a guide for the doctor when prescribing effective treatment.
Pathological discharge from the anus (mucus, pus)
The cause of discharge from the anus can be diverticula and ulcers, which are clearly visible in contrast. Also, intestinal irrigoscopy may show thickening of the walls, indicating tissue infiltration.
Persistent chronic constipation or diarrhea
Chronic constipation and diarrhea indicate a decrease or increase in intestinal tone. On x-ray they manifest themselves as an enlarged or reduced intestinal lumen. Also, intestinal irrigoscopy allows you to identify the cause of spasms.
Contraindications for surgery
The study is contraindicated in patients who have:
- Acute ulcerative colitis;
- Perforation (formation of a through hole) of the colon;
- Serious condition;
- Suspicion of perforation of the colon;
- Megacolon is toxic;
- Ischemic colitis;
- Arterial hypertension with the presence of tachycardia;
- Lactation;
- Pregnancy;
- Early childhood.
Biopsy
Irrigoscopy should be performed carefully if:
- There is diverticulitis;
- Bloody diarrhea;
- The chronicle was diagnosed with ulcerative colitis;
- There is cystic pneumatosis.
What can't you eat?
- Bread
- Any sweets (even sweets of natural origin)
- Spicy, fried, salty, fatty or smoked foods
- Vegetables and fruits in their original form
- Mushrooms
- Greenery
- Canned foods
- Porridge (barley, oatmeal, etc.)
- Any fast food is strictly prohibited
- Spices and seasonings
- Carbonated drinks and alcohol
- Coffee and strong tea
- Legumes
- Cottage cheese
Diet
The patient preparing for barium enema should consist mainly of protein-rich foods:
- Chicken eggs
- Turkey, chicken and rabbit meat
- Semolina
- Fish meat (mostly white)
- Fermented milk products (yogurt, kefir)
- Green tea
Food should be taken at least 4-5 times a day in small portions. When preparing for the procedure, the volume of fluid consumed is of great importance. You need to drink a lot, about 2 liters of regular (still) water every day.
Kinds
There are two forms of irrigoscopy.
Procedure with a simple contrast method
This form of irrigoscopy involves the use of barium alone.
This research method should be done for older people and patients whose health has deteriorated in the postoperative period. It is done to determine intestinal motility.
With such filling of the intestine, this method allows you to obtain the clearest contours.
Double contrast procedure
This method involves the use of barium suspension and air.
It reveals tumors, ulcerative defects of the intestine, polyps in the intestinal lumen, intestinal obstructions and diverticula.
X-ray of the large intestine: irrigoscopy and irrigography
X-ray examination of the intestines is widely used as a method of diagnosing its condition using X-rays. Since the organ examined in this way is hollow, the procedure is informative only with the use of a contrast agent.
Irrigoscopy and irrigography - these are the names of x-rays of the large intestine found in the medical literature. As for the differences between these categories, there are several points of view on this matter. One of them says that radiography of the large intestine can be correctly called both irrigoscopy and irrigography, that is, these are similar concepts without any differences.
According to another theory, irrigography involves recording the image obtained by X-ray irradiation on a special film, while irrigoscopy allows you to display the image on the monitor of a device for monitoring the large intestine in real time. There are no differences in terms of technique or methods of preparation.
Irrigoscopy itself can be of two types - it depends on the contrasting technique:
- classical irrigoscopy involves the introduction of a contrast agent in a liquid state;
- irrigoscopy with double contrast: in this case, the patient is first injected with liquid contrast that envelops the intestinal walls, after which gas or air is gradually introduced into the intestinal cavity.
Preparation
It is very important to properly and well prepare the patient for the procedure. If the intestines are not completely cleansed, particles from other procedures remain, there are difficulties with barium retention in the body, or there is a psychological factor, then the result of the study may be distorted.
You need to prepare for the procedure like this:
- For a week, it is recommended to go on a diet with a minimized amount of protein and fiber, as well as foods that promote gas formation;
- Four days in advance, it is necessary to discontinue medications that increase or decrease intestinal motility;
- The day before irrigoscopy, you can fast for medicinal purposes and drink water heavily so that you can drink about three liters per day;
- From six o'clock in the evening the night before irrigoscopy you do not need to eat or drink;
- Requires bowel cleansing with an enema and laxatives.
If you are taking medications that affect blood clotting or anti-inflammatory drugs, your doctor should indicate their use. The day before surgery, all medications are discontinued, with the exception of insulin.
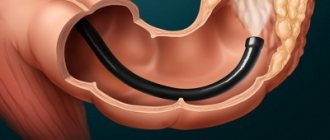
Irrigoscopy
This is an X-ray examination of the colon with retrograde injection of a barium sulfate-based X-ray contrast agent into it. Preparation
In order to examine the large intestine, it is necessary that there is no feces in its lumen.
The success and informativeness of the study is determined by the quality of preparation for the procedure.
We refuse laxatives. Drink enough liquid (mineral water, weak tea).
Option 1
– at 19.00 - 20.00 we begin to do 3-4 cleansing enemas with warm water or chamomile decoction with a volume of 1.5-2 liters. At intervals of half an hour. On the day of the study, 2-3 hours before the procedure, 1-2 enemas. It is necessary to cleanse the intestines to “clean waters” and get rid of feces.
Option 2
– the drug “Moviprep” or “Fortrans” in the pharmacy. We take it according to the instructions. It is necessary to cleanse the intestines to “clean waters” and get rid of feces.
ATTENTION! — PREPARATION IS MANDATORY. WITHOUT IT THE STUDY WILL BE DENIED. We strongly ask you to bring with you: a large sheet, toilet paper. We recommend wet wipes, additional underwear, an outpatient card or appointment, and a note from the attending physician.
We don’t starve, we can have a light breakfast in the morning.
The day before the test, you need to exclude from your diet coarse fiber and foods that cause excessive gas formation (cabbage, fruits, carbonated drinks, brown bread, dairy products, etc.). To prevent hungry gases, you can take Espumisan, activated carbon.
If two complementary procedures are prescribed - irrigoscopy and colonoscopy. Irrigoscopy can be performed only 3 days after colonoscopy. Endoscopic examination (colonoscopy) can be performed only 3-4 days after irrigoscopy, in older people after 7 days.
How the procedure will go:
The most commonly used contrast agent is barium sulfate, which is administered directly through the rectum. It is necessary to take into account the patient's ability to hold a barium enema with a volume of at least 1 liter for a successful procedure.
We take out the sheet, take off the clothes below the waist, leaving the underwear on. You will then be asked to lie down on the x-ray machine table. A white barium suspension will be injected into the rectum through a special tip (tube). A feeling of fullness of the intestine with gases, which causes the urge to defecate. Moderate pain as the intestine stretches with the introduction of barium and air. Also, when the suspension overcomes the bends of the intestinal loops, tension occurs in the folds of the peritoneum.
After the examination, you can drink and eat immediately after the procedure. Rest and bed rest for several hours are advisable, especially for older people.
Place of procedure:
— X-ray room in the reception and diagnostic building, terminal No. 1 (on the 1st floor) – tel. 41-56-25 - X-ray room in surgical building No. 3 (on the ground floor). Phone is missing
Free by appointment on weekdays - from 8.00 to 10.00 Paid by appointment on Saturday - from 9.00 to 12.00
Registration for the study: Registration office of the RCH clinic – 37-11-26
Carrying out the operation
The patient is placed on one side. Using an enema, the intestines are filled with barium, which is ready for the procedure. X-ray images are taken at the same time.
X-ray images show the location of the intestine, its length, shape, how elastic and stretchable it is.
When emptying the intestine from barium, an image is taken with air to understand whether there are functional or organic disorders in the intestinal wall.
This procedure usually takes half an hour if double contrast is done.
The results take from thirty minutes to three days to interpret (it all depends on the place where the procedure was performed).
Irrigoscopy is done without painkillers or anesthesia. It is painless, but may cause some discomfort.
Differences from colonoscopy
Irrigoscopy or colonoscopy - which is better for the intestines? Before answering this question, it is necessary to highlight their main distinguishing features. This:
- Execution method
. Colonoscopy does not require the use of contrast or x-rays. Unlike competitive medical manipulation, it only uses a flexible probe with a camera. - Purpose
. Irrigoscopic examination is used exclusively for diagnostic purposes (except for intussusception in children), and during colonoscopy, polyps can be removed, bleeding can be stopped, or a biopsy can be taken.
What complications
Typically, this type of research is not considered dangerous. Complications during irrigoscopy occur extremely rarely. It happens that a perforation of the intestine occurs and the contrast agent enters the peritoneal cavity. In this case, urgent surgery will be needed.
If suddenly after the operation signs such as nausea, vomiting, fever, pain in the abdominal area, dizziness and weakness up to loss of consciousness appear, then you need to be wary.
A feature of this type of research is the ease of execution, the ability to carry out the procedure with little equipment, and the procedure’s low invasiveness. Further, X-ray images will become visual material for subsequent consultations with doctors to assess the patient’s health status.
The Onco.Rehab clinic guarantees painless and high-quality diagnostics, which will help you in treating the disease.
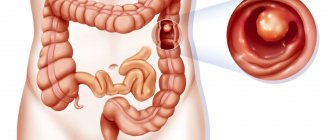
What can be examined with intestinal irrigoscopy?
A healthy intestine on an X-ray with contrast has clear outlines with physiological bulges, it is evenly filled. What anatomical features of the organ are visible on x-ray, and what does intestinal irrigoscopy reveal?
Functional state of different parts of the intestine
In the intestine straightened with the help of liquid, it is clearly visible whether the appendix is able to function, how efficient the ascending colon and the descending rectum are, as well as the small intestine. Any pathologies will be immediately identified.
Size, location and diameter of the colon lumen
In the presence of abnormal narrowings and adhesions, the parameters of the colon lumen deviate from the norm. Irrigoscopy of the intestines gives an idea of their size and dislocation.
Elasticity and distensibility of intestinal walls
During irrigoscopy, the intestines are given a natural shape, and at the same time the elasticity of the walls is checked. The contrasting fluid that fills the intestines stretches its walls and shows where this function is impaired.
Condition of the intestinal mucosa
Thanks to the contrast, intestinal motility is visualized, as well as the condition of the mucous membrane and its relief. If the fullness is small, then only the internal relief is assessed. When it is strong, you can see abnormal changes, organ contours, inflammation, ulcers, tumors, etc.
Function of the intestinal valve
The intestinal valve is the part of the organ located between the ileum and large intestine. When functioning normally, the valve allows intestinal contents to flow in only one direction. During irrigoscopy, when the intestines are filled with contrast liquid, checking this parameter is not difficult.