Increased body temperature, painful sensations in the throat, weakness, headache - people usually attribute these symptoms in the spring-winter period to a common cold. However, often such signs indicate the development of a dangerous infectious disease, which doctors call purulent tonsillitis. The disease is manifested by severe inflammation of the tonsils (glands), located in the nasopharynx. The infection primarily affects the parenchyma and lymphoid tissue lining the tonsils. The disease is dangerous due to severe complications that develop when symptoms are ignored and there is no proper treatment.
Causes
Inflammation of the palatine tonsils is provoked by infections transmitted by airborne droplets. Less commonly, infection occurs through contact and household contact (through shared dishes, towels, bed linen). The most common causative agent of purulent sore throat is hemolytic streptococcus. However, if a person’s immune system works normally, bacteria of this group die immediately after entering the body. The development of pathology is facilitated by weakened immunity and provoking factors.
Indirect causes of purulent sore throat include:
- severe hypothermia;
- chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract;
- oral infections;
- alcoholism and smoking history;
- stress, overwork, strong emotional tension;
- living in areas with difficult environmental conditions;
- deficiency of vitamins and nutrients;
- mechanical damage to the tonsils (trauma, surgery).
The disease is diagnosed with equal frequency in adults and children.
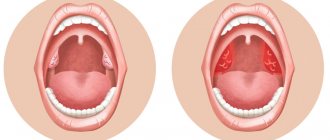
What should a healthy throat look like?
- The oral cavity does not contain visible changes, there are no ulcers or wounds.
- The surface of the tongue is clean, with a slight coating.
- The tonsils are the same size, pale pink in color.
- There are no tubercles, seals, plaque, or bubbles on the surface of the tonsils.
- There are no purulent formations, spots, plaque on the surface of the palate and palatine arches, the color is pinkish.
- The lateral area of the larynx is without swelling, pink.
- The posterior wall of the larynx is more saturated in color due to the location of a large number of vessels.
- There is no plaque, vesicles, or ulcers on the surface of the larynx, and the vessels are not enlarged.
Incubation period
The period from the moment the pathogen enters the body until the appearance of the first characteristic symptoms can range from 2 to 6 days. During the first few days, the sick person is still unaware of his condition, becoming a source of infection for others. During the incubation period, the infection is actively transmitted by airborne droplets (through coughing, sneezing, kissing, talking). The onset of the disease is manifested by a feeling of chills, increased body temperature, weakness and headache. The sooner the patient sees a doctor, the easier the treatment is.
For what changes in the throat should you call an ambulance?
Some throat diseases pose a threat to the lives of patients, especially in childhood. Calling an ambulance is necessary in the following cases:
- When examining the larynx, a narrowing of the lumen is observed. It becomes difficult for a person to breathe. This condition may indicate laryngeal stenosis, which can be fatal, especially for children.
- The throat is strewn with ulcers, ulcers, rashes, and the body temperature is higher than normal.
- Vessels bleed on the back wall of the larynx. The patient has signs of intoxication, vomiting, fever.
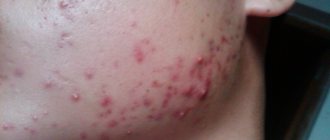
Symptoms of purulent sore throat
In most patients, the first signs of purulent tonsillitis appear 2-3 days after the pathogen enters the body. When the patient's immunity is weakened, the clinical picture is most pronounced. In adult patients, the following symptoms are observed:
- the appearance of noticeable white or yellowish spots of pus on the tonsils;
- high body temperature (in the range of 39-40 ° C);
- intense pain in the throat that increases during swallowing;
- significant enlargement of the lymph nodes located under the lower jaw;
- easily removable whitish coating on the tongue;
- severe headaches;
- feeling weak and overwhelmed;
- loss of appetite;
- aching joints.
In adults, with timely treatment, the acute stage of the disease rarely lasts longer than a week. If the patient does not seek help from specialists, there is a risk of complications.
Rules for examining the throat
To assess the condition of the throat, it is necessary to follow a certain algorithm:
- The patient should be placed near a window, and if there is insufficient lighting, use a flashlight.
- If you don’t have a sterile medical spatula, take a spoon, wash it thoroughly and pour boiling water over it.
- Use the back of the spoon to press on the middle of the tongue (if you press on the base, you can cause a gag reflex).
- To assess the condition of the tonsils, you need to press your tongue to your lower lip and open your mouth wider.
If the examination is being performed on a child, you need to wait a few seconds. During breathing, the tongue will reflexively lower. This way you can better see the tonsils and lateral walls of the larynx.
Stages of disease development
The disease progresses rapidly. This is especially true in children and adults with a weakened immune response. Symptoms depend on the current state of the body, age, concomitant diseases and the stage of infectious tissue damage.
Signs of the development of the disease at different stages from the moment of infection:
- 2-3 days.
This stage is characterized by the maximum severity of the symptomatic picture. The patient's tonsils increase significantly in size and white or yellowish ulcers appear on their surface. The inflammatory process covers the entire surface of the tonsils. The patient notes deterioration in health, weakness, loss of appetite and signs of fever, including an increase in body temperature to 39-40 ° C. The patient also experiences excruciating pain in the throat, which gets worse when swallowing. - Day 4
The ulcers that form on the tonsils begin to spontaneously open, releasing the contents (pus). In their place, lacunae are formed - characteristic depressions. If at this stage the patient follows the doctor’s recommendations, the lacunae quickly close. - 5-6 day
. At this stage, patients feel a noticeable improvement in their condition - body temperature normalizes, headaches go away, strength and appetite are restored. - 7-10 day
. The last pathological sign – sore throat – recedes. The size of the lymph nodes located under the lower jaw also decreases. The patient ceases to feel pain and discomfort in this area.
Competent and timely therapy allows you to avoid serious complications.
Forms of the disease
The form of purulent tonsillitis depends on many associated factors and conditions. The most common three forms of development are follicular, lacunar and ulcerative-membranous (necrotic). Each type is characterized by characteristics of the course, specific lesions of the tonsil tissue and varying duration.
Follicular
Follicular tonsillitis is manifested by pinpoint purulent lesions of the parenchyma of lymphoid tissue and follicles of the tonsils. The disease in 85% of cases is caused by group A streptococci. The remaining cases of infection are associated with staphylococcal infection, Haemophilus influenzae, pneumococcus, and adenovirus. This form of pathology is accompanied by a rapid increase in the symptom complex, severe hyperthermia, sweating, loss of sleep and appetite. Intense pain in the throat can radiate to the ear.
Lacunarnaya
This type of disease causes severe inflammatory damage to the tissues of the peripharyngeal ring. The opening of abscesses is accompanied by the formation of specific perforations on the surface of the tonsils - lacunae. The acute phase of the disease is manifested by an increase in the size of the tonsils, up to difficulty breathing. Along with other symptoms, a characteristic sign of the lacunar type of pathology is bad breath. Sometimes doctors note a noticeable change in voice and diction problems. Inadequate therapy can lead to the development of a paratonsillar or retropharyngeal abscess.
Necrotic
Necrotizing ulcerative tonsillitis is rare (about 5-6% of cases). The main cause of the development of this type of disease is fusospirochetous infection. The rapid development of the infectious-inflammatory process causes the formation of histological changes in the tissues of the palatine tonsils. Violations of vascular permeability, associated with the active production of histamine and cytokines, lead to hypertrophy and sometimes tissue necrosis. The first sign of the disease is the feeling of a “lump in the throat.” Later, a sharp, unpleasant putrid odor appears from the mouth and salivation increases.
Palatine tonsils - a focus of inflammation in chronic tonsillitis
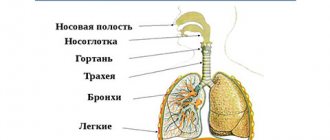
In the upper respiratory tract of a person there are a number of formations representing an accumulation of lymphoid tissue, the so-called lymphoepithelial organs - tonsils. There is a whole lymphopharyngeal ring consisting of 7 tonsils. These are unpaired pharyngeal (adenoids), lingual, laryngeal tonsils, and paired palatine and tubal tonsils. Like any organ in our body, the tonsils can be subject to inflammatory diseases.
Acute inflammation of the tonsils is a sore throat. Chronic tonsillitis refers to a long-term inflammatory process in the palatine tonsils. In most cases, tonsillitis is an exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis. The palatine tonsils (tonsils) are essentially the same mucous membrane only folded into an accordion; they are dotted inside with passages - crypts, which open on the pharyngeal surface of the palatine tonsils with lacunae.
Due to the anatomical features and location of the palatine tonsils, which are located at the crossroads of the digestive and respiratory systems, they are most often, of all other lymphoepithelial formations, susceptible to the inflammatory process, which consists of degenerative processes, as a result of which, in chronic tonsillitis, the palatine tonsils are a constant source of infection and the cause of endointoxication.
Diagnosis and treatment
To make a diagnosis and determine treatment approaches, you need to consult an otolaryngologist. Diagnostics is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- collection of medical history and complaints;
- examination of the pharynx using special lighting (pharyngoscopy);
- general and biochemical blood test;
- bacteriological examination of a smear with the preparation of an antibiogram.
How to treat a purulent sore throat is determined by an ENT specialist. In severe cases, hospitalization is required. General medical recommendations include bed rest, drinking plenty of fluids, taking vitamins and restorative medications.
Specific treatment of the disease is a complex of procedures and medications:
- Drug treatment of the oral cavity.
Complex therapy necessarily includes gargling with antiseptic solutions. For this purpose, solutions of furatsilin, manganese, hydrogen peroxide, sea salt, and natural herbal decoctions (chamomile, calendula) are used. This procedure is aimed at removing pathogenic microorganisms from the throat and mouth. - Taking systemic antibacterial drugs.
A full course of antibiotic therapy allows you to get rid of pathogenic flora. Antibiotics and their dosages can only be determined and prescribed by a doctor. The most commonly used drugs are from the groups of penicillins, macrolides and cephalosporins. - Symptomatic therapy.
To alleviate the patient’s condition during the acute stage, the specialist prescribes symptomatic treatment in the form of antipyretics, antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs. Sometimes it is recommended to undergo physiotherapeutic procedures during the recovery period.
Correctly selected treatment helps to avoid serious consequences and ensures healing of the affected tissue areas without visible defects.
Purulent sore throat in children
If the disease develops in a child, in addition to the main symptoms, digestive disorders often appear - diarrhea, nausea, vomiting. Children may complain of abdominal pain caused by intestinal spasms. The follicular type of pathology is especially difficult for children aged 5-10 years, causing inflammation of the meninges. Young patients often experience fainting, dry cough and complaints of a feeling of a foreign object in the throat.
If parents ignore the symptoms, the pathology becomes chronic. Pediatricians call this condition chronic tonsillitis, exacerbations of which occur 2-3 times a year.
Literature
- Kudryavtseva Yu. S., Kunelskaya N. L., Turovsky A. B. Sore throats: diagnosis and treatment // General Medicine - No. 3, 2010. - P. 4-9.
- Zaitseva S.V., Zastrozhina A.K., Kulikova E.V. Acute tonsillitis in the practice of a pediatrician // Medical Council.2019; 2. - pp. 113-119.
- Clinical recommendations Acute tonsillopharyngitis // National Medical Association of Otorhinolaryngologists / 2021. - P. 36.
- S. A. Artyushkin, N. V. Eremina Acute and chronic tonsillitis, pharyngitis: terminology, etiology, diagnosis, treatment // Otorhinolaryngology Pulmonology No. 10 (98) / 2014 - P. 66-70.
- A.V. Gurov, M.A. Yushkina Local therapy of inflammatory diseases of the pharynx // Breast cancer. 2021. No. 11. - pp. 792–796.
- Clinical recommendations “Differential diagnosis and treatment of acute tonsillpharyngitis.” // National Medical Association of Otorhinolaryngologists / Moscow - 2014. - P. 22.
- E.I. Krasnova. Differential diagnosis and therapeutic tactics for acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis) at the present stage // E. I. Krasnova, N. I. Khokhlova, V. P. Provorova, A. N. Evstropov // Attending physician No. 11, 2021. - C 58-63.
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® AEROSOL: .
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® SOLUTION: .
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS: .
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS CLASSIC: .
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS EXTRA: .
Up to contents
Complications and consequences
The advanced form of the disease leads to inflammatory damage to other organs, including the heart, kidneys, and joints. The most dangerous complications include:
- mediastinitis
– inflammation of the mediastinal tissue; - chronic bronchitis
- inflammatory damage to the bronchi; - sepsis –
spread of infection through the bloodstream; - arthritis -
inflammation of the joints; - glomerulonephritis is
a dangerous kidney disease; - purulent meningitis -
damage to the meninges; - peripharyngeal abscesses
- suppuration of the lymph nodes and tissue of the peripharyngeal space.
Timely access to a medical facility allows you to avoid negative health consequences.
Prevention
By paying attention to preventive measures, you can reduce the risk of developing the disease. Effective prevention includes:
- avoiding hypothermia (wearing warm clothes, monitoring microclimatic indicators in the room);
- regular preventative visits to the dentist to identify the early stages of caries and stomatitis;
- giving up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol);
- moderate physical activity, regular walks in the fresh air;
- normalization of diet, sleep and wakefulness;
- compliance with hygiene standards and requirements, maintaining cleanliness in the home and workplace;
- limiting contacts with unfamiliar people during periods of unfavorable epidemiological conditions.
Strengthening the immune system based on leading a healthy lifestyle helps to avoid infection and make it easier to endure purulent sore throat.