- What is ARVI
- How to prevent the spread of the virus
- General symptoms in adults
- Specific signs
- First aid for ARVI
- Prevention
Features of ARVI
ARVI is a large group of diseases. They are united by similar clinical manifestations and 4 factors:
- Viral origin.
- Penetration of the pathogen into the human body through the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract.
- Pathologies primarily affect the respiratory system. That is why the name of infections is respiratory (respiratory - related to breathing and respiratory tract).
- Rapid development and short period of the disease.
There are about 200 causative viruses. The most famous and dangerous ARVI virus is influenza (varieties A, B, C). The following pathogens are also common:
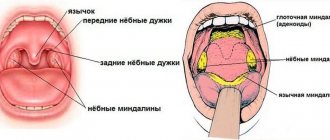
- Adenovirus – causes inflammation of the tonsils and severe sore throat.
- Parainfluenza - affects the larynx, the disease is accompanied by coughing and wheezing.
- Rhinovirus - spreads through the nasal mucosa.
- Enterovirus is localized in the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract and gastrointestinal tract.
Reasons for development
The main cause of ARVI is viral cells. Acute respiratory infections develop as a result of various infections: fungi, pathogenic bacteria, less often protozoa and parasites, and viruses.
Secondary factors provoking diseases are:
- Weak immune system.
- Nervous overstrain.
- Hypothermia of the body.
- Concomitant pathologies, including chronic forms.
- Deficiency of vitamins and minerals necessary for normal functioning.
- Poor nutrition.
- Unfavorable environment in the place of residence (dirty air, water).
Transmission of infection and disease development
Infections are transmitted by airborne droplets (most often by sneezing), less often by household contact - through unwashed hands, kisses, dishes, children's toys, etc.
When viruses enter the human respiratory tract, they are first localized on the mucous membranes. And then the infection spreads through the bloodstream throughout the body.
The disease begins abruptly and rapidly. Sometimes only a few hours pass between infection and the development of the pathological process. More often, however, this period averages 2 days. Sometimes - 4 (but no more).
Children and immunocompromised patients are at risk. ARVI, in turn, also significantly weakens the immune system. Therefore, a person who gets sick once can subsequently become infected with such viruses several times during the year.
Diagnosis of respiratory viral infections
If after a few days you cannot cope with the cold on your own, you should consult a doctor. Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to identify the type of virus at an early stage and prevent complications.
At the Anapa Diagnostic Center you can undergo examinations, undergo fluorography, and take sputum, blood and urine tests. If a bacterial infection is suspected, a bacteriological culture will be performed. Having identified the causative agent of the disease, effective treatment will be prescribed. Call and make an appointment; the earlier treatment is started, the lower the risk of complications.
Signs of ARVI
The main symptoms common to acute respiratory viral infections are:
- Increased body temperature.
- Headache.
- Runny nose, sneezing.
- Cough.
- A sore throat.
- Muscle aches.
- Sweating.
- General malaise, lethargy.
Depending on the type of ARVI, symptoms may be supplemented by pain in the lymph nodes located under the jaw. In some diseases, inflammatory processes develop in the lymph nodes. Also, in some cases, the patient has signs of conjunctivitis.
Reference! The temperature during ARVI, as a rule, does not rise above 38.5 degrees and easily drops within 2 days. The exception is the flu, in which the temperature can reach 39 degrees or higher and last a long time.
A runny nose combined with a cough and fever is often considered a non-serious ailment and people do not consult a doctor, taking independent measures. This is an error because:
- Only a doctor can choose the optimal comprehensive treatment, based on the diagnostic results. When "self-diagnosis" some nuances may be missed.
- Other diseases can be disguised as ARVI, and since the treatment in this case will initially be chosen incorrectly, the pathology can worsen.
- Incorrect treatment can lead to a more protracted course of the disease or the development of complications.
Types of respiratory infections
Rhinovirus infection is the most common among acute respiratory viral infections, affecting the nose and nasopharynx. The viruses that cause the disease are the picornavirus family, which are active year-round but are most aggressive in April and September. A person who has recovered from the disease has virtually no immunity, so you can become infected several times in a year.
Symptoms appear after 1–5 days, including nasal congestion, runny nose, chills, sneezing, sore throat, mild cough, watery eyes. Body temperature rarely rises above 38 degrees. If a bacterial infection does not occur, the symptoms disappear in about a week and the person recovers.
Adenoviral infection affects the respiratory tract, eyes, lymphoid tissue, and digestive tract. Symptoms appear 5-7 days after infection. Worries include a runny nose, fever (38-39 degrees), hoarseness, cough, lacrimation, acute conjunctivitis, weakness, joint pain, diarrhea. Adenoviruses are active in the autumn-winter period; they are not afraid of low temperatures, but quickly die from ultraviolet radiation and chlorine.
Respiratory syncytial infection affects the lower respiratory tract and can spread to the small bronchi and bronchioles. Symptoms are similar to other acute respiratory viral infections: chills, low-grade fever, serous-mucous nasal discharge, shortness of breath. A characteristic feature is a dry paroxysmal cough. The virus is most active in the winter-spring period and spreads quickly in groups. Children under three years of age are very susceptible to MS infection; they suffer the disease most severely.
Coronavirus infection occurs after infection with one of the coronaviruses. To date, seven coronaviruses that infect humans have been studied, the most famous COVID-19 being just one of them. Coronaviruses strike the upper and middle parts of the respiratory tract: nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi. The symptoms of all coronavirus infections are similar: malaise, weakness, chills, mild headaches, increased body temperature. Some types of this type of virus cause rhinitis.
The acute course of COVID‑19 is characterized by high fever, dry cough, loss of taste and smell. Covid has a high spread rate and is dangerous due to complications, one of which is pneumonia. However, a severe course of the disease is typical for weakened people with a “bouquet” of other diseases. Most suffer from Covid in the same way as other ARVIs.
Influenza can also be classified as an acute respiratory viral infection, since its causative agent is viruses transmitted from the carrier of the infection by airborne droplets through the respiratory tract during talking, coughing and sneezing. Influenza epidemics occur in autumn and winter and are caused by several of the most aggressive subtypes of viruses. The symptoms are pronounced: high fever, headache, dry mouth and nose, photophobia, dry cough with chest pain.
ARVI, acute respiratory infections and colds
There are several different terms for diseases with similar symptoms (ARVI, acute respiratory infections and colds), and patients often get confused. Why did the doctor diagnose ARVI in one case, and acute respiratory infection in another, when the clinical manifestations of the pathology were almost the same? And what then is called a cold?
In fact, understanding the differences is quite simple. ARVI and acute respiratory infections are groups of diseases with a similar mechanism of transmission, development and symptoms. However, in the first case, when it comes to an acute respiratory viral infection, the causative agent of the disease is precisely identified - it is a virus. ARI stands for acute respiratory disease. It can be caused not only by viruses, but also by bacteria and fungi. The diagnosis of acute respiratory infections is made when the causative agent of the disease is not clearly identified.
By cold, patients themselves mean both acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections. In fact, a cold is the cause of the disease, not the disease itself. This is what is called hypothermia. If in case of a cold the immune system is weakened, then viruses, pathogenic bacteria or fungi will enter the body. And in this case, acute respiratory diseases or viral infections can develop.
Risk factors
Almost every person knows first-hand what acute respiratory infections are. For the vast majority of adults, unpleasant symptoms of acute respiratory infections make themselves felt 2-3 times a year. As a rule, the peak incidence occurs in the damp and cold seasons, during a period of decreased protective function of the body and increased activity of viruses. For various reasons, acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections are particularly dangerous for people over 55 years of age, asthmatics, diabetics, with endocrinological and neurological problems, as well as for hypertensive patients. Pregnant women should be very careful.
The difference between influenza and ARVI
Despite the fact that influenza is an acute respiratory viral infection, this disease is often considered separately, since it has a slightly different course than other types of acute respiratory viral infections. The differences are as follows:
- Acute onset of the disease - other types of acute respiratory viral infections develop smoothly and gradually over several days; with influenza, a rapid deterioration in the condition is observed.
- Strong signs of intoxication of the body (headache localized in the eyes and temples, chills, sweating, muscle aches, nausea, severe weakness, photophobia) - with other types of ARVI, the general condition is not so bad.
- Later manifestation of the main symptoms - with other infections, the main symptoms appear immediately and develop gradually, and the flu begins with manifestations of intoxication, the main symptoms appear on 2-3 days.
- High temperature - with other acute respiratory viral infections, body temperature rarely rises to 38.5 degrees, and with the flu it can reach 39 and higher.
- The duration of the rehabilitation period is when the patient recovers from other types of ARVI, his strength returns within a few days, and after the flu, weakness, dizziness, appetite disturbances, and shortness of breath are observed for 7-14 days.
Reference! After the flu, it is recommended not to go to work for at least a week to avoid the development of complications.
During this period, you should devote time to rest, supplementing it with short walks in the fresh air. You should avoid exercising after the flu for 2 weeks.
How to avoid getting sick during the ARVI epidemic season
There is no vaccine against ARVI, since there are many viruses in this group, and they constantly mutate. However, before the start of the season, you can get vaccinated specifically against influenza (this is also one of the respiratory viruses). The optimal time for vaccination is September-October. But it is important to understand that the vaccine does not provide 100% protection and does not guarantee that you will not get the flu this year. It only reduces the risk and makes the course of the disease easier if infection cannot be avoided.
In general, the human immune system resists infectious agents well, and adults usually do not get sick more than once per season. Simple and accessible measures for the prevention of ARVI will additionally help reduce the risk of the disease.
What to do to avoid getting sick during the cold season:
- Do not go to crowded places unless absolutely necessary. Try to limit yourself to your place of study or work and grocery stores during the period of highest incidence; if you need to visit these places, you should use a medical mask and gloves.
- Wash your hands often with soap, and when this is not possible, use skin disinfectants: wipes, gels, etc.
- Rinse your nose or use seawater sprays every time you return from the street. In order for the nasal mucosa to retain viruses, it must be well moisturized.
- Temper yourself, that is, gradually accustom your body to cold and temperature changes. You can take a contrast shower, douse yourself with cool water, do rubbing and use other methods. The main result of hardening is an organism adapted to stressful external conditions. A seasoned person is at much less risk of hypothermia and getting sick.
- Avoid stress and lead a healthy lifestyle. For strong immunity, it is critically important to get enough sleep, eat a varied and nutritious diet, even in autumn and winter. A healthy routine is the best prevention of seasonal diseases.
- Avoid alcohol. Alcohol attacks the immune system, removes vitamin C and other substances important for protecting against the virus from the body.
- Maintain air humidity in the apartment at a sufficient level. It is important to do this not only during illness, but also all the time the heating radiators are running in the house. A high-quality humidifier device will help achieve air humidity in the house up to 60%, whereas without it in winter this figure usually does not exceed 20%.
Treatment of ARVI
Treatment is usually carried out at home. The patient is hospitalized only if the disease is severe or complications develop.
Complex therapy is carried out, which includes:
- Drug treatment.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Taking medications to improve immunity: vitamins, immunomodulators.
Depending on the specific symptoms, the following medications may be prescribed:
- Antipyretic.
- Expectorants.
- Medicines against runny nose.
- Antihistamines.
Particular attention during the treatment period should be paid to increasing immunity. The patient should be kept warm and calm, it is best to stay in bed. To quickly rid the body of viruses and toxins, it is recommended to drink plenty of warm fluids frequently:
- Decoctions, infusions of medicinal herbs.
- Chicken or vegetable broth.
- Tea.
- Diluted fruit juices, fruit drinks.
Reference!
If the temperature is more than 38 degrees and does not decrease within 3 days, this may indicate the development of complications (sinusitis, pneumonia, otitis media). A deterioration of the condition 3-5 days after the onset of the disease may indicate the addition of a bacterial infection. In this case, you should urgently consult a doctor.
Prevention of respiratory diseases
Prevention of ARVI is aimed at increasing immunity. There are many known folk ways to increase the body's defenses: hardening, a diet rich in vitamins, and the use of natural phytoncides, for example, garlic.
In order not to become infected, it is necessary to take precautions: maintain a safe distance, reduce contact during periods of epidemics, wash your hands more often, ventilate the premises, dress according to the weather, avoiding hypothermia.
Vaccination provides the most effective protection against viruses. It is necessary to get vaccinated against influenza every year. You can get a pneumococcal vaccine to prevent severe pneumonia.
Make an appointment with a doctor in Moscow with ARVI symptoms
Get help from a general practitioner for signs of ARVI at the Diagnostic and Treatment Center. With us you can take all the necessary tests within one clinic, quickly receive results and begin treatment. If necessary, the doctor will refer you to another specialist at our multidisciplinary center.
To make an appointment, call us. Registration is available any day, including Saturday and Sunday.
The contents of this article have been checked and confirmed for compliance with medical standards by general practitioner Yulia Vladimirovna Butskikh.
Division by family
One of the families of acute respiratory viral infections is the orthomycoviruses. This family, for example, includes influenza viruses. Doctors note that from a clinical point of view, it is quite logical to include influenza in the classification of ARVI, since this corresponds to the manifestations of pathology. Influenza stands out in a special group because of its ability to lead to epidemics and pandemics.
Exercise for the lungs. Simple workouts for the prevention of ARVI Read more
Another option is parmycoviruses. They include parainfluenza viruses, the clinical picture of which is represented by fever, laryngitis and bronchitis. In children, such viruses lead to severe development of laryngitis with the manifestation of acute swelling and sometimes stenosis, which is popularly called false croup.
The picornavirus family includes 4 genera, the most prominent representatives of which are rhinoviruses and enteroviruses.
The reovirus family often affects newborns under six months of age; adults are less likely to be affected. The manifestations of infection with them are varied, so the diagnosis can often be made using laboratory tests.
The adenovirus family has 47 serotypes, grouped into 7 groups. Some of them can lead to the development of diseases accompanied by inflammation of the pharynx, enlarged tonsils, fever and general intoxication and weakness. The lower respiratory tract may be involved in the pathological process, which leads to manifestations of pneumonia.
Not only ARVI. What can cause a fever? More details