This is a special category of bacterial cultures, many species of which are dangerous to human health. Staphylococci are commonly called opportunistic microbes. Living in the body constantly, they are under the control of the immune system. But when the protection is weakened, they can provoke an inflammatory process. Some bacteria are extremely resistant to antimicrobial agents and often cause superinfections.
What is staphylococcus
It is a nonmotile, spherical, Gram-positive microorganism that forms numerous colonies. Staphylococci are anaerobic - they can exist and reproduce without oxygen, in a closed environment. There are more than twenty strains of bacteria. Some of them are quite harmless, while others cause powerful pathological reactions in the human body. Parts of the body and organs most vulnerable to staphylococci:
- leather;
- mucous membranes;
- connective tissue;
- subcutaneous tissue;
- nerve tissue;
- heart muscle.
By infecting them, microbes produce toxic substances and provoke inflammation, which in severe cases leads to sepsis, irreversible changes in structures or permanent dysfunction.
Types of pathogenic staphylococci
Several types of bacteria are dangerous to humans. The most common:
- Staphylococcus aureus: golden. It got its name because of the characteristic yellow pigment on the surface. Penetrating into the body, it synthesizes the enzyme coagulase and can cause purulent inflammation of almost any internal organs. This type of pathogen quickly adapts to the effects of antibiotics, forming resistant forms.
- Staphylococcus epidermidis: epidermal. It usually affects the skin and mucous membranes. It often becomes a factor in inflammation of injuries, postoperative sutures, the development of purulent conjunctivitis, and respiratory tract infections.
- Staphylococcus saprophyticus: saprophytic. Its specificity: affects the mucous membranes of the urinary organs, provokes cystitis, urethritis, and kidney inflammation.
- Staphylococcus haemolyticus: hemolytic. Dangerous for mucous membranes and tissues of internal organs. It becomes a provocateur of the development of endocarditis, pneumonia, nephritis and other severe pathologies.
Almost all types of pathogenic staphylococci are prone to mutations as a result of improper or insufficiently long treatment.
Material and methods
From 2013 to 2015, 69 patients with PRS aged from 18 to 70 years were examined at the Otorhinolaryngology Center of the Federal State Budgetary Institution FSNKTs FMBA of Russia. All patients were admitted to the hospital for planned surgical treatment (polysinusotomy). The duration of the disease in patients did not exceed 5 years; previous operations for polyposis had not been performed. Before surgery, all patients underwent bacteriological and immunological studies.
To determine the effect of bacterial concentration on the level of eosinophilic inflammation, all patients with PRS were divided into 3 groups depending on the growth of microorganisms: group 1 consisted of 14 patients with poor growth (up to 20 colonies, 103 CFU/ml), group 2 - 28 patients with moderate growth (from 21 to 100 colonies, 104 CFU/ml), group 3 - 27 patients with abundant growth (more than 100 colonies, from 104 CFU/ml).
The control group included 45 healthy volunteers, who also underwent bacteriological and immunological studies.
For bacteriological examination, a smear was taken from the mucous membrane of the middle nasal passage, followed by inoculation of the collected material on nutrient differential diagnostic media (yolk-salt and blood agar). Sowing was carried out using the sector method. They were incubated in a thermostat at a temperature of 37.0 °C for 24 hours. Microorganisms were counted according to the calculation table [9]. For microscopic examination of the native material, Gram staining was used.
The grown colonies were isolated and a pure culture was isolated for further study. Isolated colonies were screened out on meat peptone agar slants to obtain pure cultures and study the characteristics used for identification. The purity of the culture was judged using visual and microscopic control. For species identification of the family Enterobacteriaceae
Endo agar was used. The colonies were microscopically examined, and gram-negative rods were streaked and pricked onto Olkenitsky agar slants. To determine the species, biochemical plates were used that differentiate enterobacteria (NPO Diagnostic Systems, Nizhny Novgorod).
Identification of bacteria of the genus Staphylococcus
was carried out according to the determinant of H.J.
Bergey [10]. For species identification of representatives of the genus Staphylococcus
, the following tests were used: catalase activity, coagulase activity in relation to rabbit plasma, the formation of acetoin, acids from mannitol, maltose, sucrose, lactose and glucose under anaerobic conditions, the presence of urease, β-galoctasidase and oxidase, resistance to novobiacin [11].
The immunological study included studying the level of immunoglobulins and determining the cytokine status.
For these purposes, venous blood was collected from the antecubital vein into test tubes with heparin. To determine the cytokine status, we assessed the concentration level of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin IL-1, IL-6 and IL-8 in the blood serum by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using Vector-Best test systems (JSC "Vector-Best" Best, Novosibirsk). Determination of immunoglobulins was carried out using the method of radial immunodiffusion in a Mancini gel.
Statistical data processing was carried out using Excel spreadsheets based on an IBM P-700 personal computer with the calculation of average values of the obtained indicators. The significance of the differences was determined using the Student and Fisher tests with normal distribution of comparative series.
How does a staphylococcal infection manifest?
Symptoms, its duration and intensity depend on the strain of the pathogen, the general physical condition of the patient and the characteristics of his immunity. Two characteristic signs of staphylococcal damage: inflammation of various localizations and intoxication.
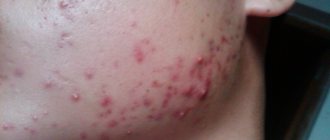
With pyoderma, the sweat, sebaceous glands, and hair follicles become inflamed, causing painful convex nodules that fill with pus to form on the skin. Boils and carbuncles are usually surrounded by areas of red, swollen skin. With intense inflammation, fever and swelling of the lymph nodes located close to the sites of inflammation are likely.
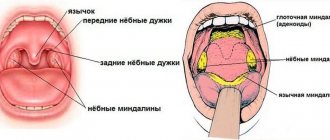
Infection of the nasal sinuses by staphylococcus is manifested by a common runny nose with viscous yellowish or green discharge. Penetration of infection deeper causes the development of sinusitis. Their symptoms are typical:
- congestion in the bridge of the nose;
- feeling of heaviness, fullness on the affected side;
- labored breathing;
- thick purulent discharge from the nose;
- increase in body temperature above +37°C.
Often the infection spreads to the middle ear, causing otitis media: sharp shooting pains, hearing loss. When the mucous membranes of the eyes are damaged, suppuration of the conjunctiva develops, the sclera turns red and swells.
When staphylococcus attacks the upper respiratory tract, purulent pharyngitis or laryngitis is inevitable. Their signs:
- hoarse voice;
- severe swelling, redness of the throat;
- difficult painful swallowing;
- dry obsessive cough, discomfort in the throat.
Staphylococcal pharyngitis often affects children under 12 years of age. In adults, this pathology is controlled by the immune system.
With the development of inflammation in the lower parts of the respiratory tract, bronchitis and pneumonia are “relevant” with a characteristic barking or wet cough, high fever and physical weakness.
Less common signs of staphylococcus infections:
- food poisoning;
- inflammation of joint tissues, muscles;
- cardiac dysfunction.
Among the serious complications caused by staphylococcus are: meningitis, lung abscesses, osteomyelitis, toxic shock syndrome, generalized sepsis.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods of treating Staphylococcus aureus in the nose in adults are used to strengthen the body's protective functions and cleanse the body of toxins. In therapy, decoctions, infusions and tinctures are used. But without taking antibiotics, folk remedies are ineffective.
Plants with immunostimulating effects:
- Echinacea inflorescences;
- rosehip berries and flowers;
- St. John's wort;
- hawthorn.
Herbs can be used one at a time, or preparations can be made from equal amounts of several ingredients. Brew 1 tbsp. l. raw materials 200 ml of boiling water, leave in a closed container for half an hour. Drink 100 ml of infusion twice a day.
In case of frequent exacerbation of staphylococcal infection, mix chopped parsley and celery roots in equal parts. Grind the mixture in a blender, squeeze out the juice. Drink 5 ml before each meal.
If you have Staphylococcus aureus, you should not warm up the area of the nose, forehead and cheeks; visiting saunas and hot baths is contraindicated.
Thermal procedures contribute to the spread of infection throughout the body. What is dangerous is the development of severe consequences and complications. Hypothermia of the head and entire body should also be avoided so as not to further weaken the immune system.
It is imperative to take vitamin complexes with a high content of ascorbic acid and retinol. Honey, apricots, blackcurrants, onions, garlic, and ginger will help strengthen your immune system. These products should be included in the diet during treatment and during epidemics of colds.
Folk remedies for rinsing the nose
From medicinal herbs you can prepare effective solutions for rinsing the nose, clearing mucus, and eliminating swelling. They act no worse than pharmaceutical products and have fewer contraindications and side effects. Medicinal infusions and decoctions are easy to prepare, and the cost of raw materials is affordable.
Recipes:
- Pour 1 tbsp. l. dry chamomile inflorescences 250 ml of boiling water, simmer in a water bath for a quarter of an hour. Cool in a sealed container to a comfortable temperature, strain. Rinse your nose 3-5 times a day, be sure to before using any local medications.
- Brew 220 ml boiling water 2 tbsp. l. linden blossom, leave for 3 hours in a thermos. Use the strained infusion to rinse the nasal passages up to 5 times a day. The product has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, immunomodulatory effects.
- Dissolve 5 g of salt in 1 liter of water. The simplest and most effective antiseptic. Use 3-4 times a day.
You can instill fresh aloe juice into your nose - it is a strong natural antibiotic. Mix juice with honey in equal proportions. Place 2-3 drops in each nostril twice a day. Duration of treatment is 1-2 weeks.
Homemade drops can be prepared from burdock or comfrey root. Pour 200 ml of water 2 tbsp. l. raw materials, heat in a water bath for 20 minutes. Cool, strain. Place 5 drops in each nostril three times a day.
How to treat staphylococcus
An accurate diagnosis—whether the microbe is to blame for the pathology—can be established only after laboratory analysis. It is not difficult to detect and identify it in urine samples, smears and scrapings from the skin and mucous membranes. But getting rid of the infection is much more difficult. The notorious Staphylococcus aurum (aurum) is extremely resistant to disinfectants, including bleach and brilliant green. Almost 15% of all cases of infection occur inside hospitals.
The use of antibiotics is also not always justified. For example, staphylococci adapt to penicillins very quickly. And golden has long been resistant to them, as to many other medications. To quickly suppress the activity of pathogens, combinations of various groups of drugs are used. Relatively new and effective: macrolides and fluoroquinolones. Medicines in these categories destroy and destroy the protein membranes of bacteria, not giving them time to develop resistance.
For therapy to be effective, it is important to use antimicrobial agents only as prescribed by a doctor and strictly follow the prescribed regimen. It is forbidden to interrupt the course at your own discretion, change one drug to another without permission, or adjust the dosage.
To prevent infection, general hygiene rules must be observed. It is important to avoid eating untested products, sanitize the oral cavity in a timely manner, and treat a runny nose. It is useful to harden yourself and take immunomodulators. And most importantly, do not use antimicrobial agents without good reason.
Diagnostics
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to conduct a high-quality diagnosis. The main analysis that is used in medical practice when the presence of a pathogenic bacteria is suspected is their isolation using bacterial culture. However, the patient will need to prepare for the study in order to obtain the most reliable result.
Firstly, you should stop using any nasal drops on this day. Secondly, do not undergo treatment with any antibacterial agents for at least a week. The only drawback of this method is that you will have to wait at least five days for the results.
If the diagnosis needs to be made faster, then the microscopic method of smear analysis comes to the rescue. But in contrast to this, the cultural method of research, namely bacterial culture, will not only clarify the data obtained, but also identify a specific type of bacterium, and also supplement the information with an antibiogram.
After the results have been received and staphylococci have been detected in the nose in an amount exceeding the maximum mark of 106 units, it is necessary to begin treatment.