Dentists recommend undergoing preventive examinations at least once a year and, if caries is detected, treating it at an early stage. Unfortunately, many patients go to the doctor with an advanced form of the disease. In this article we will tell you why and how deep caries occurs, and we will tell you about treatment methods.
In this article
- Areas affected by caries and stages of the disease
- Deep caries and its features
- Risk factors for deep caries
- Forms of deep caries
- Features of diagnosing deep caries
- How can deep caries be cured?
- Conclusion
Areas affected by caries and stages of the disease
Caries is a dental disease in which, under the influence of microorganisms and other factors, the structure of dental tissues is destroyed.
The mechanism of development of the disease is due to the vital activity of bacteria Streptococcus mutans and some other species. They have a cariogenic effect and create conditions for the development of the carious process. It goes like this. Bacteria accumulate on teeth and form a biological film called plaque. When we eat foods rich in carbohydrates, plaque bacteria actively process the sugars they contain and produce organic acids that are dangerous to our teeth. They destroy the enamel structure, deprive it of minerals, and penetrate deep into the tooth. The more acids produced by oral microorganisms, the more active and rapid the destruction of dental tissue.
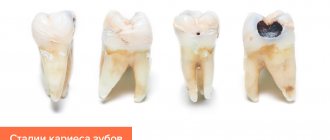
Damage to teeth by caries does not occur instantly; it can take several months from a small spot to the appearance of a hole in the tooth. Based on how deeply the carious process penetrates, several stages of the disease are distinguished.
- The earliest is the spot stage.
A small focus of demineralization appears on the surface of the enamel. It looks like a whitish dot or streak. It is almost impossible to notice such changes with the naked eye. And provided that there are no other symptoms (pain or discomfort) at this stage, a person often misses the onset of caries and does not see a doctor.
- Superficial caries.
If the stain was not noticed in time, it gradually grows, the enamel tissue is destroyed, and a cavity is formed in it - a small hole. As a rule, there is still no pain, although food may get into the cavity or tooth sensitivity may increase.
- Average caries.
The form of average caries is characterized by the penetration of the pathological process into dentin - the bone tissue under the enamel. At this stage, a carious cavity forms in the dentin, pain becomes severe, and the tooth reacts to temperature or taste stimuli. Most often, people go to the dentist with the listed symptoms.
- Deep caries.
If for some reason you do not treat average caries, the pathology progresses and approaches the pulp - the dental nerve. This is the most complex and dangerous form of caries, because there is a high risk of infection spreading to the pulp, periodontium and the development of complications.
Prevention of caries complications
Having encountered such a problem at least once, most likely, you will no longer want to exhaust your body with toothache and shell out decent sums for complex treatment. Therefore, you should not neglect preventive measures: visit the dentist once every six months and carry out hygienic cleaning. If, nevertheless, a hole has formed in the tooth and it becomes ill, you should choose a doctor with extreme caution. Remember that the result of poor treatment will be a more serious complication of caries, which may require surgery, and, worse, tooth extraction. In addition, complicated caries requires more expensive treatment than its initial formations.
Agree, you never thought that such harmless caries can cause serious consequences, including tooth extraction. Now think about what is cheaper, faster and more painless - going to the dentist for an appointment twice a year or postponing this moment for several years, then heading straight to the dentist’s office? It’s up to you to decide, of course, but life is given to enjoy joyful moments, and not to endure toothache. And dentists are ready to help us with this!
Deep caries and its features
Deep caries is always an advanced pathological process. It cannot arise instantly, in a few days. As a rule, the deep form of caries develops over many months, sometimes years. In this case, the person does not consult a doctor and does not take measures to treat the carious process.
The main feature and at the same time the danger of deep caries is that it is located in close proximity to the pulp - the neurovascular bundle - and creates a threat of the development of pulpitis and periodontitis. The risk of infection spreading to other organs and tissues, as well as tooth loss, increases.
The following symptoms are characteristic of deep caries:
- Aching pain in the area of the affected tooth, which intensifies from hot, cold or when biting. Acute pain with deep caries can occur when a lot of food debris accumulates in the carious cavity.
- Bad breath. Even regular brushing of teeth in compliance with all the rules does not lead to the disappearance of the odor, since it arises due to decay processes in the affected tooth.
- A large hole in the crown of a tooth is the most obvious sign of deep caries.
Dentists note that often with deep caries the patient has no complaints. But this does not reduce the risk of complications.
How to treat caries
You may have heard the term “blooming caries” from dentists. The name “blooming” was given to caries, which turns into the form of acute caries, when the disease affects several or all incisors at once. The appearance of blooming caries in adults is a loud signal about serious problems in the human body. How the complex treatment works 1. Preparation with a drill using local anesthesia. This is necessary to clean softened dental tissues.
Many patients are afraid of this process, explaining that the machine is too noisy and tooth brushing is painful. At the moment, the EliteDental M clinic has installed modern medical equipment with a quiet mode. And patients no longer experience discomfort with this treatment method.
2. Rinse the mouth with a weak antiseptic solution. Usually, chlorhexidine or hydrogen peroxide. 3. Filling the depressions in the incisors caused by caries with filling material. To restore minerals in the body, saliva and teeth, vitamin therapy is prescribed. The use of immunomodulators, which comprehensively restore the human immune system, is also encouraged.
Refrain from using vitamins on your own without a doctor’s prescription and testing. Excess vitamins are poorly accepted by the body, which can result in side effects. It is better to consult a doctor for the correct dosage of vitamins and a prescription. Remember: with any form of caries, it is important to work to eliminate the root cause of its development. Therefore, do not be surprised if your dentist prescribes a visit to an endocrinologist, gastroenterologist or immunologist.
Risk factors for deep caries
Deep tooth decay with caries most often occurs in the presence of the following risk factors:
- Poor oral hygiene.
- Abuse of sweet and carbohydrate foods.
- Lack of calcium, fluorine, phosphorus, vitamin D in the body.
- Chronic pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine and immune systems.
- Genetic background.
And, of course, one of the main reasons for the development of deep caries is late diagnosis and untimely treatment.
Forms of deep caries
Deep caries can occur in two forms - acute and chronic. Each has its own characteristics. Acute deep caries is characterized by rapid development and can affect a large area of the tooth in a short time. Upon superficial examination, the cavity in the tooth appears small. But further diagnostics show that this is deep-stage caries, and it has almost reached the tooth root. It is acute caries that is most often accompanied by a complication in the form of pulpitis. Therefore, when treating it, the dentist has to not only prepare the tooth and put a filling on the dental crown, but also remove the nerve and fill the canals.
Chronic deep caries, unlike acute caries, is a slow, sluggish process. Although most of the tooth with this form is destroyed, the carious cavity is smaller in area than with acute caries. The patient may complain of periodic aching pain, which does not depend on external stimuli and occurs on its own.
Depending on the affected area, deep caries can be divided into cervical, fissure or located on the front incisors.
Based on the speed of development of the pathological process, it is divided into compensated (relatively slow development), subcompensated (with an average speed of development) and decompensated (with a high speed of development). Objectively, any form of deep caries can be cured, but it will require varying amounts of time and effort.
Treatment of deep dental caries with pulp damage
When infection penetrates into the pulp chamber, in the vast majority of cases, tooth depulpation and root canal cleaning are performed. There are methods for complete or partial preservation of the pulp (biological and vital methods of treating pulpitis), however, conservative treatment is possible only at the very early stages of the disease and does not always guarantee a 100% result. After depulpation of the canals, depending on the extent of the damage, the doctor chooses the method of treatment.
- Classic filling of deep caries.
- Installation of filling and stump inlay.
- Crown installation (orthopedic treatment).
Features of diagnosing deep caries
Advanced caries often has the same clinical picture as pulpitis and some other dental diseases. Therefore, before starting treatment, the doctor must conduct a differential diagnosis and understand which pathology to treat.
Deep caries can be distinguished from focal pulpitis by a number of symptoms. With pulpitis, probing the cavity with a dental probe will cause pain only in one area - in the area of the pulp, while with deep caries pain occurs over the entire surface of the tooth.
The probing procedure will also help to distinguish deep caries from medium ones. On average, it is almost painless, because a fairly thick layer of dentin remains between the sensitive pulp and the bottom of the carious cavity. With a deep form, the tooth reacts to probing with severe pain. The method of electroodontodiagnostics helps to distinguish deep caries from fibrous pulpitis. In most cases, the doctor will order an x-ray to confirm the diagnosis.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of deep caries is carried out using a visual examination by a dentist-therapist, collection of anamnesis and complaints, as well as instrumental examination. The doctor notes visible destruction of the crown part of the tooth.
In the acute form of the disease, it reveals a deep cavity filled with light, soft dentin. Instrumental examination consists of immersing a dental probe into the cavity - its bottom is sensitive, so attempts may cause pain.
In the chronic form of deep caries, the walls and bottom of the cavity are filled with pigmented dentin of a denser structure. Its color can range from brown to black. Probing the cavity does not cause pain - this is due to the formation of secondary dentin. Tapping a tooth is also not accompanied by pain.
The doctor may also use the thermodiagnostic method. This allows you to evaluate the nature of the reaction to hot and cold. Electroodontodiagnosis allows us to identify the reaction of the pulp to the influence of a current of 2–6 μA. In some cases, a decrease in pulp excitability is observed.
If the doctor suspects secondary deep caries, radiovisiography or x-ray diagnostics will be required. The image will allow you to assess the depth of the lesion, the presence or absence of an inflammatory process in other tissues, including periodontal tissues. On a targeted image, you can see 1-3 teeth, and with the help of special computer programs, the doctor has the opportunity to enlarge the area under study for detailed analysis. On an x-ray, caries appears as a dark spot.
The basis of diagnosis in general is the differentiation of deep caries from other diseases with similar symptoms - some forms of pulpitis, chronic periodontitis, moderate caries.
How can deep caries be cured?
A disease such as deep caries can be treated in one or two visits.
The first option is carried out according to this scheme:
- The doctor numbs the affected tooth with a local anesthetic.
- Opens the carious cavity and, using a drill, cleans it of dead and diseased tissue until dense walls and bottom remain.
- If caries is complicated by pulpitis, endodontic treatment is carried out, that is, the dental canals are filled.
- To treat inflammation, isolate the sensitive pulp from the effects of filling material, and build up dentin, a therapeutic or insulating pad is placed at the bottom of the cavity.
- After all the above manipulations, the tooth is closed with a filling.
Treatment in two visits is carried out according to this scheme.
During the first visit, pain relief is performed, the cavity is opened and the affected tissue is removed. A medical pad is placed in the cavity and closed with a temporary filling. On the second visit after a few days or weeks, if the patient has no complaints, the temporary filling is replaced with a permanent one.
Treatment in two visits is considered preferable because it is possible to observe the condition of the tooth before installing a permanent filling. If pain, discomfort and other symptoms occur, additional therapeutic procedures can be performed to ensure that the affected tissue is completely removed. When treating a tooth in two visits, complications and relapses of caries occur much less frequently.