Intestinal dyskinesia - symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prevention
Details Author: LDC Neuron Published: November 10, 2015
Sometimes we say, we will never get sick with this, or, we live in a different environment and zone... but we are deeply mistaken, for this disease, namely for intestinal dyskinesia, there is neither distance nor barriers, and anyone can get sick with this insidious disease. But in this article we will look at both its symptoms and how to treat intestinal dyskinesia at home!
Causes of intestinal diseases:
- long-term and severe violation of the diet
- alcohol abuse
- food allergy
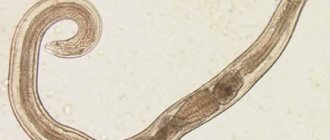
- intestinal infections and parasites (salmonella, lamblia, intestinal escherichia, helminths)
- chronic poisoning with compounds of lead, mercury, phosphorus, arsenic
- radiation damage
- uncontrolled use of medications (antibiotics, laxatives, etc.)
Intestinal diseases are promoted by a sedentary lifestyle, emotional and mental stress, and stress.
Symptoms of intestinal dyskinesia
Intestinal dyskinesia is manifested by a number of negative “surprises”, which can differ significantly in symptoms from person to person. First of all, patients are annoyed by a variety of pain and bloating in the abdomen. It can be a cutting, aching, dull, boring pain that lasts from several minutes to several hours. It is difficult for the patient to say where exactly the pain manifests itself; he notes that such sensations appear “in the whole abdomen.” Painful sensations very often stop when a person falls asleep, and resume again after waking up. In some cases, rumbling in the stomach and bloating are practically the only signs of the disease. The occurrence of these symptoms does not depend on what food a person eats.
Diagnostics
Before treating dyskinesia, doctors at the Euromedprestige clinic conduct diagnostics of the patient, aimed at determining the form of the disease and identifying foci of infection. The most important point during the examination is the initial examination, during which the bladder is palpated to identify its soreness.
To accurately determine the form of pathology, blood tests, abdominal ultrasound and cholecystography are prescribed. To establish changes in the contractile activity of the bile ducts, duodenal zoning or magnetic resonance cholangiography may be required.
Diagnosis of intestinal dyskinesia in children
Well, the treatment itself, intestinal dyskinesia is successfully treated with the use of psychotropic drugs, such as tranquilizers, antipsychotics, antidepressants, plus psychotherapy sessions. Effective will be drugs that have a general strengthening effect on the central nervous system, which, in turn, helps to normalize the functioning of the autonomic nervous system and reduce the level of excitability of the intestinal muscles. In this case, the prescription of medications, as well as the choice of tactics for psychotherapeutic assistance, is carried out by a specialist of the appropriate profile. It is important to note that psychotropic drugs are not recommended for long-term use.
LDC "Neuron"
- < Back
- Forward >
Biliary dyskinesia
Among the many causes of abdominal pain, dyskinetic biliary tract disorders (BBD) stand out. This is one of the most popular diagnoses among therapists in clinics - and at the same time, many cases of ADHD remain undiagnosed. What is the difficulty and how to make a diagnosis?
Bile activity: norm and disorders
Bile (a thick, bitter liquid produced by liver cells) is actually one of our digestive juices. It takes part in the intestinal phase of digestion, helping to break down fats.
In addition, it inactivates pepsin, “brought” by semi-digested food from the stomach, otherwise it reduces the activity of pancreatic enzymes necessary for further digestion. Produced in the liver, bile enters the gallbladder through the hepatic duct system - there it accumulates and “ripens”, becoming more concentrated.
Read also: Diet for gallstone disease
As soon as a portion of food from the stomach enters the duodenum, cystic bile is “added” to it through the common bile duct. The hepatic bile ducts, gallbladder, common bile duct and the circular sphincter muscles that separate them together make up the bile ducts.
When the coordinated work of these structures is disrupted, a condition called dyskinesia occurs (“dis” - disorder, “kinesio” - movement). Today, there are two main variants of JVP.
Hyperkinetic variant: stress and acute pain
With hyperkinetic GIB, bile, especially not remaining in the bladder, enters the intestine at an accelerated pace, and not on “demand”. In this case, firstly, the efficiency of digestion decreases, since immature bile that has not settled in the gallbladder has low chemical activity. Secondly, there is an increased and almost continuous contraction of the muscles of the ductal system.
Disorders in the movement of bile are usually provoked by fatty foods and - this is important! - stress. The muscles of the biliary tract are controlled by the autonomic nervous system. When its sympathetic (adrenaline, “stress”) part is activated, muscle contractions intensify and accelerate.
The patient experiences sharp stabbing pain in the right hypochondrium. Inadequate digestion leads to stool disturbances and lack of nutrients. However, the general condition deteriorates little, the patients do not lose their ability to work and vital activity and are not very inclined to a thoughtful diagnostic search.
Hypokinetic option: immobility and long-term pain
Here everything is exactly the opposite: bile is released slowly, remains in the gallbladder for a long time, and its concentration increases more than necessary. The bile ducts seem to be “lazy” to deliver bile to the intestines. Actually, one of the main reasons for this type of ADHD is a sedentary lifestyle.
The pain syndrome with this option looks different: the pain is dull, aching, “spread out” - that is, it can spread throughout the entire abdomen. In some cases, there may be no actual pain, but discomfort is manifested by a feeling of fullness, distension in the right hypochondrium.
The duration of unpleasant sensations reaches several hours (whereas with the hyperkinetic version - usually no more than half an hour). Here, patients are already seriously thinking about solving the problem and finally decide to visit a doctor to get a diagnosis.
How to make a diagnosis
It must be said that with moderately severe JVP, the clinic—that is, the patient’s complaints—is not very specific. Pain and heaviness in the abdomen, transient stool disorders can accompany many other diseases, not always even related to the gastrointestinal tract! However, to confirm the diagnosis in this case, there is an available technique - ultrasound with functional tests.
One of the most common causes of gallbladder gallstones is a violation of the anatomical structure: a change in the shape of the gallbladder, the presence of septa in it, sometimes even doubling. These changes, which impair the flow of bile, occur in at least 25–30% of people (which is why episodes of pain in the right hypochondrium are familiar to many).
Therefore, signs of VADP can often be detected on an ultrasound by a simple examination, but a special test is needed to study motor skills. First, the gallbladder is measured and examined on an empty stomach, and then the patient is offered a so-called “test breakfast” (usually two raw yolks). After eating breakfast, the bladder is measured again at certain intervals, monitoring the change in its shape and volume.
An x-ray examination is performed in a similar way, but it requires special preparation. Bile needs contrast, so first the patient takes special tablets (or receives an intravenous injection). But the probe method is practically not used today - it is very uncomfortable for the patient.
***
What can you do to avoid getting caught by doctors for all this complicated diagnostics? Methods for preventing ADHD are quite simple. You need regular physical activity, a healthy diet, a proper daily routine and, of course, you should take care of your nerves to prevent hyperkinetic dyskinesia.
Lidiya Kulikova
Photo istockphoto.com
General information
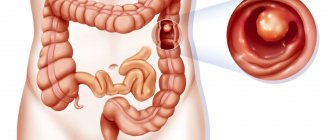
Intestinal dyskinesia is a term that defines a complex of intestinal disorders that arise as a result of disturbances in the motor functions of the intestines. Mostly such disorders occur in the colon .
Intestinal dyskinesia is characterized by the absence of organic changes, but the organ cannot perform its functions normally. According to the World Health Organization, about a third of all people on the planet suffer from this disease. In most cases, the disease is typical for women.
When is a bowel examination necessary?
- weight loss and dehydration caused by diarrhea
- nausea that lasts for a long time
- abdominal pain accompanied by fever
- mucus, blood, or pus in the stool
- change in stool properties (frequency, color, consistency)
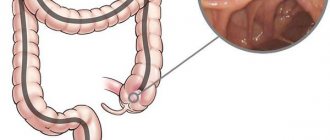
In all the variety of intestinal diseases, one can identify characteristic symptoms characteristic of the pathology of the small and large intestines. Diseases of the small intestine are characterized by diarrhea 4 or more times a day, flatulence, pain in the navel, and weight loss. Such diseases are characterized by damage to other organs and systems and metabolic disorders. Diseases of the colon are characterized by pain in the intestines, false urge to defecate, flatulence, alternating diarrhea and constipation, and mucus in the stool. Body weight remains the same or increases; the patient's general condition suffers little.
Diet, nutrition for intestinal dyskinesia
Diet Table No. 3
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 5-7 days
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of products: 1200-1300 rubles per week
Diet for the intestines
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 1-2 months
- Terms: from 1 month/permanently
- Cost of products: 1600-1700 rubles. in Week
Diet for indigestion
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 20 days
- Terms: from 2 months or more
- Cost of products: 1400-1500 rubles. in Week
If you follow the principles of the diet for intestinal dyskinesia, the disease bothers patients much less. First of all, all food should be boiled or steamed, and the food should not be chopped. To stimulate intestinal motility, you should include in your diet berries, fruits, and vegetables that have the ability to enhance the evacuation function of the intestines and do not cause fermentation and do not irritate the intestinal mucosa.
For different types of dyskinesia, it is necessary to follow a diet that corresponds to the type of intestinal motility. So, if a person suffers from hypomotor dyskinesia of the colon , then foods high in fiber should be included in the daily diet. First of all, these are vegetables - beets, carrots, cabbage, zucchini, tomatoes, herbs. At the same time, vegetables that contain a lot of essential oils are best excluded from the diet. These are onions, radishes, turnips, radishes, mushrooms. It is best to eat bread with bran, made from wholemeal flour; cereal porridge boiled in water is useful. The diet also includes soups, which should be cooked in low-fat and vegetable broths. Lean meat is allowed, fish, eggs can be eaten periodically, but no more than two pieces per day. In addition, you should consume fruit and vegetable juices, dried fruits, bananas and apples every day. The organic acids contained in these products help stimulate intestinal motility. Fermented milk products are no less useful, especially those that contain a live culture of bifidobacteria . In order to stimulate regular bowel movements, you should eat cold foods. You can consume wheat bran in its pure form for some time - it is recommended to eat it regularly for about six weeks. They should be poured with boiling water and can be consumed either on their own or added to a variety of dishes. This helps make bowel movements easier.
People who suffer from hypermotor dyskinesia are advised to regularly consume oils, both a variety of plant and animal oils. You should avoid baked goods, white bread, starchy foods, fatty meats, spicy and canned foods, strong tea and coffee. You also need to be very careful with products that contribute to increased gas formation. In the case of hypermotor dyskinesia of the colon, it is very important to follow a special slag-free diet that contains a lot of vegetable fats. At the same time, foods that contain a lot of fiber should be excluded, as they can cause increased spasticity and pain in the abdomen.
If intestinal motor functions improve, then you can gradually begin to introduce boiled vegetables into the diet, and later move on to the gradual consumption of raw vegetables.
List of sources
- Maev I.V. Irritable bowel syndrome: a manual for doctors / I.V. Maev, S.V. Cheryomushkin. - M., 2012.
- Ivashkin V.T., Komarov F.I., Rapoport S.I. A short guide to gastroenterology. M.: M-Vesti Publishing House LLC, 2001.
- Callie E. Digestive system: diseases and their treatment. - St. Petersburg: Norint, 2000.
- Grigoriev P.Ya., Yakovenko A.V. Clinical gastroenterology. M., 1998.
- Gracheva N.M., Yushchuk N.D., Chuprinina R.P. and others. Intestinal dysbacteriosis, causes, diagnosis, use of bacterial biological preparations: A manual for doctors and students. M., 1999.