Why is inflammation of the intestinal walls dangerous?
Recently, the number of Russians diagnosed with IBD has increased annually by an average of 10–12%. Most often, residents of modern megacities suffer from ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. In the first case, the mucous membrane of the colon is affected, and in the second, the end of the small intestine and the beginning of the large intestine. Inflammation leads to the formation of bleeding ulcers and progresses rapidly, leading to irreversible tissue damage if undiagnosed and treated.
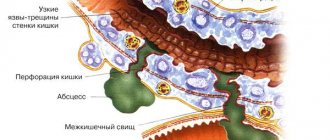
- Patients with Crohn's disease have a significantly increased risk of intestinal obstruction and, as a result, fistula formation.
- Massive bleeding in ulcerative colitis can cause intestinal perforation and life-threatening peritonitis.
- Finally, IBD is recognized as one of the factors that significantly increases the likelihood of tumor formation in the intestine.
Even at the initial stage, intestinal diseases manifest themselves with unpleasant symptoms that significantly reduce the quality of life.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammatory process involving the entire intestine or part of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). This usually leads to abdominal pain and diarrhea, and sometimes extraintestinal symptoms may occur: inflammation of the joints, skin rashes, inflammatory eye lesions.
The causes of this pathology are still not precisely known, although the involvement of the immune system and genetic factors is assumed.
The main inflammatory bowel diseases are ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease.
They also include collagenous and lymphocytic colitis, but they are usually considered separately from the main types of IBD.
The course of IBD can be long and debilitating; in addition, life-threatening complications sometimes occur: bleeding, the development of an oncological process, inflammation of the abdominal cavity due to intestinal contents entering it through a defect in the intestinal wall.
Drug therapy is often successful, leading to the disappearance of symptoms for a long time. If it is ineffective, surgical treatment is performed.
Synonyms Russian
IBD.
English synonyms
Inflammatory bowel disease, IBD.
Symptoms
Manifestations of the disease depend on the severity of the process and its location. In addition, there are periods of remission (complete disappearance of symptoms) that last for months or even years.
The most common symptoms of IBD are:
- chronic diarrhea with blood in the stool, sometimes mucus,
- abdominal pain, possibly cramping in nature,
- intestinal bleeding (more typical for Crohn's disease),
- feeling of incomplete bowel movement and false urge to defecate,
- anal fissures (characteristic of ulcerative colitis),
- fistulas (pathological passages connecting the intestine with the external environment or with another intestine in the wrong place; typical for Crohn's disease)
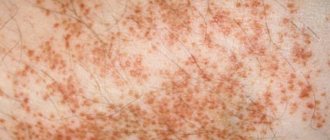
In addition, there are a number of extraintestinal symptoms:
- general weakness and malaise,
- temperature increase,
- loss of appetite and body weight,
- anemia due to bleeding and impaired iron absorption.
Sometimes joint pain, inflammatory eye lesions, red, bumpy, painful rashes appear on any part of the skin.
General information about the disease
Inflammatory bowel diseases are chronic, recurrent diseases that affect the gastrointestinal mucosa.
Currently, the cause of IBD is not completely known. They are believed to be mainly caused by:
- disorders in the immune system, leading to its increased activity and excessive production of antibodies (protective factors) against cells of the own mucous membrane,
- genetic factors, which is why people whose relatives had it are more susceptible to IBD.
Additionally, stress and dietary patterns may increase the risk of IBD.
The main forms of this pathology are ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. In ulcerative colitis, the pathological process is localized in the colon, the inflammation is continuous and affects only the upper layers of the mucous membrane, without penetrating deep into the tissue.
In Crohn's disease, any part of the gastrointestinal tract can be affected, from the oral cavity to the rectum; inflammation penetrates deep into the tissue and is characterized by segmental damage to the mucous membrane.
Chronic inflammation leads to impaired digestion and absorption of nutrients (malabsorption), as a result of which the level of microelements, glucose, protein, and vitamins in the blood decreases, which can cause depletion of the body.
Who is at risk?
- Persons whose relatives suffered from inflammatory bowel diseases.
- Young people under 30 years old.
- Smokers (smoking negatively affects the course of Crohn's disease, but quitting it can provoke its exacerbation).
- People who frequently take painkillers (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) such as ibuprofen, naproxen, aspirin.
- Residents of megacities.
Diagnostics
If you have symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease, especially frequent, loose, bloody stools or severe abdominal pain, you should consult a doctor.
The electrolyte composition of the blood may change, the level of total protein, glucose, and vitamins may decrease. In a general blood test, a decrease in hemoglobin is likely, indicating the development of anemia and/or an increase in the level of leukocytes, which indicates an infection.
A stool examination is also used to detect digestive disorders and invisible amounts of blood in the stool.
The doctor may prescribe an X-ray or endoscopic examination of the intestine, the latter allows you to take a biopsy (a piece of intestinal mucosa) for examination under a microscope, which often helps to make a final diagnosis.
Treatment
The basis of treatment is the prescription of drugs that suppress the activity of the immune system. The synthesis of antibodies to the intestinal mucosa and the activity of inflammation are reduced.
If there is no effect of therapy, a consultation with a surgeon is necessary to decide on surgical treatment.
Recommended tests
- Complete blood count (without leukocyte formula and ESR)
- Serum albumin
- Total protein in whey
- Serum iron
- Potassium, sodium, chlorine in serum
- Serum calcium
- Plasma glucose
- Diagnosis of inflammatory bowel diseases (antibodies to intestinal goblet cells and pancreatic ducts)
- Coprogram
- Histological examination of biopsy diagnostic material
IBD in children: growth and development of the body is at risk
Ulcerative colitis in children can appear even before the age of one year and very quickly lead to total damage to the colon. If left untreated, the disease can result in a serious disruption of the physiological process of development of the child’s body: growth retardation or retardation in physical development. If endocrine pathology is not detected, a good pediatrician will definitely prescribe a gastrointestinal tract diagnosis for the child. In addition, this pathology causes serious psychological problems in both children and schoolchildren.
Crohn's disease - symptoms and treatment
The diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture, course of the disease and diagnostic methods: laboratory examination, endoscopy, histology and radiology.
Laboratory research
The initial laboratory examination, in addition to standard tests (general blood and urine tests), includes the determination of inflammatory markers. First of all, the level of C-reactive protein is assessed - an indicator of tissue damage during inflammation.
Fecal calprotectin and lactoferrin are tested to distinguish inflammation from functional complaints, as these proteins are markers of intestinal inflammation. Calprotectin can help differentiate inflammatory bowel disease from irritable bowel syndrome in most cases. However, these tests are not specific for Crohn's disease, so they are mainly used to monitor patients during and after treatment.
Albumin is a parameter characterizing the ratio of muscle and fat mass; its determination is especially important in the preoperative period, since low concentrations are associated with a higher risk of complications.
Endoscopy
To establish the diagnosis, ileocolonoscopy and multifocal biopsy are performed from the terminal ileum and each segment of the colon. During ileocolonoscopy, the doctor examines the rectum, sigmoid and colon, which form the large intestine, as well as the ileum.
Endoscopy is also used to exclude damage to the upper gastrointestinal tract and in the postoperative period [2].
Radiation research methods
Ultrasound examination is indicated for acute conditions, as well as for identifying fistulas, stenoses, abscesses and for monitoring intestinal inflammation during treatment.
A plain radiograph is used in emergency situations, such as intestinal obstruction and perforation.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and CT enterography (computed tomography) for Crohn's disease accurately detect intestinal lesions and complications such as fistulas and abscesses. MRI and CT are performed during the initial examination if there is a high suspicion of Crohn's disease.
MRI is not exposed to radiation, so it is preferable to CT.
Computed tomography is used in cases where surgical intervention is planned, such as drainage of an abscess [9].
In rare situations when standard imaging methods are uninformative, capsule endoscopy is used to clarify.
Double-balloon enteroscopy is indicated only when a biopsy is required (eg, to exclude malignancy) or during therapeutic procedures, such as dilation of a stenosis.
MRI is the main method for perianal lesions. An alternative to MRI is endosonography, but it is used less frequently due to anal stenosis, which limits access, and pain, especially with severe perianal lesions.
Differential diagnosis
The main diagnoses with which it is necessary to distinguish Crohn's disease are: irritable bowel syndrome, ulcerative and infectious colitis.
For acute pain in the lower abdomen, the most important differential diagnoses are acute appendicitis and the infectious disease yersiniosis (pseudotuberculosis).
Granulomatous chronic intestinal inflammation can be caused by the systemic inflammatory disease sarcoidosis or tuberculosis. Malignant lymphomas and small bowel cancer sometimes lead to the development of small bowel stenosis and the formation of conglomerates of intestinal loops - these diagnoses should also be differentiated from Crohn's disease.
Symptoms of intestinal diseases: when should you see a doctor?
The disease often manifests itself with intimate symptoms, which the majority of patients try to fight on their own, without rushing to a paid appointment with a proctologist or gastroenterologist. In addition, intestinal inflammation is often accompanied by “masking” symptoms: for example, only stomatitis, as in Crohn's disease, or only inflammation around the anus - perianal dermatitis, or lesions of the eyes or joints. Therefore, the patient often comes to the doctor with a severe form, when the path to recovery turns out to be both longer and more financially expensive.
The following signs should alert anyone:
- frequent diarrhea - up to 15–20 times a day;
- pain and/or cramping in the abdominal area;
- weakness, increased fatigue;
- loss of appetite and noticeable weight loss;
- temperature increase;
- the appearance of traces of blood in the stool.
The likelihood of damage to the large and small intestines is increased in people who regularly and in large quantities consume dark varieties of meat and processed products (sausages, sausage, ham, bacon, etc.). But you should know that adherence to a diet with a predominance of vegetables, fruits, and foods made from whole grains is not a panacea.
A genetic factor plays a certain role: the tendency to intestinal inflammation can be inherited. Among the sick people, people who abuse smoking predominate. Also important are the lack of vitamin D in the body and frequent and uncontrolled self-administration of antipyretic medications.
An appointment with a proctologist in Moscow is recommended not only for people with unstable stools. In order not to fill the army of colorectal cancer patients, even a generally healthy person after 45 years of age should visit a doctor at least once every five years for preventive purposes. The absence of visible signs of inflammation does not exclude the possibility of a hidden disease. Symptoms of intestinal cancer detected at an early stage allow doctors to save the patient and achieve stable remission.
Diseases of the small intestine
The final process of food digestion occurs in the small intestine, followed by the absorption of digestive substances, vitamins and minerals. Various diseases of the small intestine manifest themselves in the same way. Most often, our doctor in this case diagnoses “poor absorption syndrome.”
Manifestations of the disease that you may notice in yourself
Diseases of the small intestine usually manifest themselves:
- stool disorders
- rumbling and bloating
- pain.
The most common manifestation is diarrhea 3-6 times a day. Pain occurs in the navel area, sometimes in the epigastric region or the right half of the abdomen. They are most often pulling, aching, bursting and decrease after the passage of gas. There may be intestinal colic: very severe pain with intestinal spasms.
Small intestine: briefly about diseases
Chronic enteritis is inflammation of the small intestine. The causative agents of acute intestinal diseases play a primary role in its occurrence. Enteritis itself is often a post-infectious process. Vascular diseases : abdominal pain that occurs after eating, stool disorders. Timely contact with a professional is very important, since complete blockage of blood vessels may occur. Allergies manifested by intestinal disorders. Celiac enteropathy : deficiency of the enzyme peptidase, which breaks down gluten, a protein ingredient in grain plants; The disease manifests itself as severe diarrhea and weight loss. A rare Whipple's disease , characterized by severe diarrhea, fever, cramping abdominal pain, weight loss, and enlarged lymph nodes. Tumors are mostly benign.
Colon diseases
Colon diseases are:
- ulcerative colitis
- ischemic colitis
- Crohn's disease
- irritable colon
- dolichosigma, megacolon
- diverticulosis
- colon tumors.
Symptoms you may notice
- stool disorders
- stomach ache
- pathological discharge
- rumbling and bloating.
Stool disorders: constipation is more common. Pain in the anus, sides of the abdomen, above the navel or in the epigastric region. The pain is cramping or aching, bursting and is usually not associated with eating. They weaken after bowel movements and the passage of gases.
Large intestine: briefly about diseases
Ulcerative colitis affects the mucous membrane. Dangerous due to the possible development of polyps and tumors. Irritable colon is a complex of intestinal disorders due to disruption of intestinal motility. Crohn's disease : the entire intestine, esophagus, and stomach are affected. With ischemic colitis, inflammation occurs due to narrowing of the vessels that nourish the intestinal walls. Diverticulosis means the presence of multiple diverticula (ending in blind pouch-like protrusions of limited areas of the intestine) and leads to constipation. Dolichosigma - elongation of the sigmoid colon; megacolon - expansion of individual zones or the entire colon. Both diseases cause persistent constipation. Of benign and malignant neoplasms, the latter are more common. Now colon and rectal cancer is the most common malignant tumor.
How are inflammatory diseases and bowel cancer diagnosed?
The specialists of the multidisciplinary clinic “Trit” are proficient in all the techniques that allow them to identify even the smallest changes in the intestinal mucosa.
- An ultrasound examination is performed to detect thickening of the walls of the large and small intestine and narrowing of their lumen.
- Ultrasound with Doppler function allows you to check blood flow parameters.
- If necessary, an MRI OR CT scan is prescribed, as well as an x-ray examination.
- To detect blood in the stool, indicating the presence of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, laboratory tests are performed (including determination of fecal transferrin and hemoglobin).
The “gold standard” of research is a modern endoscopic technique, intestinal colonoscopy under anesthesia. If the patient has extraintestinal manifestations of the disease, doctors of relevant specialties - an ophthalmologist, dermatologist or rheumatologist - are also involved in the diagnosis.
The main signs of diseases of the small and large intestines
Doctors, as a rule, group the symptoms of gastrointestinal disorders. First of all, this is pain in the abdomen, followed by stool disturbances, which include constipation and diarrhea. Visual signs of problems with the intestines are bloating, gas formation, flatulence, problems with appetite, metabolic disorders, weight loss, the presence of blood and mucus in the stool. Let's look at the diseases of which departments individual signs may indicate.
Diarrhea
Periodic loose stools are only a sign of the presence of the disease when their frequency exceeds 3 times a day. The problem itself indicates a disruption in the functioning of the small intestine; stool may contain food fragments and foams. In diseases of the large intestine, loose stools occur, as a rule, only during periods of exacerbation of pathologies.
Constipation
May be caused by disturbances in the functioning of the large intestine. However, hardening of stool and delays in going to the toilet are not always a sign of intestinal pathologies; they can indicate poor nutrition, lifestyle, diseases of the endocrine system, and psychological stress.
Pain in the abdominal area
Pain due to intestinal diseases can have various causes, location, strength, and differences.
In pathologies of the small intestine, pain is usually felt in the umbilical region and is of a pulling nature.
In pathologies of the large intestine, the pain is localized in the area of the ileum, symmetrically, has a bursting, dull character, and usually goes away after going to the toilet and passing gases.
Flatulence (intense gas formation)
Problems can occur with diseases of both parts of the intestine.
Metabolic disease
As a rule, it indicates problems with the small intestine, nutrients are poorly absorbed, this is quite easily recognized by external signs, body weight falls, dry skin, the appearance of microcracks in the corners of the mouth, and microbruises on the skin may be observed. Separately, I would like to note that in some women, disturbances in the menstrual cycle may be associated precisely with diseases of the small intestine.
Colonoscopy of the intestine: are patients’ fears justified?
An illness diagnosed at an early stage creates the least amount of problems for the patient. Therefore, highly informative screening colonoscopy is included in government programs to combat colon cancer in the USA, Israel and European countries. Citizens of developed countries are constantly informed about the need for regular examinations for the prevention and early diagnosis of colorectal cancer.
The specifics of such an intimate procedure do not evoke the most positive emotions among Russians. Pain is a major deterrent even for those people who are fully aware of the need for testing. But is it possible to compare the sensations that arise during a colonoscopy with the torment experienced by patients suffering from already developed oncology!
It should be understood that gentle diagnostic technology, which can be performed under anesthesia, will allow you to avoid dangerous symptoms, frightening diagnoses and a solid set of diagnostic procedures in the future.
Advantages of endoscopic examination in a paid clinic
Colonoscopy under anesthesia is carried out after appropriate preparation - following a special diet and complete cleansing of the intestines with the help of potent laxatives.
- In a European-style clinic, the patient will receive detailed recommendations on balancing the diet, which will help them calmly, without weakness or discomfort, undergo the stage of fasting and cleansing the intestines.
- Modern equipment allows a highly qualified specialist to conduct an examination with pinpoint precision without damaging the intestinal mucosa.
- The systematic process will take no more than 20 minutes, after which the patient will wake up in the room without experiencing any negative sensations.
- Patients who have already undergone intestinal endoscopy note that their expectations of something painful and terribly unpleasant were absolutely not justified.
Be attentive to your health! If sudden intestinal problems do not go away within 2-3 weeks, consult a specialist.
| +7 (495) 134-06-66 Write to WhatsApp | Moscow, st. Kantemirovskaya 53, k1 | Mon-Sat: from 9 to 21, Sun: from 9 to 20 |
| +7 (495) 134-06-66 Write to WhatsApp | Moscow, Kashirskoe highway, 51, k3 | Mon-Sat: from 9 to 21, Sun: from 9 to 20 |
What diseases are there associated with the gastrointestinal tract?
14.04.2021
Problems of the gastrointestinal tract have existed for quite a long time, but only in our time doctors been able to identify different types of diseases and systematize them. However, there are still some inaccuracies with the purpose of the diagnosis, in addition, there are diagnoses that ordinary people are unlikely to correctly understand. This article will help you deal with them.
General information on bowel function and possible symptoms of diseases
To understand the whole essence of the problems, you need, first of all, to imagine how the intestines and what it consists of. So, it consists of two sections: thick and thin. The small intestine looks like this: the duodenum, small intestine and ileum, which begin at the pylorus of the stomach and end at the ileocecal valve, which connects the large intestine to the small intestine. The large intestine , in turn, consists of the following three sections: the cecum, rectum and colon. In the submucosa of the duodenum there are special glands that help the intestines break down enzymes. In addition to this, the intestines have the following functions: absorption of nutrients into the blood , removal of toxins from the body.
The most common symptoms that patients complain about with intestinal problems.
- Various abdominal . Of course, the type, intensity and location of pain depends directly on the disease. In most cases, intense pain near the navel may indicate problems in the small intestine . In this case, the spasms can be short but strong or, on the contrary, pulling. Problems with the large intestine are characterized by dull, arching pain throughout the stomach , which may intensify or subside when eating or defecating.
- Diarrhea . In general, this symptom may indicate completely different diseases of the digestive tract, so it is important to carefully monitor what other symptoms accompany it. In addition, it is worth paying attention to the shape, color and structure of the chair. Intestinal diseases can be indicated by foam, food particles, traces of blood and mucus.
- Flatulence. This symptom, like diarrhea , can indicate many things. It is mainly accompanied by abdominal , characteristic sounds and sensations of fermentation, which mostly confuses patients. Flatulence may increase after eating or, conversely, in the absence of food for a long time. For some, it may only appear in the evening or at night. It is important to note that with an already irritated intestine, flatulence can occur with the slightest change or failure in the diet, which is why it is so necessary to follow a diet .
Major intestinal diseases
The most common disease is IBS ( irritable bowel syndrome ). Many patients do not fully understand it. Doctors themselves cannot give specific reasons for its occurrence, distinctive symptoms, etc. The main symptom of irritable bowel syndrome is diarrhea . To make sure of the diagnosis of the disease, you need to pay attention to the stool. This disease is especially characterized by the occurrence of attacks of diarrhea in the morning. Another disease very similar to irritable bowel syndrome is dysbiosis . In short, it occurs when harmful bacteria predominate over beneficial bacteria in the intestines . This may be a consequence of excessive consumption of sweet, fatty or spicy foods. One of the most dangerous intestinal is Crohn's disease . For some time it may be asymptomatic, or pain may alternate with remissions. blood can be found in the stool ; in addition, the patient is bothered by bloating, diarrhea joint pain .
It is very important to prevent the development of the disease in time, so experts advise immediately contacting doctors , describing your illness in detail, rather than making a diagnosis yourself.
Published in Gastroentorology Premium Clinic