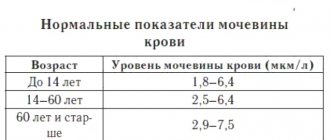
General information
Nephritis is a group of kidney diseases of an inflammatory nature. There are two main forms in children: hereditary and acquired.
The inflammatory process usually occurs in both kidneys of the child, spreading to the pyelocaliceal system, renal glomeruli and tubules. This disease can appear even in newborns; in medicine there is currently no consensus on what the mechanism of the onset and development of the disease is. Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis is usually provoked in children by a hereditary predisposition, accompanied by infection and allergies. Source: N.I. Khlebovets Tubulointerstitial nephritis in children // Journal of Grodno State University, 2014, No. 1, pp. 94-97
The main causes of illness in childhood:
- various maternal illnesses during pregnancy;
- diabetes;
- oncology;
- autoimmune processes;
- myeloma;
- vasculitis;
- acute infections;
- thrombosis;
- damage to the body by salts of heavy metals;
- self-medication with medications without specialist supervision (the use of antibiotics without appropriate prescription is especially dangerous);
- reactions to vaccines;
- hypothermia;
- tuberculosis.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms are usually the same, regardless of the cause of kidney damage, and are also similar for children of any age - from newborns to teenagers:
- swelling;
- decreased appetite;
- general weakness;
- feeling of dry mouth;
- chills;
- skin redness;
- dry skin, hair, nails;
- headache;
- pain in the lumbar area;
- convulsions;
- small volume of daily urine;
- bloating;
- vomiting and other gastrointestinal disorders.
If the disease lasts for a long time, then the death of a large number of renal glomeruli occurs. As a result, kidney failure occurs.
The chronic form of the disease is characterized by:
- intense sweating, increasing at night;
- decreased appetite;
- yellow skin tone;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- pain during urination;
- cloudy urine.
Classification of jades
| Type of jade | Peculiarities |
| Pyelonephritis | Inflammatory process in the pyelocaliceal system. It is bacterial in nature, provoked by E. coli, staphylococcus and a number of other pathogens. |
| Glomerulonephritis | The kidney glomeruli are negatively affected. It can be of three forms: acute, subacute and chronic. Characterized by swelling, blood in the urine, increased blood pressure. Source: Lechon FC, Espi MT, Abal RP, Peiro JLE Acute glomerulonephritis associated with pneumonia: review of three cases. Ped. Nephrol. 2010; 25: 161-164 |
| Interstitial nephritis in children | Damage to renal tissues and tubules. The causes are viruses, uncontrolled use of diuretics and antibiotics. |
| Tubulointerstitial | Damage to the interstitial tissue of the kidneys and tubules, aseptic inflammation of the tissues. The process involves the lymph flow and blood vessels. |
| Lupus | The cause is lupus erythematosus, which provokes inflammation not only in the kidneys. Source: G.A. Makovetskaya, L.I. Mazur, V.N. Barinov, E.A. Barannikova, E.M. Romadanova, P.V. Morinets Lupus nephritis in children: manifestation, diagnosis, treatment // Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics, 2021, No. 62(4), p.185-186 |
| Acquired diffuse | Streptococcal infection in a newborn, damage to kidney tissue. |
| Ray | It is provoked by ionizing radiation, as a result of which the function of the renal tubules is impaired. In the chronic form, renal failure or arterial hypertension develops. |
| Hereditary | At the beginning of development, symptoms are almost completely absent. As the disease progresses, hearing and vision may decrease, unusual fatigue may appear, and the skin often turns pale. |
Acute pyelonephritis - symptoms and treatment
Inpatient treatment is usually required for pregnant women, children, the elderly, immunocompromised patients, poorly controlled diabetes, kidney transplant recipients, and of course anyone with urinary tract obstruction. It is also advisable to hospitalize people with acute pyelonephritis of the only existing or only functioning kidney. Healthy, young, non-pregnant women who suffer from uncomplicated pyelonephritis can be treated on an outpatient basis.
Typically, acute pyelonephritis requires exclusively drug treatment. Indications for surgical treatment are extremely rare.
The basis of treatment for acute pyelonephritis is antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. NSAIDs reduce pain, weaken symptoms of intoxication and help cope with high fever. Antibacterial therapy for acute pyelonephritis requires a separate analysis.
The initial choice of antibiotic for acute pyelonephritis is empirical. After 4-7 days, antibacterial therapy can be adjusted based on the results of urine culture. The empirical choice of antibiotic remains at the discretion of the treating physician.
National guidelines indicate second- and third-generation fluoroquinolones as the treatment of choice for acute pyelonephritis.[4] The same is said in the recommendations of the European Association of Urology. Meanwhile, back in 2021, the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) recommended abandoning the use of these antibiotics due to a large number of complications in relation to ligaments, joints and peripheral nerves.[6] Therefore, third-generation cephalosporins are recommended as first-line therapy.
The most widely used third-generation cephalosporin is ceftriaxone. Step therapy with a smooth transition from an intravenously administered antibiotic to its oral analogue is actively practiced. You can switch from intravenous ceftriaxone to oral cefixime, which is also a third-generation cephalosporin. Cefixime is better known by its trade names: “Suprax”, “Suprax solutab” and “Pancef”.
You can often find a combination of two antibiotics for the treatment of acute pyelonephritis. As a rule, cephalosporins are combined with fluoroquinolones or aminoglycosides. Aminoglycosides in the form of amikacin have a clear nephrotoxic effect, so their use for empirical therapy is justified only in severe cases. In general, the choice of antibiotic is at the discretion of the attending physician.[9]
Indications for surgical treatment arise in purulent forms of inflammation and acute secondary pyelonephritis. In secondary pyelonephritis, the main goal of surgery is to drain the urine. This can be done either by installing a renal stent or by percutaneous puncture nephrostomy.
The purulent form of acute pyelonephritis requires revision and decapsulation of the kidney, opening of purulent foci, or even nephrectomy in case of purulent destruction of most of the kidney.[4]
Methods of treating the disease
Important! Treatment should only be carried out by a doctor who strictly controls the course of therapy. It is prohibited to try to cure a child on your own, use folk remedies, or rely on the experience of other parents.
After making a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a special diet for the child. The child must be kept in bed and not be exposed to stress or stress.
Drug therapy is carried out using vitamin complexes and antibiotics. It can be adjusted if the expected effect is not achieved. The duration of drug treatment is usually long - up to one and a half months.
Sometimes (in the presence of toxins in the blood plasma) plasmapheresis and hemosorption (blood purification) are performed.
Any therapy requires the participation of a specialist and regular tests to monitor the progress of treatment. When the main course is completed, children are often sent to sanatoriums and physiotherapy is recommended.
Treatment
A patient with signs of nephritis is given strict bed rest, which helps reduce the rate of spread of infection through the circulatory system and internal organs. You can cope with the disease by:
- Taking medications to eliminate the causes of inflammation. A course of antibiotics, antiviral drugs, hemosorption procedures and plasmaphoresis to destroy the pathogen in the patient’s blood gives a good effect.
- Blocking the development of the inflammatory process and its spread throughout the body. The effect is achieved by taking hormonal drugs, antihistamines, and medications to activate blood circulation in the kidney tissues.
- Symptomatic treatment to alleviate the patient's condition. The course includes water-electrolyte drips, monitoring of daily urination, intestinal or hemodialysis, which allows you to remove metabolic products from the body.
A prerequisite for successful treatment is a diet for nephritis, the main requirements of which are reducing the amount of salt in the diet and limiting the volume of fluid to 700-800 ml, depending on the patient’s body weight. Treatment is carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor, and its content is adjusted as monitoring indicators change and signs of recovery appear.
Methods for preventing childhood nephritis
Parents should be aware that self-prescription of preventive medications is unacceptable. Even after an examination, only a doctor should do this.
As part of prevention, it is important to monitor the child’s lifestyle, promptly identify alarming symptoms, and conduct medical examinations in this profile. For children at risk, physical therapy, hardening, moderate physical activity, and adherence to a certain diet are recommended (consult a doctor to determine this).
Diagnosis and treatment of nephritis in Moscow
The Clinic of JSC "Medicine" invites patients with suspected nephritis to undergo a comprehensive examination and course of treatment. All necessary services can be obtained at the center, which will save the patient from having to sign up for tests and wait a long time for his turn. Each patient is guaranteed confidentiality, attentive and welcoming treatment, the opportunity to undergo examination and receive advice from other specialized specialists, as well as the quality and safety of the proposed treatment procedures. You can make an initial appointment by calling the specified phone number or through the clinic’s website by filling out the appropriate application.
Advantages of SM-Clinic
Our medical center employs some of the best specialists in the Northern capital: pediatric nephrologists, urologists, pediatricians.
“SM-Clinic” has modern equipment, thanks to which diseases are diagnosed quickly and accurately. This makes it possible to return children to normal life in a short time. We have no queues, the approach to each child is always individual and delicate. If inpatient observation is required, comfortable rooms are provided.
Sources:
- N.I. Khlebovets. Tubulointerstitial nephritis in children // Journal of Grodno State University, 2014, No. 1, pp. 94-97.
- Lechon FC, Espi MT, Abal RP, Peiro JLE. Acute glomerulonephritis associated with pneumonia: review of three cases. Ped. Nephrol. 2010; 25: 161-164.
- G.A. Makovetskaya, L.I. Mazur, V.N. Barinov, E.A. Barannikova, E.M. Romadanova, P.V. Morinets. Lupus nephritis in children: manifestation, diagnosis, treatment // Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics, 2021, No. 62(4), pp. 185-186.
Lavrishcheva Yulia Vladimirovna Clinic
Author of the article
Lavrishcheva Yulia Vladimirovna
Doctor of the first qualification category
Specialty: nephrologist
Experience: 13 years
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a medical specialist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient (other specialties) | 1750 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for a period of 1 month) | 2700 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Kidney ultrasound | 1700 rub. |
| Ultrasound scanning of kidney vessels | 1800 rub. |
Diagnostics
The similarity of the symptoms of nephritis with the signs of influenza and ARVI forces specialists to resort to methods of differentiated diagnosis. The following methods for diagnosing nephritis can confirm doctors’ assumptions about inflammation in the kidney area:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- bacteriological urine culture;
- general urine analysis, study according to Zimnitsky and Nechiporenko;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys with the effect of contrast illumination (Doppler);
- ECG, blood pressure monitoring;
- immunological studies;
- radioisotope method for diagnosing inflammatory diseases.
In rare cases, if test results are in doubt, a decision is made to perform a kidney tissue biopsy. Often, third-party specialists from other fields of medicine are involved in the examination: ENT doctor, gynecologist, dentist, infectious disease specialist, etc. Their participation in the examination allows us to accurately identify the cause of the disease and identify the source of infection hidden inside the body.