What is mycosis of the feet
Mycosis of the foot is a group of fungal skin diseases, often with simultaneous damage to the nails. These infections cause similar clinical manifestations. They can only be distinguished after a microscopic examination of the skin and nails. Mycosis of the feet is a highly contagious disease. It is transmitted from person to person through household items: rugs in locker rooms, showers and swimming pools, footstools, basins and flooring in baths and saunas. Sharing shoes and socks is dangerous. The surface layer of the skin, which is constantly peeling off, contains a lot of fungi and their spores. Initially, the interdigital folds are affected and skin itching occurs. Subsequently, the infection takes over the entire foot and spreads to the nails. The course of the disease is long-term and requires constant treatment. To prevent mycosis of the foot, in our online store you can buy an effective prophylactic product - Mycospray.
Classification
Fungal pathogenic organisms are divided into several groups:
- Anthropophilic - they only affect people.
- Zoophilic - affects exclusively animals.
- Zooanthropphilic - affects all representatives of the fauna.
In medicine, fungal diseases are divided into five groups:
- Keratomycosis (trichosporia nodosum, lichen versicolor ).
- Dermatomycosis (athlete's foot, athlete's foot, rubromycosis, trichophytosis , microsporia).
- Candidiasis (superficial candidiasis, chronic generalized candidiasis, visceral candidiasis)
- Deep mycoses (blastomycosis, histoplasmosis, sporotrichosis, coccidioidosis, etc.).
- Pseudomycosis (superficial and deep pseudomycosis).
Causes of mycosis of the feet
The cause of the disease is microorganisms of the genus Trichophyton, less commonly mold fungi and Epidermophyton floccosum:
- red trichophyton (Tr. Rubrum) causes up to 95% of all cases of the disease;
- approximately a third of patients also have interdigital trichophyton (Tr. Interdigitale);
- inguinal epidermophyton (E. floccosum) causes the disease in 1% of cases.
The likelihood of infection increases in unfavorable external conditions:
- high humidity;
- tight shoes;
- frequent visits to swimming pools, saunas and other wet areas;
- presence of a sick person in the family.
Some internal diseases also contribute to the development of fungal infections:
- sweaty feet;
- immunodeficiency;
- taking corticosteroid hormones orally;
- flat feet;
- Raynaud's disease, atherosclerosis of peripheral arteries, obliterating endarteritis, varicose veins;
- diabetes.
Hand fungus caused by Trichophyton interdigitale
Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. interdigitale rarely affects the hands. The disease occurs with a pronounced inflammatory component and the development of allergic reactions in the form of a rash on the skin of the limbs, trunk and face. The disease begins acutely with damage to the interdigital folds, where hyperemia and maceration of the skin are noted. In appearance, the affected area resembles eczema.
Rice. 16. Fungi Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. interdigitale under a microscope (photo on the left). The mycelium is long, with spiral curls at the ends. The photo on the right shows pathogen colonies growing on a nutrient medium. The colonies are mealy, velvety, surrounded on the periphery by a rim consisting of young shoots.
Rice. 17. Fungus on the fingers when affected by Trichophyton interdigitale. The disease is acute, the inflammatory component is significantly expressed.
What happens during the disease
Mycosis of the feet rarely develops on healthy skin. Even if the fungus gets to the surface, it will not be able to penetrate the thick layer of intact epithelium. Under the influence of unfavorable external factors, the epidermis accumulates moisture and loosens. Fungi penetrate into the thickness of the skin and begin to actively multiply. This is further facilitated by vascular diseases and immune disorders, which are accompanied by impaired nutrition and local protective mechanisms on the feet. The proliferation of fungi causes damage to the interdigital areas, intense peeling and discomfort. The rejected epithelium ends up in socks and shoes, becoming a source of re-infection. Therefore, during the treatment of mycosis, it is necessary to treat the inner surface of the shoe with Mycospray.
In children
In children, such a disease is not uncommon due to non-compliance with hygiene rules, active contacts with peers, pets, etc. But since children may develop other skin lesions associated with allergic reactions, infectious diseases, etc., parents should definitely contact see a dermatologist so that the doctor can determine the diagnosis. In no case should you practice self-medication, since you must initially establish an accurate diagnosis. In addition, many antifungal agents cannot be used to treat children. Parents must not only ensure proper treatment of the disease, but also teach their children the basic rules of personal hygiene.
Symptoms
Conventionally, the following forms of mycosis of the feet are distinguished, which are presented in the photo:
- Squamous: unilateral peeling and mild itching in the arch of the foot. This form often goes unrecognized.
- Intertriginous: the folds between the toes are affected, then the process moves to the back of the foot. Weeping cracks appear, accompanied by itching. A bacterial infection may accompany the development of erysipelas.
- Dyshidrotic: on the arch of the foot, vesicles with light and then cloudy contents form, merging with each other. They open with the formation of painful erosions. This type is accompanied by itching and pain.
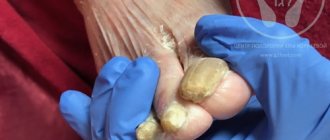
Mycosis of the skin of the foot in the acute period can be accompanied by fever, poor health, headache, and enlarged inguinal lymph nodes. When infected with trichophyton, the nail of the 1st or 5th finger is affected, and subsequently the process spreads to all nail plates. First, yellow spots appear at the free edge of the nail, then it thickens, loosens and crumbles. Therefore, to treat foot fungus, you need to use complex action products, for example, Clotrimazole lotion for skin and nails.
Diet
Antifungal Diet
- Efficacy: no data
- Terms: 3-6 months
- Cost of products: 1500-1600 rubles. in Week
In the process of treating a fungal disease, doctors recommend following some recommendations. Proper nutrition promotes a speedy recovery and helps fight fungal infections. The antifungal diet requires the following rules:
- Do not consume foods that contain yeast.
- Minimize, or better yet completely eliminate, the consumption of sweets, since carbohydrates are a breeding ground for fungus.
- The use of dishes made by fermentation (kvass, etc.) is contraindicated.
- It is recommended to eat freshly prepared food and consume as many raw vegetables and fruits as possible. It is important to introduce more greens, carrot and orange juice into your diet.
- It is prohibited to consume alcohol.
- During the treatment process, it is important to consume as much fermented milk products as possible in order to normalize intestinal functions.
- It is recommended to drink rosehip decoction, green tea, herbal teas, and mineral water. You need to drink as much fluid as possible.
Treatment of mycosis of the feet
Therapy is carried out in 2 stages. First, it is necessary to eliminate acute inflammation and remove horny deposits on the feet. Warm foot baths with potassium permanganate and lotions with a solution of boric acid are shown. After removing the dense epithelium, creams containing anti-inflammatory hormones and antibiotics are used. After the inflammation subsides, these creams are replaced with similar ointments. At the second stage of treatment, antifungal ointments and creams (for example, Clotrimazole) are used. They should be applied to clean, dry skin 1 – 2 times a day, lightly rubbing. Not only the affected area is treated, but also the surrounding surface of the foot. The course of treatment takes about a month. Mycosis of the foot is successfully treated with the drug Clotrimazole lotion for skin and nails, which is offered in our online store for residents of Moscow and all regions. Its advantages:
- high activity against the fungus that causes mycosis of the feet;
- safety;
- hypoallergenic;
- affordable price.
Clotrimazole lotion can be used to treat other skin diseases:
- pityriasis versicolor;
- skin candidiasis;
- erythrasma;
- secondary bacterial infection against the background of mycosis.
The medicine is used 2 times a day, gently rubbing it into the affected areas. The skin must first be washed with soap and dried well, especially between the fingers. The course of treatment lasts until the symptoms of the disease disappear and for another 2 weeks. The drug is well tolerated. Only occasionally does it cause skin irritation. It has the only contraindication – the first trimester of pregnancy. Of course, clotrimazole is not used if you are hypersensitive to it. One of the advantages of clotrimazole lotion is the excellent penetration of the drug into the nail plates, which distinguishes it from cream or ointment. Regular use of this drug provides excellent results for mycosis of the feet and nails without the use of additional agents. Nail damage requires oral antifungal medications:
- itraconazole;
- fluconazole;
- griseofulvin;
- terbinafine
At the same time, medicinal varnishes are used, which are applied to the nails 1 – 2 times a week until complete healing.
Tests and diagnostics
what fungus looks like on hands photo of the initial stage
If a person shows signs of a fungal infection, he should immediately contact a dermatologist and undergo an examination.
The doctor conducts an examination, assessing the signs of the disease, and also interviews the patient.
The study requires scraping of scales from foci of disease on the skin. Analyzes are carried out using the following methods:
- Microscopic examination - biomaterial is examined under a microscope.
- Sowing - allows you to obtain more accurate information about the causative agent of the disease. This analysis takes longer - from several days to several weeks. To carry it out, the biomaterial is placed in a nutrient medium. If there is a fungus in it, characteristic colonies appear after a certain time.
- Enzyme immunoassay - used for the diagnosis of deep mycoses. It is used to determine the titer of antibodies to a specific fungus. For ELISA, blood is taken from a vein.
- PCR method - with this test you can determine the type of fungus. This is a fast and reliable, but narrowly focused research method. That is, to carry out this analysis you need to know what exactly to look for.
In addition, other studies are carried out during the diagnostic process. Before prescribing systemic antimycotic drugs, a biochemical blood test is performed to determine a number of indicators.
Preventive methods
Treatment of a fungal infection takes a long time. Mycosis of the feet requires the use of drugs, the cost of which is quite high. Prevention of the disease is especially important in people with risk factors for the disease. Athletes, swimmers, and hot shop workers are recommended to regularly use antifungal and antibacterial drugs, for example, Mycospray. This product is safe, does not damage the skin and does not cause irritation. With its regular use, the likelihood of becoming infected with foot fungus is sharply reduced. Mycospray is useful for preventing re-infection. To do this, the drug must be sprayed monthly on the inner surface of the shoes. Mycospray is safe even with long-term use. It should be applied to dry, clean skin of the feet before each visit to the pool and other similar places. There are no contraindications to the use of this drug. It should be used with caution only by pregnant and breastfeeding women. It is necessary to eliminate the external causes of the disease:
- wear boots and shoes that fit;
- use high-quality sports shoes made from natural materials;
- wash your feet daily and treat your nails on time;
- fight sweaty feet;
- When visiting a bathhouse, swimming pool, or beach, it is better to use lightweight silicone or rubber slippers.
General strengthening of the immune system, treatment of diabetes and vascular diseases are necessary.
General information
Every day a person is faced with many factors that can negatively affect his health.
Not everyone realizes that simple actions, such as visiting a sauna or getting a manicure in a salon, can lead to a fungal infection, which can subsequently cause numerous problems. Fungus on the hands - this is how this disease is usually called in everyday life - or mycosis very often develops precisely because of a banal failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene and a person’s inattention. It is important to understand that fungus on the hands, as in other places on the body, spreads very quickly. Therefore, if alarming symptoms appear in both adults and children, you should definitely consult a doctor and follow the treatment regimen that he prescribes. How exactly to treat mycosis on the hands and how to recognize this disease will be discussed in this article.
Hand skin candidiasis
Yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida most often affect the palms of women, and dermatophyte fungi in men. The disease affects people whose hands are exposed to a humid environment for a long time - housewives, people working in food factories, confectionery shops, when working with vegetables and fruits, etc. The disease in men is more often occupational.
Rice. 18. Candida albicans fungi under a microscope. Round pathogen cells and filaments of pseudomycelium are visible.
Damage to interdigital folds
The disease begins with the appearance of very small blisters on the skin of the contacting surfaces (usually 3 and 4 interdigital folds). Hyperemia of the transitional fold and maceration are noted. The rejected epidermis becomes white. A hyperemic, shiny, smooth surface is exposed underneath. The boundaries of the lesion are clear, surrounded at the periphery by a rim of exfoliating epithelium, rarely extending to the back of the hand. Subjectively, the patient experiences itching and burning.
Rice. 19. Damage to interdigital folds due to candidiasis.
Rice. 20. Candidiasis of interdigital folds.
Damage to the skin of the palms
This form of the disease is rare and has several forms of manifestation:
- In some cases, the disease occurs as dry lamellar dyshidrosis (superficial ring-shaped, garland-shaped or lamellar peeling is noted). The disease should be distinguished from dyshidrotic eczema.
- The vesicular-pustular form is characterized by the appearance of vesicles and pustules against the background of hyperemia and edema.
- Hyperkeratotic eczema is characterized by the appearance of wide skin furrows of a dirty brown color in areas of keratinized skin.
Rice. 21. Candidiasis of the palms. Dry lamellar dyshidrosis.
Candidiasis of the periungual fold
Prolonged stay in a humid environment and trauma contribute to the development of candidal inflammation of the periungual ridges. The disease begins with hyperemia and edema. The skin becomes thinner and becomes shiny. The nail skin disappears. When pressed, ichor, a crumbly white mass, or a drop of pus may be released. In some cases, the nail plates are affected. Patients are bothered by pain.
Rice. 22. Candida paronychia - inflammation of the periungual fold.
Rice. 23. Candidiasis of the hands (photo on the left) should be distinguished from eczema (photo on the right).
Rice. 24. Interdigital candidiasis (photo on the left) and skin lesions on the hands due to rubrophytosis (photo on the right).
Types of fungal infections
Fungal infections can appear at any age. Infants most often encounter this problem - redness and peeling appear. The symptoms are similar to those of an allergic reaction, so therapy is often carried out, which is ineffective.
The clinical picture depends on the type of disease:
- Because Candida thrives in moist and warm environments, it multiplies in the diaper area of babies. This manifests as intense, large-scale redness with scaly edges.
- Oral thrush is characterized by the appearance of a tight, gray-whitish film in the cheeks and throat. This type of disease is also caused by Candida and is most common among infants.
- Ringworm is accompanied by severe itching, the appearance of round bald spots and blackheads. There is excessive hair fragility, which results in bald spots.
- Vaginal (genital) candidiasis also occurs in childhood, although much less frequently. The victims may be babies in the first weeks of life, whose mother gave them Candida at birth. Babies still have their mother's female sex hormones (estrogens) in their bodies. They appear to inhibit the regenerative ability of the mucous membranes, which in turn contributes to the progression of the disease.
Pet-borne dermatophytes should not be underestimated. The head and torso are affected. The main carriers are cats, as well as guinea pigs and rabbits. Accompanied by severe itching, redness and excessive dryness.
Table - Classification of mycosis pathogens
| Pathogen name | Localization area | How it manifests itself |
| Tinea capitis or Microsporum (microsporia or “ringworm”) | Scalp | Ring-shaped, sharply limited red spots appear, in which the hair either breaks or falls out. Sometimes the scalp starts to ooze due to weeping. Small red pustules may appear. |
| Tinea corporis (dermatophytosis) | Torso and upper limbs | It appears as pale red areas with characteristic peeling. In addition, there is unbearable itching. Therefore, it is important to start treatment as soon as possible to avoid spreading the fungus to other parts of the child’s body through scratching. |
| Tinea pedis (onychomycosis) | Nail plates | The filamentous fungus damages the toes or nails and gives them a characteristic yellowish coloration. The plates with onychomycosis become thick and brittle, with a “loose” structure. With the exception of visual changes, symptoms such as itching do not appear, so onychomycosis is usually diagnosed in the later stages of progression. |