How to treat a hernia of the linea alba
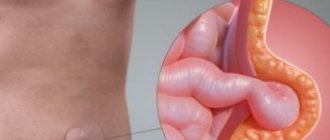
Hernia of the white line of the abdomen is a pathological process during which a protrusion of the abdominal organs is formed between the slits of the tendon fibers of the muscles of the midline (white line). This disease is otherwise called epigastric hernia, and it occurs in 10% of all cases, more often among men.
Protrusion of organs occurs anywhere along the midline of the abdomen at the site of the opening. The linea alba acts as an interlacing of tendon bundles of the broad abdominal muscles in the form of a plate. The line is localized along the central axis from the xiphoid process to the pubic symphysis, its thickness is about three centimeters.
What it is?
A hernia of the white line is a protrusion of subcutaneous fatty tissue and internal organs through large gaps between the plexus of tendons of the white line of the abdomen.
As practice shows, pathology is 3-10% more common in men under the age of 30. With this form of the disease, parts of internal organs and fat begin to appear through the openings between the muscles. A typical location is the epigastric region.
Depending on the location relative to the umbilical cavity, the following types of hernias are distinguished:
- Supraumbilical (located above the navel);
- Peri-umbilical (located near the umbilical cavity);
- Subumbilical (localized below the umbilical cavity).
The location of a hernia of the white line near and below the navel is uncommon.
Modern treatment methods make it easy to get rid of the disease, but to identify it at the initial stage, you need to become familiar with the causes of the development of the pathology and the symptoms that accompany it. A hernia, like any other disease, is easier to treat at the initial stage of development.
At first glance, education does not cause significant discomfort, but the disease is still fraught with danger. The main threat is pinching of organs trapped inside the hernial sac. In some cases, compression of the nerves occurs.
What is needed to make a diagnosis?
Diagnosis begins with clarifying complaints, how long ago the disease was, and examining a doctor. It is necessary to establish the degree of muscle divergence and which organs are included in the hernial sac. The following methods are used for this:
Gastric hernia
- Ultrasound diagnostics - the study is carried out with the patient standing, allows you to identify adhesions;
- fluoroscopy of the stomach and intestines with preliminary administration of a contrasting barium suspension;
- computed tomography in multispiral mode.
Patients should remember that the appearance of any formation, even a painless one, on the body is a serious reason to consult a doctor. A hernia must be distinguished from diastasis (widening) of the central junction of the rectus abdominis muscles. It forms after childbirth in women in the second or third month. The reason is the special physiological looseness of the connective tissue, which ensures normal contractions.
If you start early training to correct your abdomen, diastasis appears. In men, this phenomenon can occur under heavy loads and obesity. In appearance, diastasis differs from the hernial sac in a roller-like stripe along the white line; it manifests itself when the muscles are tense. The symptoms do not differ from hernia-like ones.
Causes
Factors that provoke the development of the disease are divided into 2 categories: causes arising from weakness of the white line, and factors caused by increased pressure inside the peritoneum.
The reasons belonging to the first group act as prerequisites for the occurrence of a hernia. This:
- Genetic predisposition If you have relatives with this diagnosis, the risk of the disease increases.
- Excess weight Due to a thick layer of subcutaneous fat, the anterior abdominal wall becomes weak and the linea alba begins to stretch.
- Scars formed as a result of surgical interventions Each of them is a vulnerable place where a hernia can bulge.
- Injuries Any injury to the abdomen makes the anterior abdominal wall weaker.
- Pregnancy During this period, the abdominal muscles weaken and the abdominal wall stretches.
Factors included in the second group are direct provocateurs of the disease. These include:
- strong and prolonged crying in children;
- difficult birth, large baby;
- diseases occurring against the background of problems with urination;
- great physical activity;
- constipation;
- diseases of the abdominal cavity occurring against the background of a severe cough.
What to pay attention to during rehabilitation?
To ensure a sufficiently strong fusion during the rehabilitation period, restrictions are established. They concern:
- ability to carry heavy loads - 2 months, not more than two kg;
- playing sports and training - only from the third month with the permission of a doctor;
- food - only boiled, light dishes, milk porridges, juices, low-fat soups, kefir, cottage cheese (the rest is in accordance with the above dietary requirements).
The photo shows a neat postoperative suture on days 2–3
Symptoms of hernia of the white line of the abdomen, photo
The symptoms of a hernia of the white line of the abdomen (see photo) are the same in men and women, the pathology does not depend on gender characteristics. In some cases, a hernia may even manifest itself only as a protrusion, which is typical for the initial stage of the pathology.
Over time, the hernia begins to manifest itself as pain, which intensifies significantly during intense movements and when straining. Pain in each specific case may be of a different nature. They can be sharp, dull, pulling, prolonged or paroxysmal, sharp and even “dagger-like”.
Also, the disease in men and women is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- nausea followed by vomiting;
- pain of a different nature - when bending, turning and other movements;
- stretching of the midline abdominal muscles;
- pain after meals;
- belching, heartburn, hiccups.
As the disease progresses, the signs of pathology intensify:
- pain intensifies and becomes unbearable for the patient;
- vomiting constantly torments the patient;
- blood may be found in the stool;
- it becomes impossible to repair the hernia.
In the event of a pinched hernia, assistance to the patient should be urgent. If any of the manifestations occur, you should immediately contact the clinic.
Do I need a special diet?
The purpose of the diet for patients with a hernia of the linea alba is to prevent bloating of intestinal loops and stagnation of feces (coprostasis). Both processes make it possible to slow down the formation of the hernial sac. Nutritional recommendations are applied both before and after surgery until the integrity of the abdominal wall is completely restored.
The following are excluded from the diet:
- nuts;
- legumes;
- white cabbage, asparagus;
- tomatoes;
- animal fats and butter;
- all fried foods;
- canned food;
- fresh baked goods and culinary products;
- fast food;
- chocolate;
- coffee;
- carbonated drinks;
- hot sauces and seasonings;
- fresh apples.
The patient needs to eat 6–7 times a day, in small portions, not to overeat, and drink a lot of water (1.5–2 l).
Allowed:
- porridge;
- milk if well tolerated;
- low-fat meat and fish dishes;
- fresh fruit juices;
- carrots, beets, cucumbers;
- kefir;
- cheese;
- low-fat cottage cheese;
- boiled sausage;
- eggs no more than two per week;
- broccoli;
- citrus fruit;
- apricots, dried apricots, prunes;
- dried white bread.
Stages
Normally, the white line from the sternum to the navel is 10–25 mm wide, and below it it narrows to several millimeters. In the place where a hernia of the linea alba develops, the tendon fibers can diverge by 100 and even 120 mm, forming hernial orifices of various shapes (oval, diamond-shaped, round).
Wide hernial orifices do not appear immediately - the hernial protrusion goes through several stages of development:
- The first stage is preperitoneal lipoma. It occurs when one or more provoking factors appear, which we discussed earlier. In this case, through the still small holes in the diverging tendon, fatty tissue protrudes under the skin.
- Initial stage. The peritoneum enters the hernial orifice, which begins to form a membrane for the internal organs that extend under the skin. The peritoneum is a thin membrane that covers the inner walls of the abdominal cavity and the surface of the internal organs.
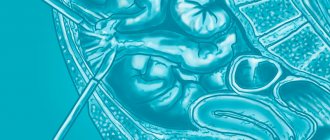
A hernia of the white line of the abdomen at the stage of final formation includes all the required elements:
- hernial orifice - an opening in the linea alba from which organs emerge;
- hernial sac - peritoneum;
- contents of the bag: omentum, intestines, stomach walls, some ligaments.
Depending on when the disease was discovered, the complexity of the operation depends.
Features of the anatomy of the zone
The linea alba is a powerful fusion of muscle tendons that runs from the lower end of the sternum to the pubic bone. It is not visible on the surface of the abdomen. Projected along the midline. The bilateral oblique muscles carry a constant load and provide position and movement of the body. Their tendons converge in front and represent a relatively thin formation (1–2 mm), poorly supplied with blood supply and nerve endings.
The width of the fusion is individual, varying from 20 to 30 mm. The fibers of the aponeurosis (the dense membrane of the muscle) are capable of twisting and forming cracks in the form of diamonds. In terms of quantity, they are maximally located in the upper and middle parts of the line. Normally, they are filled with adipose tissue from the anterior peritoneal tissue (preperitoneal) and are capable of stretching.
Strangulated hernia
Infringement of a hernia of the white line of the abdomen is compression of the organs and tissues located in the hernial sac. Depending on the mechanism of development, elastic, fecal and retrograde strangulated hernias are distinguished.
Elastic strangulation of a hernia occurs when there is a sharp increase in intra-abdominal pressure (for example, during defecation, coughing, sneezing, etc.), when the hernial orifice expands sharply, and most of the abdominal organ protrudes into it. Then the hernial orifice returns to its original state, since the tissues are elastic, and the prolapsed organs do not have time to return back to the abdominal cavity.
With fecal strangulation, the loop of intestine trapped in the hernial sac is gradually filled with feces and gases. As a result, the intestinal loop stretches and increases in size, as a result of which it is pinched.
With retrograde strangulation, a part of the intestinal loop or other organ that is not in the hernial sac, but in the abdominal cavity, is compressed. With this type of strangulation, peritonitis and intestinal necrosis develop very quickly, and the severity of clinical symptoms increases rapidly.
Why does a hernia form?
The expansion of the white line in men is often determined by a discrepancy between the development of muscle tissue and its aponeurosis. Abdominal hernias in women occur due to weakening of the abdominal wall due to frequent repeated pregnancies. The causes of the pathology are conventionally divided by nature: into factors that increase intra-abdominal pressure, contributing to the weakening of the tendons of the abdominal muscles.
The first include:
- heavy physical work, weight lifting for weightlifters;
- the passion of teenagers, young men and girls for bodybuilding, the desire to “pump up the abs”;
- enlarged abdomen due to abdominal fat in obesity, ascites due to fluid accumulation caused by venous blood retention (portal hypertension in liver cirrhosis, circulatory failure);
- diseases leading to prolonged constipation;
- suffered complicated pregnancies and childbirths;
- diseases that cause prolonged severe coughing and vomiting;
- pathology of the genitourinary system, contributing to urinary retention (prostatitis, malignant and benign tumors of the prostate, bladder, urolithiasis);
- babies cry for various reasons.
Weakness of the aponeurosis and tendons can be caused by sudden weight loss
Postoperative scars in the white line area lead to tendon weakness. Such hernias are called ventral. Many abdominal surgeries require an incision along the linea alba (laparotomy). This improves access to the required area, provides more opportunity to examine the entire abdominal cavity, ligate vessels and eliminate bleeding during the recovery period. However, there is an increased risk of postoperative hernia.
Traumatic injuries to the abdomen are most common among athletes; closed and open types occur from bruises, falls from a height, during road accidents, gunshot and knife wounds. There may be a hereditary predisposition caused by impaired collagen synthesis in connective tissue.
Most often, the reasons are mixed. But finding out the main factors is important for deciding on the treatment of a particular person and preventing relapse. You can learn more about the causes of linea alba hernia in newborns from this article.
Diagnostics
The primary diagnosis can be made based on an external examination of the patient; additional examinations are required to accurately determine the condition.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity. The condition of the internal organs is checked.
- X-ray examination of the hernial sac. Before the examination, the patient is given a barium preparation to increase the contrast of the image.
- Multislice tomography. Used in the most difficult cases, it allows you to completely eliminate errors during diagnosis and assessment of the current condition.
What are the methods of anterior abdominal wall plastic surgery?
Plastic methods can be tension or non-tension.
Tension is a type of plastic surgery performed using the patient’s own tissues. This method received this name because, in order to eliminate a hernia defect, the tissues must be “tightened” and sewn together. The resulting tension in the tissues can cause pain after surgery and result in a possible relapse. At the present stage of development of medicine, this method of closing hernias defects is significantly inferior to non-tension methods.
Tension-free plastic surgery involves the use of modern mesh prostheses to strengthen the anterior abdominal wall. The prosthesis is a polypropylene network, which, due to its flexibility, strength and high degree of tissue “germination”, has shown its reliability and safety when used in hernia repair. Mesh prostheses come in different sizes, from small ones with a diameter of 5 cm for umbilical hernias, to large ones of 50 x 50 cm for giant incisional hernias. Modern three-dimensional mesh systems make it possible not only to strengthen the hernia defect in the form of a “patch”, but to completely fill it, significantly reducing the risk of relapse. In some situations, a special mesh is installed, the surface of which is coated with a special composition that allows it to safely contact the abdominal organs and avoid the formation of adhesions between them.
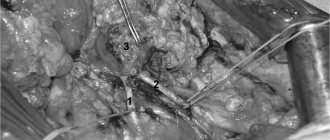
The open hernia repair operation consists of several stages:
- Isolation of the hernial sac. A skin incision is made above the hernial protrusion, the hernial sac is freed from the surrounding subcutaneous fatty tissue. The “hernial orifice” is distinguished.
- The hernial sac is opened, the condition of the contents of the hernial sac is assessed, and if there are no complications, the contents are immersed in the abdominal cavity.
- The hernial sac is excised, stitched and plunged into the abdominal cavity.
- The integrity of the anterior abdominal wall is restored (plasty is performed).
Treatment
Often, when treating a disease, mistakes are made that negatively affect the pathology:
- Treatment with painkillers or anti-spasm drugs will only eliminate the pain.
- Constantly wearing a bandage. The device must not be used for an extended period. The belt does not replace full muscle work. With frequent use of the device, muscle fibers may lose tone, which will lead to their atrophy.
- Folk remedies (infusions of drupe leaves, immortelle, wormwood), taken orally, can reduce gas formation and improve intestinal function. This will reduce the degree of intestinal protrusion, but the defect in the tendons will not heal due to the properties of this tissue.
- Using medications to enhance gastric motility. Over time, this type of treatment does provide relief, but does not solve the problem. It is recommended to treat the pathology with surgery.
- Exercise is good for preventing hernia formation, but not for treating it.
Refusal of self-medication, timely diagnosis of pathology and its correct therapy is the only way to avoid complications and return to a normal lifestyle.
Is treatment possible without surgery?
You cannot listen to the advice of strangers and try to cure a hernia yourself using folk remedies. There is only one method of radical treatment - surgery. Other treatment options temporarily relieve unpleasant symptoms (pain, increased gas formation), but do not stop the process that has begun, and even stretch the hernial opening even more.
Advertised “hernia exercises” lead to increased growth of the hernia sac. They are good for prevention, but not at the stage of an already formed hernia. Conservative therapy is indicated for the period of preparation of the patient for planned surgical treatment, for patients with severe general diseases.
Complete tissue restoration occurs only by the end of the year after childbirth.
Temporary measures include the following:
- We recommend wearing a special bandage belt. It should be clearly understood that no bandage can replace the muscular frame. Its purpose is to reduce the risk of prolapse and strangulation of the hernial sac and damage to internal organs. Surgeons believe that long-term use of a bandage reduces muscle tone, promotes the process of atrophy, and reduces strength and elasticity.
- Medicines with antispasmodic and analgesic effects. Indeed, good analgesics and antispasmodics can relieve pain. But at the same time, the patient is blocked from all pain sensitivity. Signs of infringement can be blurred and difficult to diagnose. This prevents doctors from assessing symptoms and making the right treatment decisions.
- Laxative medications that reduce gas formation and constipation. If the intestines begin to work hard, then, on the one hand, this reduces intra-abdominal pressure and protrusion of the hernial sac, on the other hand, motor activity contributes to the intestinal wall entering the formed formation. And, of course, medications do not matter for closing the hernial orifice.
The folk remedies recommended by healers are selected according to the principle of action of the described drugs. Decoctions of plants are used (chamomile, immortelle, Alexandria leaf, wormwood, senna). They are not capable of causing fusion of the hernial orifice into tendon tissue, but they facilitate bowel function and relieve bloating.
If a patient has an asymptomatic preperitoneal lipoma, he is informed about the initial stage of hernia formation and is offered observation. Treatment in such cases is not indicated.
Preparing for surgery
Self-preparation of the patient includes the following points:
- abstinence from alcohol no later than three days before the scheduled surgery;
- eliminating drugs that impair blood clotting and increase the risk of bleeding (you must tell your doctor about all medications you are taking, and he will give you a list of prohibited ones);
- 14 days before the operation, provide yourself with a balanced diet, which includes all the necessary microelements and vitamins (this will help you endure the procedure and anesthesia more easily, and also improve rehabilitation);
- complete refusal to eat after 20.00 on the day before surgery.
The hospital must take the necessary laboratory tests to check sugar levels, exclude HIV, hepatitis and other sexually transmitted diseases, and accurately determine the blood type and Rh factor. An ECG is also performed to check the heart's function to make sure the patient will tolerate the anesthesia.
Is it possible to operate a hernia without incisions using modern mesh prostheses?
Yes, you can!
At the moment, laparoscopic hernioplasty is the operation of choice for the treatment of various types of hernias. This operation is performed through punctures in the anterior abdominal wall. The surgeon inserts a video camera into the abdominal cavity and, using additionally inserted manipulators, releases the hernial sac from its contents. In the second stage, the surgeon separates the peritoneum of the hernial sac from the tissues of the anterior abdominal wall, dissects it and places a special mesh prosthesis on the hernial orifice. Then, the mesh is reinforced on top with the previously separated peritoneum.
Thanks to this, the prosthesis does not form adhesions with internal organs. This method of plastic surgery avoids tissue tension and greatly reduces the likelihood of relapse. The absence of large incisions on the anterior abdominal wall contributes to a comfortable course of the postoperative period.
Surgery to remove a hernia of the linea alba
Surgical intervention is carried out as planned. The doctor examines the patient, establishes a diagnosis, prescribes an examination and a date for hospitalization.
Types of operations for hernia of the white line of the abdomen:
- Open surgery with tension-free plastic surgery. To strengthen the linea alba, the surgeon uses special mesh prostheses. This method is used most often today, since after it a relapse is least likely.
- Open surgery with tension plasty. After removing the hernia, the surgeon tightens the linea alba with sutures, thereby strengthening it - hence the word “tension” in the name. This type of operation is simple, but has disadvantages: you have to make a fairly long incision (a large scar remains), and the risk of relapse is high.
- Paraperitoneal surgery. Three punctures are also made, but, unlike laparoscopic surgery, the instruments are not inserted into the abdomen or pierced the peritoneum. A special balloon is placed between it and the surrounding tissues and inflated - a space is formed from which you can access the hernial sac and perform surgery. The advantages of this operation are the same as those of laparoscopic surgery. However, its implementation is technically more complex; it is impossible to reliably fasten the mesh prosthesis.
- Laparoscopic surgery. With the advent of high-tech equipment in modern clinics, this type of operation for hernia of the white line of the abdomen has become increasingly popular. Instead of an incision, the surgeon makes three holes through which he removes the hernia and installs a mesh prosthesis. Laparoscopic surgery provides a low risk of relapse and allows the rehabilitation period to be reduced to 10 days - after which the patient can return to normal activities. But this operation cannot be performed for diseases of the lungs and heart. It is also impossible if the clinic does not have the appropriate equipment and specialists.
In case of a strangulated hernia of the white line of the abdomen, surgical intervention should be carried out as an emergency. The surgeon opens the hernial sac and examines the part of the intestine located in it. If it is dead, it must be removed. Sometimes it turns out that a large area of the intestine has become necrotic; the incision has to be enlarged and all the dead tissue has to be removed.
Symptoms
At the stage of preperitoneal lipoma, the hernia can exist asymptomatically for a long time. If touched, acute abdominal pain develops, which can be confused with pathology of the gastrointestinal tract. It often happens that the hernia is in a stable state and exists at this stage for years without progression of the process.
If it increases, a protrusion forms along the midline of the abdomen. It causes painful sensations that intensify with palpation, after eating, when straining, etc. The pain can radiate under the shoulder blade, under the ribs or in the lower back. When the impact on the hernia stops, or intra-abdominal pressure normalizes, the pain subsides and may even stop for a while.
A serious complication of a hernia is strangulation, when the contents of the hernia are compressed by the hernial orifice. In this case, the patient experiences severe increasing pain. After some time, vomiting occurs, stool retention develops and symptoms of intestinal obstruction increase. In this case, the hernia cannot be repaired.
A strangulated hernia is a life-threatening condition and requires immediate hospitalization in a hospital followed by surgical care.
Rehabilitation period
After a planned operation, that is, when the hernia was not strangulated, recovery occurs quite quickly. The patient is kept in the hospital for no more than three days. During this period, the nurse regularly makes dressings, and the doctor monitors the condition of the stitches and the patient’s well-being to exclude the possibility of infection. For the same purpose, a prophylactic course of antibiotics is prescribed.
The rehabilitation period requires compliance with certain rules:
- It is forbidden to lift weights over 5 kg (the restriction is valid for at least 3 months from the date of surgery);
- Leaning forward, sudden movements and too intense training are prohibited;
- moderate physical activity is indicated, especially walking;
- it is necessary to take laxatives prescribed by the doctor (constipation can cause sutures to come apart);
- It’s worth reviewing your diet and switching to a balanced diet.
People whose profession involves heavy physical labor are transferred to light work for a period of up to 6 months.
Features of the postoperative period
After the operation, the patient is observed and wound infection is prevented (a course of antibiotics, dressings with disinfectants). Men often have difficulty urinating. Walking is allowed on the second day. It is recommended to wear a bandage.
They are discharged home on days 8–10, immediately after the stitches are removed, but complete restoration of the tissue and wound will occur only after several months. At home, it is recommended to treat the wound with brilliant green. Dieting. Showering is allowed after two weeks. The doctor may prescribe physical therapy.
Diet
Sometimes situations arise when immediate surgical treatment cannot be performed for various reasons, and it has to be postponed for a certain time. Following a diet can alleviate the course of the disease and minimize the risk of strangulation.
- It is recommended to introduce more rice cereals, fish, eggs and dairy products into the diet. Be sure to drink the physiological norm of fluid. All foods should be digested quickly with a minimum amount of gases.
- It is not recommended to eat foods that cause bloating: legumes, fried and smoked foods, chocolate, nuts, butter, pickled vegetables.
If there are initial problems with digestion, then they should be eliminated by any means, from medications to traditional methods. The condition for choosing the right diet is the final diagnosis made in a medical institution.
Why is a hernia dangerous?
Any hernia is dangerous for the development of complications. The most serious complication of a hernia is strangulation. It occurs when the blood supply to the contents of the hernial sac is disrupted and tissue necrosis occurs.
An equally serious complication is intestinal obstruction. As a result of the prolonged presence of intestinal loops inside the hernial sac, they are compressed, the movement of intestinal contents through them is disrupted, and intestinal obstruction forms.
It is very important to understand that the development of complications can occur suddenly, against the background of complete well-being: on vacation, at the dacha, while traveling - in situations where qualified medical care is difficult to access or not available at all. Treatment of hernia complications requires emergency intervention, and delay can lead to a sharp deterioration in a person’s condition and significantly worsen the prognosis of delayed treatment.
Therefore, it is better to get rid of the hernia before complications develop.
Prevention
Prevention of white line hernia includes the following measures:
- identifying the causes of extra pounds and normalizing body weight;
- timely cure of diseases accompanied by cough;
- avoiding heavy lifting;
- adherence to the principles of a balanced healthy diet that would promote regular bowel movements;
- avoiding injuries to the anterior abdominal wall;
- regular physical exercise to strengthen the abdominal muscles (morning exercises, gym classes);
- dosing physical activity that involves the abdominal muscles, proportionate to one’s own physical training;
- compliance with all doctor’s recommendations (including wearing an abdominal bandage) during pregnancy and in the postoperative period.
Remember that a bandage does not cure a hernia. When worn for a long time, on the contrary, it can contribute to its occurrence, since it begins to perform the function of the abdominal muscles, which, as a result of inactivity, weaken and diverge even more, which contributes to the occurrence of a hernia.
How do hernias form?
Hernias occur in the area of “weak spots” of the anterior abdominal wall, under the influence of intra-abdominal pressure. Factors that cause its increase are called producing factors and include: physical activity, cough, childbirth and all those cases when the abdominal press tenses.
“Weak spot” is the area of the abdominal wall where the muscular aponeurotic part is most thinned. This may be the place of muscle attachment to the aponeurosis or physiological openings (inguinal rings, umbilical ring).
An increased risk of hernias is observed in people with predisposing factors: connective tissue weakness syndrome, damage to the nerves innervating the abdominal wall, as well as the presence of postoperative scars.
Rehabilitation
Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed to speed up healing. For the first 2 months, you should not carry more than 2 kg and strain your abdominal muscles. Sports activities are postponed for 3 months, during which a postoperative bandage is worn.
It is important to monitor your diet. It should be gentle and not cause problems with the gastrointestinal tract:
Canned and spicy foods and baked goods are completely excluded. Eat food 5 times a day in small portions. It is better to steam meat dishes, and boil the rest.
Who deals with surgical treatment of external abdominal hernias?
You can always contact the clinic of coloproctology and minimally invasive surgery for surgical treatment.
Qualified specialists regularly perform laparoscopic interventions for hernias of the anterior abdominal wall. In some cases, we also use traditional open surgery.
At KKMH, treatment of hernias is carried out both on a paid basis and under the compulsory medical insurance policy.
Sign up for a consultation by phone +7 (499) 11-03-222.