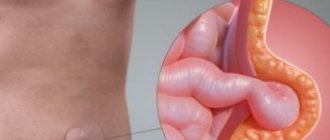
The main manifestation of a postoperative hernia is the appearance of a tumor-like protrusion along the line of the postoperative scar and on its sides.
With sudden movements and physical stress, the hernia increases and painful sensations appear. In the lying position, the hernia decreases or disappears.
As the name implies, a postoperative hernia, or ventral hernia, develops as a consequence of surgery on the abdominal organs.
The appearance of postoperative hernias is associated with thinning of the muscles and connective tissue in the area of the postoperative scar, due to which the internal organs (intestines, greater omentum) protrude through the defects of the surgical scar beyond the abdominal wall under the skin.
The cause of the appearance of a postoperative hernia may be technical errors when applying a suture, non-compliance with recommendations for postoperative rehabilitation, as well as the individual characteristics of the patient (weakness of connective tissue, obesity, diabetes, etc.)
Why is it necessary to treat a postoperative hernia?
The very appearance of a hernia indicates that the organs have changed their location, and their normal mutual pressure on each other has been disrupted. This leads to disruption of the functions of all organs involved in the formation of a hernia.
Postoperative hernia is often accompanied by chronic constipation. Constipation, in turn, leads to general intoxication of the body and can affect the condition of the entire gastrointestinal tract.
Lack of treatment will eventually lead to serious complications
- coprostasis - stagnation of feces in the large intestine,
- inflammation of the hernia - inflammation of the organs located in the hernial sac,
- strangulated hernia - sudden compression of the hernial contents in the hernial orifice, leading to disruption of the blood supply to the organs in the hernial sac, and as a result - necrosis (death) of tissue. Strangulation of a postoperative hernia quite often (in 8.8% of cases) leads to death.
If a protrusion appears in the area of a postoperative scar, you should immediately consult a doctor, since it is much easier to treat a fresh hernia than one that has existed for a long time.
Over time, the hernia increases in size, the tissue surrounding it becomes thinner, so the operation becomes more complex, with a worse prognosis.
Course of the disease
Postoperative hernias in the early stages are reducible and are not accompanied by pain. However, with sudden straining, falling, or lifting, pain appears and the protrusion increases. As the hernia progresses, the pain intensifies, sometimes becoming cramping in nature. At the same time, intestinal lethargy, constipation, flatulence, nausea, belching develop, the activity of patients sharply decreases, fecal stagnation, accompanied by intoxication, is periodically observed.
Are there non-surgical methods for treating incisional hernia?
Treatment of postoperative hernia is carried out only with the help of surgery - hernioplasty. There are several methods used depending on the stage of development of the hernia.
The intervention must be performed as early as possible, because A long-existing hernia is prone to progression and the appearance of various complications.
The use of new technologies, the use of modern plastic and suture materials, and many years of experience of our surgeons guarantee the highest quality of operations to eliminate postoperative hernia, the absence of postoperative complications and relapse (recurrence of the disease).
Preoperative preparation
Necessary for patients with large and giant postoperative hernias, as well as in the presence of diseases that predispose to the occurrence of hernias. Preparation should include not only drug correction of concomitant diseases, but also preparation of the skin in the area of surgery (treatment of ligature fistulas, diaper rash, maceration); bowel preparation (constipation treatment); prevention of respiratory and cardiovascular complications, prevention of intra-abdominal hypertension syndrome. Most of the preparatory activities are carried out on an outpatient basis under the supervision of a therapist (cardiologist) and a surgeon.
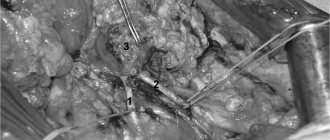
Postoperative hernia surgery
Operations for postoperative hernias are technically more complex and require highly qualified specialists, because surgical intervention is performed on tissues with scar changes.
Our clinic uses the most modern methods of treating postoperative hernias: for example, tension-free hernioplasty using the latest endoprostheses (including 3D), open and endoscopic hernioplasty.
Hernia repair using endoprosthesis
Hernioplasty is the most effective surgical method for treating hernia of the white line of the abdomen. During the operation, the defect of the postoperative scar through which the hernia emerges is closed with a special mesh endoprosthesis.
The foreign-made high-tech synthetic endoprostheses we use are very reliable, elastic, highly extensible and therefore do not limit the mobility of the abdominal wall.
The use of a mesh endoprosthesis protects the suture area from tension and thus provides three main advantages compared to the traditional surgical technique (tension plasty with local tissue):
- Extremely mild pain syndrome. Patients generally do not need to take pain medications after surgery.
- Short rehabilitation period. The patient goes home on his own the next day after the operation, and a month after the operation he can lift weights and play sports.
- Minimal risk of relapse. With proper placement of the endoprosthesis, recurrence of the hernia is practically impossible, whereas with the traditional technique it ranges from 6 to 14 percent.
The implant is not felt at all and does not cause any pain or discomfort.
Within a month after the operation, the mesh grows with connective tissue and over time, complete engraftment of the endoprosthesis occurs. The result is an anatomically unified complex that reliably closes the defect (weak spot) of the anterior abdominal wall and protects the tissue from repeated stretching.
We use two methods of installing an endoprosthesis: open and closed (endoscopic).
Open hernioplasty
With open hernioplasty, access to the contents of the hernia and the hernial orifice is through an external incision.
Next, hernia repair proceeds according to the following algorithm:
- isolation and opening of the sac with the contents of the hernia
- elimination of organ adhesions in the hernial sac, their reduction into the abdominal cavity
- removal of the hernial sac
- closing the hernial orifice using a special type of plastic surgery (hernioplasty)
- application and fastening of a special mesh implant of an individual shape
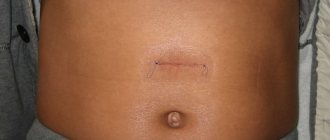
- if necessary, excision of the old postoperative scar, formation of a cosmetic intradermal suture with special suture material
Our surgeons always perform the operation taking into account aesthetic requirements: the incisions made are minimal, the instruments used are atraumatic, and the sutures are applied using ultra-thin suture material.
Endoscopic hernioplasty
The most modern and low-traumatic method of hernia removal is endoscopic, or closed, hernioplasty.
Endoscopic access in the treatment of postoperative hernias is widely used abroad.
This method is actively used in our clinic, since it has a number of undeniable advantages in the treatment of postoperative hernias:
- no risk of developing postoperative hernias at puncture sites,
- complete absence of pain syndrome,
- short recovery period (start of physical activity after a few days)
- the shortest rehabilitation period (one hundred percent return to active life in a maximum of two weeks)
- minimal number of relapses (less than 1%).
Unlike the classic open surgery technique, surgery is performed not through one large incision, but through three small punctures (0.5 - 0.6 cm).
Special endoscopic manipulators with a miniature video camera are inserted into them, sending an image to the monitor. With its help, the doctor monitors the progress of the operation.
The operation is carried out according to the same algorithm as with open access. But with endoscopic plastic surgery, a mesh implant is installed not through an external incision, but from inside the abdominal cavity at the site of the defect.
Endoscopic hernioplasty gives better results because... the location of the mesh on the side of the abdominal cavity more reliably protects the defect of the abdominal wall with an increase in intra-abdominal pressure.
This method of treating postoperative hernias is carried out using special expensive multilayer meshes. One of the layers of such a mesh is made of a special chemical compound that prevents the formation of adhesions between the endoprosthesis and the abdominal organs.
Abdominoplasty
If there are stretch marks, excess skin and subcutaneous fat on the abdomen, then it is recommended to combine the removal of a postoperative hernia with abdominoplasty.
This allows, simultaneously with hernia repair, to remove the skin-fat “apron”, eliminate sagging skin and stretch marks, and form a flat stomach and thin waist.
The operation to eliminate a postoperative hernia can also be supplemented with liposuction of the abdomen or other parts.
Survey
Detecting a hernia is usually not difficult. Most often, a visual inspection and palpation of the protrusion is enough. If necessary, an ultrasound examination is performed.
However, when preparing for surgical treatment, it is necessary to conduct a full examination in order to identify and timely correct concomitant diseases that may become risk factors for hernia recurrence. And also evaluate the function of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems in order to choose the most suitable method of operation for each patient.
If difficulties arise in diagnosis - in case of complex multi-chamber hernias, when it is necessary to determine the topography of the hernia defect, measure the hernial orifice for individual selection of a mesh implant - an MRI of the abdominal organs is performed.
What is the most effective method for removing a postoperative hernia?
Our surgeons are fluent in endoscopic technology, but this technique is not always applicable for complex hernias. Often, much better results can be achieved by open hernioplasty.
Based on many years of experience in hernia repair, our surgeon will choose the optimal access method based on the characteristics of your particular disease.
The main factor in the successful outcome of hernia surgery is its impeccable technical execution. Poor surgical technique can ruin any method, even the best one. If all stages of the operation are performed correctly, then with any type of access the probability of hernia recurrence is minimal.
Contraindications for surgery
Acute infections, late pregnancy, dermatitis and eczema in the hernia area.
Since the herniotomy operation is performed under general anesthesia, the presence of decompensation of severe diseases of the internal organs, including coronary heart disease, stroke, diabetes, is a contraindication to the operation due to the high degree of anesthetic risk.
In cancer patients, a hernia of the anterior abdominal wall is treated according to the same principles as in other patients.
Postoperative hernia rehabilitation
Immediately after the operation, an elastic bandage is put on, which must be worn for a month.
At the BEAUTY DOCTOR clinic, patients are accommodated in single and double comfortable rooms.
The wards are equipped with continuous monitoring systems to monitor the patient's condition after surgery. Multifunctional beds create the opportunity to position and feed the patient after surgery in the most convenient position for him.
Each patient is provided with individual nursing care.
Since we use minimally invasive and maximally gentle techniques when repairing postoperative hernias, the postoperative period proceeds easily and without any special complications.
The next day after the operation, the patient goes home on his own, and after another 8-9 days comes for a follow-up examination and removal of sutures.
Two weeks after surgery, you are allowed to resume moderate physical activity (running, brisk walking). After endoscopic hernioplasty, such loads can be resumed within a few days.
A month after the operation, the patient can lead a normal lifestyle and play sports.
Hernia of the anterior abdominal wall as a disease
A hernia itself is a protrusion of internal organs or parts thereof without violating the integrity of the skin and the membrane lining the cavity. The opening through which this occurs is called the hernial orifice. The anatomical structure of the anterior abdominal wall is such that there are several “weak” places, which, due to the features of their structure, are predisposed to be hernial orifices. The most common hernial orifice is the inguinal ring (66% of hernias) and the adjacent area called the medial inguinal fossa. The contents of the hernial protrusion in this case may include the small intestine, omentum, occasionally the cecum, appendix, bladder, sigmoid colon, and internal female genital organs. Over time, the hernial sac descends into the scrotum in men, and into the labia majora in women. Inguinal hernias are divided into direct and oblique according to the location of the hernial canal.
Less common are femoral, umbilical hernias, and hernias of the white line of the abdomen.
In addition, the following types of hernias are distinguished: congenital and acquired, traumatic, postoperative; complete and incomplete, reducible and irreducible, complicated and uncomplicated.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Postoperative hernia surgery cost
| Postoperative hernia: hernioplasty | 46,000 rub. |
| Postoperative hernia: advanced hernioplasty | 51,000 rub. |
| Postoperative hernia: hernioplasty of recurrent hernia | 63,000 rub. |
| Postoperative hernia: endoscopic hernioplasty | 87,000 rub. |
| Hernioplasty with abdominoplasty | 260,000 190,000 rub. |
The cost of an operation to eliminate an incisional hernia includes all necessary examinations and dressings, as well as observation by a surgeon for six months after the operation.
Operations to remove a postoperative hernia are performed by highly qualified herniologist surgeons with extensive experience, trained in Russia and abroad:
| Gaboyan Aram Sergeevich, Doctor of Medical Sciences | Soboleva Polina Yurievna, Candidate of Medical Sciences | Malkarov Marat Azretovich, Candidate of Medical Sciences |
Sources
- Romain B., Fabacher T., Ortega-Deballon P., Montana L., Cossa JP., Gillion JF., Antor R., Beck M., Barrat C., Berney C., Binot D., Bousquet J., Blazquez D., Bonan A., Cas O., Champault-Fezais A., Chastan P., Chollet JM., Cossa JP., Dabrowski A., Delaunay T., Démaret S., Drissi F., Demian H., Dubuisson V., Dugue T., Fromont G., Gillion JF., Jacquin C., Jurczak F., Khalil H., Launay-Savary M., Lepère M., Lépront D., Longeville JH., Le Toux N. , Loriau J., Magne E., Ngo P., Oberlin O., Passot G., Pavis d'Escurac X., Putinier JB., Renard Y., Romain B., Soler M., Roos S., Thillois JM ., Tiry P., Vu P., Verhaeghe R., Warlaumont M., Zaranis C. Longitudinal cohort study on preoperative pain as a risk factor for chronic postoperative inguinal pain after groin hernia repair at 2-year follow-up. // Hernia - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33891224
- Santos DA., Zhang L., Do KA., Bednarski BK., Robinson Ledet C., Limmer A., Gibson H., You YN. Chemotherapy and Abdominal Wall Closure Technique Increase the Probability of Postoperative Ventral Incisional Hernia in Patients With Colon Cancer. // Am Surg - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.31348211011149; PMID:33877925
- Min JS., Seo KW., Jeong SH., Kim KH., Park JH., Yoon KY., Kim TH., Jung EJ., Ju YT., Jeong CY., Kim JY., Lee YJ. A comparison of postoperative outcomes after open and laparoscopic reduction of Petersen's Hernia: a multicenter observational cohort study. // BMC Surg - 2021 - Vol21 - N1 - p.195; PMID:33858393
- Du Z., Wei SW., Zhang XY., Xiang Z., Qu SQ. The effect of dexmedetomidine premedication on postoperative systemic inflammatory response in children undergoing hernia repair surgery: A randomized controlled trial. // Paediatr Anaesth - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33825304
- Danneberg S., Sayk F., Marquardt JU. [61/m-Postoperative wound healing disorder after umbilical hernia repair and unclear elevation of transaminases: Preparation for the medical specialist examination: part 41]. // Internist (Berl) - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33822244
- Yörükoğlu H.U., İçli D., Aksu C., Cesur S., Kuş A., Gürkan Y. Erector spinae block for postoperative pain management in lumbar disc hernia repair. // J Anesth - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33751203
- Espinosa-de-Los-Monteros A., Frias-Frias R., Alvarez-Tostado-Rivera A., Caralampio-Castro A., Llanes S., Saldivar A. Postoperative Abdominal Bulge and Hernia Rates in Patients Undergoing Abdominally Based Autologous Breast Reconstruction: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. // Ann Plast Surg - 2021 - Vol86 - N4 - p.476-484; PMID:33720921
- Rodoman GV., Malgina NV., Razbirin VN., Epiphanova SV., Dolgina TY., Kuznetsov AI. . // Khirurgiia (Mosk) - 2021 - Vol - N3 - p.36-41; PMID:33710824
- Seher N., Nayman A., Koplay M., Çiftci İ. Comparison of Preoperative and Postoperative Testicular Elasticity and Vascularity in Pediatric Patients with Inguinal Hernia. // J Ultrasound Med - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33665883
- Schaaf S., Willms A., Schwab R., Güsgen C. Recommendations on postoperative strain and physical labor after abdominal and hernia surgery: an expert survey of attendants of the 41st EHS Annual International Congress of the European Hernia Society. // Hernia - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33629178
Do you want to get rid of a hernia quickly and permanently?
You're lucky to have found us. Contact us for advice.
- We will conduct an in-depth diagnosis of the condition of your abdominal cavity
- We will select for you the optimal treatment method from the entire range of modern high-tech surgical techniques
- Our highly qualified specialists - candidates and doctors of medical sciences - will perform the operation using the latest technologies, expensive specialized equipment and materials
- Your stomach will become healthy and beautiful, and traces of the intervention will be completely invisible to prying eyes
- We will carry out follow-up examinations and monitor your abdominal condition for six months to ensure there is no recurrence (free of charge)
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures include surgical examination with palpation and a number of laboratory and instrumental studies:
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Irrigoscopy
- Survey X-ray
- Herniography
- Blood and urine tests
To clarify some parameters, it may be necessary to prescribe MSCT or MRI of the abdominal cavity, colonoscopy and other examination methods.
You have questions? We will be happy to answer any questions Coordinator Tatyana