Method of performing splenectomy for splenic rupture and the presence of adhesive disease of the abdominal cavity
A new method of surgical treatment for splenic rupture has been introduced at the emergency hospital.
Splenic rupture is accompanied by dangerous bleeding, the mortality rate of which ranges from 5-45%, especially with massive ruptures and late diagnosis. The incidence of splenic rupture ranges from 0.5 to 12.5%. Large main blood vessels pass through the spleen. When the spleen ruptures, the volume of blood loss is calculated in liters per minute. Therefore, the main cause of death for the victim is large blood loss and hemorrhagic shock, in which cardiac activity stops. After treatment of splenic rupture (splenectomy), other complications are possible - these are post-traumatic pseudocysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, thrombocytosis. Although the spleen is not a vital organ, it is the main source of lymphocytes, produces antibodies, participates in the destruction of old platelets and red blood cells, and functions as a blood depot. Predisposing factors that increase the likelihood of damage to the spleen include an insufficiently strong thin capsule, congestion of the organ and its low mobility. On the other hand, these factors are somewhat offset by the fact that the spleen is protected from external influences by the ribs. The likelihood of splenic rupture as a result of injury increases with pathological processes accompanied by its enlargement and increased parenchyma friability. In addition, the strength of the spleen to some extent depends on the degree of its blood supply, the position of the organ at the time of injury, the phase of breathing, and the filling of the intestines and stomach. Most often, simultaneous ruptures of the spleen are observed with the immediate occurrence of bleeding into the abdominal cavity. Two-stage ruptures account for about 13% of the total number of closed injuries to the spleen; the time period between the moment of injury and the onset of bleeding into the abdominal cavity ranges from several hours to 1-2.5 weeks. The cause of capsule rupture in an existing central or subcapsular hematoma can be physical stress, sneezing, coughing, walking, defecation, turning in bed and other circumstances that cause an increase in pressure in the spleen. Most splenic ruptures are small, accompanied by mild symptoms and are diagnosed only after a few hours, when the patient’s condition worsens due to ongoing blood loss and accumulation of a sufficient amount of blood in the abdominal cavity. With two-stage injuries of the spleen, profuse bleeding is observed more often and clinical symptoms are more clearly expressed.
We used a modified pararectal approach on the left, which differs from the traditional pararectal and T-shaped incision in that in the proximal direction it runs 5-7 cm parallel to the left costal arch. This access is less traumatic than the T-shaped one and it allows the most optimal access to the hilum of the spleen, performing splenectomy and adequately sanitizing the abdominal cavity in case of existing adhesive disease of the abdominal cavity. The outcome of the disease is recovery.
The surgical approach proposed by the authors for rupture of the spleen in patients with a concomitant diagnosis of adhesive disease of the abdominal cavity is optimal, since it allows for the most adequate inspection and sanitation of the abdominal cavity, which is essential for avoiding various severe complications that often arise after splenectomy. Therefore, in such clinical situations, it can be used in any surgical department, since no additional funds are required for this.
Splenic rupture is a dangerous complication in abdominal surgery, which can be caused by either trauma or various diseases. The mortality rate of this complication, if the diagnosis is not made in a timely manner or complications arise, after splenectomy, especially purulent ones, remains high. Therefore, timely and adequate treatment of splenic rupture allows one to avoid these complications and achieve the patient’s recovery. Taking this into account, the surgical approach proposed by the authors for rupture of the spleen in patients with a concomitant diagnosis of adhesive disease of the abdominal cavity is optimal and can be used in any surgical department in such clinical situations.
Authors:
Kvetko Vladimir Vladimirovich, resident of the surgical department of the State Clinical Emergency Hospital of Grodno,
Klimovich Joseph Iosifovich – Professor of the 2nd Department of Surgical Diseases of GrSMU.
Spread of the disease.
Spleen cysts are observed in 0.5 - 1% of the population. Moreover, in half of the patients, cysts are detected by chance, during a routine examination. In women, splenic cysts are 3–5 times more common than in men, and are detected mainly between 35 and 55 years. Similar to liver cysts, spleen cysts can be single, multiple, true or false.
Puchkov K.V., Ivanov V.V., Poddubny I.V., Tolstov K.N. Laparoscopic splenectomy: surgical tactics and technical aspects: monograph. - M.: ID MEDPRACTIKA - M. - 2007. - 88 p.
Treatment of pathology
When a patient develops alarming symptoms, he needs immediate first aid.
| Priority actions | Description |
| The patient is placed on his back | If a person feels a push in the side from the side of the spleen, then he needs to be laid on his back, then there should be a small cushion under his head |
| Press in the middle of the chest | This action will help stop heavy bleeding that occurs due to organ rupture |
| Repeat chest compressions | Pressure manipulation helps block internal bleeding until the ambulance arrives |
| Apply a cold compress | It is recommended to apply cold compresses to the abdominal area to block bleeding. |
It is worth noting that the causes that provoke this pathology can cause both single large ruptures and small-area but multiple damage to this organ. Typically, a large rupture of the spleen tissue will immediately show the symptoms mentioned in this article.
In the second case, symptoms may not appear immediately and may be delayed. Sometimes multiple ruptures of the spleen tissue are diagnosed only when blood oozing through the wounds fills most of the abdominal cavity. Such complications can pose a great risk to human health. Treatment of splenic tissue rupture is carried out only in inpatient conditions. There are two ways to get rid of this problem: surgery aimed at partial removal of tissue, or complete resection of the organ.
It is important to understand that treatment of this pathology, although it will get rid of the main problem, will not be able to completely restore a person’s health. As a rule, in people who have suffered from rupture of splenic tissue, with a successful operation, there is a total decrease in the body’s defenses, loss of immunity and a strong increase in the number of platelets in the blood. These consequences are difficult to eliminate.
Preventive actions
To prevent possible damage to the spleen tissue, you should follow the following basic rules:
- Never break bed rest if you have respiratory viral illnesses.
- Exercise regularly.
- Observe precautions against injury to the spleen area.
- Minimize heavy lifting.
- Pregnant women are advised to wear a bandage.
- Promptly treat infectious and other ailments that may become chronic.
These preventive rules will help minimize the risks of possible splenic rupture.
Diagnosis
A splenic rupture is accompanied by intense pain that cannot be ignored. It is this that forces a person to see a doctor. The specialist takes into account not only the victim’s complaints, but the physical examination data, the results of measuring pulse and pressure. When examining a patient, doctors pay attention to the abdominal wall that is swollen and hard to the touch, to the presence of abrasions, hematomas and other signs of injury. However, making a diagnosis based on symptoms alone is quite difficult. Similar manifestations occur when other internal organs are affected.
At the initial stages, the diagnosis of pathology is carried out taking into account clinical symptoms, the results of radiography, laparoscopy and other methods.
splenic rupture, subphrenic hematomaOn the radiograph on the left, under the diaphragm, a uniform darkening is visualized, displacing the dilated stomach, kidney and part of the intestine to the right and down. In the absence of obvious symptoms, X-ray data are considered nonspecific - not allowing a diagnosis.
- Angiography is a radiopaque study that can detect vascular damage and determine the extent of bleeding. This method requires a lot of time, expensive equipment and specially trained personnel. It is used extremely rarely.
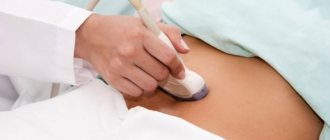
- Ultrasonography - assessment of the condition of the damaged organ, detection of free fluid in the abdominal cavity and immobility of the diaphragm, determination of the symptom of “floating loops” and decreased echogenicity of the spleen.
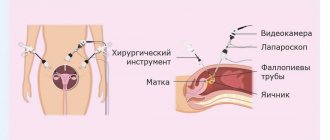
- Laparoscopy is a diagnostically significant, informative and widely used method for detecting damage. It allows you to confirm the suspected diagnosis and accurately determine the location of the source of bleeding. Specialists on the surgical table puncture the abdominal cavity and insert an endoscope inside. It is used to determine the presence of injury.
- Laparocentesis is performed in the absence of endoscopes or if the patient has contraindications to laparoscopy. This is an alternative technique that consists of piercing the anterior abdominal wall with a trocar, inserting a catheter through it and removing contents from the abdominal cavity. Laparocentesis confirms the presence of bleeding, but does not determine its source.
- Blood tests may initially give normal results. Their lack of information is due to the compensatory restoration of the composition of peripheral blood. Subsequently, signs of anemia, hypovolemia, and endotoxemia increase.
Detecting a splenic rupture is not at all easy. Diagnosis requires a thorough examination of the victim, study of the clinical picture, and correct interpretation of the results of hardware studies. Only during surgery can specialists confirm with 100% certainty that the spleen has ruptured.
Reasons that provoke damage and rupture of the spleen
There are many reasons why the integrity of an organ is damaged. It is also worth noting that the spleen can be damaged not only by mechanical factors, but also by pathological processes that are present in the body.
Among the most common reasons are the following:
- Mechanical injuries (force impact on the area where the organ is located).
- Infectious diseases that cause enlargement of the spleen and lead to a critical condition.
- Excessive physical activity.
- High level of blood filling of the organ.
- Difficult process of childbirth.
- Inflammatory processes that are observed in neighboring organs (hepatitis virus, cirrhosis, etc.).
- The occurrence of benign or malignant neoplasms.
- Clonal diseases of the hematopoietic system.
Sometimes it is very difficult to independently diagnose a ruptured spleen and prevent a critical condition. Complex symptoms help specialists establish a diagnosis in the shortest possible time and promptly stop the pathology, preventing consequences after its rupture.
If we consider the clinical picture after rupture of the spleen and competent care, the prognosis for the patient’s life remains favorable.
However, if the patient did not call an ambulance in a timely manner, but self-medicated in the form of painkillers, then death cannot be ruled out.
Causes
High-energy injuries are the immediate cause of splenic rupture. The organ is damaged by a fall, injury or blow to the stomach, as a result of a car, household or industrial accident. Injuries to the spleen can be professional or criminal in nature. In children, it is damaged during fights or outdoor games. The child falls or is hit in the left chest and abdomen.
Factors contributing to organ rupture:
- Thinned capsule, full-blooded and loose parenchyma,
- Immobility of the spleen
- Dysfunction of the hematopoietic system,
- Increased load on the spleen during prolonged and severe infectious processes,
- Excessive physical stress
- Difficult birth
- Colonoscopy and other invasive diagnostic and treatment procedures,
- Weakness of the abdominal muscles.
Diseases in which splenomegaly develops often lead to organ rupture. Non-traumatic causes of injury include:
- Infectious mononucleosis,
- Enlarged spleen of toxic, autoimmune or infectious origin,
- Hematological diseases,
- Oncological pathologies,
- Abscess of the spleen,
- Malarial infection
- Metabolic disorders
- Congenital anomalies of the spleen,
- Inflammation of nearby organs - liver, kidneys.
If a patient has the listed diseases, the lining of the spleen gradually becomes thinner, and sensitivity increases. The spleen can rupture regardless of a person's general well-being. The ideal functioning of internal organs minimizes the risk of such an event occurring. If the functioning of the bone marrow, endocrine glands and immune system is impaired, the likelihood of rupture increases significantly.
There is also spontaneous splenic rupture, which occurs for no apparent reason. This name is considered conditional, since in most cases, organ damage is preceded by minor trauma. In the presence of normal parenchyma, it does not lead to a violation of integrity. For spontaneous rupture of a pathologically altered spleen to occur, it is enough to make an awkward movement or sneeze.
What are the symptoms of the pathology?
When free intraperitoneal blood appears, persistent diffuse abdominal pain, peritoneal irritation and severe sensitivity begin to develop. If intra-abdominal bleeding exceeds 5-10% of blood volume, clinical signs of early shock may appear.
- Symptoms include tachycardia, tachypnea, restlessness and anxiety.
- Paleness of the skin is a nonspecific and mildly manifested symptom; it can only be distinguished by the patient’s close people who have known him for a long time.
- In addition, clinical signs include decreased capillary refill and pulse pressure.
- As blood loss increases in the abdominal cavity, abdominal distension, peritoneal symptoms, and apparent shock occur.
Hypotension in a patient with suspected splenic injury, especially when young and healthy, is a major cause of urgent surgical intervention. This condition should lead to immediate diagnostic evaluation and intervention either in the operating room or interventional radiology setting, especially in the case of uncompensated shock.
Diagnosis of splenic cyst.
Splenic cysts are detected in most cases during a clinical examination and routine examination, as well as during a diagnostic search for gastrointestinal diseases during ultrasound examination and computed tomography with bolus contrast.
In the diagnostic algorithm for identifying single splenic cysts, the key issue is to determine the non-parasitic nature of the detected cysts. To resolve this issue, it is necessary to conduct serological studies with parasitic diagnostics for the presence of echinococcosis (Cazzoni reaction and hemagglutination) and alveococcosis (latex agglutination reaction).