If a person experiences pain in the area of the left side of the hypochondrium, the first suspicions immediately fall on the pancreas or stomach. However, another, neighboring organ may also be disturbing.
The spleen is one of the most mysterious organs, the functions of which are not fully understood. This is the most important organ that helps the immune system: it is the one that copes with filtering blood cells infected with viruses. The spleen is a reservoir organ, a blood depot.
Pain syndrome in the spleen without the influence of external factors occurs only in one case - when it is significantly enlarged. Often, patients simply complain of discomfort, a pulling sensation in the left half of the abdomen.
Diseases that cause pain in the spleen:
- Infectious diseases (typhoid fever, hepatitis, anthrax, infectious mononucleosis, syphilis, tuberculosis) Many infectious diseases affect the spleen, causing pain and starting a destructive process.
- Traumatic conditions of the spleen They are divided into two types: open and closed type. The first includes stab and gunshot wounds of the chest area on the left or the upper part of the abdominal cavity. Closed injuries - bruises and fractures. In some cases, the spleen may rupture, which is accompanied by internal bleeding. Damage to an organ is usually characterized by acute pain radiating to any part of the body, as well as a general deterioration of the condition.
- Organ infarction Occurs as a result of thromboembolism, as well as thrombosis. The condition of a person with a splenic infarction is directly related to the magnitude of the pathology. If it is small, then it is probably asymptomatic. With a large heart attack, pain occurs in the left hypochondrium with irradiation to the back area, which responds to breathing.
- Spleen abscess The pathology picture is fever, pain in the abdomen and chest, muscle tension.
- Parasitic diseases (most often echinococcosis)
- Benign and malignant neoplasms
- An enlarged spleen is often combined with an enlarged liver (hepatolienal syndrome), which is observed in liver cirrhosis, portal hypertension, and blood diseases.
Any pain in the body is a signal for help.
Do not blindly ignore it and take painkillers indiscriminately. Pain and discomfort in the left hypochondrium may indicate several problems.
Only a doctor can identify the exact cause.
If you experience pain of an unclear nature in the left hypochondrium, you can contact our clinic. To make a correct diagnosis, specialists will conduct an examination and interview, and also prescribe the necessary tests. During the consultation, you can discuss all the symptoms in order to choose the most effective and safe therapy.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis of spleen diseases begins with a thorough examination by a doctor. After palpation and history taking, additional studies will be required - ultrasound, radiography, MRI or puncture. Laboratory diagnostics are also required.
The primary task is to correctly diagnose in order to prescribe effective treatment. It should only occur under the supervision of an experienced specialist.
Preventive measures to maintain the organ in a healthy state are very simple: proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle. The spleen begins to work better with regular physical activity, as well as with special breathing exercises.
Pain in the spleen occurs when the organ has significantly increased in size. This may indicate various diseases, which can only be diagnosed by a qualified doctor. It is highly recommended not to make a diagnosis on your own, much less select a treatment.
After all, the spleen is one of the important organs responsible for supporting human immunity.
Timely contact with specialists will help you solve the problem at an early stage with minimal damage.
For early diagnosis of health problems, you can undergo a comprehensive diagnostics of the body at our center.
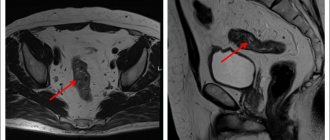
The best diagnosis of pain in the spleen is MRI of the spleen
You can sign up for a consultation right now: online or by phone
Why does the spleen hurt?
The main functions of the spleen in the body are to filter blood and produce antibodies to fight bacteria and viruses. In case of illness or injury, the spleen hurts, and heaviness in the side may occur. Discomfort is felt in the left hypochondrium - this is where the organ is located.
A doctor at the MedEx clinic will help you determine why the pain occurred and whether it is related to pathologies of the spleen.
Nature of pain in the spleen area
Pain in the spleen can be sharp or constant. Sometimes it feels like a girdle or radiates to the lower back, shoulder blade, left shoulder, and can become more intense when inhaling. In some cases, the pain is accompanied by other symptoms: cold sweat, fever, nausea.
Be sure to note the nature of the pain and tell your doctor in detail about your feelings: this is important for an accurate diagnosis.
What pathologies of the spleen are accompanied by pain?
Soreness in the spleen area can appear at any age and regardless of gender.
Why does the spleen hurt in women and men:
- Due to organ enlargement. The spleen may enlarge, for example, if there are problems with the liver and the normal flow of blood is disrupted.
- With an abscess: acute throbbing pain can be caused by an inflammatory process in the spleen.
- In case of a splenic infarction, when the artery is blocked by a blood clot and the blood supply to the organ is seriously impaired. This is a dangerous condition that is often accompanied by severe pain.
- In the presence of neoplasms of various types, for example, cysts.
- For injuries. After an accident or a fall from a height, ruptures of the spleen and internal bleeding are possible, therefore, in such cases, if there is a sharp pain in the left side, an ambulance is urgently called.
Pain in the spleen can also be caused by viral diseases, during which the spleen performs its immune function especially actively and may become slightly enlarged. Such pain is temporary and goes away along with the infectious disease.
Other causes of pain in the left hypochondrium
Even if it seems that it is the spleen that hurts, the source of pain on the left side may be the organs of the digestive system:
- Stomach;
- Upper intestines;
- The pancreas, which is also located on the left under the ribs.
Only a doctor can distinguish pain in the spleen from pathologies of other organs and prescribe the correct treatment.
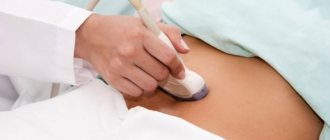
Ultrasound of the spleen or general ultrasound of the abdominal organs will help determine the cause of pain in men and women - a safe and comfortable ultrasound examination. In order for the result to be accurate, without extraneous noise and interference, it is important to do ultrasound using modern premium equipment. This is exactly the kind of equipment that MedEx clinic doctors work with: we use the Siemens ACUSON S 1000 device.
Make an appointment with a doctor in Moscow for pain in the spleen
If pain in the area of the spleen and adjacent organs occurs frequently, it is important to consult a doctor in time. A general practitioner, a universal specialist who coordinates the treatment of all systems and organs in the human body, will help you draw up a diagnostic plan at the MedEx personal medicine clinic.
Price
| Name of service | price, rub. |
| Primary appointment with a general practitioner (examination, consultation with a candidate of medical sciences) | 3500 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a general practitioner (examination, consultation with a candidate of medical sciences) | 3000 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the spleen | 1500 rub. |
| Ultrasound of lymph nodes (one anatomical zone) | 1200 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the salivary glands | 1200 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the pleural cavity | 1700 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the liver | 1500 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary zone | 2400 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the gallbladder with determination of its contractility | 2000 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the pancreas | 1500 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (comprehensive) | 2700 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs, kidneys and adrenal glands | 3700 rub. |
| Ultrasound detection of fluid in the abdominal cavity | 1500 rub. |
All prices are inclusive of tax deduction.
Sign up
Contact our doctor
Make an appointment
Dzhgarkava Tea Gochaevna
Therapist-cardiologist
Experience: 5 years
Read more
Causes of enlarged spleen in children
A child has an enlarged spleen; the causes and treatment have their own characteristics. The main causes of splenomegaly in children are blood diseases and infections. In infants, the disease often develops due to low filling of the organ with blood, as well as against the background of flabbiness of the abdominal muscles and rickets.
Other common diseases that provoke pathology in children include:
- typhoid fever;
- Congenital heart defect;
- tuberculosis;
- measles, rubella, diphtheria;
- leukemia;
- toxoplasmosis.
The development of pathology in children can be facilitated by helminthiasis, in particular schistosomiasis and echinococcosis (rare for CIS countries).
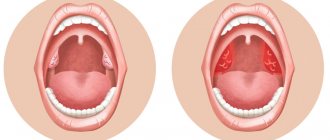
What is splenomegaly
The spleen is the largest lymph node in the human body
, it is located on the left side of the peritoneum, in close contact with the colon, kidney (left), pancreas and diaphragm.
Splenomegaly
- a diagnosis made by doctors when the weight of the spleen exceeds 200g.
An enlarged organ is able to capture more blood cells, but its filtering function deteriorates. Removing large numbers of cells from the blood reduces the number of white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets
. Such rapid and active destruction of blood cells leads to anemia, private infectious diseases, and deterioration of blood clotting.
An enlarged spleen can be caused by diseases of various natures, from simple infections to cancer. If the spleen is not greatly enlarged, then there may be no pain, but sometimes the organ becomes so large that it begins to compress the nearby internal organs, causing discomfort and pain.
Prevention of splenomegaly
It should be understood that an enlarged spleen itself rarely leads to serious consequences. The root cause of splenomegaly is much more dangerous. It is important to take preventive measures to prevent the development of the disease:
- rejection of bad habits;
- timely vaccination;
- treatment of all diseases in history;
- preventive examinations by specialists.
It is important to get vaccinated before traveling to exotic countries.
Prevention of splenomegaly involves taking measures against possible organ rupture. This means always wearing seat belts, not jumping from heights, and avoiding strong impacts to the abdominal area.
Etiology of the disease
The reasons for an enlarged spleen are as follows:
- liver diseases (the most common cause): cirrhosis, alcoholic hepatitis, hepatosis, hepatitis B, C;
- blood cancer;
- various infections: microbacteria, brucellosis, sepsis, etc.;
- blood flow disorders and thrombosis;
- viruses: rubella, mononucleosis, measles, AIDS, etc.;
- autoimmune diseases: rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus, periarteritis;
- entry into the body of arthropods and helminths;
Damage to the spleen (from a fall) can provoke the appearance of ulcers, tumors, heart attacks or splenic cysts, which also leads to malfunctions of the organ.
Liver pathologies
– the most common cause of spleen dysfunction. It is these two organs that interact most closely: blood filtered in the spleen from the digestive system enters the portal vein, and from there to the liver, where it is further cleansed of toxins. Thus, any disruption of the natural course of this process leads to splenomegaly. It is also true that improper functioning of the spleen necessarily leads to liver dysfunction.
How does splenomegaly manifest?
Symptoms of the disease become more intense as the organ grows. Sometimes it is possible to notice pathology only when the spleen is very enlarged. Doctors distinguish 4 stages of splenomegaly:
- Stage 1
– the organ can be palpated, which is impossible given its normal size; - Stage 2
– the spleen occupies the area from the navel to the hypochondrium; - Stage 3
– the organ reaches the midline of the abdomen; - Stage 4
- the spleen protrudes into the pelvic region and the right side of the peritoneum.
Complications
A malignant tumor can spread to the brain, spinal cord and cause neurological complications. Compression of the nerves leads to pain. Lesions in the lymph nodes, which are located inside the chest, can lead to coughing, difficulty breathing, and chest pain.
The spleen is not a vital organ, so after it is removed, a person can live as before without experiencing any symptoms associated with its absence. However, immune defenses are reduced to some extent and the patient becomes more vulnerable to infections.
List of sources
- V.V. Voitsekhovsky, N.D. Goborov. Splenomegaly in clinical practice / Amur Medical Journal. — No. 2 (26) 2021, p. 62-77.
- Russian clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of lymphoproliferative diseases / ed. ed. I.V. Poddubnoy, V.G. Savchenko. M. 2021. 419 p. Fainshtein F.E., Kozinets G.I.,
- Vorobiev A.I. Guide to Hematology. 3rd ed., revised, additional. M.: Newdiamed, 2005. T.3. 409 p.
- L.M. Pasieshvili, L.N. Beaver. Splenomegaly syndrome in the practice of a family doctor / Ukrainian Therapeutic Journal. - No. 2, 2007, pp. 112-119.
- S.P. Krivopustov. Splenomegaly in pediatric practice / Children's doctor. — No. 5 (26), 2013. pp. 5-8.
Examination of the blood vessels of the arms and legs
Diseases of the blood vessels of the arms and legs rarely appear on their own; most often there is a specific reason for this. Our task is to determine the degree of vascular damage and identify the cause of the disease.
The main methods of vascular examination that we will offer you: Doppler ultrasound (vascular ultrasound) of the arms and legs, consultation with a vascular surgeon. If necessary, we will offer you additional examination methods and assistance from a doctor of the appropriate specialty.
Examination of the vessels of the arms and legs in our clinic is carried out in two directions:
- Examination of the structure of blood vessels and the quality of blood flow; both arteries and veins can be examined;
- Search for the cause of damage, vascular disease.
examination of the structure of blood vessels and the quality of blood flow
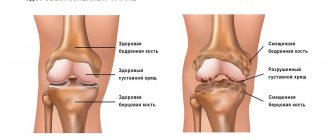
- Ultrasound examination of the vessels of the arms and legs. During an ultrasound examination of the vessels of the arms and legs, our task is to determine the diameter of the vessel, determine the presence of narrowing of the vessel, and exclude the presence of cholesterol plaques, blood clots, and pathological dilation of the vessel (aneurysm). Of great importance in the diagnosis of vascular diseases of the lower extremities is determining the quality of the valve apparatus. Ultrasound scanning of the lower extremities is important in the diagnosis of thrombophlebitis, varicose veins, and the presence of blood clots in the veins of the legs. Ultrasound examination of the vessels (arteries and veins) of the upper extremities is advisable for Raynaud's disease, impaired thermoregulation of the hands (in cases where the hands are constantly cold).
1 – Healthy vessel, 2- Narrowed vessel with poor blood flow
Search for the cause of vascular damage.
- Biochemical blood test. First of all, we are interested in indicators of fat metabolism (including cholesterol).
- Coagulogram and examination for antiphospholipid syndrome . If there is a blood clotting disorder, there is a risk of increased thrombosis. Including in the venous system of the lower extremities. This situation is dangerous due to the detachment of a blood clot and blockage of blood vessels in vital organs: pulmonary arteries, cerebral vessels, and heart.
- Immunological examination is important in the search for immune factors that damage blood vessels in Raynaud's disease and various vasculitis. These systemic diseases harm not only the vessels of the arms and legs, but also the entire body as a whole. in this case, the aggression of the immune system is directed not only at the vessels of the arms and legs, but also at the vessels of other organs.
- Determination of antibodies to infection. In some cases, vasculitis-like diseases with damage to the veins of the arms and legs occur when blood vessels are damaged by viruses or toxins. Our task is to accurately identify the pathogen and carry out targeted treatment.
In more complex cases, various options for angiography, CT, MRI, and capillary studies (capillaroscopy) can be used.
The vessels of the legs are arteries that supply blood to the legs and veins that carry blood that has given off oxygen back to the heart. The arteries and veins of the legs can be examined either together or separately, depending on the purposes of the diagnostic study. If we are talking mainly about varicose veins, then there will be no need to study the arteries.
Study of the arteries of the legs
Ultrasound examination of the arteries of the legs is usually indicated when it comes to insufficient blood flow to the legs, which can occur due to atherosclerosis, when atherosclerotic plaques narrow the lumen of the vessel or when the artery is blocked by a blood clot. Other causes are much less common and require more detailed examination.
Examination of leg veins
Vein examination is often prescribed for venous insufficiency, when varicose veins and swelling of the legs occur. But it is important to know that swelling of the legs can be caused by problems with the heart (heart failure) and then it would be advisable to conduct a heart examination along with the examination of the vessels of the legs.
Most often, when examining the vessels of the legs, it is enough to take a few steps:
- Perform an ultrasound examination of arteries and veins;
- Assess blood clotting for risk of blood clots
- Determine blood cholesterol levels to assess the risk of atherosclerotic plaque deposition and vasoconstriction and blood glucose levels for diabetes mellitus.
If these studies are not enough, we can offer you a more detailed and comprehensive diagnosis.
The main methods for studying the veins and arteries of the lower extremities used in our clinic:
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the legs (duplex scanning) - using an ultrasound diagnostic device, the doctor determines the structure of the vessels of the legs, assesses their condition, blood flow speed, the presence of blood clots, atherosclerotic plaques and aneurysms. Usually, an ultrasound scan of the leg veins is sufficient to confirm the diagnosis of varicose veins.
- Angiography of the vessels of the legs using X-rays, computed tomography with contrast injection, or MRI. These studies are needed quite rarely - if an ultrasound of the blood vessels of the legs does not provide the doctor with the necessary information.