Ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity) is detected in 50% of patients in the early stages of cancer and in almost all patients in whom the cancer process is at the last stage.
The Oncology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital is equipped with the latest diagnostic equipment from the world's leading manufacturers, with the help of which oncologists identify the early stages of oncological pathology. Chemotherapists, radiologists, and oncologists treat patients with ascites in accordance with international standards of medical care. At the same time, doctors take an individual approach to choosing a treatment method for each patient.
Reasons for development
Ascites is a serious complication of stomach and colon cancer, colorectal cancer, malignant tumors of the pancreas, and oncological pathology of the mammary glands, ovaries and uterus. When a large volume of fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity, intra-abdominal pressure increases, and the diaphragm moves into the chest cavity. This leads to disruption of the heart and lungs. There is a violation of blood circulation in the vessels.
In the presence of ascites, the patient's body loses a large amount of protein. Metabolism is disrupted, heart failure and other imbalances in the internal environment of the body develop, which worsen the course of the underlying disease.
There is always a small amount of fluid in the abdominal cavity of a healthy person. It prevents the sheets of peritoneum from sticking together. The produced intra-abdominal fluid is reabsorbed by the peritoneum.
With the development of cancer, the normal functioning of the body is disrupted. The secretory, resorptive and barrier functions of the peritoneal layers fail. In this case, either excess fluid production or disruption of its absorption processes may be observed. As a result, a large volume of exudate accumulates in the abdominal cavity. It can reach twenty liters.
The main reason for damage to the peritoneum by malignant cells is its close contact with organs that are affected by a cancerous tumor. Ascites in the presence of oncological pathology develops under the influence of the following factors:
- A large accumulation of blood and lymphatic vessels in the peritoneum through which cancer cells spread;
- Tight fit of the folds of the peritoneum to each other, which contributes to the rapid spread of malignant cells to adjacent tissues;
- Germination of a cancerous tumor through the peritoneal tissue;
- Transfer of atypical cells to peritoneal tissue during surgery.
Chemotherapy may be the cause of ascites. The accumulation of fluid in the peritoneum occurs due to cancer intoxication. If the liver is affected by a primary cancerous tumor, metastases of malignant cells from tumors of a different location, the outflow of blood through its venous system is disrupted, and portal hypertension develops - an increase in pressure inside the portal vein. The lumen of the venous vessels increases, plasma sweats from them and accumulates in the abdominal cavity.
The cause of ascites may be peritoneal carcinomatosis. In the presence of a cancerous tumor of the abdominal organs, atypical cells settle on the parietal and visceral sheets of the peritoneum. They block the resorptive function, as a result of which the lymphatic vessels do not cope well with the intended load, and lymph outflow is impaired. Free fluid gradually accumulates in the abdominal cavity. This is the mechanism of development of carcinomatous ascites.
Make an appointment
Our doctors
Perepechay Dmitry Leonidovich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
40 years of experience
Make an appointment
Kochetov Sergey Anatolievich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
34 years of experience
Make an appointment
Khromov Danil Vladimirovich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
35 years of experience
Make an appointment
Mukhin Vitaly Borisovich
Urologist, Head of the Department of Urology, Candidate of Medical Sciences
34 years of experience
Make an appointment
Stages of severity
There are three stages of abdominal hydrops depending on the amount of accumulated fluid:
- Initial stage - up to one and a half liters of fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity;
- Moderate ascites - manifested by an increase in the size of the abdomen, edema of the lower extremities. The patient is concerned about severe shortness of breath, heaviness in the abdomen, heartburn, constipation;
- Severe dropsy - from 5 to 20 liters of fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity. The skin on the abdomen tightens and becomes smooth. Patients experience heart failure and respiratory failure. When the fluid becomes infected, ascites-peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneal layers) develops.
Mechanism of bubble formation
Human skin can be figuratively described as a water-spring “mattress” covered with a kind of “wall”. The “mattress” does not participate in the formation of bubbles - only the top layer, the epidermis, suffers.
The epidermal layer consists of 10-20 cell layers, which look like bricks under a microscope. The “bricks” of the second layer of the epidermis are connected to each other by peculiar “bridges”. On top of the “wall” there are layers of cells that are no longer quite similar to cells, reminiscent of applied cream. These are scales, corneocytes, necessary for protection from mechanical, chemical and physical damage.
If, under the influence of internal or external causes, antibodies are formed that destroy the “bridges” - desmosomes between the cells of the basal layer (this is called acantholysis and can be seen under a microscope), this is true pemphigus. If tissue fluid penetrates between the basal and upper layers of the epidermis without destroying the “bridges,” it is pemphigoid. Viral pemphigus also occurs without destruction of desmosomes.
Symptoms
The main manifestation of ascites is a significant increase in size and pathological bloating of the abdomen. Signs of abdominal dropsy can increase rapidly or over several months. Ascites is manifested by the following clinical symptoms:
- Feeling of fullness in the abdominal cavity;
- Pain in the abdomen and pelvis;
- Increased gas formation (flatulence);
- Belching;
- Heartburn;
- Digestive disorders.
Visually, the patient’s abdomen enlarges, in a horizontal position it hangs down and begins to “blur” on the sides. The navel gradually protrudes more and more, and blood vessels are visible on the stretched skin. As ascites develops, it becomes difficult for the patient to bend over and shortness of breath appears.
Doctors at the Oncology Clinic evaluate the clinical manifestations of the disease and carry out a differential diagnosis of cancer with other diseases, the manifestation of which is ascites.
Postoperative period
Surgeries for dropsy are usually well tolerated by children and do not significantly interfere with their movements. However, with sudden movements or constipation as a result of increased intra-abdominal pressure or direct impacts, the formation of hematomas in the scrotum and groin area is possible. Therefore, children should limit their activity until the postoperative wound heals and follow a diet.
On the first day after surgery, non-narcotic painkillers (analgin, paracetamol, ibuprofen, Panadol and others) are usually prescribed. Laxatives are used for 4-5 days after surgery.
For 2 weeks after surgery, do not wear underwear that compresses the scrotum to avoid pushing the testicle up toward the inguinal canal, due to possible fixation of the testicle above the scrotum.
School-age children are exempt from physical education for 1 month.
Diagnostics
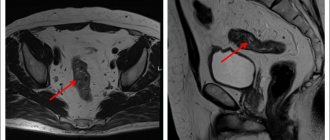
Doctors identify ascites during an examination of the patient. Oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital conduct a comprehensive examination of patients, which allows them to identify the cause of fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity. One of the most reliable diagnostic methods is ultrasound. During the procedure, the doctor not only clearly sees the liquid, but also calculates its volume.
In case of ascites, oncologists necessarily perform laparocentesis. After puncturing the anterior abdominal wall, the doctor aspirates fluid from the abdominal cavity and sends it to the laboratory for testing. Computed tomography radiology scans are used to determine the presence of malignant tumors in the liver that cause portal hypertension.
Magnetic resonance imaging makes it possible to determine the amount of accumulated fluid and its location.
When is surgery performed for hydrocele?
- Operations for communicating hydrocele of the testicle are most often performed in children aged 2 years.
- From 1 to 2 years, operations for communicating hydrops are performed if:
- combined dropsy and inguinal hernia
- when the volume of the scrotum clearly changes with changes in body position
- dropsy increases, causing discomfort
- infection joins
- Surgeries for post-traumatic dropsy – 3-6 months after injury.
- Lymphocele that occurs after surgery for an inguinal hernia or varicocele is operated on 6 to 18 months after the appearance of fluid in the membranes of the testicle.
Treatment
Drug therapy for ascites is not carried out due to low effectiveness. Aldosterone antagonists and diuretics normalize water-salt metabolism and prevent excess secretion of peritoneal fluid. Oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital offer palliative surgery to patients with ascites in the late stages of cancer:
- Omentohepatophrenopexy;
- Deperitonization;
- Installation of a peritoneovenous shunt.
Doctors at the Oncology Clinic carry out traditional or intracavitary chemotherapy for ascites - after removing the fluid, a chemotherapy drug is injected into the abdominal cavity. Laparocentesis is performed to remove fluid. The procedure is not performed if the following contraindications are present:
- Adhesive process inside the abdominal cavity;
- Severe flatulence;
- Perforation of the intestinal walls;
- Purulent infectious processes.
Laparocentesis is prescribed in cases where taking diuretics does not lead to a positive result. The procedure is also indicated for resistant ascites.
Laparocentesis is carried out in several stages using local anesthesia:
- the patient is in a sitting position, the doctor treats the subsequent puncture site with an antiseptic and administers painkillers;
- An incision is made in the abdominal wall along the linea alba at a distance of 2-3 centimeters below the navel;
- The puncture itself is performed using a trocar using rotational movements. A special flexible tube is attached to the trocar, through which excess fluid is removed from the body. The fluid is pumped out quite slowly, and the doctor constantly monitors the patient’s condition. As the exudate is removed, the nurse tightens the patient's abdomen with a sheet to slowly reduce the pressure in the abdominal cavity;
- After the fluid is pumped out, a sterile bandage is applied to the wound.
Using laparocentesis, up to 10 liters of fluid can be removed from the patient’s body. In this case, it may be necessary to administer albumin and other drugs to prevent the development of renal failure.
If necessary, temporary catheters can be installed in the abdominal cavity, through which excess fluid will gradually be removed. It should be noted that the use of catheters can lead to a decrease in blood pressure and the formation of adhesions.
There are also contraindications to laparocentesis. Among them:
- pronounced flatulence;
- adhesive disease of the abdominal organs;
- stage of recovery after surgery on a ventral hernia.
Diuretics are prescribed to patients with developing ascites in cancer over a long course. Such drugs as Furosemide, Diacarb and Veroshpiron are effective.
When taking diuretics, medications containing potassium must also be prescribed. Otherwise, there is a high probability of developing disturbances in water and electrolyte metabolism.
Dietary nutrition primarily involves reducing the amount of salt consumed, which retains fluid in the body. It is also important to limit the amount of fluid you drink. It is recommended to include more foods containing potassium in your diet.
After removal of fluid from the abdominal cavity, patients are provided with a balanced and high-calorie diet. This allows you to meet the body's needs for proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals. Fat consumption is reduced.
Prevention
Swelling cannot always be prevented, since it can occur under the influence of uncontrollable factors. There is no way to prevent a bruise or insect bite. But in general, maintaining hydrobalance in the body is easy:
- Observe the drinking regime: fully quench your thirst, but do not drink more than you should.
- Stick to a diet during the hot season: minimize the consumption of salty and spicy foods, eat more fruits, drink tea with lemon instead of coffee.
- Arrange water treatments: contrast showers, foot baths.
- Move more: walking, swimming, aerobics do not allow fluid to stagnate.
In summer, you should avoid tight, high-heeled shoes. It is useful to periodically place your feet on an elevation so that fluid concentrated in the lower part of the body drains. There is no need to abuse medications. Urinary and antihypertensive drugs should be prescribed by a doctor. Any diseases that have a similar symptom must be treated in a timely manner.
Tokareva Lyudmila Georgievna, therapist, medical offices 36.6.
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS, BEFORE USE YOU MUST CONSULT WITH A SPECIALIST
Non-cancerous ascites
Ascites is a consequence of various disorders that occur in the body. Treatment tactics depend on the pathological process that caused the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity:
- To treat acute heart failure, cardiologists at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe metabolites, beta blockers, and ACE inhibitors to patients;
- For infectious and toxic liver lesions, therapy with hepatoprotectors is carried out;
- If ascites has developed due to low protein levels in the blood, albumin infusions are performed;
- Ascites that develops as a result of peritoneal tuberculosis is treated with anti-tuberculosis drugs.
To remove fluid from the body, patients with ascites are prescribed diuretics. The main method of eliminating ascites is to remove accumulated fluid by puncturing the abdominal wall, followed by installing drainage. For persistent ascites, peritoneal fluid is reinfused after filtration. A peritoneovenous shunt for abdominal ascites ensures the flow of fluid into the general bloodstream. To do this, surgeons form a structure with a valve, through which fluid from the abdominal cavity enters the superior vena cava system during inhalation.
Omentohepatophrenopexy for abdominal ascites is performed to reduce pressure in the venous system. The surgeon sutures the omentum to the diaphragm and liver. Then, during breathing movements, the veins are unloaded from blood. As a result, the release of fluid through the vascular wall into the abdominal cavity decreases. As a result of deperitonization (excision of areas of the peritoneum), additional outflow pathways for peritoneal fluid are created.
How to relieve swelling after a bruise
Treatment for a leg bruise usually comes down to eliminating pain and swelling. The swelling in this case is caused by damage to the blood vessels and the accumulation of fluid from them under the skin. The latter puts pressure on the nerve endings, hence the pain. So eliminating swelling also helps to get rid of unpleasant sensations.
You can help a bruised limb at home:
- stretch and provide peace;
- apply a wet towel, ice or a heating pad with cold water;
- apply a tight bandage.
You can also resort to drug treatment. External agents containing troxerutin or heparin will help. They strengthen capillaries, optimize blood viscosity and relieve inflammation.
Forecast
Ascites in cancer significantly worsens the general well-being of the patient. As a rule, such a complication occurs in the later stages of oncology, in which the survival prognosis depends on the nature of the tumor itself and its distribution throughout the body.
Life expectancy with ascites depends on the following factors:
- Functioning of the kidneys and liver;
- Activities of the cardiovascular system;
- The effectiveness of therapy for the underlying disease.
The development of ascites can be prevented by an experienced doctor observing the patient. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital have extensive experience in dealing with various types of cancer. Qualified medical personnel and the latest equipment allow for accurate diagnosis and high-quality, effective treatment in accordance with European standards.
Surgery for hydrocele (hydrocele). Surgical options.
The type of operation depends on the age of the patient and the characteristics of the dropsy.
Surgery for communicating hydrocele of the testicle. Operation Ross.
For communicating dropsy, as a rule, the Ross technique is used - isolation from the elements of the spermatic cord, excision and ligation of the internal inguinal ring of the peritoneal process, as well as the formation of a “window” in the membranes of the testicle. The operation is performed through a small incision in the groin area.
The operation is delicate, requiring good technique - careful and careful preparation while preserving all the anatomical formations of the spermatic cord - the vas deferens and testicular vessels, as well as the inguinal nerve.
Laparoscopic operations are sometimes used for testicular hydrocele, but the morbidity, risk of relapses and complications when using them are higher, and the duration of anesthesia is longer, so they are not widely used.
Operations for isolated hydrocele of the testicular membranes and lymphocele in children and adolescents.
Isolated hydrocele and lymphocele are indications for Bergman's operation - excision of the inner membranes of the testicle from the scrotal approach. In cases of large hydroceles and lymphoceles, drainage is often left in the wound and pressure bandages are applied.
Winkelmann's operation is a dissection of the testicular membranes in front and suturing the resulting edges of the membranes behind the epididymis. Currently used rarely due to changes in the appearance of the scrotum and testicular contours.
Among the complications, the most common is recurrence of dropsy (5-20%), which in case of lymphocele can reach 70%. A particularly high percentage of relapses is observed when operations are not performed on time.
Classification
Types of non-acantholytic pemphigus:
- Non-acantholytic pemphigus is benign. Pathological elements are formed exclusively in the human oral cavity. Upon examination, inflammation of the mucous membrane, as well as its slight ulceration, can be detected.
- Bullous form of non-acantholytic pemphigus. This is a benign disease that develops in both adults and children. Blisters form on the skin, but there are no signs of acantholysis. These pathological elements can spontaneously disappear without scarring.
- Cicatricial non-acantholytic pemphigus. This pemphigoid is called pemphigus of the eye in the medical literature. Most often it is diagnosed in women who have crossed the 45-year age limit. A characteristic symptom is damage to the visual apparatus, skin and oral mucosa.
Classification of true pemphigus:
- Erythematous form. This pathological process combines several diseases. Its symptoms are similar to seborrheic dermatitis, an erythematous variant of systemic lupus, as well as true pemphigus. Erythematous pemphigus in adults and children is very difficult to treat. It is worth noting that the disease is diagnosed not only in people, but also in some animals. A characteristic symptom is the appearance of red spots on the skin of the body and face, covered with crusts on top. Simultaneously with this symptom, seborrheic manifestations appear on the scalp.
- Pemphigus vulgare. This type of pathology is diagnosed in patients more often. Blisters form on the skin, but there are no signs of inflammation. If pemphigus is not treated on time, pathological elements can spread throughout the entire skin. It is worth noting that they can merge and form large lesions.
- Pemphigus foliaceus. This form received its name due to the characteristics of the pathological elements. Blisters form on the human skin, which practically do not rise above the epidermis (not tense). Crusts form on top of them, which tend to layer on top of each other. The effect of sheet material folded in stacks is created.
- Brazilian pemphigus. There are no restrictions regarding gender and age. Cases of its development have been recorded in both young children and elderly people aged 70 to 80 years. It is also possible that it may progress in middle-aged people. It is worth noting that this variety is endemic and is therefore found only in Brazil.
Preventive measures
There are no specific measures to prevent the development of pathology. The higher the level of immune protection, the less chance of dermatological diseases.
Important:
- control the nature of chronic diseases;
- strengthen immunity;
- maintain personal hygiene;
- Healthy food.
Measures to prevent pemphigus in newborns:
- change your underwear more often;
- Caring for newborns with pustular skin lesions is prohibited;
- Take regular care of your child’s skin;
- strengthen the immune system of weakened children;
- daily wet cleaning and ventilation of the room are required.
If you notice any rashes on the skin, the formation of pustules and blisters, immediately contact a dermatologist.