Why does hives occur?
This is a systemic disease, the occurrence of which can be contributed by a variety of factors. People who are prone to allergic reactions or have a family history of this disease often suffer from urticaria.
The following factors can lead to the appearance of nettle rash:
- medications, most often antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- insect bites (bees, wasps);
- viral and chronic infectious diseases;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- products, including various spices and food additives;
- problems with the immune system;
- stressful situations;
- the presence of helminths or other parasites in the body;
- external physical phenomena (cold, pressure, water, sun, vibration).
The list of causes of chronic urticaria is headed by drugs and food, and the acute form of the disease in most cases occurs against the background of viral infections and gastrointestinal diseases.
Hormonal imbalance in the body can provoke the disease in women. This may be due to menstrual irregularities, taking hormonal medications, pregnancy or menopause.
Nettle rash is not always an independent diagnosis. Often it acts as a symptom of other pathologies. For example, such rashes are characteristic of autoinflammatory diseases, angioedema and mastocytosis (blood disease).
Urticaria: symptoms of the disease
The main manifestation is the appearance of red or pink spots of various shapes on the skin, as well as blisters up to several centimeters in diameter. The skin may have slight swelling, which is temporary. Most often it disappears after 1-2 days. If the swelling affects the deep layers of the dermis or mucous membranes, then Quincke's edema is formed (a sharp increase in some part of the body). This is a very dangerous condition that requires immediate help.
The hives rash is almost always accompanied by severe itching, and sometimes a burning sensation may occur. Scratching itchy areas of skin leads to infection. In this case, the disease is complicated by the appearance of ulcers, bruises, and wounds.
A feature of the course in adults is the suddenness of the onset and disappearance of all signs of the disease. In most cases, this occurs without treatment.
Minor symptoms that are not always present include:
- Redness and swelling of the skin.
- Headache.
- Fever.
- Sleep disorder.
Such symptoms greatly affect a person’s overall well-being and quality of life. He becomes irritable, mental activity decreases, and appetite is impaired. Often an itchy rash leads to mental disorders (this can be high anxiety, apathy, depression) and forced isolation.
Prevention
There are no special measures to help prevent the development of hives. But you can reduce the risk of a skin reaction by following some tips:
- Apply cool, wet compresses. They will help soothe the skin.
- Keep a food diary. If you suspect a food is causing your hives, but you don't know which food, start keeping a food diary in which you write down everything you eat and your symptoms.
- Avoid contact with potential triggers. Try to figure out what factors cause your skin to react. These could be some medications, food products, household chemicals, high or low temperatures.
- Take a cool bath. You can add baking soda, raw or colloidal oatmeal to it. This will help relieve the itching.
- Wear loose cotton clothing. Avoid wearing rough, tight, itchy clothing, especially wool. This will help prevent skin irritation.
Keep an antihistamine, such as loratadine (Claritin) or cetirizine (Zyrtec), on hand. They will help quickly relieve symptoms and relieve itching.
Classification: types of urticaria
There are many varieties of this dermatological disease. According to the nature of the disease, it is divided into 2 types:
- Acute urticaria is the most common form. It is characterized by the sudden appearance of blisters or swollen areas of the skin. Usually does not require treatment, as symptoms resolve on their own within 2-6 weeks. Caused mainly by external causes or food. According to statistics, in the world it occurs once in more than 25% of the population.
- Chronic urticaria - this form is said to occur when symptoms persist for more than 6 weeks. It is characterized by a wave-like course with periods of complete health and acute exacerbations. Sometimes the disease may not appear for 10-20 years. Often accompanied by Quincke's edema and severe attacks of itching. Inflamed elements can merge, expanding into healthy areas of the skin.
Depending on the reasons that lead to the appearance of blisters, autoimmune, allergic and contact forms are distinguished. Contact urticaria always occurs due to contact with physical factors. It is divided into several types:
- cold - occurs due to low air temperature, cold wind or water;
- thermal - local exposure to high temperature or very heated air, water;
- solar - the cause is UV radiation;
- vibration;
- aquagenic - reaction to water;
- slowed by pressure - can occur from tight clothing, prolonged sitting, or leaning on a piece of furniture.
- urticarial dermographism (mechanical) - occurs as an irritation in response to exposure of the skin to any object (towel, pen).
All of these types of physical urticaria are chronic and can occur suddenly.
Methods of treatment with traditional methods
The following methods will help relieve itching, soothe the skin and speed up the healing of blisters.
Honey and horseradish:
- Mix honey and horseradish juice in a 1:1 ratio.
- Take the resulting mixture 1 tsp. 3 times a day.
Mint tincture:
- Pour 20 grams of boiling water over it. mint, leave for several hours.
- Strain and take 3 tbsp. l. in a day.
Mint decoction for lotions:
- Pour 30 gr. fresh nettle leaves 2 tbsp. water.
- Bring to a boil and simmer over low heat for 2 minutes.
- Leave for one hour, strain.
- Soak gauze in the infusion and apply to the sore spot several times a day.
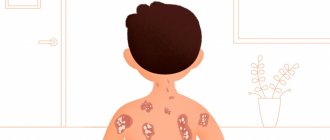
hives in a child photo
Features of the course of urticaria in children
For toddlers (up to 2-3 years), the acute form of the disease is more typical. In infants, this is often associated with food.
At younger and school age, both chronic and acute forms of the disease can occur, but the acute variety still predominates. In adolescents, the disease increasingly begins to manifest itself in attacks, that is, it becomes chronic.
In more than 50% of cases of urticaria symptoms in children, other allergic diseases are also detected. This could be dermatitis, chronic rhinitis, allergies to medications.
In children, diagnosis can be difficult, as it is often associated with other dermatological pathological manifestations. Often the rash affects areas of skin near the joints, but there is no restriction in movement. The child may react to pain when palpating the inflamed area of skin.
Nettle rashes in children require special attention - you should definitely consult a pediatrician.
Sources
- Federal clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of urticaria. M.: Russian Association of Allergists and Clinical Immunologists, 2015. p. 34.
- Federal clinical guidelines for the management of patients with urticaria. M.: Russian Society of Dermatovenerologists and Cosmetologists, 2015. p. 24.
- Guideline for the definition, classification, diagnosis and management of urticaria: the 2013 revision and update / Zuberbier T., Aberer W., Asero R. // Allergy 2014: 69: 868-887.
- Luss. L.V. Causes and treatment of urticaria in children // Medical Council, 2015. – No. 14.
Diagnosis of the disease
If you find blisters or inflamed itchy areas on your skin, you should contact a dermatologist or allergist-immunologist.
Reception and diagnosis of the patient’s condition consists of 2 stages.
Anamnesis collection and interview
Here the doctor clarifies the nature of the rash, when it appeared, and what it is associated with. Is there any itching or painful sensations - at what time of day they intensify. Attention is paid to the localization and frequency of spread of the rash, the doctor checks whether pigmentation remains after the blisters. Be sure the doctor finds out about the presence of other allergic reactions in the anamnesis, as well as whether close relatives have had similar diseases.
Physical examination (external examination)
A thorough inspection of areas with rashes and blisters is carried out. If necessary, a test for dermographism is performed, i.e. how the skin reacts to mechanical stress. The activity of urticaria is determined according to a certain medical scale. If necessary, a skin biopsy may be prescribed for a more detailed microscopic examination.
In order to choose the right treatment regimen, it is necessary to find out the nature of the rash. To do this, a series of skin allergy tests are performed to identify the body’s nonspecific reaction to certain irritants. General laboratory tests are also prescribed to determine infections, endocrine pathologies or parasitic diseases.
Considering that urticaria can be caused by diseases of internal organs, specialists of other profiles are involved in the examination. This is a neurologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, pulmonologist, psychiatrist, hematologist.
Additional research:
- skin test when using autologous serum;
- rheumatological tests;
- nasal swab for the presence of eosinophils;
- TSH, T3, T4, antibodies to thyroid peroxidase and thyroglobulin;
- culture of throat flora, throat culture for sensitivity to antibiotics and bacteriophages;
- stool analysis for sensitivity to bacteriophages and dysbacteriosis;
- antibodies to helminths, as well as roundworms and lamblia;
- coprogram;
- HBsAg, AT to hepatitis C, RW, AT to HIV;
- ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- consultation with a gastroenterologist to identify H. pylori, endoscopy, consultation with a neurologist, ENT specialist (VSD);
- ECG;
- if urticarial vasculitis is suspected, a dermatovenerologist performs a skin biopsy.
How to treat urticaria
If a contact form of the disease is identified, then the main principle of treatment is to exclude the provoking factor. In the case of food urticaria, allergenic foods are excluded from the diet. Usually this is enough for the rash to stop after 2-3 days.
Drug therapy is to eliminate symptoms and alleviate a person’s condition. The doctor selects antihistamines individually. Anti-inflammatory drugs and immunomodulators are also recommended. In severe cases, a course of sedative medications is required to reduce the level of anxiety and nervousness.
To reduce itching and inflammation, menthol-based ointments and lotions with a cooling effect are used. Treatment of concomitant diseases is mandatory.
Preventive measures
To reduce the number of flare-ups of chronic urticaria, it is recommended to avoid conditions that can trigger it. List of recommendations:
- Avoid excessive heat or hypothermia.
- Don't wear tight clothes.
- Instead of a backpack, use a bag with a handle.
- Avoid long hikes and strenuous physical activity.
- Follow your diet.
- Always use sunscreen when going outside.
- In summer, try to wear closed clothes.
- Avoid vacationing in areas with high levels of UV radiation.
If severe itching occurs, try not to scratch the affected areas. Contact your doctor to find an effective antihistamine. Give up bad habits and strengthen your immune system.